Professional Documents
Culture Documents
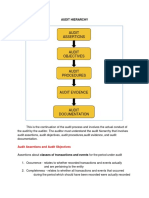
In Testing Transactions, The Auditor Is Concerned With Tests of
Uploaded by
MarieOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
In Testing Transactions, The Auditor Is Concerned With Tests of
Uploaded by
MarieCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Involved In Substantive Testing? C.
Completeness
Tests of transactions
[1]. Obtain bank cutoff statement and determine
Tests of details of account balances
propriety of year-end outstanding checks and
Analytical procedures
deposits-in-transit.
In testing transactions, the auditor is concerned
[2]. Examine or prepare year-end bank
with tests of:
reconciliation.
Omitted transactions and account
understatement (tracing source
documents to the books of entry) [3]. Prepare a proof of cash.
Invalid or unsupported transactions and
account overstatement (tracing [4]. Perform analytical procedures.
recorded transactions to source
documents). D. Existence or Occurrence (See Valuation or
Allocation)
Substantive Tests of Cash
E. Rights and Obligations
A. Presentation and Disclosure
[1]. Read or review the financial statements to [1]. Read minutes of the board of directors’
verify proper classification. meetings.
[2]. Read or review the financial statements to [2]. Determine existence of compensating
verify disclosures such as those relating to balances, levies, etc.
compensation balances.
[3]. Verify names on accounts through
[3]. Determine the conformity with GAAP. confirmation requests
B. Valuation or Allocation
Substantive Procedures for Cash
[1]. Simultaneously count cash on hand and 1. Confirm cash balances
negotiable securities.
2. Vouch reconciling items to the subsequent
[2]. Confirm directly with the bank:
month’s bank statement
Account balances
Direct liabilities to bank
Contingent liabilities to bank 3. Ask if all bank accounts are included on the
Letters of credit general ledger
Security agreements under the Uniform
Commercial Code
Authorized signatures 4. Inspect final deposits and disbursements for
[3]. Count petty cash fund and reconcile with
proper cutoff
vouchers.
You might also like
- In Testing Transactions, The Auditor Is Concerned With Tests ofDocument1 pageIn Testing Transactions, The Auditor Is Concerned With Tests ofMarieNo ratings yet
- Accounts Payable: A Guide to Running an Efficient DepartmentFrom EverandAccounts Payable: A Guide to Running an Efficient DepartmentNo ratings yet
- Substantive Procedures-CashDocument3 pagesSubstantive Procedures-CashEll VNo ratings yet
- Accounting for Goodwill and Other Intangible AssetsFrom EverandAccounting for Goodwill and Other Intangible AssetsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Audit of Cash and Bank Balances Learning ObjectivesDocument8 pagesAudit of Cash and Bank Balances Learning ObjectivesDebbie Grace Latiban LinazaNo ratings yet
- Accounting for Real Estate Transactions: A Guide For Public Accountants and Corporate Financial ProfessionalsFrom EverandAccounting for Real Estate Transactions: A Guide For Public Accountants and Corporate Financial ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- Audit of Cash and Bank BalancesDocument14 pagesAudit of Cash and Bank BalancesArlyn Pearl PradoNo ratings yet
- Audit CH 2 Part IDocument10 pagesAudit CH 2 Part IbikilahussenNo ratings yet
- Audit of Other Items of Statement of Financial PositionDocument13 pagesAudit of Other Items of Statement of Financial PositionArlyn Pearl PradoNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet Substantive TestingDocument12 pagesBalance Sheet Substantive TestingangaNo ratings yet
- Problem CH 6,7,8 - Amelia Zulaikha Pratiwi - MAKSI43BDocument4 pagesProblem CH 6,7,8 - Amelia Zulaikha Pratiwi - MAKSI43Bamelia zulaikhaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Auditing Theory L. R. Cabarles/J.M. D. Maglinao AT.2812-Performing Further Audit Procedures (FAP) MAY 2020Document9 pagesLecture Notes: Auditing Theory L. R. Cabarles/J.M. D. Maglinao AT.2812-Performing Further Audit Procedures (FAP) MAY 2020MaeNo ratings yet
- Audit ProgramDocument16 pagesAudit Programanon_806011137100% (4)
- Audit of ReceivableDocument14 pagesAudit of ReceivableMr.AccntngNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Audit of Other Items of Statement of Financial PositionDocument13 pagesChapter 15 Audit of Other Items of Statement of Financial PositionMiaNo ratings yet
