Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Email Security - SPF, DKIM and DMARC
Uploaded by
Mahendran Loganathan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views7 pagesSPF, DKIM and DMARC are authentication methods used in email security to prevent spoofing and phishing. SPF uses DNS to verify sending mail servers, DKIM digitally signs emails using public key cryptography, and DMARC tells recipients what to do with emails based on SPF and DKIM results. SPF operates at the domain level to check if emails originate from authorized IP addresses, while DKIM signs individual emails with private keys and allows validation with public keys. DMARC policies enforce actions for emails that fail SPF or DKIM authentication checks.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSPF, DKIM and DMARC are authentication methods used in email security to prevent spoofing and phishing. SPF uses DNS to verify sending mail servers, DKIM digitally signs emails using public key cryptography, and DMARC tells recipients what to do with emails based on SPF and DKIM results. SPF operates at the domain level to check if emails originate from authorized IP addresses, while DKIM signs individual emails with private keys and allows validation with public keys. DMARC policies enforce actions for emails that fail SPF or DKIM authentication checks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views7 pagesEmail Security - SPF, DKIM and DMARC
Uploaded by
Mahendran LoganathanSPF, DKIM and DMARC are authentication methods used in email security to prevent spoofing and phishing. SPF uses DNS to verify sending mail servers, DKIM digitally signs emails using public key cryptography, and DMARC tells recipients what to do with emails based on SPF and DKIM results. SPF operates at the domain level to check if emails originate from authorized IP addresses, while DKIM signs individual emails with private keys and allows validation with public keys. DMARC policies enforce actions for emails that fail SPF or DKIM authentication checks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
SPF, DKIM and DMARC Explained
This Photo by Unknown author is licensed under CC BY-SA-NC.
Definition and Overview
• SPF, DKIM and DMARC are used in email security as an authentication
methods.
• They are helpful to prevent spam, Spoofing, phishing and unauthorized
persons to impersonate the legitimate domains.
• SPF is Sender Policy Framework and it lists all the tags(IP address and
Domain names) associated with the Email servers where the email could
originate from for a domain.
• DKIM is DomainKey Identified Mail, is the technic used to digitally sign
the email from the legitimate domain. DKIM uses Public Key Cryptography
technic to digitally sign the email
• DMARC is Domain-based Message Authentication Reporting and
Conformance, which tells the recipient Email server what to do based on
SPF and DKIM results.
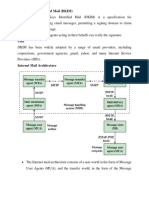
SPF – Sender Policy Framework
• TXT (text) based authentication used to identify the mail servers identify if the mail was originate from the
authorized IP addresses.
• SPF operates at domain level, not user level. So, SPF can only verify the domain not users who sends the
email.
• SPF Record needs to be updated in the DNS server.
• The Recipient Email server will reach Sender DNS server and verify the SPF record to ensure the email
originates from its domain IP address or domain names.
• If the check pass – email will be delivered to recipient user by recipient email server
• If the check fails – email will be dropped to spam, quarantine or delete based on recipient email server configuration
How SPF record works:
1. Establish or create policy
1. Define which hosts/Email servers has authority to send emails
2. DNS Lookup
1. Inbound server checks if the IP Address or domain is authorised
3. Authentication
1. Mail Server accepts, flags or reject the emails
How SPF works:
[object File]
DKIM – DomainKey Identified Mail
• DKIM signs the emails using Private Key – Digital Signature.
• DKIM uses PKI – Publis Key Cryptography.
• Sender Email server – should have Private Key
• DNS server – should have public key
• Email server sends the email signing with the Private key it has, and the
recipient Email server reach senders DNS server and check the Public key
associated with the private key.
