0% found this document useful (0 votes)
286 views29 pagesConstruction Management Essentials Guide
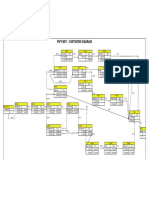
This document provides an introduction to project planning and construction management. It defines key concepts like projects, project management, and the triple constraints of scope, time and cost. It discusses the project life cycle and risks during a project's life. It also outlines the roles and responsibilities of various project parties like the client, designer, and contractor. The importance of communication, planning, and managing the project team and stakeholders is emphasized.
Uploaded by
Rush YoganathanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
286 views29 pagesConstruction Management Essentials Guide
This document provides an introduction to project planning and construction management. It defines key concepts like projects, project management, and the triple constraints of scope, time and cost. It discusses the project life cycle and risks during a project's life. It also outlines the roles and responsibilities of various project parties like the client, designer, and contractor. The importance of communication, planning, and managing the project team and stakeholders is emphasized.
Uploaded by
Rush YoganathanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd