Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Domainkeys Identified Mail: Read in Another Language Watch Edit
Uploaded by
Putukan Rangers0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageDKIM is an email authentication method that detects forged sender addresses by affixing a digital signature to outgoing emails, linked to the domain name. This allows recipients to verify the signature against the domain owner's public key to confirm the email was authorized and unaltered. DKIM signatures are usually invisible to users and are applied and verified by email infrastructure instead of individuals.
Original Description:
DOMAIN ACHUCHUCHUJWJDOSKSOOSOAOSOSOSSOODOSODOD DID SIS SIS AI DLF QOWHF IS DOCK
Original Title
Domain Keys
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDKIM is an email authentication method that detects forged sender addresses by affixing a digital signature to outgoing emails, linked to the domain name. This allows recipients to verify the signature against the domain owner's public key to confirm the email was authorized and unaltered. DKIM signatures are usually invisible to users and are applied and verified by email infrastructure instead of individuals.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageDomainkeys Identified Mail: Read in Another Language Watch Edit
Uploaded by
Putukan RangersDKIM is an email authentication method that detects forged sender addresses by affixing a digital signature to outgoing emails, linked to the domain name. This allows recipients to verify the signature against the domain owner's public key to confirm the email was authorized and unaltered. DKIM signatures are usually invisible to users and are applied and verified by email infrastructure instead of individuals.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
DomainKeys Identified Mail
Read in another language
Download PDF
Watch
Edit
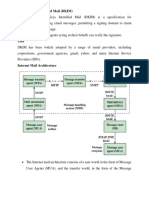
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) is an email authentication method designed to
detect forged sender addresses in emails (email spoofing), a technique often used
in phishing and email spam.
DKIM allows the receiver to check that an email claimed to have come from a
specific domain was indeed authorized by the owner of that domain.[1] It achieves this
by affixing a digital signature, linked to a domain name, to each outgoing email
message. The recipient system can verify this by looking up the sender's public
keypublished in the DNS. A valid signature also guarantees that some parts of the
email (possibly including attachments) have not been modified since the signature
was affixed.[2] Usually, DKIM signatures are not visible to end-users, and are affixed or
verified by the infrastructure rather than the message's authors and recipients.
DKIM is an "Internet standard".[3] It is defined in RFC 6376, dated September 2011;
with updates in RFC 8301 and RFC 8463.
DomainKeys Identified Mail
Read in another language
Download PDF
Watch
Edit
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) is an email authentication method designed to
detect forged sender addresses in emails (email spoofing), a technique often used
in phishing and email spam.
DKIM allows the receiver to check that an email claimed to have come from a
specific domain was indeed authorized by the owner of that domain.[1] It achieves this
by affixing a digital signature, linked to a domain name, to each outgoing email
message. The recipient system can verify this by looking up the sender's public
keypublished in the DNS. A valid signature also guarantees that some parts of the
email (possibly including attachments) have not been modified since the signature
was affixed.[2] Usually, DKIM signatures are not visible to end-users, and are affixed or
verified by the infrastructure rather than the message's authors and recipients.
DKIM is an "Internet standard".[3] It is defined in RFC 6376, dated September 2011;
with updates in RFC 8301 and RFC 8463.
