Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Chemistry of Hangovers PDF
Uploaded by
Silvio Latini SpahnOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Chemistry of Hangovers PDF
Uploaded by
Silvio Latini SpahnCopyright:
Available Formats
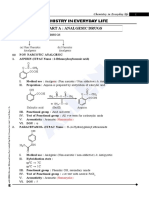
THE CHEMISTRY OF A HANGOVER
For most of us, a hangover is the price to pay for a night of drinking. However, we still don’t know what exactly it is that causes
them. In this graphic, we look at what happens to alcohol in your body, and some of the prime suspects for causing your hangover.
WHAT HAPPENS TO ALCOHOL IN YOUR BODY?
O
OH O -
In the liver, ethanol is converted to acetaldehyde by the alcohol
O dehydrogenase enzyme, and then subsequently converted into
acetate by the aldehyde dehydrogenase enzyme. Acetate can be
broken down into carbon dioxide and water, then eliminated from
the body. On average, the liver can break down alcohol at the rate
ETHANOL ETHANAL ETHANOATE of one unit (8 grams or 10 millilitres of pure alcohol) every hour.
(ethyl alcohol) (acetaldehyde) (acetate)
1 DEHYDRATION 2 ACETALDEHYDE 3 CONGENERS 4 IMMUNE SYSTEM
Acetaldehyde is rapidly converted into acetate in the liver Methanol is found in very small amounts in many alcoholic drinks Cytokines are small proteins released by cells which affect other
OH cells. They play an important role in the immune system.
S
OH O O
S N
ETHANOL ADH URINATION
O
N S
H C H
H
C
H H
C
OH
IL-10 IL-12 IFN- γ
S H
Disulfiram (above), a drug to support CYTOKINES INCREASED BY ALCOHOL CONSUMPTION
treatment of alcoholism, works by inhibiting
During alcohol intoxication, release of the anti-diuretic hormone the breakdown of acetaldehyde, producing
METHANOL METHANAL METHANOIC ACID
ACETALDEHYDE In particular, IL-12 & IFN-γ concentration changes show significant
(ADH) vasopressin is decreased, resulting in increased urination. unpleasant, hangover-like symptoms. (methyl alcohol) (formaldehyde) (formic acid)
correlations with hangover severity
Alcohol has a diuretic effect on the Acetaldehyde, produced by the Congeners are compounds other Alcohol causes changes in cytokine
body, increasing urine production. breakdown of alcohol, has toxic than ethanol in drinks. These include concentrations in the immune
Alcohol-induced dehydration has effects that could cause hangover alcohols such as methanol, which system. Studies have shown the
been suggested as a cause for some symptoms. However, acetaldehyde breaks down into toxic formaldehyde effects caused by some cytokines are
hangover symptoms, but research concentration doesn’t significantly and formic acid. Congeners can very similar to those of a hangover,
suggests it isn’t a major factor. correlate with hangover severity. increase hangover severity. strongly supporting their role.
© COMPOUND INTEREST 2016 - WWW.COMPOUNDCHEM.COM | Twitter: @compoundchem | Facebook: www.facebook.com/compoundchem
C This graphic is shared under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives licence. BY NC ND
You might also like
- Module-3 (Part-I)Document218 pagesModule-3 (Part-I)Prajay GNo ratings yet
- Ch3e4 Stereoselective Synthesis MW Handout Reorganised 021111Document51 pagesCh3e4 Stereoselective Synthesis MW Handout Reorganised 021111Kethavath VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Mandelic AcidDocument6 pagesSynthesis of Mandelic AcidBea A.No ratings yet
- Chemistry in Everyday Life - (Eng)Document24 pagesChemistry in Everyday Life - (Eng)Dr StrangeNo ratings yet
- Starch Project UpdateDocument34 pagesStarch Project UpdateIsworo RukmiNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds Notes-4Document9 pagesCarbonyl Compounds Notes-4CBIT CIVIL A1No ratings yet
- 2009GA Stevia-rebaudianaPosterDocument1 page2009GA Stevia-rebaudianaPostermagdamayalagNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - 6 Biological MoleculesDocument5 pagesKami Export - 6 Biological MoleculesNicholas Crowell100% (1)
- FCU With PCO Technology - LRDocument2 pagesFCU With PCO Technology - LR유승범No ratings yet
