Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lec15 - Renal System
Uploaded by
George Constante Valiente-SebastianOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lec15 - Renal System
Uploaded by
George Constante Valiente-SebastianCopyright:
Available Formats
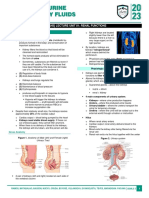
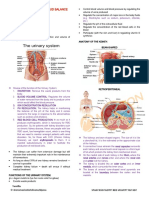
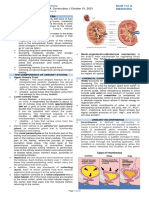
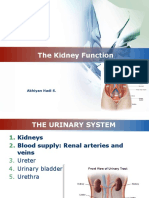
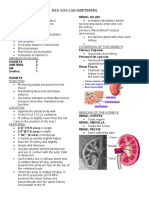
Renal System
Components
Nephrons
Functional unit of the kidney
1 M per kidney
Responsible for urine formation
Cortex: cortical collecting tubule
Medulla: medulla collecting tubule
[KUBU]
Kidneys (2) – responsible for urine formation
[The following are passageways]
Ureter (2)
Bladder (1)
Urethra (1)
General Functions
Elimination of waste products
Control the plasma volume in the body
Acid-base balance
Controls BP
o Enzyme: Renin – activates the Renin Angiotensin
Aldosterone system (RAAS)
Dehydration/excessive bleeding dec in blood
volume and dec in BP activation of the
juxtoglomerular cells release of Renin
Increase in Renin (converts Angiotensinogen to
Angiotensin I) Inc in Angiotensin I As
blood flow occurs in the capillaries of the lungs
and meets angiotensin converting enzyme
(ACE) (converts AI to AII) Angiotensin II
(potent vasoconstrictor) stimulates adrenal
cortex to release Aldosterone (reabsorption of
the H20 and maintaining electrolytes) Inc in
blood volume Normalize BP
Produce hormones
o Calcitriole: Active form of Vit D (for Ca++
rebasoprtion) Aka 1, 25 Dihydroxylcholcalfierol 2 main structures of the nephron
Vs. Calcitonin which dec Ca++ levels o Renal corpuscle: glomerulus + bowman’s capsule
o Erythropoietin stimulates new RBCs in the bone o Renal tubules: DCT + PCT + Loop of Henle +
marrow collecting tubule
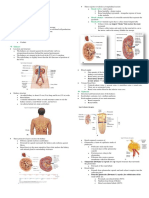
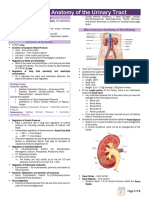
Anatomy 2 types of nephron
Bean shaped o Cortical nephron: part of a nephron that lies in the
Level: T12- L 3 renal cortex
Location: retroperitoneal o Juxtamedullary nephron: part of a nephron that
R is lower dt presence of liver lies in the renal medulla
External anatomy Urine formation
o Layers of Tissue Glomerular filtration
Renal Capsule: barrier to trauma o Filtration membrane: allow H2O and small solute
Adipose tissue: composed of fats; middle to pass thru
layer o Does not allow:
Renal fascia: anchors kidney to the Proteins
abdominal wall Platelets
Internal anatomy Blood cells
o Renal cortex: outer region o Net filtration pressure: 10 mmHg
o Renal medulla: inner regions, (+) renal pyramids o Glomerular filtration rate: amount of filtrate
formed in all renal corpuscle in both kidneys in
each minuet
Male: 125 mL/min (on average)
Female: 105 mL/min
No gender: over GFR = 125 mL
Renal system || OTPT Boards Review LOPEZ 1
Filtration membrane: H2O, small solutes: o Internal urethral sphincter: involuntary sphincter
Luminal fluid Types of incontinence
Overflow incontinence
o Atonic bladder
o Inability of urinary bladder to empty completely
o (+) dribbles
o Mgt: credes (push downward manual pressure on
superpubic region
Stress incontinence
o N urinary bladder
o Weakness of supporting structures (pelvic floor
muscles)
o Activities: laughing, lifting, sneezing, coughing
(increase abdominal pressure)
o Ms: Kegel’s exercise
Urge incontinence
o Overactive bladder
o Neurogenic bladder
o Involuntary contraction of urinary bladder
Tubular reabsorption – H2O back to the body o Causes: secondary to drugs, alcoholism, bladder
o Proximal convoluted tubule infection, bladder tumor
Workhorse of the nephron Endocrine System
65% reabsorption of H2O most 2nd great controlling center
permeable to H2O Hormones: to arouse, to activate the activity of the cell
luminal fluid becomes: concentrated Pituitary gland
o Thin descending loop of henle Hypophysis
