Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Growth Exit
Uploaded by
Mary Grace Dy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views4 pagesGrowth and exit strategies
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGrowth and exit strategies
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views4 pagesGrowth Exit
Uploaded by
Mary Grace DyGrowth and exit strategies
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Exit Strategy • Usually applicable to family-owned
businesses
o The way for business owners or
stakeholders to reduce involvement in the
business until they can leave it or let go of
it completely.
o If the business is successful, how does
one profit from the business/investment?
o If the business is not successful, how does
one limit losses and liability?
Common Exit Strategies
1) Merger and Acquisition
• Combining with a similar company
or being acquired by a larger one.
• Normally a win-win situation when
companies have complementary
skills and resources.
• For bigger companies, it is a more
efficient and quicker way to grow
2) Initial Public Offering (IPO)
• Offer the company ownership for
sale to the public
• Used to be preferred way of exiting
but success rates are lower.
3) Sell to Friendly Individuals
• Easy way to cash out
• Ideally, the buyer has more skills
and interest on operations and is
able to scale the company up
4) Liquidation and closing
• For failing businesses, normally
• Close up shop and liquidate (let go
or turn to cash) assets.
5) Family Succession
• Handing over the business and
enterprise to the next generation in
the family
• Common in the Philippines
Growth Strategies ✓ How can we grow our market?
• There can be further exploitation of the
products without necessarily changing
the product or the outlook of the
product.
2) Market Development
• Market Development is about selling
more of the company’s existing
products to new markets.
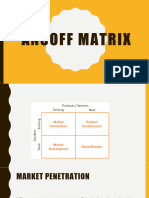
Ansoff growth matrix • This strategy is about reaching new
o assists organizations to map strategic customer segments or expanding
product market growth internationally by targeting new
o also known as the Ansoff product and geographic areas.
market growth matrix • This strategy focuses on reaching
o is a marketing planning tool which usually new markets with existing products in
aids a business in determining its product the portfolio.
and market growth. ✓ How can we extend our market?
o usually determined by focusing on ✓ Through new market sectors?
whether the products are new or existing ✓ Through new geographical
and whether the market is new or existing. areas?
o invented by H. Igor Ansoff 3) Product Development
✓ Ansoff was primarily a mathematician • This strategy focuses on reaching the
with an expert insight into business existing market with new products.
management. • Product Development is about
1) Market Penetration developing and selling new products
• Market Penetration is about selling to existing markets.
more of the company’s existing • Companies could for example
products to existing markets. make some modifications in the
• To penetrate and grow the customer existing products to give increased
base in the existing market, a value to the customers for their
company may cut prices, improve its purchase or develop and launch new
distribution network, invest more in products alongside a company’s
marketing and increase existing existing product offering. Ex: Apple
production capacity. iPhone
• This strategy focuses on increasing ✓ How can we expand our product
the volume of sales of existing portfolio by modifying or creating
products to the organization’s existing products?
market. 4) Diversification
✓ How can we defend our market • This strategy focuses on reaching
share? new markets with new products.
Diversification can be either related Failed companies
or unrelated.
• It is about entering new markets with
new products that are either related
or completely unrelated to a
company’s existing offering.
• Concentric/horizontal
diversification (or related
diversification) is about entering a
new market with a new product that
a) Virgin Cola
is somewhat related to a company’s
o most highly-publicized of Virgin's failed
existing product offering.
businesses
• Conglomerate diversification (or o soft-launched exclusively on Virgin's
unrelated diversification) on the planes and cinemas
other hand is about entering a new o managed to peak at a small but
market with a new product that is significant 0.5% market share in the
completely unrelated to a company’s US (The Guardian).
existing offering. o Production stopped in 2012
Case Study: Diversification of VIRGIN GROUP ✓ US soft drink giants fought back.
OF COMPANIES "That business taught me not to underestimate
Company Profile the power of the world's leading soft drink
makers. I'll never again make the mistake of
• multinational private limited company
thinking that all large, dominant companies are
located in London, Britain
sleepy!"
• started in 1970 by Sir Richard Branson,
CEO b) Virgin Vodka
• has more than 250 companies and is o the whole of Virgin Drinks (1994)
organized into layers of holding turned out to be a failure (The
companies, employing over 25,000 Guardian).
people. ✓ One of the most surprising of
these products is Virgin Vodka.
• Virgin headquarter is located in London,
o The entirety of Virgin Drinks (Virgin
Britain and it has a lot of subsidiaries
Vines, Virgin Energy Shot, and Virgin
around the world such as in: UK, USA,
Ooze) — folded in 2007.
Australia, South Africa, Europe, and Asia.
o Virgin Wines (sold to Direct Wines in
• Its main market activities are Producing,
2005 and was bought out in 2013 by
Marketing, Providing Services and
management) is thriving.