- Alcohols-Structure and Synthesis 2Document82 pagesAlcohols-Structure and Synthesis 2Ali Issa OthmanNo ratings yet
- Stereochemistry & Reactions of MonosaccharidesDocument2 pagesStereochemistry & Reactions of MonosaccharidesSamiya ZamanNo ratings yet
- Guide To Fruit AcidsDocument1 pageGuide To Fruit AcidsJay McKearnNo ratings yet
- E12 AtqDocument5 pagesE12 AtqCharlene InaoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Common Name.Document1 pageChemistry Common Name.jangidlokeshkumar11No ratings yet
- Available Compound As A Starting Material: Oxalic Acid Glyxol As Aqueous Solution Amino Acid Co2HDocument10 pagesAvailable Compound As A Starting Material: Oxalic Acid Glyxol As Aqueous Solution Amino Acid Co2HAfifaNo ratings yet
- CD 4Document19 pagesCD 4زينب عيسىNo ratings yet
- Lecture 09Document10 pagesLecture 09CataNo ratings yet
- DisaccharidesDocument5 pagesDisaccharidesHello KittyNo ratings yet
- APIChem Featured Products PDFDocument5 pagesAPIChem Featured Products PDFTezozómocNo ratings yet
- (Solvent) Diol Aldehyde-Alcohol Ketone-Alcohol Compound 1 Compound 2 Compound 3Document10 pages(Solvent) Diol Aldehyde-Alcohol Ketone-Alcohol Compound 1 Compound 2 Compound 3Ilias YacNo ratings yet
- Carbohidratos Estructura PDFDocument6 pagesCarbohidratos Estructura PDFPatricia NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Alchohol ResearchASDocument18 pagesAlchohol ResearchASAhmed SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Polymer ProblemsDocument13 pagesPolymer ProblemssanesamesaniNo ratings yet
- Mike Virnig - Crud PresentationDocument34 pagesMike Virnig - Crud Presentationworquera2507No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ContiuedDocument24 pagesChapter 4 ContiuedumarNo ratings yet
- Acetate Mevalonate PathwayDocument17 pagesAcetate Mevalonate PathwayNikhil TalrejaNo ratings yet
- Biodegradable Polymers: Chemistry, Degradation and ApplicationsDocument26 pagesBiodegradable Polymers: Chemistry, Degradation and ApplicationsAnand GuptaNo ratings yet
- An Aldol Condensation To Synthesize ChalconesDocument6 pagesAn Aldol Condensation To Synthesize ChalconesAssyakurNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Mechanistic Patterns Canadian 1St Edition Ogilvie Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesOrganic Chemistry Mechanistic Patterns Canadian 1St Edition Ogilvie Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFmaria.topolosky417100% (11)
- Aldol ReactionDocument4 pagesAldol ReactionRavi Seedath100% (1)
- BIO LabManual OrganicCompoundMysteryU1L11Document10 pagesBIO LabManual OrganicCompoundMysteryU1L11Miguel FierroNo ratings yet
- Isomers of Coordination ComplexesDocument12 pagesIsomers of Coordination ComplexesNov IndaNo ratings yet
- 02 - Haze FormationDocument22 pages02 - Haze FormationGiorgi GhambashidzeNo ratings yet
- Glyc o SidesDocument22 pagesGlyc o Sidessiddra khalidNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Mechanistic Patterns Canadian 1st Edition Ogilvie Solutions Manual 1Document32 pagesOrganic Chemistry Mechanistic Patterns Canadian 1st Edition Ogilvie Solutions Manual 1nancyyorkddsmcfjqakdow100% (27)
- TCI - Asymmetric OrganocatalystsDocument8 pagesTCI - Asymmetric OrganocatalystsDeath Dealer61No ratings yet
- Aldol ReactionDocument4 pagesAldol ReactionhafizNo ratings yet
- Named ReactionsDocument15 pagesNamed ReactionsSony mulgundNo ratings yet
- Ch05 MacromoleculesCampbellDocument69 pagesCh05 MacromoleculesCampbellCarl Jasper AquinoNo ratings yet
- N Comms 8332Document7 pagesN Comms 8332Dương 10 Hoá TiêuNo ratings yet
- Kraft Reactin-Dye SynthesisDocument7 pagesKraft Reactin-Dye Synthesisgulft1777No ratings yet
- Preparation of Asperine and Oil of WintergreenDocument4 pagesPreparation of Asperine and Oil of WintergreenKaye ArcherNo ratings yet
- (Edexcel) SNAB Unit 1 - Topic 1 and Topic 2 RESIT 2010Document8 pages(Edexcel) SNAB Unit 1 - Topic 1 and Topic 2 RESIT 2010Jonathan SmithNo ratings yet
- Kuang Viana DRXDocument14 pagesKuang Viana DRXWilliam MelloNo ratings yet
- Oxetane PresentationDocument60 pagesOxetane PresentationEena BarmanNo ratings yet