You might also like
- PROTECT - How To Combat Fake Emails (August 2019)Document14 pagesPROTECT - How To Combat Fake Emails (August 2019)Evil Terms OnlyNo ratings yet
- Email Header AnalysisDocument15 pagesEmail Header AnalysisBryam Molina BatistaNo ratings yet
- Emaildfsdfsd Configuration2Document13 pagesEmaildfsdfsd Configuration2dsdfdfNo ratings yet
- Phishing Email AnalysisDocument11 pagesPhishing Email AnalysisnagarjunaNo ratings yet
- Securing Email Communication: How to Protect Your Correspondence from Wiretapping Using Free ToolsFrom EverandSecuring Email Communication: How to Protect Your Correspondence from Wiretapping Using Free ToolsNo ratings yet
- Domain Keys Identified MailDocument6 pagesDomain Keys Identified MailledjeeswaransinthujaNo ratings yet
- Email Security For IT: How To Keep Your Brand Safe: /deliversDocument6 pagesEmail Security For IT: How To Keep Your Brand Safe: /deliversCatalin StoicescuNo ratings yet
- Using Dkim With MdaemonDocument14 pagesUsing Dkim With MdaemonDaniel BarriosNo ratings yet
- What Is DMARC-huntmetricsDocument2 pagesWhat Is DMARC-huntmetricsSarah KhanNo ratings yet
- How To Set Up Dmarc For Your OrganizationDocument13 pagesHow To Set Up Dmarc For Your OrganizationManishNo ratings yet
- Email Security - SPF, DKIM and DMARCDocument7 pagesEmail Security - SPF, DKIM and DMARCMahendran LoganathanNo ratings yet
- Composition Kills: A Case Study of Email Sender AuthenticationDocument17 pagesComposition Kills: A Case Study of Email Sender AuthenticationWhally wonzkkaNo ratings yet
- DKIM Teaser 03Document3 pagesDKIM Teaser 03Chintan JustinTestNo ratings yet
- (DMARC) Overview: Domain Based Message Authentication, Reporting, and ConformanceDocument21 pages(DMARC) Overview: Domain Based Message Authentication, Reporting, and ConformanceredNo ratings yet
- KB 4 D Marc Slides 1626293010926Document91 pagesKB 4 D Marc Slides 1626293010926Alvin BosqueNo ratings yet
- Ondmarc A Buyers GuideDocument21 pagesOndmarc A Buyers GuideMuhammad Waseem AhsanNo ratings yet
- SPF Dkim DmarcDocument1 pageSPF Dkim DmarcGary GrandjeanNo ratings yet
- Protecting Your Brand From PhishingDocument5 pagesProtecting Your Brand From Phishingaariya goelNo ratings yet
- O365 Interview Questiones & AnswersDocument16 pagesO365 Interview Questiones & AnswersShaik AmanullahNo ratings yet
- rfc5585 PDFDocument23 pagesrfc5585 PDFoam901995No ratings yet
- Securing Email and Digitizing Workflows With E-Signatures: Rmail Specializes in Security and ComplianceDocument2 pagesSecuring Email and Digitizing Workflows With E-Signatures: Rmail Specializes in Security and CompliancekiranNo ratings yet
- Sender ID Framework - Deployment OverviewDocument5 pagesSender ID Framework - Deployment Overviewapi-3725016No ratings yet
- Ch5 NISDocument61 pagesCh5 NISshrey6346No ratings yet
- Domain Keys Identified Mail (DKIM) SignaturesDocument63 pagesDomain Keys Identified Mail (DKIM) Signatureseugen_2409No ratings yet
- An Empirical Analysis of Email Delivery SecurityDocument13 pagesAn Empirical Analysis of Email Delivery Securitybig datalabNo ratings yet
- Cisco Domain Protection: Implementation Process: Primary Project TasksDocument2 pagesCisco Domain Protection: Implementation Process: Primary Project TasksKherkhour MustaphaNo ratings yet
- SSL Protocol: SSL Objectives and ArchitectureDocument6 pagesSSL Protocol: SSL Objectives and Architecturemuntaha_ahmedNo ratings yet
- 3 Secrets Email Deliverability UsDocument12 pages3 Secrets Email Deliverability UskrakraoNo ratings yet
- What Do You Understand by A Digital Signature? Explain Its Application and Verification DiagrammaticallyDocument4 pagesWhat Do You Understand by A Digital Signature? Explain Its Application and Verification DiagrammaticallyDipankar GogoiNo ratings yet
- Atharva Nivalkar - IEEE - 2019 - DMARCBox-Corporate Email Security and Analytics Using DMARCDocument5 pagesAtharva Nivalkar - IEEE - 2019 - DMARCBox-Corporate Email Security and Analytics Using DMARCkunal.patil16585No ratings yet
- RFC 2632Document14 pagesRFC 2632TitoNo ratings yet
- Mdaemon SettingsDocument4 pagesMdaemon SettingswawanNo ratings yet
- Email Tip Sheet v2Document2 pagesEmail Tip Sheet v2Mevan WickramasingheNo ratings yet
- Crypto Unit 5 ...Document9 pagesCrypto Unit 5 ...Roshan PradhanNo ratings yet
- Security Issues Unit 2Document10 pagesSecurity Issues Unit 2Richa GargNo ratings yet
- Email Deliverability Terms To KnowDocument6 pagesEmail Deliverability Terms To KnowKristine BigcasNo ratings yet
- 10 My PGP Email SecurityDocument37 pages10 My PGP Email SecuritybabyNo ratings yet
- D2-S1-Cybersecurity in Banking Threats, Challenges and SolutionsDocument67 pagesD2-S1-Cybersecurity in Banking Threats, Challenges and SolutionsANJALIAGARWALNo ratings yet
- 8Document2 pages8cnpnrajaNo ratings yet
- SYMANTEC MESSAGING GATEWAY Issue ReportDocument6 pagesSYMANTEC MESSAGING GATEWAY Issue ReportatherNo ratings yet
- Digital Signatures: Homework 6Document10 pagesDigital Signatures: Homework 6leishNo ratings yet
- Digital Signature Forming and Keys Protection BaseDocument7 pagesDigital Signature Forming and Keys Protection BaseMadani ShafurahNo ratings yet
- Digital Signature Forming and Keys Protection Base PDFDocument7 pagesDigital Signature Forming and Keys Protection Base PDFMadani ShafurahNo ratings yet
- US MDaemon-Mail-Server DatasheetDocument2 pagesUS MDaemon-Mail-Server DatasheetazizanNo ratings yet
- Security Services For E-Mail Attacks Possible Through E-Mail Establishing Keys Privacy Authentication of The Source Message Integrity Non-RepudiationDocument76 pagesSecurity Services For E-Mail Attacks Possible Through E-Mail Establishing Keys Privacy Authentication of The Source Message Integrity Non-RepudiationPapithaNo ratings yet
- Second ReviewDocument11 pagesSecond ReviewUmaMaheshwari ViswanathanNo ratings yet
- Topic1 Lesson1to9 IAaS1Document62 pagesTopic1 Lesson1to9 IAaS1Kervi Sanares BacuelNo ratings yet
- 1-Advanced Social EngineeringDocument318 pages1-Advanced Social Engineeringfutdh9404No ratings yet
- SPF Dkim Dmarc Quick DeploymentDocument3 pagesSPF Dkim Dmarc Quick DeploymentNathan SwiftNo ratings yet
- Kerberos NotesDocument7 pagesKerberos Notesskhanshaikh3No ratings yet
- 4.2 Understand Kerberos Authentication and Domain SecurityDocument22 pages4.2 Understand Kerberos Authentication and Domain SecurityChitra TamilchelvanNo ratings yet
- 17 PGP Services 05 Apr 2021material I 05 Apr 2021 PGP SecurityDocument24 pages17 PGP Services 05 Apr 2021material I 05 Apr 2021 PGP SecuritySharath KumarNo ratings yet
- 3-Red Teaming Active DirectoryDocument286 pages3-Red Teaming Active Directoryfutdh9404No ratings yet
- 1 Email Architecture Refers To The Structure and Components Involved in The Transmission and Delivery of Email Messages Over NetworksDocument2 pages1 Email Architecture Refers To The Structure and Components Involved in The Transmission and Delivery of Email Messages Over NetworkscnpnrajaNo ratings yet
- Ict Prefinal HandoutsDocument5 pagesIct Prefinal HandoutsTawny ClaireNo ratings yet
- Rajagiri School of Engineering & Technology: Security in Computing - Module IvDocument21 pagesRajagiri School of Engineering & Technology: Security in Computing - Module IvAdhnan Rafeek KNo ratings yet
- Student AssignmentsDocument61 pagesStudent AssignmentsShashank GosaviNo ratings yet
- VVFGC Cns Unit2 (Final)Document13 pagesVVFGC Cns Unit2 (Final)ArthiNo ratings yet
- Phishing Analysis Glossary 1Document2 pagesPhishing Analysis Glossary 1rNo ratings yet
- E&clDocument10 pagesE&clSBANo ratings yet