Retailing.
✓ £50 million ($73 million) by 2018
(The Drinks Business).
c) Virgin Cosmetics
o Virgin Cosmetics sold beauty products,
jewelry, and homeware.
o sold online, in Virgin stores, and at
home parties as two companies: Virgin
Vie at Home and The Virgin Cosmetics
company (Virgin's website).
o In 2009, the business was sold in a
management buyout to Ros Simmons
and Ratan Daryani
✓ renamed Vie at Home (The
Telegraph).
✓ became defunct in 2011.
d) Virgin Clothing
o a line of men's and women's clothing,
footwear, and accessories aimed at
those aged from 18-to-35-years-old.
✓ sold in UK retailers and department
stores
✓ dissolved soon after its launch
(CEO world magazine).
e) Virginware
o expanded rapidly after its launch, as a
result of high online sales.
o It opened 30 retail stores between
2003 and 2004 (Retail Week) including
a flagship store near Carnaby Street in
London.
o (April 2005) the brand collapsed into
administration (the Telegraph).
o In July, Virginware closed with a fire
sale of 35,000 pairs of Virgin-branded
bras and G-strings.
You might also like
- Active Directory FactsDocument171 pagesActive Directory FactsVincent HiltonNo ratings yet
- Mckinsey Growth Pyramid: Name: Ravi Chevli Batch: ITBM 2009-11 PRN: 9030241026 Topic: Growth StrategyDocument6 pagesMckinsey Growth Pyramid: Name: Ravi Chevli Batch: ITBM 2009-11 PRN: 9030241026 Topic: Growth Strategyravi_29_08No ratings yet
- Dealing with Darwin (Review and Analysis of Moore's Book)From EverandDealing with Darwin (Review and Analysis of Moore's Book)No ratings yet
- Types of StrategiesDocument62 pagesTypes of StrategiesSnigdha BansalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Strategies in ActionDocument64 pagesChapter 4 - Strategies in ActionNetsanet Workineh ነፃነት ወርቅነህ0% (1)
- The Invincible Company: How to Constantly Reinvent Your Organization with Inspiration From the World's Best Business ModelsFrom EverandThe Invincible Company: How to Constantly Reinvent Your Organization with Inspiration From the World's Best Business ModelsNo ratings yet
- Capsule Research ProposalDocument4 pagesCapsule Research ProposalAilyn Ursal80% (5)
- Types of Growth StrategiesDocument35 pagesTypes of Growth StrategiesYash MittalNo ratings yet
- 08-Developing Evaluating Strategic Options (Part 1) SVDocument12 pages08-Developing Evaluating Strategic Options (Part 1) SVJaymis DenisNo ratings yet
- Delta PresentationDocument36 pagesDelta Presentationarch_ianNo ratings yet
- Ansoff Matrix & Growth: Cesim FirmDocument17 pagesAnsoff Matrix & Growth: Cesim FirmHarshita LodhiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Building Value Through Acquisitions - DiversificationDocument16 pagesChapter 9 - Building Value Through Acquisitions - DiversificationNabil MustaqimNo ratings yet
- Revit 2019 Collaboration ToolsDocument80 pagesRevit 2019 Collaboration ToolsNoureddineNo ratings yet
- Integration StrategiesDocument7 pagesIntegration StrategiesKevin P. Bacud50% (2)
- Interview Preparation Series - Session 3Document32 pagesInterview Preparation Series - Session 3danielNo ratings yet
- Corporate Level Strategies: Dr. Nishikant C. Warbhuwan Ph. D. Mba (HRM) Be (It)Document166 pagesCorporate Level Strategies: Dr. Nishikant C. Warbhuwan Ph. D. Mba (HRM) Be (It)Salil BoranaNo ratings yet
- Business Growth StrategiesDocument19 pagesBusiness Growth StrategiesChayan GargNo ratings yet
- 9 Corporate StrategyDocument80 pages9 Corporate StrategyAyrton Cubas BulejeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Business and Management (IBM) : MA 2020/2021 Week 07aDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Business and Management (IBM) : MA 2020/2021 Week 07a林泳圻No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 ENT530Document27 pagesChapter 8 ENT530MUHAMMAD KHAIROL BIN BINTAJOLNo ratings yet
- Ansoff Matrix & Growth: Cesim FirmDocument17 pagesAnsoff Matrix & Growth: Cesim FirmHarshita LodhiNo ratings yet
- Fifth LessonDocument33 pagesFifth LessonGiorgio FranchiniNo ratings yet
- Strategic MGMT 2ADocument62 pagesStrategic MGMT 2ARiya JaiswalNo ratings yet
- GBM - MKT - Unit 3Document41 pagesGBM - MKT - Unit 3Santiago Czop0% (1)