- Chem SampleMultipleChoiceQuestionsDocument5 pagesChem SampleMultipleChoiceQuestionslinaNo ratings yet
- Biodegradable Materials 1Document26 pagesBiodegradable Materials 1Louie Shaolin LungaoNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Mutagenicity of Antimalarial ProDocument6 pagesEvaluation of The Mutagenicity of Antimalarial ProerikaNo ratings yet
- Read PDFDocument11 pagesRead PDFsindy mNo ratings yet
- Molecular Mechanisms of Enzyme Action: (WEEK 7)Document44 pagesMolecular Mechanisms of Enzyme Action: (WEEK 7)oczhinviaNo ratings yet
- Structure of LactoseDocument3 pagesStructure of LactoseBhavaniNo ratings yet
- Peptide BondDocument2 pagesPeptide BondJENIFER PEARLINNo ratings yet
- 생체의학공학 04 BiomaterialsDocument124 pages생체의학공학 04 Biomaterials생따일괄기No ratings yet
- Tandem Reaction SequencesDocument18 pagesTandem Reaction SequencesivanNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem NotesDocument49 pagesOrganic Chem NotesPriyaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Constituents of The Mexican Mistletoe (Psittacanthus Calyculatus)Document7 pagesChemical Constituents of The Mexican Mistletoe (Psittacanthus Calyculatus)Educación UniversidadNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Ws10s09keyDocument2 pagesMicrosoft Word - Ws10s09keynm1006055No ratings yet
- Synthesis of Aspirin and Wintegreen Spring 2006Document6 pagesSynthesis of Aspirin and Wintegreen Spring 2006apzzzzNo ratings yet
- Experiment: CarbohydratesDocument10 pagesExperiment: CarbohydratesAriane Kyle GlodoveNo ratings yet
- Computing Azeotropes in Multicomponent Mixtures: Z. FidkowskiDocument15 pagesComputing Azeotropes in Multicomponent Mixtures: Z. FidkowskiSilvio Latini SpahnNo ratings yet
- Multiple Steady States in Binary Distillation-Theoretical and Experimental ResultsDocument13 pagesMultiple Steady States in Binary Distillation-Theoretical and Experimental ResultsSilvio Latini SpahnNo ratings yet
- Multicomponent Homogeneous Azeotropic Distillation 2. Column DesignDocument24 pagesMulticomponent Homogeneous Azeotropic Distillation 2. Column DesignSilvio Latini SpahnNo ratings yet
- Multicomponent Three-Phase Azeotropic Distillation. Phase-Stability and Phase-Splitting AlgorithmsDocument19 pagesMulticomponent Three-Phase Azeotropic Distillation. Phase-Stability and Phase-Splitting AlgorithmsSilvio Latini SpahnNo ratings yet
- Multicomponent Three-Phase Azeotropic Distillation. 3. Modern Thermodynamic Models and Multiple SolutionsDocument13 pagesMulticomponent Three-Phase Azeotropic Distillation. 3. Modern Thermodynamic Models and Multiple SolutionsSilvio Latini SpahnNo ratings yet
- Multicomponent Homogeneous Azeotropic Distillation 1. Assessing Product FeasibilityDocument23 pagesMulticomponent Homogeneous Azeotropic Distillation 1. Assessing Product FeasibilitySilvio Latini SpahnNo ratings yet
- Düssel, R., & Stichlmair, J. (1995) - Separation of Azeotropic Mixtures by Batch Distillation Using An Entrainer. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 19, 113-118.Document6 pagesDüssel, R., & Stichlmair, J. (1995) - Separation of Azeotropic Mixtures by Batch Distillation Using An Entrainer. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 19, 113-118.Silvio Latini SpahnNo ratings yet
- Stichlmair, J. (2010) - Distillation, 2. Equipment. Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry.Document22 pagesStichlmair, J. (2010) - Distillation, 2. Equipment. Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry.Silvio Latini SpahnNo ratings yet
- Multiple Steady States in Distillation: Effect of VL L E InaccuraciesDocument25 pagesMultiple Steady States in Distillation: Effect of VL L E InaccuraciesSilvio Latini SpahnNo ratings yet
- The Ternary System: Ethyl Alcohol, Toluene and Water At: A Commercial Grade of Absolute Ethyl Alcohol WasDocument2 pagesThe Ternary System: Ethyl Alcohol, Toluene and Water At: A Commercial Grade of Absolute Ethyl Alcohol WasSilvio Latini SpahnNo ratings yet
