Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ninja - Autacoids PDF
Uploaded by
Erica Hyeyeon LeeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ninja - Autacoids PDF
Uploaded by
Erica Hyeyeon LeeCopyright:
Available Formats
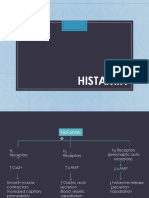
Autacoids:
Histamine Agonists
→ Autacoids have diverse physiological and pharmacological activities; have brief lifetime and act near their site of synthesis
→ Formed by decarboxylation of L-histidine
→ Exists in bound form in granules of mast cells or basophils and in enterochromaffin-like cells in the fundus of the stomach! release histamine to activate parietal cells
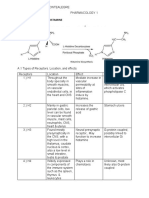
Drug Name Receptor Mechanism Indication/Effects Storage and Release
CVS: Immunologic release: Type I HSN
-Vasodilation with H1 and H2 receptors (flushing) -Ag binds to IgE on mast cells/ basophils! Ca2+ mediated
→ H1 receptors: higher affinity but rapid and short lived; degranulation ! release histamine, ATP and other mediators
-linked to G-proteins stimulation leads to release of NO :vasodilation
-constitutive activity! active even in the absence of histamine (anti-histamines → H2 receptors: develops slowly and is more sustained Chemical/Mechanical release:
are thus inverse agonists) -Amines (morphine and tubocurarine) displace bound histamine from
Heart: heparin complex; no energy required
- H2mediated ↑contractility and ↑conduction velocity -mast cell injury causes degranulation and histamine release
- H1 mediated ↓contractility and ↑capillary permeability! edema Adverse Effects
-Located on postsynaptic membranes in brain -Triple response: intradermal injection causes a localized red
-present in endothelium, smooth mm., nerve endings spot(vasodilation), brighter red flush/flare (stimulation of axon Histamine Toxicity: dose related
Histamine H1 -Gq: ↑PLC ! ↑IP3/DAG!↑Ca2+ reflexes) and a wheal (reflects capacity to cause edema) -Flushing
-Hypotension
GI Tract: H1 mediated contraction -Reflex tachycardia d/t vasodilation
-Located on postsynaptic membranes in brain
H2 -present in gastric mucosa, cardiac muscle cells & immune cells
-Gs!↑Adenylyl cyclase!↑cAMP
Bronchioles: H1 mediated bronchoconstriction
-Headache
-GI upset
-bronchoconstriction
Reduces transmitter release from histaminergic and other neurons
H3 CNS: H1 mediated sensory never stimulation (esp. pain/itching)
-wheals
-Found on leukocytes in the BM and blood
Secretory Tissue: H2 mediated activation of gastric parietal cells! -Urticaria (hives) d/t ↑ capillary permeability
-Chemotactic on eosinophils and mast cells
HCl secretion, pepsin/IF production -Anaphylaxis: txt with Epinephrine
H4 -Role in inflammation and allergies
Clinical Uses: Pulmonary Function Testing! provokes bronchial DO NOT give to asthmatics or patients with PUD/GI bleed
hyperactivity (peptic ulcer)
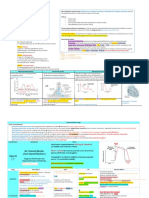
Autacoids: Histamine Antagonists Anti-histamines
Drug Name Class/Description Mechanism/Effects Uses Adverse Effects
Physiological Antagonist DOC for Anaphylaxis and other
Epinephrine Acts at a separate receptor conditions that involve massive
Actions on smooth mm. cells opposite to histamine histamine release
Cromolyn Mast cell stabilizer Reduce mast cell degranulation via unknown
Asthma [mild asthma; slow action]
Nedocromil (release inhibitor) mechanism (β-2 agonists may have same effect)
• diphenhydramine -Sedation (caution with other drugs that cause sedation!
• dimenhydrinate Chlorpheniramine
Inverse Agonist!↓ constitutive activity contraindicated while operating machinery)
Cyclizine 1st generation alone: motion
• promethazine
Px: motion sickness First Generation H1 Antagonists -Dry mouth d/t anticholinergic effects
Dimenhydrinate sickness and nausea;
Also block cholinergic, α-adrenergic, serotonin -Autonomic blocking actions are additive with those of muscarinic
Diphenhydramine somnifacient! insomnia
Cross the BBB! Sedative effects -M1 and local anesthetic receptor sites (unrelated to antagonists and α-antagonists
Hydroxyzine • M blocker ^like scopolamine
More likely to block autonomic receptors • α blocker their blocking of H1 receptors) -Acute poisoning: common in young children; hallucinations,
Meclizine Allergic conditions:
• 5HT blocker
excitement, ataxia, convulsions; untxted! coma and collapse of
Promethazine • Na channel blocker
-allergies caused by antigens acting
(local anesthetic) cardiorespiratory system
of IgE-antibody sensitized mast
Cardiac toxicity: involves blockade of HERG K+ channels in heart!
cells
prolongation of the action potential by blocking cardiac K+ channels
Second generation H1 Antagonist
Fexofenadine -Astemizole and Terfenadine withdrawn from US! torsades de
DOC in controlling sxs of allergic
Loratadine pointes (potentially fatal)
Less sedating b/c they are less able to cross the BBB !less Inverse Agonist!↓ constitutive activity rhinitis and urticaria
Cetirizine -Combo with ketoconazole, itraconazole, macrolide antibiotics
liposoluble
Astemizole (erythromycin) or grapefruit juice! toxicity by inhibiting CYP3A4!↑
!actively pumped out of brain by P-glycoprotein Ineffective in txt of bronchial
Terfenadine antihistamine concentration in blood
transporter asthma
**Fexofenadine lacks cardiac toxicity effects
Peptic ulcers (promotes healing) -Extremely safe and usually don’t occur: HA, dizzy, diarrhea,
constipation, muscular pain
Competitively and reversible H2 inhibitors! Acute stress ulcers associated with - IV !confusion, hallucination, agitation (more common w/
↓cAMP! ↓ gastric acid secretion induced by major trauma in ICU pts. cimetidine)
Cimetidine
histamine or gastrin NOT secretion induced by - Rapid IV infusion!bradycardia and hypotension (give over 30min)
Antacids Ranitidine
H2 Antagonist muscarinic agonists GERD prevention and txt (may not -blood dyscrasias and reversible liver abnormalities (Rare)
Famotidine
work for at least 45min)
Nizatidine
Can cross placenta but have not shown harmful Cimetidine:
-tidine effects!give only when necessary - inhibits CYP450!slow metabolism of other drugs
-binds to androgen receptors! gynecomastia, ↓sperm count,
galactorrhea
no problems
in pregnancy
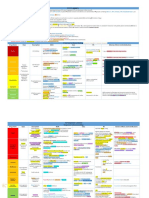
Autacoids: Serotonin Agonists and Antagonists
→ Formed from L-tryptophan via hydroxylation followed by decarboxylation
→ Stored or rapidly inactivated by MAO mediated oxidation
→ Found in enterochromaffin cells in the GI tract, platelets, and raphe nuclei of the brain stem (where the cell bodies of serotonergic neurons are found)
→ Precursor of melatonin in the pineal gland
→ Brain serotonergic neurons involved in mood, sleep, appetite, temperature regulation, perception of pain, blood pressure regulation and vomiting
Drug Name Class/Description Mechanism/Effect Uses Adverse Effects
Seven families of
GI tract:
5-HT receptor
-5-HT2 mediated ↑GI motility & vasoconstriction
subtypes
-5-HT4 mediated ↑ ACh release! mediates
prokinetic effects of serotonin agonists
Serotonin (5-HT) -5-HT3 is the only No clinical applications as a drug overproduction of 5-HT! severe diarrhea
CVS: 5-HT2 mediated constriction of veins/arteries
ligand-gated ion
Platelets: 5-HT2A mediated platelet aggregation
channel, all
CNS: 5-HT3 mediated vomiting reflex and pain/itch
others are G-
perception ^ion channel
protein coupled
on CN5
DOC for acute severe migraines (not Contraindications:
on BV
-Reduce both sensory activation in the periphery prophylaxis) • patients with CAD or angina
5-HT 1D/1B
Sumatriptan and nociceptive transmission in the brainstem - may cause coronary vasospasm
Agonist
(prototype) trigeminal nucleus!diminish central sensitization Migraines are d/t calcitonin gene-related
(Triptans)
-cause vasoconstriction peptide, substance P and neurokinin A!
vasodilation
Prokinetic Agent! promote and organize gut
motility Somnolence, Nervousness, & Dystonic rxns :5HT3R
-facilitates ACh release from enteric neurons Extrapyramidal effects & tardive dyskinesia (Rare) D2R
Galactorrhea (infrequent)
Gastroparesis
Metoclopramide Central anti-dopaminergic actions! antinauseant,
5-HT4 Agonist Emesis
Cisapride antiemetic Cisapride no longer available in US d/t cardiac effects!
D2 antagonist GERD
↑ action potential! QT prolongation! v-tach, v-fib,
Peripheral anti-dopaminergic actions!enhance torsades de pointes (esp. with other drugs that inhibit
prokinetic activity by counteracting the inhibitory CYP3A4)
effect of D2 receptors
Antagonists Allergic/ Vasomotor rhinitis
H1 effect
Allergic conjunctivitis
Potent H1 blocking actions
Cold urticaria
Dermatographism :hives - able to draw on skin
Cyproheptadine 5-HT2 Antagonist Blocks smooth mm. effects of serotonin and
Carcinoid Tumor effects on smooth mm.
H1 antagonist histamine, but has no effect on gastric acid
M antagonist Serotonin Syndrome ( ↑5-HT1A and 5-HT2
secretion
stimulation! hyperthermia, mm. rigidity,
myoclonus! can be fatal)
controls severe nausea and vomiting in
Ondansetron 5-HT3 Antagonist Powerful anti-emetic
patients undergoing chemotherapy
Ergotamine Nausea and vomiting (most common)
Migraine
Dihydroergotamine α receptors
Bromocriptine 5HT receptors Ergotamine and Ergonovine- vasospasm
Agonist, partial agonist, and antagonist actions at Hyperprolactinemia d/t pituitary tumor
Cabergoline - agonist
- partial agonist
α-adrenoceptors and 5-HT receptors
- antagonist Contraindicated in pregnant women, pts with
Ergot Alkaloids Postpartum Hemorrhage when oxytocin is
peripheral vascular disease. CAD, HTN, and impaired
DAgonist or partial agonist action at CNS dopamine
receptors ineffective [IM]
Ergonovine hepatic/renal fxn
receptors
- agonist
Methylergonovine - partial agonist
[IV] Ergonovine: provoke coronary artery
Should not be used concurrently with drugs that cause
spasm! diagnose variant angina
vasoconstriction
coronary aa
look like a vine
Autacoids: Eicosanoids and Eicosanoid Antagonists
→ Subgroups includes prostaglandins, prostacyclins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes
→ Generated de-novo from arachidonic acid found esterified in phospholipids; not found preformed
→ Direct activation of phospholipase A2 or ↑ Ca2+ can activate eicosanoid synthesis
→ Cyclo-oxygenase pathway: initiates biosynthesis of PGs, Prostacyclins and thromboxanes
o COX1 found in most cells as a constitutive enzyme and the PGs it produces are involved in normal homeostasis
o COX2 found in inflammatory cells and is expressed by growth factors, tumor promoters, and cytokines (LPS endotoxin associated)
→ Lipoxygenase Pathway: initiate the synthesis of leukotrienes and lipoxins via 5-lipoxygenase
o Present in inflammatory cells
o Associated with asthma, anaphylactic shock, and cardiovascular disease
o LTC4 and LTD4! potent bronchoconstriction and are primary components of slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRS-A) secreted in asthma and anaphylaxis
o LTB4 is a potent neutrophil chemoattractant
Drug Name Class Description MOA Uses
Ripen cervix at or near term ≈induce labor
Dinoprostone PGE2
Abortion
Ripen cervix at or near term ≈induce labor
Postpartum hemorrhage
Misoprostol PGE1 synthetic derivative Abortion when used in combination with a progesterone
antagonist (mifepristone/methotrexate)