Reabsorption of H20 (10%) Lies in the sella turcica
Luminal fluid: concentrated 2 lobes: anterior and posterior
Part with highest concentration of Anterior pituitary gland
luminal fluid o Adenohypophysis
Thin ascending loop of Henle o Origin: pharyngeal epithelium
Reabsorption of solutes (Na, Cl) o Control: hypothalamic releasing and inhibitor
Luminal fluid: diluted hormones
Thick ascending loop of henle o 7 hormones:
Reabsorption of solutes (Na, Cl, K, Prolactin: production of milk
other ions) Inc in prolactin
Luminal fluid is more diluted o F: Amenorrhea; present even
Distal convoluted tubule when not pregnant
LF: Diluted minor calyx major o M: Erectile Dysfunction;
calyx urethra present in males but very few
Urine – diluted in nature and fxn is unknown
o Urobilin/Urochromo Growth hormone (GH)
Responsible for color of urine Growth of long bones and soft tissues
o Pale yellow to orange Increase GH at adult life: acromegaly
o If dehydrated: o Thickening of nose, ears,
ADH/Vasopression vertebra
Reabsorption of H20 (kidneys) o Enlargement of hands (2x),
Attachment at Distal convoluted (kyphotic), feet
tubule (DCT), Cortical convoluted o Inc GH at childhood: gigantism
tubule (CCT), Medullary convoluted o Dec GH at childhood: Dwarfism
tubule (MCT) [MCT is most Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
concentrated LF in presence of ADH] Stimulates the thyroid
PCT – most permeable to H2O Melanocyte stimulating hormone (MSH)
Ureter Stimulates the skin pigmentation
25-30 cm long (melanin)
Composed of smooth muscle (contraction: peristalsis) Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Urinary Bladder Stimulates the cortisol
Smooth muscle: detrusor muscle Follicle Stimulating Hormones (FSH)
Storage of urine: N: 500 mL Female: stimulates estrogen (for
o Max: 700 – 800 mL; At 800 mL, patient experiences feminine effect and deposition of fat)
dribbles and progesterone (development of
Innervation: sacral plexus: S2, S3, S4 breasts)
Reflex: micturition reflex Male: Stimulates sperm
o 200 – 300 mL of urine Lutenizing hormone
o voiding Female: triggers ovulation
Male: stimulates testosterone
Urethra
o Masculinity effect
Terminal portion of renal system
o Deposition of protein
Male: ~20 cm long
o Posterior pituitary gland
Female: 3-4 cm long
Neurohypophysis
2 sphincters
Origin: neural tissues
o external urethral sphincter: voluntary sphincter
Control: hypothalamus
Renal system || OTPT Boards Review LOPEZ 2
Storage of hormones Location Hormone Action
Hormones: Pituitary gland
Oxytocin: milk ejection (with sucking Anterior Prolactin Milk
reflexes); contraction of urine wall GH Long bones, soft
Antidiuretic hormone/vasopressin – tissues
reabsorption of H2O from kidneys MSH Stimulates
Thyroid Gland melatonin
Inferior to the larynx ACTH Stimulates cortex
Thyroid hormone: FSH F: stimulates
o T3: triiodothyronine estrogen
o T4: Tetraiodothyronine/thyroxine M: Sperm
o Maturation, growth and development of CNS LH F: ovulation
o Dec Th at birth: cretinism M: testosterone
Mental retardation Posterior Thyroid hormone CNS
o Dec TH at adult life: myxedema -T3
Lethargic -T4
Cold intolerance Calcitonin Dec Ca 2++ in
Calcitonin blood
o Ca++ in blood stream Parathyroid Parathormone Inc Ca2++in the
Parathyroid gland blood
Posterior surface of the lateral lobe of the thyroid gland Adrenal gland
Parathromone: increase Ca++ in the blood
Cortex Aldosterone Reabsorption of
Adrenal gland
H2O; electrolytes
Superior to each kidney
Cortisol stress
Cortex
Medulla Androgen Hair
o Zona Glomerulosa
Aldoesterone: reabsorption of H2O and Norepinephrine
maintaining electrolytes Epinephrine
o Zona Fasciculata Pancreas Glucagon Inc blood sugar
Cortisol: resistance to stress Insulin Dec glucagon
o Zona Reticularis Somatostatin Equalizes
Androgen: growth of hair (axillary, pubic, Glucagon and