- Stichlmair, J. (2010) - Distillation, 1. Fundamentals. Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry.Document30 pagesStichlmair, J. (2010) - Distillation, 1. Fundamentals. Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry.Silvio Latini SpahnNo ratings yet
- Property Methods: Thermodynamic Calculation ModelsDocument1 pageProperty Methods: Thermodynamic Calculation ModelsSilvio Latini SpahnNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Distillation Sequences For Separating Multicomponent Azeotropic MixturesDocument23 pagesSynthesis of Distillation Sequences For Separating Multicomponent Azeotropic MixturesSilvio Latini SpahnNo ratings yet
- Stichlmair, J. (2010) - Distillation, 3. Processes. Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry.Document18 pagesStichlmair, J. (2010) - Distillation, 3. Processes. Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry.Silvio Latini SpahnNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Azeotropic Distillation Systems With RecyclesDocument12 pagesSynthesis of Azeotropic Distillation Systems With RecyclesefzukowskiNo ratings yet
- Tabla de Colores PDFDocument21 pagesTabla de Colores PDFSilvio Latini SpahnNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Optimization of Distillation Sequences For The Separation of Azeotropic MixturesDocument6 pagesSynthesis and Optimization of Distillation Sequences For The Separation of Azeotropic MixturesSilvio Latini SpahnNo ratings yet
- Van Dongen, D. B., & Doherty, M. F. (1984) - On The Dynamics of Distillation Processes-V. Chemical Engineering Science, 39 (5), 883-892.Document10 pagesVan Dongen, D. B., & Doherty, M. F. (1984) - On The Dynamics of Distillation Processes-V. Chemical Engineering Science, 39 (5), 883-892.Silvio Latini SpahnNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Multicomponent Distillation of Non-Ideal Mixtures by A Short-Cut MethodDocument5 pagesCalculation of Multicomponent Distillation of Non-Ideal Mixtures by A Short-Cut MethodSilvio Latini SpahnNo ratings yet
- On The Dynamics of Distillation Processes-Iv: (Received I December 1980Document12 pagesOn The Dynamics of Distillation Processes-Iv: (Received I December 1980Silvio Latini SpahnNo ratings yet
- Injection MoldingDocument8 pagesInjection MoldingDebasmiti MishraNo ratings yet
- Tabla de Colores PDFDocument21 pagesTabla de Colores PDFSilvio Latini SpahnNo ratings yet
- Super Critical Steam TableDocument12 pagesSuper Critical Steam TabledhineshtNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Hangovers PDFDocument1 pageThe Chemistry of Hangovers PDFSilvio Latini SpahnNo ratings yet
- Super Critical Steam TableDocument12 pagesSuper Critical Steam TabledhineshtNo ratings yet
- UltraSonic Processors - CatalogDocument2 pagesUltraSonic Processors - Catalogdéborah_rosalesNo ratings yet
- A Review On Potential Toxicity of Artificial Sweetners Vs Safety of SteviaDocument13 pagesA Review On Potential Toxicity of Artificial Sweetners Vs Safety of SteviaAlexander DeckerNo ratings yet
- EASL 2021 Version 4 NewDocument691 pagesEASL 2021 Version 4 NewGupse Köroğlu AdalıNo ratings yet
- đề thi hsg 12 cấp trường LTK 23-24 - KEYSDocument6 pagesđề thi hsg 12 cấp trường LTK 23-24 - KEYShan nguyenNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 3.6: Determining The Concentration of An External Solution Which Is Isotonic To The Cell Sap of A PlantDocument2 pagesEXPERIMENT 3.6: Determining The Concentration of An External Solution Which Is Isotonic To The Cell Sap of A PlantAmsyidi AsmidaNo ratings yet
- Hamsters - A General DescriptionDocument5 pagesHamsters - A General Descriptiondulce crissNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S222541102200030X MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S222541102200030X Mainaman babuNo ratings yet
- (Springer Series in Wood Science) W. E. Hillis (auth.), John W. Rowe (eds.)-Natural Products of Woody Plants_ Chemicals Extraneous to the Lignocellulosic Cell Wall-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (1.pdfDocument1,274 pages(Springer Series in Wood Science) W. E. Hillis (auth.), John W. Rowe (eds.)-Natural Products of Woody Plants_ Chemicals Extraneous to the Lignocellulosic Cell Wall-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (1.pdfArmandoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Label Worksheet PDFDocument4 pagesNutrition Label Worksheet PDFCha Marie100% (2)