- Substantive ProcedureDocument8 pagesSubstantive ProcedureGoldaNo ratings yet
- Substantive ProceduressDocument8 pagesSubstantive ProceduressayyazmNo ratings yet
- Substantive Test of CashDocument29 pagesSubstantive Test of CashCeline Marie AntonioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Liabilities - Substantive Tests of Details of BalancesDocument30 pagesLesson 6 - Liabilities - Substantive Tests of Details of BalancesNiña YastoNo ratings yet
- Substantive Tests of Receivables and SalesDocument4 pagesSubstantive Tests of Receivables and SalesKeith Joshua Gabiason100% (1)
- Substantive Testing For Deposit LiabilitiesDocument3 pagesSubstantive Testing For Deposit LiabilitiesChristian PerezNo ratings yet
- Audit AssertionsDocument5 pagesAudit AssertionsJazzyNo ratings yet
- Credit Audit - AdhukiaDocument144 pagesCredit Audit - AdhukiaDr. KishoreNo ratings yet
- Substantive Tests and Audit ProgramDocument35 pagesSubstantive Tests and Audit ProgramPamimoomimap Rufila100% (1)
- AU Locks Auditing Services: Audit Program Batangas Bestfeeds Multipurpose CooperativeDocument5 pagesAU Locks Auditing Services: Audit Program Batangas Bestfeeds Multipurpose CooperativeMirai KuriyamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two-Auditing CashDocument6 pagesChapter Two-Auditing CashBantamkak FikaduNo ratings yet
- Audit of The Acquisition and Payment Cycle: Tests of Controls, Substantive Tests of Transactions, and Accounts PayableDocument33 pagesAudit of The Acquisition and Payment Cycle: Tests of Controls, Substantive Tests of Transactions, and Accounts Payable김현중No ratings yet
- Audit of Cash PDFDocument11 pagesAudit of Cash PDFRyan Prado AndayaNo ratings yet
- BKAA3023 Take Home Exercise 6: Rubiatul Adawiyah Binti Mohd Ashari (264831) Group CDocument2 pagesBKAA3023 Take Home Exercise 6: Rubiatul Adawiyah Binti Mohd Ashari (264831) Group CRubiatul AdawiyahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Audit of Current LiabilityDocument14 pagesChapter 6: Audit of Current LiabilityYidersal DagnawNo ratings yet
- AFS 2023 - Lecture 10 - CashDocument28 pagesAFS 2023 - Lecture 10 - CashKiều TrangNo ratings yet
- Current LiabilitiesDocument2 pagesCurrent LiabilitiesPrio DebnathNo ratings yet
- 57060aasb46101 8Document20 pages57060aasb46101 8Wubneh AlemuNo ratings yet
- Substantive Audit For AssetsDocument7 pagesSubstantive Audit For AssetsHenry MapaNo ratings yet
- Concepts and PrinciplesDocument13 pagesConcepts and PrinciplesJonafhel RaguinNo ratings yet
- Audit of Cash and Marketable SecuritiesDocument21 pagesAudit of Cash and Marketable Securitiesዝምታ ተሻለNo ratings yet
- G N A L: Uidance Ote On Udit of IabilitiesDocument22 pagesG N A L: Uidance Ote On Udit of IabilitiesPaula MerrilesNo ratings yet
- Cash ProgramDocument13 pagesCash Programapi-3828505No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 AnsDocument6 pagesChapter 12 AnsDave Manalo100% (1)
- AP.3404 Audit of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument5 pagesAP.3404 Audit of Cash and Cash EquivalentsMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- Reporting Under Lfar PDFDocument50 pagesReporting Under Lfar PDFSHAHNo ratings yet
- Audit of The Capital Acquisition and Repayment CycleDocument7 pagesAudit of The Capital Acquisition and Repayment Cyclerezkifadila2No ratings yet
- Sol18 Sebagian2Document11 pagesSol18 Sebagian2Chotimatul ChusnaaNo ratings yet
- GN 23Document17 pagesGN 23Uddeshya KumarNo ratings yet
- Audit Tutorial 10Document6 pagesAudit Tutorial 10Chong Soon KaiNo ratings yet
- Prepaymentsand ReceivablesDocument3 pagesPrepaymentsand ReceivablesAsim JavedNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four The Audit of Accounting Information SystemsDocument20 pagesChapter Four The Audit of Accounting Information SystemsPrince Hiwot EthiopiaNo ratings yet
- Auditing Problems Usl PDFDocument226 pagesAuditing Problems Usl PDFmusic niNo ratings yet
- I. General Information: Audit Program: Treasury Audit ProgramDocument17 pagesI. General Information: Audit Program: Treasury Audit ProgramChinh Le DinhNo ratings yet
- Acco 30053 - Audit of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument19 pagesAcco 30053 - Audit of Cash and Cash EquivalentsmarkNo ratings yet
- Cash and BankDocument19 pagesCash and BankJatinNo ratings yet
- Cash and Bank AuditDocument9 pagesCash and Bank Auditzeebee17No ratings yet
