Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Honeypots 1. High-Interaction Honeypots
Uploaded by
Karen GarzaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Honeypots 1. High-Interaction Honeypots
Uploaded by
Karen GarzaCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Honeypots
1. High-Interaction Honeypots
High-Interaction Honeypots are configured with a verity of services which is basically
enabled to waste the time of an attacker and gain more information from this
intrusion. Multiple honeypots can be deployed on a single physical machine to be
restored if attacker even compromised the honeypot.
2. Low-Interaction Honeypots
Low-Interaction Honeypots are configured to entertain only the services that are
commonly requested by the users. Response time, less complexity and few resources
make Low-interaction honeypot deployment more easy as compared to High-
interaction honeypots.
Detecting Honeypots
The basic logic of detecting a honeypot in a network is by probing the services. The
attacker usually crafts a malicious packet to scan running services on the system and
open and closed ports information. These services may be HTTPS, SMTPS or IMAPS or
else. Once attacker extracts the information, it can attempt to build a connection, the
actual server will complete the process of three-way handshaking but the deny of
handshaking indicates the presence of a honeypot. Send-Safe Honeypot Hunter,
Nessus, and Hping tools can be used to detect honeypots.
Page 374 of 503
IDS, Firewall and Honeypot System
Intrusion Detection Tools
Snort
Snort is an open source intrusion prevention system which delivers the most effective
and comprehensive real-time network defense solutions. Snort is capable of protocol
analysis, real-time packet analysis, and logging. It can also search and filter content,
detect a wide variety of attacks and probes including buffer overflows, port scans, SMB
probes and much more. Snort can also be used in various forms including a packet
sniffer, a packet logger, network file logging device, or as a full-blown network
intrusion prevention system.
Snort Rule
Rules are a criterion for performing detection against threats and vulnerabilities to the
system and network, which leads to the advantage of zero-day detection. Unlike
signatures, rules are focused on detecting the actual vulnerabilities. There are two
ways to get Snort rules:
1. Snort Subscribers Rule
2. Snort Community Rule
There is no much difference in between Snort Subscribers rule and Community rule.
However, Subscriber rules are updated frequently and updated on the device as well. It
requires a paid subscription to get real-time updates of Snort Rules. Community rules
are updated by Snort Community containing all rules as the Subscribers set of the rule
contains but they are not updated quickly as subscriber rule is.
Snort rules are comprised of two logical sections:
1. The rule header
The rule header contains the rule's action, protocol, source and destination IP
addresses and netmasks, and the source and destination ports information.
2. The rule options
The rule option section contains alert messages and information on which parts of the
packet should be inspected to determine if the rule action should be taken.
Categories of Snort Rules
Snort rules are categorized into different categories and frequently updated by TALOS.
Some of these categories are
Application Detection Rule Category includes the rules monitoring Controlling of
traffic of certain application. These rules control the behavior and network activities of
these applications.
app-detect.rules
Black List Rules category include the URL, IP address, DNS and other rules that have
been determined to be an indicator of malicious activities.
blacklist.rules
Page 375 of 503
You might also like
- CompTIA Security - SY0-601 CertDocument437 pagesCompTIA Security - SY0-601 CertGayatri Naidu88% (8)
- Wireless Packet Analyzer Tool With Ip Traceroute PDFDocument9 pagesWireless Packet Analyzer Tool With Ip Traceroute PDFIrfan YudanurNo ratings yet
- IT Data Security: Assignment-1Document12 pagesIT Data Security: Assignment-1ManthanNo ratings yet
- Network Behavior-Analysis Systems With The Use of Learning Set and Decision Rules Based On DistanceDocument12 pagesNetwork Behavior-Analysis Systems With The Use of Learning Set and Decision Rules Based On DistanceThanh Mon100% (1)
- Packet SniffingDocument13 pagesPacket SniffingMohan KokkulaNo ratings yet
- HTML 5 in Simple StepsDocument1 pageHTML 5 in Simple StepsDreamtech Press50% (4)
- Packet Sniffing: - by Aarti DhoneDocument13 pagesPacket Sniffing: - by Aarti Dhonejaveeed0401No ratings yet
- What Is A Honeypot?Document8 pagesWhat Is A Honeypot?Anup SahuNo ratings yet
- Packet SniffersDocument42 pagesPacket SniffersAmit BoraNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP Vulnerabilities Explored: Sniffing, Spoofing, HijackingDocument17 pagesTCP/IP Vulnerabilities Explored: Sniffing, Spoofing, HijackingHemant Sudhir WavhalNo ratings yet
- How to Defeat Advanced Malware: New Tools for Protection and ForensicsFrom EverandHow to Defeat Advanced Malware: New Tools for Protection and ForensicsNo ratings yet
- Top 50 Ethical Hacking Interview Questions and AnswersDocument11 pagesTop 50 Ethical Hacking Interview Questions and AnswersAHMED MOHAMED100% (1)
- Final ReportDocument22 pagesFinal ReportSitansu Sekhar MohantyNo ratings yet
- Soft Token User GuideDocument27 pagesSoft Token User GuideSreekar PamuNo ratings yet
- GDP R Contents ListDocument2 pagesGDP R Contents ListNipun MistryNo ratings yet
- NAT Practice With BGP and PBR: Lab TopologyDocument6 pagesNAT Practice With BGP and PBR: Lab TopologyAye KyawNo ratings yet
- Installing and Using Snort To Monitor and Control A NetworkDocument5 pagesInstalling and Using Snort To Monitor and Control A NetworkjbascribdNo ratings yet
- Honey PotDocument17 pagesHoney PotManu KumarNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument5 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemArchana AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Technical Seminar On Packet Sniffing: Sailatha.SDocument15 pagesTechnical Seminar On Packet Sniffing: Sailatha.SAnonymous ty7mAZNo ratings yet
- Detect Packet Sniffers with Anti-Sniffing TechniquesDocument15 pagesDetect Packet Sniffers with Anti-Sniffing Techniquessathvik patilNo ratings yet
- Packet Sniffers: Media". Sharing Means That Computers Can Receive Information That Was Intended ForDocument42 pagesPacket Sniffers: Media". Sharing Means That Computers Can Receive Information That Was Intended ForSHAIK CHAND PASHANo ratings yet
- IDPSDocument12 pagesIDPSمطيع برهومNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Given A Scenario, Implement Configuration Changes To Existing Controls To Improve SecurityDocument3 pages3.2 Given A Scenario, Implement Configuration Changes To Existing Controls To Improve Securityw aizuqNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.5 - Cyber SecurityDocument10 pagesExperiment No.5 - Cyber SecurityNIRANJAN KALENo ratings yet
- Honeypot Vicky1Document42 pagesHoneypot Vicky1vickyNo ratings yet
- Honey PotsDocument7 pagesHoney PotsSusmita MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection Using SnortDocument1 pageIntrusion Detection Using SnortAditya KumarNo ratings yet
- A New Cell-Counting-Based Attack Against TorDocument13 pagesA New Cell-Counting-Based Attack Against TorBala SudhakarNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 Web-SecurityDocument21 pagesUnit-5 Web-SecurityJay ZalaNo ratings yet
