Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GastroIntestinal 2 PDF
Uploaded by
George KanparOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GastroIntestinal 2 PDF
Uploaded by
George KanparCopyright:
Available Formats
- Fluoroscopic examination – stomach – lumen fills – barium – stomach motility, thickness
– gastric wall, mucosal pattern, patency – pyloric valve, anatomy – duodenum.
- Obstructions, ileitis, diverticula – detected
- Enteroclysis – detailed study – entire small intestine
- Nursing interventions – advices – against – smoking, chewing gum, using mints
- Follow – up care – eliminate – ingested barium.
Lower Gastrointestinal Tract Study
- Barium enema – detect – presence – polyps, tumours, other lesions – of large intestine
- Procedure – 15 to 30 minutes
- Double contrast studies & water – soluble contrast study – visualizing – colon.
- Nursing Interventions – emptying & cleansing – lower bowel – low – residue diet – 1 to
2 days before – test
- Postprocedural – increasing fluid intake – evaluating bowel movements – noting
increased number – bowel movements.
Computed Tomography
- Cross – sectional images – abdominal organs & structures.
- Multiple x – ray images
- Detecting & localizing – many inflammatory conditions – colon – appendicitis,
diverticulitis, regional enteritis, ulcerative colitis, diseases – liver, spleen, kidney,
pancreas, pelvic organs, structural abnormalities – abdominal wall.
- Three – dimensional CT – detailed pictures – GI organs.
- Nursing Interventions – allergies - contrast agents – iodine, shellfish, patient’s current
serum creatinine level – urine human chorionic gonadotropin - must be determined –
before administration – contrast agent
- Allergic – contrast agent – IV prednisone 24 hours, 12 hours, & 1 hour – before scan.
- Renal protective measures – administration – IV sodium bicarbonate 1 hour before & 6
hours after IV contrast & oral acetylcysteine before or after – study.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Gastroenterology - supplement – ultrasonography & CT
- Uses – magnetic fields & radio waves – produce images – area – being studied
- Use – oral contrast agents – application – diagnosis – GI diseases.
- Useful – evaluating – abdominal soft tissues, blood vessels, abscesses, fistulas,
neoplasms, other sources – bleeding.
- Not totally safe – all people – attracted – magnet – cause injury.
- Contraindicated – patients – permanent pacemakers, artificial heart valves and
defibrillators, implanted insulin pumps, implanted transcutaneous electrical nerve
stimulation devices, internal metal devices, intraocular metallic fragments, cochlear
implants.
- Nursing Interventions - removal – all jewelry – other metals.
- Deep breaths – intervals.
Endoscopic Procedures
- Fibroscopy/ esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) – small bowel enteroscopy,
colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, proctoscopy, anoscopy, endoscopy through ostomy.
Upper Gastrointestinal Fibroscopy/ Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
- Direct visualization – esophageal, gastric, & duodenal mucosa through – lighted
endoscope
- Collect secretions – tissue specimens – further analysis
- PillCam ESO2 – pill sized instrument – two cameras – seven photographs per second –
transmits – wirelessly – nearby storage device
- Side – viewing flexible scopes – visualize – common bile duct & pancreatic & hepatic
ducts – through – ampulla of Vater – in duodenum.
- Evaluating jaundice, pancreatitis, pancreatic tumours, common bile duct stones, & biliary
tract disease.
- Therapeutic endoscopy – remove common bile duct stones, dilate strictures, treat gastric
bleeding & esophageal varices.
- Nursing Interventions – local anesthetic gargle or spray – Midazolam, sedative –
administered. Atropine – reduce secretions, Glucagon – relax smooth muscle. Patient –
left lateral position – clearance of pulmonary secretions.
Fibreoptic Colonoscopy
- Computer – simulated endoluminal – air – filled distended colon – using conventional
spiral or helical CT scanning.
- Direct visual inspection – large intestine – flexible fibreoptic colonoscope.
- Cancer screening – previous colon cancer or polyps.
- Other uses: evaluation – diarrhea of unknown cause, occult bleeding, or anemia,
abnormalities – detected – barium enema, other bowel disease.
- Therapeutically – remove – visible polyps
- Colonoscopic polypectomy – early detection – prevention – colorectal cancer.