Act in autocrine and paracrine fashion
Prevention of peptic ulcers in patients taking ↑doses of NSAIDS
Bind to G-protein coupled receptors (Gs, Gi or Gq)
Carboprost Postpartum hemorrhage
15-methyl-PGF2α
Tromethamine Eicosanoids Abortion
Contractile effects on smooth mm. are mediated by release of
Ca2+ IV!maintain patency of the ductus arteriosus in infants with
transposition of the great vessels
Alprostadil PGE1 Relaxing effects are mediated by elevation in cAMP
Impotence
(vasodilator) Severe pulmonary HTN (↓ peripheral, pulm, and coronary
PGI2
Epoprostenol resistance)
Prostacyclin
Prevents platelet aggregation in dialysis machines
AE:
Latanoprost PGF2α Glaucoma (↑ outflow of aqueous humor) •• conjunctival hyperemia
iris pigmentation
• hypertrichosis
Zileuton Inhibits 5-lypoxygenase Moderate-severe asthma in pts. who are poorly controlled by
Eicosanoid
Zafirlukast Leukotriene inhibitors conventional therapy or experience adverse effects with
Antagonists Inhibits binding of LTD4 to its receptor on target tissues
Montelukast corticoids
Stimulate lipocortin! Inhibit cytosolic phospholipase A2!
block arachidonic acid
Glucocorticoids Anti-inflammatory actions
Inhibit COX-2 synthesis
NSAIDs Inhibit COX 1 and COX 2 Antipyretic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity
You might also like
- Histamine 5-ht Angiotensin Kinin Endothelins Eicosanoids Interleukins TNF Interferones Growth FCDocument57 pagesHistamine 5-ht Angiotensin Kinin Endothelins Eicosanoids Interleukins TNF Interferones Growth FCFaisal 'arifNo ratings yet
- Ninja - Anti-HTN PDFDocument6 pagesNinja - Anti-HTN PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (2)
- Immunopharmacology PDFDocument2 pagesImmunopharmacology PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- Approximate Equivalents:: 0.100 Gmn. 1.00 GMDocument8 pagesApproximate Equivalents:: 0.100 Gmn. 1.00 GMakane ryuNo ratings yet
- Opioids PDFDocument2 pagesOpioids PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- Sphere: These DiarrheaDocument3 pagesSphere: These Diarrheamed testNo ratings yet
- GI Drugs PDFDocument6 pagesGI Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Cell Wall Inhibitors and Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Antibiotics Mechanisms of ActionDocument3 pagesCell Wall Inhibitors and Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Antibiotics Mechanisms of Actionyanks1120No ratings yet
- Ninja - Antianginal Drugs PDFDocument2 pagesNinja - Antianginal Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- 0.5. ANS Quicksheet PDFDocument1 page0.5. ANS Quicksheet PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- Ninja - Anemias PDFDocument1 pageNinja - Anemias PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- Drug ClassDocument13 pagesDrug ClassEdfren Salazar Colon100% (1)
- Northern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016Document48 pagesNorthern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016dreneavalentinstefanNo ratings yet
- (OS 213) LEC 03 Drugs Acting On The Respiratory System (1) - 1Document16 pages(OS 213) LEC 03 Drugs Acting On The Respiratory System (1) - 1Yavuz DanisNo ratings yet
- Pharma ChartsDocument33 pagesPharma ChartsNooreen Hussain100% (1)
- Adrenergic AgentsDocument45 pagesAdrenergic AgentsAmit ShahNo ratings yet
- ANS DrugsDocument2 pagesANS Drugsmed testNo ratings yet