- Case Study Based On Intrusion Detection SystemDocument5 pagesCase Study Based On Intrusion Detection SystemAnonymous tIi0h0No ratings yet
- Review On Packet Sniffer Tools: KEYWORD: Reconnaissance, Social Engineering, Foot PrintingDocument21 pagesReview On Packet Sniffer Tools: KEYWORD: Reconnaissance, Social Engineering, Foot PrintingharshNo ratings yet
- Information Security LectureDocument5 pagesInformation Security LectureIsrafil TagulaoNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument35 pagesProject ReportKshitij BhilareNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.5 - Cyber SecurityDocument10 pagesExperiment No.5 - Cyber SecurityNIRANJAN KALENo ratings yet
- Snort - A Network Intrusion Prevention and Detection SystemDocument15 pagesSnort - A Network Intrusion Prevention and Detection SystemAshish MeenaNo ratings yet
- SnortDocument20 pagesSnortChoi SiwonNo ratings yet
- The Honeypot ProjectDocument28 pagesThe Honeypot ProjectVaibhav VermaNo ratings yet
- Sec+ Study Guide 401Document34 pagesSec+ Study Guide 401Tuan NamNo ratings yet
- Honey Pot Seminar REportDocument35 pagesHoney Pot Seminar REportparzpinku90% (10)
- BSIT 3-2 Student's Network Security Tools and Concepts AssignmentDocument3 pagesBSIT 3-2 Student's Network Security Tools and Concepts AssignmentJOEL JR. MANALOTONo ratings yet
- ExerciseAssigment ManalotojoelDocument3 pagesExerciseAssigment ManalotojoelJOEL JR. MANALOTONo ratings yet
- Method To Monitor The Transfer of Packets: Packet Sniffer: AbstractDocument3 pagesMethod To Monitor The Transfer of Packets: Packet Sniffer: AbstractNikhil ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Snort - An Network Intrusion Prevention and Detection SystemDocument20 pagesSnort - An Network Intrusion Prevention and Detection SystemChintanNo ratings yet
- 1) - System VulnerabilityDocument7 pages1) - System Vulnerabilitykanaiya valviNo ratings yet
- EHDFchapter 4Document14 pagesEHDFchapter 4Ahmad Raza AnsariNo ratings yet
- Snort - An Network Intrusion Prevention and Detection SystemDocument20 pagesSnort - An Network Intrusion Prevention and Detection SystemPhạm Trần Hồng QuânNo ratings yet
- Design & Implementation of Linux Based Network Forensic System Using HoneynetDocument5 pagesDesign & Implementation of Linux Based Network Forensic System Using HoneynetIjarcet JournalNo ratings yet
- Distributed Host IDS Detects AttacksDocument6 pagesDistributed Host IDS Detects Attacksanand_gsoft3603No ratings yet
- Honeypot: A Security Tool in Intrusion DetectionDocument6 pagesHoneypot: A Security Tool in Intrusion DetectionIonut ConstantinNo ratings yet
- Agent Based Efficient Anomaly Intrusion Detection System in Ad Hoc NetworksDocument74 pagesAgent Based Efficient Anomaly Intrusion Detection System in Ad Hoc NetworksdineshshaNo ratings yet
- Published Research PaperDocument14 pagesPublished Research PaperharshNo ratings yet
- Detect Intruders with IDSDocument11 pagesDetect Intruders with IDSShem KiprutoNo ratings yet
- Section C Lecture 2Document9 pagesSection C Lecture 2Anushka NigamNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument23 pagesIntrusion Detection Systemabhijitkakati100% (1)
- Detect Network Sniffing with Mobile AgentsDocument4 pagesDetect Network Sniffing with Mobile AgentsAayush AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Honeypot Seminar Report Analysis and DeploymentDocument23 pagesHoneypot Seminar Report Analysis and Deploymenttanuj kumarNo ratings yet
- EnumerationDocument12 pagesEnumerationNiranjana KarandikarNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Packet SniffingDocument6 pagesResearch Paper On Packet Sniffinggz8pheje100% (1)
- Detecting Backdoors: Yin Zhang and Vern PaxsonDocument11 pagesDetecting Backdoors: Yin Zhang and Vern PaxsonombidasarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document24 pagesLecture 8Alhussain DarbiNo ratings yet
- Systems and Network Security QuestionsDocument8 pagesSystems and Network Security QuestionsAndima Jeff HardyNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection Systems: An IntroductionDocument7 pagesIntrusion Detection Systems: An IntroductionBùi Tuấn SơnNo ratings yet
- Advanced Networks and Security Part 2 - Partial Exam 11 January 2017Document3 pagesAdvanced Networks and Security Part 2 - Partial Exam 11 January 2017diegoantivirusNo ratings yet
- Ceh V10-54-3Document2 pagesCeh V10-54-3Karen GarzaNo ratings yet
- Patch Management: Patches and HotfixesDocument1 pagePatch Management: Patches and HotfixesKaren GarzaNo ratings yet
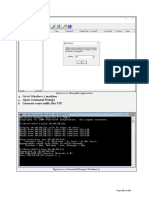
- Go To Windows 7 Machine 5. Open Command Prompt 6. Generate Some Traffic Like FTPDocument1 pageGo To Windows 7 Machine 5. Open Command Prompt 6. Generate Some Traffic Like FTPKaren GarzaNo ratings yet
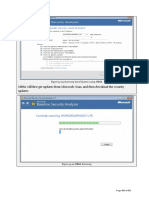
- MBSA Will First Get Updates From Microsoft, Scan, and Then Download The Security UpdatesDocument1 pageMBSA Will First Get Updates From Microsoft, Scan, and Then Download The Security UpdatesKaren GarzaNo ratings yet
- Advantages Disadvantages: 3. Stateful Multilayer Inspection FirewallDocument2 pagesAdvantages Disadvantages: 3. Stateful Multilayer Inspection FirewallKaren GarzaNo ratings yet
- Ceh V10-56-6Document1 pageCeh V10-56-6Karen GarzaNo ratings yet
- Ceh V10-52-1Document1 pageCeh V10-52-1Karen GarzaNo ratings yet
- Ceh V10-52-2Document1 pageCeh V10-52-2Karen GarzaNo ratings yet
- Back To Windows Server 2016 and Observe The LogsDocument1 pageBack To Windows Server 2016 and Observe The LogsKaren GarzaNo ratings yet
- Fragmentation Attack: Denial-Of-Service Attack (Dos)Document2 pagesFragmentation Attack: Denial-Of-Service Attack (Dos)Karen GarzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: Evading IDS, Firewall and HoneypotsDocument1 pageChapter 12: Evading IDS, Firewall and HoneypotsKaren GarzaNo ratings yet
- Ceh V10-55-3Document2 pagesCeh V10-55-3Karen GarzaNo ratings yet
- Web Application Concepts: Server AdministratorDocument1 pageWeb Application Concepts: Server AdministratorKaren GarzaNo ratings yet
- Ceh V10-58-7Document1 pageCeh V10-58-7Karen GarzaNo ratings yet
- Evading Firewalls: Firewall IdentificationDocument2 pagesEvading Firewalls: Firewall IdentificationKaren GarzaNo ratings yet
- Lab 13-1: Web Server Footprinting Using ToolDocument1 pageLab 13-1: Web Server Footprinting Using ToolKaren GarzaNo ratings yet
- Web Server Misconfiguration VulnerabilitiesDocument1 pageWeb Server Misconfiguration VulnerabilitiesKaren GarzaNo ratings yet
- Ceh V10-55-3Document2 pagesCeh V10-55-3Karen GarzaNo ratings yet
- Enter The Query The Server/buttonDocument1 pageEnter The Query The Server/buttonKaren GarzaNo ratings yet
- CEH v10 Module 21 - References ESDocument7 pagesCEH v10 Module 21 - References ESKaren GarzaNo ratings yet
- Ceh V10-57-4Document1 pageCeh V10-57-4Karen GarzaNo ratings yet
- Ceh V10-56-6Document1 pageCeh V10-56-6Karen GarzaNo ratings yet
- IIS Web Server Architecture: Components of IIS Protocol ListenerDocument1 pageIIS Web Server Architecture: Components of IIS Protocol ListenerKaren GarzaNo ratings yet
- Fragmentation Attack: Denial-Of-Service Attack (Dos)Document2 pagesFragmentation Attack: Denial-Of-Service Attack (Dos)Karen GarzaNo ratings yet
- Evading Firewalls: Firewall IdentificationDocument2 pagesEvading Firewalls: Firewall IdentificationKaren GarzaNo ratings yet
- Go To Windows 7 Machine 5. Open Command Prompt 6. Generate Some Traffic Like FTPDocument1 pageGo To Windows 7 Machine 5. Open Command Prompt 6. Generate Some Traffic Like FTPKaren GarzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13: Hacking Web Servers: Technology BriefDocument1 pageChapter 13: Hacking Web Servers: Technology BriefKaren GarzaNo ratings yet