- Biopsy forceps or a cytology brush – through – scope – obtain specimens – histology &
cytology examinations.
- Nursing Interventions – polyethylene glycol electrolyte lavage solutions – intestinal
lavages – effective cleansing – bowel.
- Clear liquid diet – ingests – lavage solution – orally – intervals – 3 to 4 hours.
- Monitoring elderly patients – nurse’s knowledge – daily medication – instructs –
maintain adequate fluid, electrolyte & caloric intake
- Cannot be performed – suspected or documented colon perforation, acute severe
diverticulitis, or fulminant colitis.
- Informed consent – before – patient is sedated
- After – test – signs & symptoms – of bowel perforation.
Sigmoidoscopy
- Endoscopic examination – anus, rectum sigmoid & descending colon – evaluate chronic
diarrhea, fecal incontinence, ischemic colitis, & lower GI hemorrhage – observe –
ulceration, fissures, abscesses, tumour, polyps, or other pathologic processes.
- Flexible fibreoptic sigmoidoscope – colon – examined – up to 40 to 50 cm – from anus –
with rigid sigmoidoscope.
- Biopsies & polypectomies – performed – during procedure.
- Nursing Interventions – limited bowel preparation – warm tap water or Fleet’s enema
- Monitor – vital signs, skin colour, temperature, pain tolerance, vagal response.
- After – procedure – rectal bleeding, intestinal perforation.
Laparoscopy (Peritoneoscopy)
- After – pneumoperitoneum – small incision – lateral – umbilicus – insertion – fibreoptic
laparoscope.
- Direct visualization – organs – structures – within – abdomen, any growths, anomalies,
inflammatory processes.
- Evaluate peritoneal disease, chronic abdominal pain, abdominal masses, gallbladder, &
liver disease.
- General anesthesia – gas – insufflated – peritoneal cavity – create – working space –
visualization
Hepatobiliary System
Ultrasonography
- Rapid and accurate – used – patients – liver dysfunction – jaundice
- Does not expose – ionizing radiation
- Can detect calculi – in gallbladder – or dilated common bile duct
Radionuclide Imaging or Cholescintigraphy
- Diagnosis – acute cholecystitis or blockage – of bile duct
- Radioactive agent – administered intravenously – taken up – hepatocytes – excreted –
through biliary tract
- Cannot detect gallstones.
Cholecystography
- Oral cholangiography – detect gallstones
- Healthy gallbladder – fills – radioplaque substance
- Gallstones – present – appear – shadows – x – ray film.
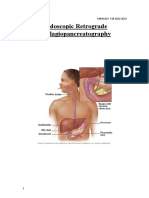
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
- Direct visualization – structures – could be seen – during laparotomy
- Flexible fibre optic endoscope – inserted – through – esophagus – to descending
duodenum
- Require – multiple position changes
- Fluoroscopy & multiple x – rays – used – ERCP – evaluate – presence of ductal stones
- Insertion – catheter – through – endoscope – into common bile duct – important step – in
sphincterotomy – gallstone extraction
- Nursing Implications – patient – explanation – procedure. Moderate sedation –
administer medications – glucagon or anticholinergics – to make – cannulation easier –
decreasing duodenal peristalsis.
- Observes – signs of respiratory & CNS depression, hypotension, oversedation, vomiting.
During ERCP – intravenous (IV) fluids, medications & positions.
- After procedure – observe – vital signs & signs – perforation or infection – side effects –
return of the gag – cough reflexes – after – use – anesthetics.
Percutaneous Transhepatic Cholangiography
- Injection – dye – directly – into biliary tract
- Entire length – common bile duct, cystic duct, gallbladder – outlined clearly
- Carried out – presence – liver dysfunction & jaundice
- Useful: distinguishing jaundice – caused by liver disease from – caused by biliary
obstruction
- Investing – GI symptoms – patient – gall – bladder – removed.
- Locating stones – within – bile ducts
- Diagnosing – cancer – involving – biliary system
- Procedure –moderate sedation – been fasting. Coagulation parameters – platelet count –
normal – minimize bleeding. Broad spectrum antibiotics – administered.
- Flexible needle – inserted – liver – right side – in midclavicular line – beneth – right
costal margin.
- Bile – aspirated – samples – sent – bacteriology & cytology.
- Water – soluble contrast agent – injected – fill – biliary system. Fluoroscopy – table –
tilted – repositioned – allow x – rays – taken – multiple projections.
You might also like
- GastrontestinalSystem PDFDocument1 pageGastrontestinalSystem PDFGeorge KanparNo ratings yet
- Imaging of Git & Hepatobiliary Systems CSLDocument70 pagesImaging of Git & Hepatobiliary Systems CSLSara ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Surgical Treatment: Shany Schwarzwald s1711 DR Cojocaru CristinaDocument12 pagesSurgical Treatment: Shany Schwarzwald s1711 DR Cojocaru CristinaShany SchwarzwaldNo ratings yet
- Symptomatology of GUT DisordersDocument75 pagesSymptomatology of GUT DisordersMaraJoRNNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis Cholelithiasis PresentationDocument21 pagesCholecystitis Cholelithiasis PresentationPrincess Meinny JeanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Teaching ErcpDocument8 pagesClinical Teaching ErcpDeep Kaur100% (1)
- Clinical Examination of Genitourinary SystemDocument43 pagesClinical Examination of Genitourinary SystemKeamina .aNo ratings yet
- 3 Obat Sedasi Dan Analgesia-Prof Munar - LubisDocument93 pages3 Obat Sedasi Dan Analgesia-Prof Munar - LubisFahmi NurNo ratings yet
- Endoscopic Retrograde CholagiopancreatographyDocument5 pagesEndoscopic Retrograde CholagiopancreatographyDavid SalamounNo ratings yet
- Imaging in Genitourinary SystemDocument77 pagesImaging in Genitourinary SystemIrvan R. Loho100% (1)
- Gynaecological Laproscopy: By: DR - Hanaa Al-HeideryDocument22 pagesGynaecological Laproscopy: By: DR - Hanaa Al-Heideryzianab aliNo ratings yet
- Diagon SticDocument79 pagesDiagon SticRamyaNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint: Lecture 10, The Small Bowel and AppendixDocument89 pagesPowerpoint: Lecture 10, The Small Bowel and Appendixj.doe.hex_87100% (1)
- Imaging Tractus UrinaryDocument94 pagesImaging Tractus UrinaryJuan Ortega PutraNo ratings yet
- Endoscopic Diagnosis of Diseases of The Intestine.Document12 pagesEndoscopic Diagnosis of Diseases of The Intestine.Roy D RogerNo ratings yet
- Definition of The Disease: Risk FactorsDocument13 pagesDefinition of The Disease: Risk FactorsDivine Ballesteros Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Paeds Surgery Open Question HintsDocument5 pagesPaeds Surgery Open Question Hintsferdosjm74No ratings yet
- Imaging of The Genitourinary Tract: Mashuri, DR.,SP - Rad.,M.KesDocument90 pagesImaging of The Genitourinary Tract: Mashuri, DR.,SP - Rad.,M.KesmirzasullivanNo ratings yet
- Imaging in Genitourinary System - 17 Agustus 2013 - by Robby HermawanDocument80 pagesImaging in Genitourinary System - 17 Agustus 2013 - by Robby HermawanFitria Dewi LestariNo ratings yet
- Liver StudiesDocument59 pagesLiver Studiesgothandaramanr74No ratings yet
- Irregular Bowel HabitDocument66 pagesIrregular Bowel Habitfahim ahamedNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Urography (IVU)Document35 pagesIntravenous Urography (IVU)sushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Investigations:) - To Diagnose Lesions in The Oesophageal orDocument4 pagesInvestigations:) - To Diagnose Lesions in The Oesophageal orMarwan M.No ratings yet
- Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP)Document3 pagesIntravenous Pyelogram (IVP)Nestle FolienteNo ratings yet
- Imaging Diagnostic TestsDocument3 pagesImaging Diagnostic Testscornergirl_flameNo ratings yet
- Endoscopic Retrograde CholangiopancreatographyDocument7 pagesEndoscopic Retrograde CholangiopancreatographyMat JawiNo ratings yet