- Ninja - Antihyperlipidemics PDFDocument3 pagesNinja - Antihyperlipidemics PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Different Body Receptors PDFDocument1 pageDifferent Body Receptors PDFSantosh patelNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Mnemonics: SinduDocument14 pagesPharmacology Mnemonics: SinduSindu SaiNo ratings yet
- Path CNS Robbins Outline: Owl Club Review Sheets 1Document37 pagesPath CNS Robbins Outline: Owl Club Review Sheets 1Coy NuñezNo ratings yet
- Drug Suffixes and Their MeaningsDocument3 pagesDrug Suffixes and Their MeaningsSharon TanveerNo ratings yet
- Ninja - Cholinergic Drugs PDFDocument4 pagesNinja - Cholinergic Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (2)
- Common MedicationsDocument4 pagesCommon MedicationsFatima CarricoNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Medication Chart - EBM Consult v3Document2 pagesAntiarrhythmic Medication Chart - EBM Consult v3Linlin100% (1)
- Lang 10 EditionDocument235 pagesLang 10 Editionraju niraulaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Cardiovascular DrugsDocument21 pagesRespiratory and Cardiovascular DrugsCandace Flowers100% (3)
- Primary Care Antibiotic Guideline FINAL May 2015Document10 pagesPrimary Care Antibiotic Guideline FINAL May 2015Atta Muhammad MemonNo ratings yet
- Diuretics - AMBOSS PDFDocument9 pagesDiuretics - AMBOSS PDFOpio Isaac100% (1)
- Mechanisms of Drug Toxicity: Proceedings of the Third International Pharmacological MeetingFrom EverandMechanisms of Drug Toxicity: Proceedings of the Third International Pharmacological MeetingH. RaškováNo ratings yet
- Year 2 Drug ListDocument8 pagesYear 2 Drug ListRay100% (1)
- UWorld - Psych Review Charts (From Questions)Document47 pagesUWorld - Psych Review Charts (From Questions)uowhywxuuiragjadchNo ratings yet
- Dyslipidemia: Hisham Aljadhey, Pharmd, PHDDocument55 pagesDyslipidemia: Hisham Aljadhey, Pharmd, PHDRany Waisya0% (1)
- NSAIDS and SteroidsDocument2 pagesNSAIDS and Steroidsmed testNo ratings yet
- AntimicrobialsDocument1 pageAntimicrobialsRomaine Barrett100% (1)
- Anxiety Disorders Treatment OptionsDocument5 pagesAnxiety Disorders Treatment OptionsJohn HolmesNo ratings yet
- Uworld JournalDocument3 pagesUworld JournalJayNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 22: Antipsychotic Agents & Lithium: OutlineDocument5 pagesLECTURE 22: Antipsychotic Agents & Lithium: OutlineRosa PalconitNo ratings yet
- Drug Side Effects No1Document5 pagesDrug Side Effects No1Kacper DaraszkiewiczNo ratings yet
- Rosh ReviewsDocument19 pagesRosh ReviewsTracy NwanneNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology SummaryDocument16 pagesPharmacology Summaryshenric16No ratings yet
- Pharmacology MnemonicsDocument17 pagesPharmacology MnemonicsAzfar AkramNo ratings yet
- SJDWHDJSDJSDDocument358 pagesSJDWHDJSDJSDwide mind hackerNo ratings yet
- Review Handouts For Medical Pharmacology PDFDocument21 pagesReview Handouts For Medical Pharmacology PDFAndres F. TorresNo ratings yet
- Classification of DrugsDocument10 pagesClassification of DrugsSafura IjazNo ratings yet
- AntiemeticsDocument25 pagesAntiemeticsPridho GaziansyahNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsDocument18 pagesPharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsPadmavathy Naidu Chokkapu100% (2)
- Pharmacology Mnemonics (Part 01) by M IhtishamDocument32 pagesPharmacology Mnemonics (Part 01) by M Ihtishammuhammad ihtisham ul hassan100% (1)