- Web Server Misconfiguration VulnerabilitiesDocument1 pageWeb Server Misconfiguration VulnerabilitiesKaren GarzaNo ratings yet
- IIS Web Server Architecture: Components of IIS Protocol ListenerDocument1 pageIIS Web Server Architecture: Components of IIS Protocol ListenerKaren GarzaNo ratings yet
- Diskstation: An Ideal First Nas For EveryoneDocument7 pagesDiskstation: An Ideal First Nas For EveryoneAlex Raiker Yañez CastroNo ratings yet
- Atlanta Public Library Benchmark AnalysisDocument10 pagesAtlanta Public Library Benchmark AnalysisMason RouseyNo ratings yet
- Share and Discover Knowledge On SlideShareDocument6 pagesShare and Discover Knowledge On SlideShareDionelioM100% (1)
- Onair2 HTML Instructions: Structure of The ProjectDocument2 pagesOnair2 HTML Instructions: Structure of The ProjectSubash DNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of Practical Materia Medica Vol 1 by John Henry ClarkeDocument949 pagesDictionary of Practical Materia Medica Vol 1 by John Henry ClarkeYaniv AlgrablyNo ratings yet
- C.Cure 9000 System Architecture: TCP/IP NetworkDocument1 pageC.Cure 9000 System Architecture: TCP/IP NetworkSarvan KumarNo ratings yet
- Command CenterDocument1 pageCommand Centeryemeru67No ratings yet
- Silver Peak Training BrochureDocument4 pagesSilver Peak Training BrochureMin HtutNo ratings yet
- AEM Application Server (JBOSS) Install - TA Digital LabsDocument8 pagesAEM Application Server (JBOSS) Install - TA Digital LabsGourav ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- DC-13221 DCMC14 LogDocument403 pagesDC-13221 DCMC14 LogPurshottam ReddyNo ratings yet
- Communication Via Video ConferencingDocument6 pagesCommunication Via Video ConferencingChad CagurolNo ratings yet
- Lgrac-20180820 075452.logDocument15 pagesLgrac-20180820 075452.logAbraham0% (1)
- OSPF Interview Questions - CSL Training - CISCO, Microsoft, Linux, Juniper, Asterisk, MikroTik, CCNA Training in BangladeshDocument11 pagesOSPF Interview Questions - CSL Training - CISCO, Microsoft, Linux, Juniper, Asterisk, MikroTik, CCNA Training in BangladeshChetan ShivamurthyNo ratings yet
- Cisco UCS C-Series GUI Configuration Guide 131 Chapter8Document6 pagesCisco UCS C-Series GUI Configuration Guide 131 Chapter8dayscholar2013No ratings yet
- Internship report on networking coursesDocument7 pagesInternship report on networking courses188W1A0520-SEC-A GUTTIKONDA HARSHA SRINo ratings yet
- Python Sending Email Using SMTPDocument10 pagesPython Sending Email Using SMTPJames NgugiNo ratings yet
- Cisco Identity Services Engine Troubleshooting Guide, Release 1.0.4Document40 pagesCisco Identity Services Engine Troubleshooting Guide, Release 1.0.4Claudio GuzmanNo ratings yet
- BCom Practical Exam ScheduleDocument2 pagesBCom Practical Exam ScheduleRoshan BagariaNo ratings yet
- Web Programming Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesWeb Programming Exam QuestionsHemanthNo ratings yet
- Guarantee 100% Pass Cisco 350-801 ExamDocument4 pagesGuarantee 100% Pass Cisco 350-801 ExamArsic AleksandarNo ratings yet
- tryVPN EE Tallinn TCP80.ovpnDocument2 pagestryVPN EE Tallinn TCP80.ovpnirNo ratings yet
- Test Cases 6.3.1 Field Validation Test Cases Table 6.3.1 Field Validation Test CasesDocument5 pagesTest Cases 6.3.1 Field Validation Test Cases Table 6.3.1 Field Validation Test CasesPrabha BaskaranNo ratings yet
- How To Get Started With BloggerDocument39 pagesHow To Get Started With BloggerFariza KhalidNo ratings yet
- Configuring The iDRAC Using The Web InterfaceDocument30 pagesConfiguring The iDRAC Using The Web InterfacemzardarNo ratings yet
- SoloLearn (HTML)Document22 pagesSoloLearn (HTML)Md Tanvir MahtabNo ratings yet