• If the Key pairs matches – DKIM pass
• If the Key pair fails – DKIM fail
DKIM – How it works
DMARC – Domain-based Message
Authentication Recording and Conformance
You might also like
- Protecting Your Brand From PhishingDocument5 pagesProtecting Your Brand From Phishingaariya goelNo ratings yet
- How To Set Up Dmarc For Your OrganizationDocument13 pagesHow To Set Up Dmarc For Your OrganizationManishNo ratings yet
- PROTECT - How To Combat Fake Emails (August 2019)Document14 pagesPROTECT - How To Combat Fake Emails (August 2019)Evil Terms OnlyNo ratings yet
- Using Dkim With MdaemonDocument14 pagesUsing Dkim With MdaemonDaniel BarriosNo ratings yet
- O365 Interview Questiones & AnswersDocument16 pagesO365 Interview Questiones & AnswersShaik AmanullahNo ratings yet
- Email Header AnalysisDocument15 pagesEmail Header AnalysisBryam Molina BatistaNo ratings yet
- Phishing Email AnalysisDocument11 pagesPhishing Email AnalysisnagarjunaNo ratings yet
- KB 4 D Marc Slides 1626293010926Document91 pagesKB 4 D Marc Slides 1626293010926Alvin BosqueNo ratings yet
- What Is DMARC-huntmetricsDocument2 pagesWhat Is DMARC-huntmetricsSarah KhanNo ratings yet
- Mdaemon SettingsDocument4 pagesMdaemon SettingswawanNo ratings yet
- Email AnalysisDocument11 pagesEmail AnalysisRishi KaulNo ratings yet
- (DMARC) Overview: Domain Based Message Authentication, Reporting, and ConformanceDocument21 pages(DMARC) Overview: Domain Based Message Authentication, Reporting, and ConformanceredNo ratings yet
- Email Tip Sheet v2Document2 pagesEmail Tip Sheet v2Mevan WickramasingheNo ratings yet
- Email Reputation - How To Manage It - Rob Van Slyke 4-2010Document9 pagesEmail Reputation - How To Manage It - Rob Van Slyke 4-2010Rob Van SlykeNo ratings yet
- SPF RecordDocument3 pagesSPF Recordsemperor81No ratings yet
- Domainkeys Identified Mail: Read in Another Language Watch EditDocument1 pageDomainkeys Identified Mail: Read in Another Language Watch EditPutukan RangersNo ratings yet
- Emaildfsdfsd Configuration2Document13 pagesEmaildfsdfsd Configuration2dsdfdfNo ratings yet
- Composition Kills: A Case Study of Email Sender AuthenticationDocument17 pagesComposition Kills: A Case Study of Email Sender AuthenticationWhally wonzkkaNo ratings yet
- Securing Email and Digitizing Workflows With E-Signatures: Rmail Specializes in Security and ComplianceDocument2 pagesSecuring Email and Digitizing Workflows With E-Signatures: Rmail Specializes in Security and CompliancekiranNo ratings yet
- Sender ID Framework - Deployment OverviewDocument5 pagesSender ID Framework - Deployment Overviewapi-3725016No ratings yet
- Email Gateway DefenceDocument8 pagesEmail Gateway DefenceNiven MaharjanNo ratings yet
- 8Document2 pages8cnpnrajaNo ratings yet
- Email Deliverability CheatsheetDocument2 pagesEmail Deliverability CheatsheetTushar WaghNo ratings yet
- Email Security For IT: How To Keep Your Brand Safe: /deliversDocument6 pagesEmail Security For IT: How To Keep Your Brand Safe: /deliversCatalin StoicescuNo ratings yet
- Advanced ConfigurationDocument9 pagesAdvanced Configurationsomanet64No ratings yet
- 1-Advanced Social EngineeringDocument318 pages1-Advanced Social Engineeringfutdh9404No ratings yet
- Domain Keys Identified MailDocument6 pagesDomain Keys Identified MailledjeeswaransinthujaNo ratings yet
- FortiMail Troubleshooting. Antispam IssuesDocument4 pagesFortiMail Troubleshooting. Antispam Issueslig030No ratings yet
- RUDocument11 pagesRURicky NavidonNo ratings yet
- Implementation Guidelines: How Sender ID WorksDocument8 pagesImplementation Guidelines: How Sender ID WorksIvan MelgratiNo ratings yet
- Mail ServerDocument6 pagesMail ServerNaveen KolliparaNo ratings yet
- Ondmarc A Buyers GuideDocument21 pagesOndmarc A Buyers GuideMuhammad Waseem AhsanNo ratings yet
- Email Authentication: Small BusinessDocument2 pagesEmail Authentication: Small BusinessNguyễn Khắc AnhNo ratings yet
- D. Chandrika 21075A0401Document10 pagesD. Chandrika 21075A0401Chandrika Dasari.No ratings yet
- Email Deliverability Terms To KnowDocument6 pagesEmail Deliverability Terms To KnowKristine BigcasNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Office 365: Security SuggestionsDocument2 pagesMicrosoft Office 365: Security SuggestionsRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Instantly - Ai Masterclass - Land in The Inbox Every Single Time With Our Ultimate Cold Email FrameworkDocument44 pagesInstantly - Ai Masterclass - Land in The Inbox Every Single Time With Our Ultimate Cold Email Framework6figuresalesrepNo ratings yet
- Email Security ChecklistDocument10 pagesEmail Security ChecklistAhm HamzaNo ratings yet
- SYMANTEC MESSAGING GATEWAY Issue ReportDocument6 pagesSYMANTEC MESSAGING GATEWAY Issue ReportatherNo ratings yet
- Yahoo Spam Industry InitiativeDocument39 pagesYahoo Spam Industry InitiativeSuryaNo ratings yet
- Silo - Tips Ciphermail Encryption Ciphermail White PaperDocument14 pagesSilo - Tips Ciphermail Encryption Ciphermail White PaperRahil SarwarNo ratings yet
- Chapter# 8 Secure E-Mail ServiceDocument28 pagesChapter# 8 Secure E-Mail ServiceTooba ArshadNo ratings yet
- SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)Document7 pagesSMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)CodeYt WithNo ratings yet
- 2012-Dec - AUS Gov - Mitigating Spoofed Emails - Sender Policy Framework ExplainedDocument4 pages2012-Dec - AUS Gov - Mitigating Spoofed Emails - Sender Policy Framework ExplainedhhhzineNo ratings yet
- 1 Email Architecture Refers To The Structure and Components Involved in The Transmission and Delivery of Email Messages Over NetworksDocument2 pages1 Email Architecture Refers To The Structure and Components Involved in The Transmission and Delivery of Email Messages Over NetworkscnpnrajaNo ratings yet
- US MDaemon-Mail-Server DatasheetDocument2 pagesUS MDaemon-Mail-Server DatasheetazizanNo ratings yet
- Reply & ZeroBounce Webinar. Email DeliverabilityDocument26 pagesReply & ZeroBounce Webinar. Email DeliverabilityAlfychNo ratings yet
- Dmarc FaqDocument1 pageDmarc FaqsherryNo ratings yet
- An Empirical Analysis of Email Delivery SecurityDocument13 pagesAn Empirical Analysis of Email Delivery Securitybig datalabNo ratings yet
- Debian Mail Server, Part II: SPF and DKIM - Stéphane Caron PDFDocument3 pagesDebian Mail Server, Part II: SPF and DKIM - Stéphane Caron PDFASNo ratings yet
- All About Exchange Server Management and Other IdentitiesDocument19 pagesAll About Exchange Server Management and Other IdentitiesAkanksha PandeNo ratings yet
- Emails Training New (Autosaved)Document17 pagesEmails Training New (Autosaved)zainabNo ratings yet
- Dkim For ExchangeDocument26 pagesDkim For Exchangekamakom78No ratings yet
- A Study of Spam Mail Detection System Before Receiving The Message BodyDocument15 pagesA Study of Spam Mail Detection System Before Receiving The Message Bodyscribed004No ratings yet
- Electronic Mail SecurityDocument35 pagesElectronic Mail SecurityKAVITHA TNo ratings yet
- E Mailforensics 161124053030Document22 pagesE Mailforensics 161124053030gadisa gemechuNo ratings yet
- IT221 T Project Template - 1444Document9 pagesIT221 T Project Template - 1444Rr rNo ratings yet
- Investigating E-Mail AttacksDocument20 pagesInvestigating E-Mail AttacksShehroz Chishty100% (1)
- Cyber Security Long Type Pdf000-1Document14 pagesCyber Security Long Type Pdf000-1Tora SarkarNo ratings yet