- Science Paper 7 - SolvedDocument10 pagesScience Paper 7 - SolvedRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- Final Project Report Kiran MazumdarDocument31 pagesFinal Project Report Kiran MazumdarPrajot Morajkar100% (3)
- L&M ResearchDocument145 pagesL&M ResearchJulia PurperaNo ratings yet
- Can The Unconscious Mind Be Persuaded? An Overview With Marketing ImplicationsDocument9 pagesCan The Unconscious Mind Be Persuaded? An Overview With Marketing ImplicationsAhmed El-ShafeiNo ratings yet
- CAPE Bio Mark SchemeDocument4 pagesCAPE Bio Mark Schemeron97150% (2)
- 7 Pearson SquareDocument19 pages7 Pearson Squareapi-235944649No ratings yet
- Preliminary Experiment: Visual Observation and InterpretationDocument3 pagesPreliminary Experiment: Visual Observation and InterpretationRuchie Ann Pono BaraquilNo ratings yet
- Clave Genero Dermanura (Otros) PDFDocument520 pagesClave Genero Dermanura (Otros) PDFJuan D Garcia Peluffo100% (1)
- MoPSE Science Module Volume 1 - FINAL4WEBDocument336 pagesMoPSE Science Module Volume 1 - FINAL4WEBSibusiso Ntomby NkalaNo ratings yet
- Killing of Kangaroos For Meat and SkinDocument34 pagesKilling of Kangaroos For Meat and SkinVegan FutureNo ratings yet
- A New Species of Riverine Crab of The Genus Sundathelphusa Bott, 1969 (Crustacea: Brachyura: Gecarcinucidae) From Northeastern Luzon, PhilippinesDocument10 pagesA New Species of Riverine Crab of The Genus Sundathelphusa Bott, 1969 (Crustacea: Brachyura: Gecarcinucidae) From Northeastern Luzon, PhilippinesNel YagosNo ratings yet
- Social Institutions - Kinship, Family&Marriage PDFDocument47 pagesSocial Institutions - Kinship, Family&Marriage PDFAbhijith KNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Cardio Tayang by Gextha 30 Maret 2015Document82 pagesStudy Guide Cardio Tayang by Gextha 30 Maret 2015Adi ParamarthaNo ratings yet
- CV Christopher Lean Jan 2024 Without ReferencesDocument5 pagesCV Christopher Lean Jan 2024 Without Referencesapi-399765628No ratings yet
- Life Span: HumanDocument738 pagesLife Span: HumanWAJEEHA GOHARNo ratings yet
- TGD FrameworkDocument10 pagesTGD FrameworkMatthew KleeNo ratings yet
- Chest TubesDocument34 pagesChest TubesMuhd ShafiqNo ratings yet
- Proposed Pre Final-1 Time Table With Weightage.. MPC, Bipc&Civils-AP&TsDocument17 pagesProposed Pre Final-1 Time Table With Weightage.. MPC, Bipc&Civils-AP&TsAbhiram muddanaNo ratings yet
- Analisis AlantoinaDocument6 pagesAnalisis Alantoinarsevilla3No ratings yet
- 3 - Plasma Membrane and Transport MechanismsDocument67 pages3 - Plasma Membrane and Transport MechanismsThom PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- CROSS TREE - Sorte I Selekcije Voćaka I Vinove Loze Iz Severozapadne Srbije I Istočne Hrvatske PDFDocument153 pagesCROSS TREE - Sorte I Selekcije Voćaka I Vinove Loze Iz Severozapadne Srbije I Istočne Hrvatske PDFrraattaarrrraattaaNo ratings yet
- Summary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Instant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookFrom EverandInstant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Forever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellFrom EverandForever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellNo ratings yet
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (378)
- Summary of Mary Claire Haver's The Galveston DietFrom EverandSummary of Mary Claire Haver's The Galveston DietRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- The Beck Diet Solution Weight Loss Workbook: The 6-Week Plan to Train Your Brain to Think Like a Thin PersonFrom EverandThe Beck Diet Solution Weight Loss Workbook: The 6-Week Plan to Train Your Brain to Think Like a Thin PersonRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- The Body Book: The Law of Hunger, the Science of Strength, and Other Ways to Love Your Amazing BodyFrom EverandThe Body Book: The Law of Hunger, the Science of Strength, and Other Ways to Love Your Amazing BodyNo ratings yet