chest, linea alba) insulin
Increase in androgen: more pronounced in Thymus Thymosin T-cells
females; broad shoulders, deep voice and Pineal Melatonin Sleep; biological
enlargement of clitoris clock
Pancreas Gonads Estrogen
Greater curvature of stomach Progesterone
Both exocrine (enzyme production) and endocrine Relaxin
(hormone production) Testosterone
Cells: Islets of Langerhans
[GABiDS]
o Alpha cells: glucagon (blood sugar)
o Beta cells: insulin (lowers the # of glucagon—
source of ATP)
o Delta cells – somatostatin (equalizes # of
glucagon and insulin)
Thymus gland
Behind the sternum between two lungs
Thymosin: maturation of T cells
Pineal Gland
Roof of the 3rd ventricle of brain
Melatonin: body’s biological clock
o Inc: dark
o Dec: bright
Gonads
Ovary oocyte
Testes sperm
Estrogen
Progesterone
Testosterone
Relaxin – increases flexibility of symphysis pubis
Sexual rehabilitation stages [EPOR]
o Excitement
o Plateau
o Orgasm
o Resolution
Renal system || OTPT Boards Review LOPEZ 3
You might also like
- URS SummaryDocument26 pagesURS SummaryMohamed HaridyNo ratings yet
- Aubf LecDocument97 pagesAubf Lechinata shoyoNo ratings yet
- Page of 1 3 Renal Histology & Function Renal Biology L1Document3 pagesPage of 1 3 Renal Histology & Function Renal Biology L1Fazreena EleenaNo ratings yet
- QUIAMBAO - Urinary System Reviewer - AnaPhy LecDocument8 pagesQUIAMBAO - Urinary System Reviewer - AnaPhy LecqlouisamarieNo ratings yet
- 10 Urinary SystemDocument3 pages10 Urinary SystemELI GOZONNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes Introduction: The Kidneys Rifle Criteria For Renal FailureDocument2 pagesFluid and Electrolytes Introduction: The Kidneys Rifle Criteria For Renal FailureAila HinlogNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter 26 Urinary System Doran MLS 1 FDocument15 pagesAnaphy Chapter 26 Urinary System Doran MLS 1 FayenaNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology: Xiaohong XiaDocument128 pagesRenal Physiology: Xiaohong XiashaheenNo ratings yet
- Renal Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument51 pagesRenal Anatomy and PhysiologyAn Zheng100% (3)
- Urinary SystemDocument66 pagesUrinary SystemJustine Vens G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- VSP-UG-7 (Kidney - Excretory System)Document50 pagesVSP-UG-7 (Kidney - Excretory System)6qhx62pr42No ratings yet
- The Urinary System Kidneys: Calcitriol - Active Form of Vitamin D, Circulates As A HormoneDocument10 pagesThe Urinary System Kidneys: Calcitriol - Active Form of Vitamin D, Circulates As A HormonemasorNo ratings yet
- 15 Renal System - ATFDocument47 pages15 Renal System - ATFipek terimNo ratings yet
- Revision FileDocument14 pagesRevision FileBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- 2 - Renal PhysiologyDocument8 pages2 - Renal PhysiologyKunware TropaNo ratings yet
- Urinary System: Division of Histology and EmbryologyDocument58 pagesUrinary System: Division of Histology and Embryologyapi-19641337No ratings yet
- Nephrons (Functional Unit)Document44 pagesNephrons (Functional Unit)Nur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Excretion Human BeingsDocument3 pagesExcretion Human BeingsRahul Ecka100% (1)
- LECTURE Urinary SystemDocument45 pagesLECTURE Urinary Systemjaveria choudharyNo ratings yet
- Renal Anatomy & Physiology: NotesDocument5 pagesRenal Anatomy & Physiology: NotesTawhid ZihadNo ratings yet
- Genitourinary SampleDocument19 pagesGenitourinary SampleDanica FrancoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Handout # 17 Urinary SystemDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Handout # 17 Urinary SystemJounri Arsted Dimabuyu (Kaiz)No ratings yet
- 1 - The Urinary System and Fluid Balance - de Veyra - Silvano&tajalaDocument12 pages1 - The Urinary System and Fluid Balance - de Veyra - Silvano&tajalaMika SaldañaNo ratings yet