- Audit ProgrammesDocument63 pagesAudit ProgrammesSarah Hashem100% (1)
- Chapter 24 AnsDocument10 pagesChapter 24 AnsDave Manalo100% (1)
- Audit of BanksDocument23 pagesAudit of BanksJoris YapNo ratings yet
- AP.3407 Audit of LiabilitiesDocument6 pagesAP.3407 Audit of LiabilitiesMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- Other Assets: Audit ObjectivesDocument5 pagesOther Assets: Audit ObjectivesIvoryBriginoNo ratings yet
- Audit of Debtors Loans and AdvancesDocument17 pagesAudit of Debtors Loans and Advanceseequals mcsquaredNo ratings yet
- WP Asset B - Trade ReceivablesDocument15 pagesWP Asset B - Trade ReceivablesDikdikNo ratings yet
- Notes in Prevention CostsDocument2 pagesNotes in Prevention CostsMarieNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled DocumentMarieNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled DocumentMarieNo ratings yet
- Notes in Prevention CostsDocument2 pagesNotes in Prevention CostsMarieNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled DocumentMarieNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled DocumentMarieNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled DocumentMarieNo ratings yet
- CIS ReportDocument10 pagesCIS ReportMarieNo ratings yet
- CIS ReportDocument10 pagesCIS ReportMarieNo ratings yet
- Class Notes in Applied AuditingDocument1 pageClass Notes in Applied AuditingMarieNo ratings yet
- CIS ReportDocument10 pagesCIS ReportMarieNo ratings yet
- CIS ReportDocument10 pagesCIS ReportMarieNo ratings yet
- Substantive Test Cash and Cash Equivalents QuizDocument2 pagesSubstantive Test Cash and Cash Equivalents QuizMarieNo ratings yet
- ServingDocument5 pagesServingMarieNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel BrochureDocument2 pagesStainless Steel BrochureEvi KusumaningrumNo ratings yet
- Bali Hai LawsuitDocument14 pagesBali Hai LawsuitLas Vegas Review-JournalNo ratings yet
- Instructions: This Affidavit Should Be Executed by The PersonDocument1 pageInstructions: This Affidavit Should Be Executed by The PersonspcbankingNo ratings yet
- Cyclical Iterative Design Process, Learning From ExperienceDocument7 pagesCyclical Iterative Design Process, Learning From ExperiencemartinsmitNo ratings yet
- Risk, Return & Capital BudgetingDocument18 pagesRisk, Return & Capital BudgetingMuhammad Akmal HussainNo ratings yet
- Cost Volume Profit AnalysisDocument7 pagesCost Volume Profit AnalysisMatinChris KisomboNo ratings yet
- The Perceived Barriers and Entrepreneurial Intention of Young Technical ProfessionalsDocument6 pagesThe Perceived Barriers and Entrepreneurial Intention of Young Technical ProfessionalsAnatta OngNo ratings yet
- Ex 6 Duo - 2021 Open-Macroeconomics Basic Concepts: Part 1: Multple ChoicesDocument6 pagesEx 6 Duo - 2021 Open-Macroeconomics Basic Concepts: Part 1: Multple ChoicesTuyền Lý Thị LamNo ratings yet
- San Francisco Chinese Christian Union, Et Al. v. City and County of San Francisco, Et Al. ComplaintDocument25 pagesSan Francisco Chinese Christian Union, Et Al. v. City and County of San Francisco, Et Al. ComplaintFindLawNo ratings yet
- Helsingborg EngDocument8 pagesHelsingborg EngMassaCoNo ratings yet
- About UPSC Civil Service Examination Schedule and Subject ListDocument4 pagesAbout UPSC Civil Service Examination Schedule and Subject Listjaythakar8887No ratings yet
- God Save The Queen Score PDFDocument3 pagesGod Save The Queen Score PDFDarion0% (2)
- LG+32LX330C Ga LG5CBDocument55 pagesLG+32LX330C Ga LG5CBjampcarlosNo ratings yet
- TM9-238 Deepwater Fording of Ordnance Materiel PDFDocument35 pagesTM9-238 Deepwater Fording of Ordnance Materiel PDFdieudecafeNo ratings yet
- Ins200 Assignment Hazardous PlaceDocument10 pagesIns200 Assignment Hazardous PlaceNur Syafatin Natasya86% (7)
- 04.CNOOC Engages With Canadian Stakeholders PDFDocument14 pages04.CNOOC Engages With Canadian Stakeholders PDFAdilNo ratings yet
- Collection of Solid WasteDocument38 pagesCollection of Solid WasteMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- AMCA 210-07 PreDocument10 pagesAMCA 210-07 PretiagocieloNo ratings yet
- HyderabadDocument3 pagesHyderabadChristoNo ratings yet
- Case Title: G.R. No.: Date: Venue: Ponente: Subject: TopicDocument3 pagesCase Title: G.R. No.: Date: Venue: Ponente: Subject: TopicninaNo ratings yet
- TX Open RS232 - 485 Module (TXI2.OPEN)Document8 pagesTX Open RS232 - 485 Module (TXI2.OPEN)harishupretiNo ratings yet