- Clinical Pharmacology: Proceedings of the 7th International Congress of Pharmacology, Paris 1978From EverandClinical Pharmacology: Proceedings of the 7th International Congress of Pharmacology, Paris 1978P. Duchêne-MarullazNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Cardiology and Pulmonology: A Practically Painless ReviewFrom EverandPediatric Cardiology and Pulmonology: A Practically Painless ReviewNo ratings yet
- AntihistaminDocument44 pagesAntihistaminDWI RAHMA HALIDANo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument93 pagesPharmacologyPh SamerNo ratings yet
- Medichem Unit-1 Remaining NotesDocument7 pagesMedichem Unit-1 Remaining Notesarunpandey651No ratings yet
- Topnotch Pharma Supertable JAN 2016Document166 pagesTopnotch Pharma Supertable JAN 2016Dar AD50% (2)
- SNS and PNS Drugs (Cholinergics and Adrenergics)Document5 pagesSNS and PNS Drugs (Cholinergics and Adrenergics)Whitney Krabbenhoft100% (1)
- Biosynthesis of HistamineDocument11 pagesBiosynthesis of HistamineAnaliza Kitongan LantayanNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric DrugDocument10 pagesPsychiatric DrugKollebeng Pangda PasiwatNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology, II SemDocument186 pagesPharmacology, II SemSheba RoymonNo ratings yet
- Ninja - Anemias PDFDocument1 pageNinja - Anemias PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- Nsaids: Celecoxib, Meloxicam Aspirin, Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Indomethacin Ketorolac, Naproxen, PiroxicamDocument2 pagesNsaids: Celecoxib, Meloxicam Aspirin, Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Indomethacin Ketorolac, Naproxen, PiroxicamErica Hyeyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- GI Drugs PDFDocument6 pagesGI Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Pharmacogenomics PDFDocument1 pagePharmacogenomics PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- Asthma - Respiratory PDFDocument1 pageAsthma - Respiratory PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee0% (1)
- Ninja - Antihyperlipidemics PDFDocument3 pagesNinja - Antihyperlipidemics PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Ninja - Drugs Heart Failure PDFDocument4 pagesNinja - Drugs Heart Failure PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- Ninja - Antiarrhythmic Drugs PDFDocument7 pagesNinja - Antiarrhythmic Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Ninja - Antianginal Drugs PDFDocument2 pagesNinja - Antianginal Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- Ninja - Anti-Coagulants PDFDocument3 pagesNinja - Anti-Coagulants PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Ninja - Adrenergic Drugs PDFDocument6 pagesNinja - Adrenergic Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- 0.5. ANS Quicksheet PDFDocument1 page0.5. ANS Quicksheet PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- Ninja - Diuretics PDFDocument3 pagesNinja - Diuretics PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Pharmacokinetics - Introduction To ANS PDFDocument2 pagesPharmacokinetics - Introduction To ANS PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Ninja - Cholinergic Drugs PDFDocument4 pagesNinja - Cholinergic Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (2)
- Combiflam Tablets PI - 08072019Document13 pagesCombiflam Tablets PI - 08072019ArunNo ratings yet
- Ah102 Syllabus 20180417lDocument7 pagesAh102 Syllabus 20180417lapi-399629502No ratings yet
- Temazepam (Restoril)Document1 pageTemazepam (Restoril)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- RIS2018 - For Pullout MedDocument156 pagesRIS2018 - For Pullout MedJZik SibalNo ratings yet
- 634729889337886250Document50 pages634729889337886250Santosh PayghanNo ratings yet
- ARSENAL Hospital OvalleDocument23 pagesARSENAL Hospital OvalleLeonardo AlcotaNo ratings yet
- Medical Marijuana Dispensary Laws: Fees and TaxesDocument4 pagesMedical Marijuana Dispensary Laws: Fees and TaxesMPP100% (2)
- Opioid Abusers Prefer Hydrocodone or Oxycodone For Different ReasonsDocument1 pageOpioid Abusers Prefer Hydrocodone or Oxycodone For Different Reasonsobx4everNo ratings yet
- NsaidDocument29 pagesNsaidEditya Apriliani100% (1)
- Leaflet Interaksi ObatDocument4 pagesLeaflet Interaksi ObatHabibahNo ratings yet
- 2.tukak PeptikDocument42 pages2.tukak PeptikEfvi VhyLiaNo ratings yet
- D Pharm.Document20 pagesD Pharm.Gaurav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Sedative HypnoticsDocument39 pagesSedative HypnoticsFatima ShaukatNo ratings yet
- Ketoprofen PMDocument39 pagesKetoprofen PMWahyu AttariaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing Process Worksheet: USF College of Nursing: NUR 4467LDocument4 pagesPediatric Nursing Process Worksheet: USF College of Nursing: NUR 4467Lapi-324566318No ratings yet
- MEDIKAMENTEDocument6 pagesMEDIKAMENTEmihalciucioanaaNo ratings yet
- ACMD Meth Annex November 2005Document32 pagesACMD Meth Annex November 2005Tara-lea GrillsNo ratings yet
- Treating Major Depressive Disorder: A Quick Reference GuideDocument28 pagesTreating Major Depressive Disorder: A Quick Reference GuideMortumDamaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studymisstheatricality130No ratings yet
- Scalp PsoriasisDocument11 pagesScalp Psoriasisvasu7900No ratings yet
- Drug Study Classification and Effects of Piperacillin Sodium and TazobactamDocument6 pagesDrug Study Classification and Effects of Piperacillin Sodium and TazobactamArvin BeltranNo ratings yet
- ASHP Guidelines On Pharmacist-ConductedDocument3 pagesASHP Guidelines On Pharmacist-ConductedGirba Emilia100% (1)
- Cymbalta (Duloxetine HCL) Patient Information - Side Effects and Drug Images at RxlistDocument7 pagesCymbalta (Duloxetine HCL) Patient Information - Side Effects and Drug Images at Rxlisteiad-mahmoudNo ratings yet
- Excipients As Absorption Enhancers For Drug Delivery ApplicationsDocument37 pagesExcipients As Absorption Enhancers For Drug Delivery ApplicationsAsadZahidNo ratings yet
- Maxicare Reimbursement Claim Form PDFDocument1 pageMaxicare Reimbursement Claim Form PDFJolina de VeraNo ratings yet
- Benign Disorders of The Vulva: Pruritus (Itchy) Vulva Vulval Skin and Pain DisordersDocument106 pagesBenign Disorders of The Vulva: Pruritus (Itchy) Vulva Vulval Skin and Pain DisordersMichelle Fynes100% (2)
- Code of Ethics for Kenyan PharmacistsDocument20 pagesCode of Ethics for Kenyan PharmacistsKevin Chapley50% (2)
- Best medication-taking solution with DISPILL blister packsDocument4 pagesBest medication-taking solution with DISPILL blister packstonygogo100% (1)
- S19640en PDFDocument47 pagesS19640en PDFDrSyeda RimaNo ratings yet
- At-A-Glance Outpatient Management Reference For Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Document8 pagesAt-A-Glance Outpatient Management Reference For Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)RushdaNo ratings yet