- Hepatobiliary SystemDocument66 pagesHepatobiliary SystemBikash SubediNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Surgery Exit Test 2022Document11 pagesPaediatric Surgery Exit Test 2022ferdosjm74No ratings yet
- Topic 23. X-RayDocument2 pagesTopic 23. X-RayMadeline WanhartNo ratings yet
- BiliaryDocument41 pagesBiliaryayundyawibowoNo ratings yet
- Investigation JF The Urinary TractDocument139 pagesInvestigation JF The Urinary TractВладимир КурпаянидиNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis - Gallbladder Inflammation, Symptoms, TreatmentDocument6 pagesCholecystitis - Gallbladder Inflammation, Symptoms, TreatmentJubitta JobyNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint: Colorectal Surgical DiseasesDocument74 pagesPowerpoint: Colorectal Surgical Diseasesj.doe.hex_87100% (1)
- Gastrointestinal System DisordersDocument112 pagesGastrointestinal System DisordersTaate MohammedNo ratings yet
- Hepato-Biliary System 26.4.2016Document59 pagesHepato-Biliary System 26.4.2016S B SayedNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Disorders Billiary Disorder HandoutsDocument12 pagesMetabolic Disorders Billiary Disorder HandoutsEdelen GaleNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan IVPDocument41 pagesPemeriksaan IVPChandra Noor SatriyoNo ratings yet
- Imaging of The Genitourinary TractDocument86 pagesImaging of The Genitourinary TractNor AinaNo ratings yet
- GIT & Urinary SystemDocument50 pagesGIT & Urinary SystemRenishya ManiarasuNo ratings yet
- Lecture-3 GIT RKDocument46 pagesLecture-3 GIT RKmuhammadameerhamza4786No ratings yet
- ASWATHYDocument61 pagesASWATHYJuvana LachuNo ratings yet
- What Is Pancreatitis?Document8 pagesWhat Is Pancreatitis?Medi JoNo ratings yet
- ErcpDocument22 pagesErcpPutu YoanaNo ratings yet
- ConciseDocument10 pagesConciseLeiNo ratings yet
- Urology Notes 1Document43 pagesUrology Notes 1Shazaan NadeemNo ratings yet
- Examination of The Gastrointestinal TractDocument44 pagesExamination of The Gastrointestinal TractDrNaveen Singh Rajpurohit Kadu100% (1)
- Vijendra Kumar: Compiled byDocument15 pagesVijendra Kumar: Compiled byvijendrakumarsahuNo ratings yet
- Abdominal TBDocument53 pagesAbdominal TBnaveen kumar kushwahaNo ratings yet
- Bowel Obstruction - ppt1Document30 pagesBowel Obstruction - ppt1Elfrida Aulia100% (1)
- Surgical Management of Benign Causes of Obstructive JaundiceDocument29 pagesSurgical Management of Benign Causes of Obstructive JaundiceNaviNo ratings yet
- Bowel ObstructionDocument10 pagesBowel Obstructionenke.nwekeNo ratings yet
- Colostomy and The GallbladderDocument13 pagesColostomy and The GallbladderJustin Ahorro-DionisioNo ratings yet
- Vaginal FistulaDocument14 pagesVaginal FistulaNainesh RavaliyaNo ratings yet
- Renal System (Output)Document30 pagesRenal System (Output)Tiffy SuarezNo ratings yet
- Referat EndosDocument29 pagesReferat EndosShenaquitaIvandraNo ratings yet
- Methods of ExaminationDocument56 pagesMethods of Examinationj.doe.hex_87No ratings yet
- Principles and Practice of GI EndosDocument101 pagesPrinciples and Practice of GI Endosrajan kumar90% (21)
- Endoscopic, Retrograde Cholangio Pancreatography ERCPDocument17 pagesEndoscopic, Retrograde Cholangio Pancreatography ERCPHamzeh AlmasriNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Interventional Endoscopy: Advanced TechniquesFrom EverandGastrointestinal Interventional Endoscopy: Advanced TechniquesMihir S. WaghNo ratings yet
- Diversity in NursingDocument9 pagesDiversity in NursingGeorge KanparNo ratings yet
- LS2 Disorders of The Uterus and Ovaries Pelvic Organ ProlapseDocument2 pagesLS2 Disorders of The Uterus and Ovaries Pelvic Organ ProlapseGeorge KanparNo ratings yet