- Strategies On ActionDocument25 pagesStrategies On ActionDory Amalia Mae GayonaNo ratings yet
- C C C CCCCCDocument3 pagesC C C CCCCCNikita BediNo ratings yet
- Corporate Level Strategies: DR - Hameed AkhtarDocument30 pagesCorporate Level Strategies: DR - Hameed AkhtarNazir AnsariNo ratings yet
- Ansoff MatrixDocument22 pagesAnsoff MatrixEdo DellacasaNo ratings yet
- Strategies in ActionDocument28 pagesStrategies in ActionClarissa Micah VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Group 14 Business GrowthDocument18 pagesGroup 14 Business GrowthJanette NañadiegoNo ratings yet
- Growth StrategyDocument14 pagesGrowth Strategyyoussefyasser59No ratings yet
- E57105 - PPT Lecture 3 StrategiesDocument45 pagesE57105 - PPT Lecture 3 StrategiesShahid Ullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument57 pagesChapter TwochuchuNo ratings yet
- 4.1.1. Strategies in ActionDocument67 pages4.1.1. Strategies in Actiondimpledhillon2000No ratings yet
- Which Strategies Are Normally AppropriateDocument13 pagesWhich Strategies Are Normally Appropriatealok kumar singhNo ratings yet
- SM - 07Document82 pagesSM - 07Jithma RanawakeNo ratings yet
- Prestige Institute of Management & Research Gwalior: Case Folio - 2010Document18 pagesPrestige Institute of Management & Research Gwalior: Case Folio - 2010Satya Kam JawalNo ratings yet
- Session 9 International Strategy New - 6377790b17033Document66 pagesSession 9 International Strategy New - 6377790b17033champika de alwisNo ratings yet
- Ch-4 Strategic ChoicesDocument24 pagesCh-4 Strategic Choicesdhwanitshah03No ratings yet
- Ansoff Matrix For DettolDocument9 pagesAnsoff Matrix For DettolMisbah ShamsNo ratings yet
- 05 - Strategic Management - Strategies in Action ClassDocument52 pages05 - Strategic Management - Strategies in Action Classmsohaib7No ratings yet
- Strategy and Implementation - Business Growth: Market PenetrationDocument17 pagesStrategy and Implementation - Business Growth: Market PenetrationHafeel MohamedNo ratings yet
- CM - Firm PositioningDocument101 pagesCM - Firm PositioningSarah MajumderNo ratings yet
- Slides02 StrategyMarketing PARTIDocument20 pagesSlides02 StrategyMarketing PARTIFrancisco Ribeiro e SilvaNo ratings yet
- Growth Strategies: Prepared By: Hilwana Abd KARIMDocument23 pagesGrowth Strategies: Prepared By: Hilwana Abd KARIMhilwanaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Concepts & Cases: Strategies in ActionDocument48 pagesStrategic Management Concepts & Cases: Strategies in ActionAdina BadeaNo ratings yet
- 4.5 The Four PS 2022Document47 pages4.5 The Four PS 2022Paula ReinosoNo ratings yet
- Business Policy&StrategyDocument15 pagesBusiness Policy&StrategyDhruv RekhiNo ratings yet
- Ansoff Matrix 1 1Document2 pagesAnsoff Matrix 1 1ahmedbaloNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management: Strategies in ActionDocument53 pagesStrategic Management: Strategies in ActionAli ShanNo ratings yet
- Boston Matrix & The Product PortfolioDocument5 pagesBoston Matrix & The Product Portfoliomeyo fredNo ratings yet
- 3.5 GlobalisationDocument4 pages3.5 GlobalisationEmperor SaladinNo ratings yet
- Fm8 Midterm Study GuideDocument14 pagesFm8 Midterm Study GuideBryce ApitNo ratings yet
- SM Unit 3 Ansoff MatrixDocument9 pagesSM Unit 3 Ansoff Matrixvishal bommineniNo ratings yet
- 3-Internal Analysis: ResourcesDocument13 pages3-Internal Analysis: ResourcesLaila RashedNo ratings yet
- Mod 6 Grand StrategiesDocument131 pagesMod 6 Grand Strategieskimsr100% (3)
- New Product Development 01Document18 pagesNew Product Development 01ravi anandNo ratings yet
- Corporate StrategyDocument41 pagesCorporate StrategymussaiyibNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Topic: Concentration and Integration StrategiesDocument19 pagesPresentation On Topic: Concentration and Integration StrategiesMalmarugan DNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management: A Report Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For The Degree of MBADocument10 pagesStrategic Management: A Report Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For The Degree of MBAYukendhar G SNo ratings yet