- Metabolism Revolution: Lose 14 Pounds in 14 Days and Keep It Off for LifeFrom EverandMetabolism Revolution: Lose 14 Pounds in 14 Days and Keep It Off for LifeNo ratings yet
- The Food Lover's Cleanse: 140 Delicious, Nourishing Recipes That Will Tempt You Back into Healthful EatingFrom EverandThe Food Lover's Cleanse: 140 Delicious, Nourishing Recipes That Will Tempt You Back into Healthful EatingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Sugar Crush: How to Reduce Inflammation, Reverse Nerve Damage, and Reclaim Good HealthFrom EverandSugar Crush: How to Reduce Inflammation, Reverse Nerve Damage, and Reclaim Good HealthRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- How Not to Die by Michael Greger MD, Gene Stone - Book Summary: Discover the Foods Scientifically Proven to Prevent and Reverse DiseaseFrom EverandHow Not to Die by Michael Greger MD, Gene Stone - Book Summary: Discover the Foods Scientifically Proven to Prevent and Reverse DiseaseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (83)
- The Volumetrics Eating Plan: Techniques and Recipes for Feeling Full on Fewer CaloriesFrom EverandThe Volumetrics Eating Plan: Techniques and Recipes for Feeling Full on Fewer CaloriesNo ratings yet
- Secrets From the Eating Lab: The Science of Weight Loss, the Myth of Willpower, and Why You Should Never Diet AgainFrom EverandSecrets From the Eating Lab: The Science of Weight Loss, the Myth of Willpower, and Why You Should Never Diet AgainRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- Eat to Lose, Eat to Win: Your Grab-n-Go Action Plan for a Slimmer, Healthier YouFrom EverandEat to Lose, Eat to Win: Your Grab-n-Go Action Plan for a Slimmer, Healthier YouNo ratings yet
- The Arm: Inside the Billion-Dollar Mystery of the Most Valuable Commodity in SportsFrom EverandThe Arm: Inside the Billion-Dollar Mystery of the Most Valuable Commodity in SportsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (49)
- The Diabetes Code: Prevent and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes NaturallyFrom EverandThe Diabetes Code: Prevent and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes NaturallyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Body Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomFrom EverandBody Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Grit & Grace: Train the Mind, Train the Body, Own Your LifeFrom EverandGrit & Grace: Train the Mind, Train the Body, Own Your LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Find Your Path: Honor Your Body, Fuel Your Soul, and Get Strong with the Fit52 LifeFrom EverandFind Your Path: Honor Your Body, Fuel Your Soul, and Get Strong with the Fit52 LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- How to Be Well: The 6 Keys to a Happy and Healthy LifeFrom EverandHow to Be Well: The 6 Keys to a Happy and Healthy LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Diet Trap Solution: Train Your Brain to Lose Weight and Keep It Off for GoodFrom EverandThe Diet Trap Solution: Train Your Brain to Lose Weight and Keep It Off for GoodNo ratings yet
- Glucose Revolution: The Life-Changing Power of Balancing Your Blood SugarFrom EverandGlucose Revolution: The Life-Changing Power of Balancing Your Blood SugarRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (351)
- The Complete Guide to Fasting: Heal Your Body Through Intermittent, Alternate-Day, and Extended FastingFrom EverandThe Complete Guide to Fasting: Heal Your Body Through Intermittent, Alternate-Day, and Extended FastingNo ratings yet
- The Candida Cure: The 90-Day Program to Balance Your Gut, Beat Candida, and Restore Vibrant HealthFrom EverandThe Candida Cure: The 90-Day Program to Balance Your Gut, Beat Candida, and Restore Vibrant HealthNo ratings yet
- Keto Friendly Recipes: Easy Keto For Busy PeopleFrom EverandKeto Friendly Recipes: Easy Keto For Busy PeopleRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)