- KidneyDocument40 pagesKidneyOlaifa victorNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Handout # 17 Urinary SystemDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Handout # 17 Urinary SystemJounri Arsted Dimabuyu (Kaiz)No ratings yet
- Control of Water PotentialDocument24 pagesControl of Water PotentialiSundae17No ratings yet
- Renal AnatomyDocument13 pagesRenal AnatomyApril Lady Faith P. PaundogNo ratings yet
- 6 Bodyfluidregulationandexcretionc-150331101430-Conversion-Gate01Document11 pages6 Bodyfluidregulationandexcretionc-150331101430-Conversion-Gate01Yay SandovalNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Urine & Body Fluids Lecture - : Sison The Kidney AnatomyDocument7 pagesAnalysis of Urine & Body Fluids Lecture - : Sison The Kidney AnatomyCherry BlossomNo ratings yet
- Renal PhysiologyDocument129 pagesRenal PhysiologyPhysiology by Dr Raghuveer100% (3)
- 6.1 Concepts of UrinaryDocument10 pages6.1 Concepts of UrinaryIvy VillalobosNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Notes - The KidneyDocument39 pagesUnit 7 Notes - The Kidneyshrilpatel2001No ratings yet
- Lec5 Sem4 RENWK1 20140526Document12 pagesLec5 Sem4 RENWK1 20140526Uloko ChristopherNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Renal Physiology 1Document8 pages1.1 Renal Physiology 1Carmela MarianoNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Urinary System (2020)Document55 pagesFundamental of Urinary System (2020)Nadya PutriNo ratings yet
- Excretory Products and Their EliminationDocument13 pagesExcretory Products and Their Eliminationaravind kishanNo ratings yet
- DR Laxman Khanal Bpkihs 07-06-2013Document86 pagesDR Laxman Khanal Bpkihs 07-06-2013Bilal YimamNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument2 pagesUrinary SystemIzelwyn DaguioNo ratings yet
- The Urinary System & Fluid BalanceDocument8 pagesThe Urinary System & Fluid BalanceMarianne DugosNo ratings yet
- YU - Activity 11 - Urinary SystemDocument5 pagesYU - Activity 11 - Urinary SystemDenise Kyla Bernadette YuNo ratings yet
- Introduction RenalDocument38 pagesIntroduction RenalYahya JuneydiNo ratings yet
- Kidney: PDF Generated At: Sun, 26 Jan 2014 03:55:26 UTCDocument15 pagesKidney: PDF Generated At: Sun, 26 Jan 2014 03:55:26 UTCVijay RajendiranNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument9 pagesUrinary SystemPrincess OrsinoNo ratings yet
- Renal Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument70 pagesRenal Anatomy & PhysiologyDeshi SportsNo ratings yet
- C-6 Urinary SystemDocument32 pagesC-6 Urinary SystemHarsh PatelNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument46 pagesThe Urinary SystemWeb AredomNo ratings yet
- Histology KUBDocument31 pagesHistology KUBkhiks34No ratings yet
- Fisiologi Ginjal Dr. BernDocument193 pagesFisiologi Ginjal Dr. Bernheta aprianaNo ratings yet
- 10 Renal System (FINAL) PDFDocument3 pages10 Renal System (FINAL) PDFJohn Juan TwanNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology 1 170407164141Document76 pagesRenal Physiology 1 170407164141Vhutshilo MasithembiNo ratings yet
- Renal System 2022Document78 pagesRenal System 2022Rahil PatelNo ratings yet
- 9-ch 26 - Urinary System CDocument95 pages9-ch 26 - Urinary System Clouise navorNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi GinjalDocument33 pagesAnatomi Dan Fisiologi GinjalRizha Zhetira100% (1)
- Chapter 26 - Introduction To The Urinary System (Also Table 27.4)Document7 pagesChapter 26 - Introduction To The Urinary System (Also Table 27.4)tomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- Lect-2 Kidneys (RAAS Micturition) PDFDocument11 pagesLect-2 Kidneys (RAAS Micturition) PDFBinisha KapadiaNo ratings yet
- Urinary System PearsonsDocument13 pagesUrinary System Pearsonsblando.shaneNo ratings yet