- International Journal On Cryptography and Information Security (IJCIS)Document2 pagesInternational Journal On Cryptography and Information Security (IJCIS)ijcisjournalNo ratings yet
- InvitationDocument4 pagesInvitationSai SatishNo ratings yet
- 7 - Digital SignatureDocument12 pages7 - Digital SignatureMangala SemageNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument154 pagesUntitledJuanca100% (1)
- US Proxy List - Free Proxy List PDFDocument3 pagesUS Proxy List - Free Proxy List PDFEzequiel SalesNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment (I, Ii, Iii, & Iv) of Cyber SecurityDocument15 pagesIndividual Assignment (I, Ii, Iii, & Iv) of Cyber SecurityjavedNo ratings yet
- Finals Exam in Information Assurance and SecurityDocument3 pagesFinals Exam in Information Assurance and SecurityJovanna Lagradilla OcampoNo ratings yet
- Security 4CSDocument6 pagesSecurity 4CSEsraa Sayed Abdelhamed SayedNo ratings yet
- 2020 21 May CE348 ISDocument5 pages2020 21 May CE348 ISMmmNo ratings yet
- Compression N SecurityDocument29 pagesCompression N SecurityArun Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Quiz For Chapter 4 IASDocument5 pagesQuiz For Chapter 4 IASeliza marie luisNo ratings yet
- ICDL IT Security - Syllabus - V2.0 - Sample Part-Test - MSWIN7IE10 - V1 - 0Document9 pagesICDL IT Security - Syllabus - V2.0 - Sample Part-Test - MSWIN7IE10 - V1 - 0Jhasfer Harris EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Safety and SecurityDocument33 pagesSafety and Securitylatoya andersonNo ratings yet
- Nadar Saraswathi College of Engineering and Technology, TheniDocument8 pagesNadar Saraswathi College of Engineering and Technology, TheniHEMALATHA SHANMUGAMNo ratings yet
- Free Proxy ListDocument27 pagesFree Proxy ListhuhNo ratings yet
- Internet Technology Sheet 2Document8 pagesInternet Technology Sheet 2Abdelrahman ElattarNo ratings yet
- Philippine National Public Key Infrastructure (Pnpki) : Department of EducationDocument7 pagesPhilippine National Public Key Infrastructure (Pnpki) : Department of EducationJergens JackNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cyber Law: DR Topi BasarDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Cyber Law: DR Topi BasarAkhand Pratap Singh BhadouriaNo ratings yet
- IEEE P1363.3: Standard For Identity-Based Cryptographic Techniques Using Pairings Call For SubmissionsDocument2 pagesIEEE P1363.3: Standard For Identity-Based Cryptographic Techniques Using Pairings Call For SubmissionshhhzineNo ratings yet
- CNS PART B QuestionsDocument3 pagesCNS PART B Questionsஜெயபிரகாஷ் பிரபுNo ratings yet
- FTDDocument15 pagesFTDRiteesh AgrawalNo ratings yet
- WebDocument2 pagesWebMuhammad Jawad NoonariNo ratings yet
- OWASPAppSecINDIA2008 Dr. Kamlesh BajajDocument10 pagesOWASPAppSecINDIA2008 Dr. Kamlesh Bajajharshitha200516No ratings yet
- Question Bank PDFDocument10 pagesQuestion Bank PDFjayaprasanna123No ratings yet
- Public Integrity Auditing For Shared Dynamic Cloud Data With Group User RevocationDocument15 pagesPublic Integrity Auditing For Shared Dynamic Cloud Data With Group User RevocationSikkandhar Jabbar100% (1)
- Program C++ RSADocument8 pagesProgram C++ RSAAulia RaffifNo ratings yet
- Encryption Methods JackieDocument4 pagesEncryption Methods JackieJackilene Anne EleazarNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 1 NotesDocument21 pagesUNIT - 1 NotesSushant YadavNo ratings yet
- Ms GeeksDocument6 pagesMs GeeksHamid100% (1)
- Computer Project On Encryption and Decryption For Class 12thDocument13 pagesComputer Project On Encryption and Decryption For Class 12thAtul SharmaNo ratings yet