- Alkaline Cell Batteries PDFDocument1 pageAlkaline Cell Batteries PDFGeorge KanparNo ratings yet
- MATH SolutionDocument2 pagesMATH SolutionGeorge KanparNo ratings yet
- Glomerular FilterationDocument2 pagesGlomerular FilterationGeorge KanparNo ratings yet
- Basic Medical Procedures NoteDocument14 pagesBasic Medical Procedures NoteGeorge KanparNo ratings yet
- Hardy Weinberg Calculation1Document8 pagesHardy Weinberg Calculation1Rishikaphriya Rauichandran100% (1)
- Quiz On Burn and ScaldsDocument9 pagesQuiz On Burn and ScaldsSalinKaur0% (1)
- Patient NCPDocument8 pagesPatient NCPlouie john abilaNo ratings yet
- Resume Updated 2-18.2Document1 pageResume Updated 2-18.2Keith CarsonNo ratings yet
- Bell's Palsy - Symptoms and Causes - Mayo ClinicDocument6 pagesBell's Palsy - Symptoms and Causes - Mayo ClinicRoxan PacsayNo ratings yet
- Western Mindanao State University College of Nursing: Zamboanga CityDocument11 pagesWestern Mindanao State University College of Nursing: Zamboanga CitySHAINA ALIH. JUMAANINo ratings yet
- Anestheology Latest PDFDocument254 pagesAnestheology Latest PDFSamiir DNo ratings yet
- Overview On Cucurbita MaximaDocument4 pagesOverview On Cucurbita MaximaIRFAN KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Typology of Nursing Problems FNCPDocument9 pagesTypology of Nursing Problems FNCPPrsnigarbha Dasi D PotianNo ratings yet
- Pentra 60Document308 pagesPentra 60Leonardo M. MonteiroNo ratings yet
- Teaching Care Plan For CancerDocument6 pagesTeaching Care Plan For CancerAinah Kristia Manzon67% (3)
- Prinsip OnkologiDocument20 pagesPrinsip OnkologiTitaPuspitasariNo ratings yet
- LeishmaniasisDocument77 pagesLeishmaniasisjaveria choudharyNo ratings yet
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Review 2017 PDFDocument12 pagesAcute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Review 2017 PDFOsiithaa CañaszNo ratings yet
- NCP PainDocument4 pagesNCP PainFlauros Ryu JabienNo ratings yet
- Oral Health Care Industry in IndiaDocument3 pagesOral Health Care Industry in IndiaSaranya KRNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 - Reading and WritingDocument6 pagesGrade 11 - Reading and Writingelika.alfonsoNo ratings yet
- Family Health AssessmentDocument47 pagesFamily Health Assessmentangeleigh viernesNo ratings yet
- 2022 25 E1351 E1366Document16 pages2022 25 E1351 E1366Ricardo PietrobonNo ratings yet
- Biology Assignment Draft Copy Minna and AishDocument7 pagesBiology Assignment Draft Copy Minna and AishAish ThangalNo ratings yet
- Wheat Belly by Dr. William DavisDocument9 pagesWheat Belly by Dr. William DavissimasNo ratings yet
- Circular ExcisionDocument2 pagesCircular ExcisionIde Bagoes InsaniNo ratings yet
- Operon Problems 1Document2 pagesOperon Problems 1Anwesha BoseNo ratings yet
- Enteral and Parenteral NutritionDocument46 pagesEnteral and Parenteral NutritionbashiruaminuNo ratings yet
- SB7 Lessons-1and10 FDocument24 pagesSB7 Lessons-1and10 FJenny ChoNo ratings yet
- Autoantibodies: Prof Sami Salman, FRCP, MRCP, DMR, Ces, MB CHBDocument40 pagesAutoantibodies: Prof Sami Salman, FRCP, MRCP, DMR, Ces, MB CHBamereNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Boon or A Curse: Chemical IndustryDocument1 pageChemistry - Boon or A Curse: Chemical IndustryproodootNo ratings yet
- 10 Early Signs of LupusDocument3 pages10 Early Signs of LupusJessica RomeroNo ratings yet
- The Seven Basic ChakrasDocument4 pagesThe Seven Basic ChakrasAlesha Rose100% (1)
- 2021 Article 2376Document6 pages2021 Article 2376Anna Sofía ParedesNo ratings yet