- Urinary System (Renal System) : Arba Pramundita RamadaniDocument36 pagesUrinary System (Renal System) : Arba Pramundita RamadaniReeds Riko Renjer RivaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 The Urinary SystemDocument18 pagesChapter 15 The Urinary SystemYeshia InocencioNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument3 pagesUrinary SystempsychelastwishNo ratings yet
- Genitourinary Syndrome of MenopauseDocument8 pagesGenitourinary Syndrome of Menopauserizky ferdina kevinNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Kegel Exercise Terhadap Inkontinensia Urine Pada Ibu Postpartum MultiparaDocument8 pagesPengaruh Kegel Exercise Terhadap Inkontinensia Urine Pada Ibu Postpartum MultiparaYunita RahayuNo ratings yet
- The Pros and Cons of Spaying A SheltieDocument15 pagesThe Pros and Cons of Spaying A SheltiepsykosomatikNo ratings yet
- HLTENN004 Assignment - NursingDocument4 pagesHLTENN004 Assignment - NursingJulianneTintNo ratings yet
- Genito-Urinary FistulaDocument33 pagesGenito-Urinary Fistuladr_asaleh100% (4)
- Chapter 27 - GU Female SystemDocument13 pagesChapter 27 - GU Female SystemAnnetta AronovaNo ratings yet
- Dog Incontinence - An Incontinent Dog Dry and Treat Urine ScaldDocument28 pagesDog Incontinence - An Incontinent Dog Dry and Treat Urine ScaldJerome SiegelNo ratings yet
- Nanda 2021 2023Document6 pagesNanda 2021 2023Khimberly UmbaoNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostate HypertrophyDocument22 pagesBenign Prostate Hypertrophyjyoti kunduNo ratings yet
- Vaginal FistulaDocument3 pagesVaginal FistulaDaryl TarucNo ratings yet
- Skill 12-5 Applying An External Condom CatheterDocument6 pagesSkill 12-5 Applying An External Condom CatheterFitrio Citizen AntonyNo ratings yet
- Beitz 2014Document10 pagesBeitz 2014Anna Beatriz Silva EspindolaNo ratings yet
- Patent US6447462Document15 pagesPatent US6447462Yodi SoebadiNo ratings yet
- Safety and Pain-Relief Efficacy of Urethral Catheter With Local-Anesthetic Injection PortDocument5 pagesSafety and Pain-Relief Efficacy of Urethral Catheter With Local-Anesthetic Injection PortYudhi AuliaNo ratings yet
- Gordon S Functional Health Pattern Assessment ToolDocument17 pagesGordon S Functional Health Pattern Assessment Toolmiss RN96% (45)
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument5 pagesImpaired Urinary Eliminationapi-279878989No ratings yet
- Sensordevices 2017 9 10 20010Document3 pagesSensordevices 2017 9 10 20010EliasA.TiongkiaoNo ratings yet
- Abnormal PuerperiumDocument21 pagesAbnormal PuerperiumNatukunda DianahNo ratings yet
- Renal Health Advocacy For Nurses in La Union 1325915359Document13 pagesRenal Health Advocacy For Nurses in La Union 1325915359Rizki MatondangNo ratings yet
- Neurourology and Urodynamics - 2023 - B - Can You Breathe Yourself To A Better Pelvic Floor A Systematic ReviewDocument19 pagesNeurourology and Urodynamics - 2023 - B - Can You Breathe Yourself To A Better Pelvic Floor A Systematic ReviewDanielle GadelhaNo ratings yet
- Incontinentia Urine Kuliah Uniba 6-11-12. ADocument53 pagesIncontinentia Urine Kuliah Uniba 6-11-12. AHumaira AzmiNo ratings yet
- Practice Test Pediatric Nursing 100 ItemsDocument16 pagesPractice Test Pediatric Nursing 100 ItemsEdRobertArnad100% (1)
- Rintala 2008Document11 pagesRintala 2008Emmeralda PancanithaNo ratings yet
- EnuresisDocument26 pagesEnuresisAlexNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics - GynaecologyDocument137 pagesObstetrics - GynaecologyCiel100% (1)
- Elimination Needs 04Document52 pagesElimination Needs 04Kishore RathoreNo ratings yet
- A Nurse-Driven Process For TimelyDocument7 pagesA Nurse-Driven Process For TimelyWardah Fauziah El SofwanNo ratings yet
- Medical MnemonicsDocument65 pagesMedical MnemonicsMIRZA MUHAMMAD ADNAN100% (1)
- Surgery FINAL 2023Document140 pagesSurgery FINAL 2023TayaNo ratings yet