- Balanza Pediatrica Health o Meter 549KL Mtto PDFDocument18 pagesBalanza Pediatrica Health o Meter 549KL Mtto PDFFix box Virrey Solís IPSNo ratings yet
- Nxivm: 2nd Superseding IndictmentDocument32 pagesNxivm: 2nd Superseding IndictmentTony Ortega100% (2)
- OMS - Kangaroo Mother CareDocument54 pagesOMS - Kangaroo Mother CareocrissNo ratings yet
- Hi 3 Yt 318201Document3 pagesHi 3 Yt 318201partha khatuaNo ratings yet
- cv20672778 Prashanth - Sadak Operations-ManagerDocument4 pagescv20672778 Prashanth - Sadak Operations-ManagerBhasker NiftyNo ratings yet
- User Custom PP Install74Document2 pagesUser Custom PP Install74Zixi FongNo ratings yet
- Year Warranty: 1575 - 90 Ave Edmonton, AB Canada T6P 0E2Document2 pagesYear Warranty: 1575 - 90 Ave Edmonton, AB Canada T6P 0E2juanchingarNo ratings yet
- Case Chart Complete (Business Law)Document29 pagesCase Chart Complete (Business Law)LimShuLingNo ratings yet
- NumaConcert ManualDocument96 pagesNumaConcert ManualPippo GuarneraNo ratings yet
- A Pocket Guide to Risk Mathematics: Key Concepts Every Auditor Should KnowFrom EverandA Pocket Guide to Risk Mathematics: Key Concepts Every Auditor Should KnowNo ratings yet
- (ISC)2 CISSP Certified Information Systems Security Professional Official Study GuideFrom Everand(ISC)2 CISSP Certified Information Systems Security Professional Official Study GuideRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- Business Process Mapping: Improving Customer SatisfactionFrom EverandBusiness Process Mapping: Improving Customer SatisfactionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bribery and Corruption Casebook: The View from Under the TableFrom EverandBribery and Corruption Casebook: The View from Under the TableNo ratings yet
- Guide: SOC 2 Reporting on an Examination of Controls at a Service Organization Relevant to Security, Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, or PrivacyFrom EverandGuide: SOC 2 Reporting on an Examination of Controls at a Service Organization Relevant to Security, Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, or PrivacyNo ratings yet
- Audit. Review. Compilation. What's the Difference?From EverandAudit. Review. Compilation. What's the Difference?Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Layman's Guide GDPR Compliance for Small Medium BusinessFrom EverandThe Layman's Guide GDPR Compliance for Small Medium BusinessRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Frequently Asked Questions in International Standards on AuditingFrom EverandFrequently Asked Questions in International Standards on AuditingRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- GDPR for DevOp(Sec) - The laws, Controls and solutionsFrom EverandGDPR for DevOp(Sec) - The laws, Controls and solutionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Scrum Certification: All In One, The Ultimate Guide To Prepare For Scrum Exams And Get Certified. Real Practice Test With Detailed Screenshots, Answers And ExplanationsFrom EverandScrum Certification: All In One, The Ultimate Guide To Prepare For Scrum Exams And Get Certified. Real Practice Test With Detailed Screenshots, Answers And ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- A Step By Step Guide: How to Perform Risk Based Internal Auditing for Internal Audit BeginnersFrom EverandA Step By Step Guide: How to Perform Risk Based Internal Auditing for Internal Audit BeginnersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- GDPR-standard data protection staff training: What employees & associates need to know by Dr Paweł MielniczekFrom EverandGDPR-standard data protection staff training: What employees & associates need to know by Dr Paweł MielniczekNo ratings yet
- Audit and Assurance Essentials: For Professional Accountancy ExamsFrom EverandAudit and Assurance Essentials: For Professional Accountancy ExamsNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Fraud Casebook: Baking the Ledgers and Cooking the BooksFrom EverandFinancial Statement Fraud Casebook: Baking the Ledgers and Cooking the BooksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Executive Roadmap to Fraud Prevention and Internal Control: Creating a Culture of ComplianceFrom EverandExecutive Roadmap to Fraud Prevention and Internal Control: Creating a Culture of ComplianceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)