- Market Research &analysis: by PanipakDocument22 pagesMarket Research &analysis: by PanipakNICE TanzaniaNo ratings yet
- Unit 8: The Marketing Mix As A Business Strategy Lesson 1: ProductDocument20 pagesUnit 8: The Marketing Mix As A Business Strategy Lesson 1: ProductJulito Escalera Jr.No ratings yet
- 01 Ansoffs Matrix 121206001233 Phpapp01Document56 pages01 Ansoffs Matrix 121206001233 Phpapp01Ifeanyi Olabode IkeomumuNo ratings yet
- Business Policy & Strategy: Unit 4Document73 pagesBusiness Policy & Strategy: Unit 4Harsh y.No ratings yet
- COGELSA Food Industry Catalogue LDDocument9 pagesCOGELSA Food Industry Catalogue LDandriyanto.wisnuNo ratings yet
- Vicente, Vieyah Angela A.-HG-G11-Q4-Mod-9Document10 pagesVicente, Vieyah Angela A.-HG-G11-Q4-Mod-9Vieyah Angela VicenteNo ratings yet
- Computer System Architecture: Pamantasan NG CabuyaoDocument12 pagesComputer System Architecture: Pamantasan NG CabuyaoBien MedinaNo ratings yet
- Caso Kola RealDocument17 pagesCaso Kola RealEvelyn Dayhanna Escobar PalomequeNo ratings yet
- Intro S4HANA Using Global Bike Solutions EAM Fiori en v3.3Document5 pagesIntro S4HANA Using Global Bike Solutions EAM Fiori en v3.3Thăng Nguyễn BáNo ratings yet
- Nat Law 2 - CasesDocument12 pagesNat Law 2 - CasesLylo BesaresNo ratings yet
- Admissibility of Whatsapp Messages in Court For Family MattersDocument3 pagesAdmissibility of Whatsapp Messages in Court For Family Mattersnajihah adeliNo ratings yet
- Engagement Letter TrustDocument4 pagesEngagement Letter Trustxetay24207No ratings yet
- Copeland PresentationDocument26 pagesCopeland Presentationjai soniNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics: Production, Cost Minimisation, Profit MaximisationDocument19 pagesMicroeconomics: Production, Cost Minimisation, Profit Maximisationhishamsauk50% (2)
- Insurance Smart Sampoorna RakshaDocument10 pagesInsurance Smart Sampoorna RakshaRISHAB CHETRINo ratings yet
- IEEE Conference Template ExampleDocument14 pagesIEEE Conference Template ExampleEmilyNo ratings yet
- Certification and LettersDocument6 pagesCertification and LettersReimar FerrarenNo ratings yet
- MSA Chair's Report 2012Document56 pagesMSA Chair's Report 2012Imaad IsaacsNo ratings yet
- Starkville Dispatch Eedition 12-9-18Document28 pagesStarkville Dispatch Eedition 12-9-18The DispatchNo ratings yet
- Tindara Addabbo, Edoardo Ales, Ylenia Curzi, Tommaso Fabbri, Olga Rymkevich, Iacopo Senatori - Performance Appraisal in Modern Employment Relations_ An Interdisciplinary Approach-Springer Internationa.pdfDocument278 pagesTindara Addabbo, Edoardo Ales, Ylenia Curzi, Tommaso Fabbri, Olga Rymkevich, Iacopo Senatori - Performance Appraisal in Modern Employment Relations_ An Interdisciplinary Approach-Springer Internationa.pdfMario ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Hardware Architecture For Nanorobot Application in Cancer TherapyDocument7 pagesHardware Architecture For Nanorobot Application in Cancer TherapyCynthia CarolineNo ratings yet
- TP1743 - Kertas 1 Dan 2 Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM Sains 2023-20243Document12 pagesTP1743 - Kertas 1 Dan 2 Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM Sains 2023-20243Felix ChewNo ratings yet
- Department of Labor: 2nd Injury FundDocument140 pagesDepartment of Labor: 2nd Injury FundUSA_DepartmentOfLabor100% (1)
- Ssasaaaxaaa11111......... Desingconstructionof33kv11kvlines 150329033645 Conversion Gate01Document167 pagesSsasaaaxaaa11111......... Desingconstructionof33kv11kvlines 150329033645 Conversion Gate01Sunil Singh100% (1)
- (ENG) Visual Logic Robot ProgrammingDocument261 pages(ENG) Visual Logic Robot ProgrammingAbel Chaiña Gonzales100% (1)
- DT2 (80 82)Document18 pagesDT2 (80 82)Anonymous jbeHFUNo ratings yet
- Acevac Catalogue VCD - R3Document6 pagesAcevac Catalogue VCD - R3Santhosh KumarNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument2 pagesReviewerAra Mae Pandez HugoNo ratings yet
- Tate Modern London, Pay Congestion ChargeDocument6 pagesTate Modern London, Pay Congestion ChargeCongestionChargeNo ratings yet
- Bisleri 2.0Document59 pagesBisleri 2.0Dr Amit Rangnekar100% (4)