Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Research Proposal JMVD
Uploaded by
Sahil BakliwalOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Research Proposal JMVD
Uploaded by
Sahil BakliwalCopyright:
Available Formats
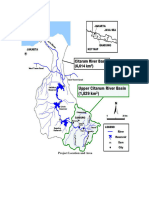
Introduction
The World has realized the significance of Land subsidence (LS) long ago, but very little
attention has been given to it in India. Even today, subsidence is mainly confined to coal mining
areas only in India. The subsidence is caused due to the large-scale extraction of natural
resources such as oil, gas, coal, and groundwater.
However, long term groundwater overdraft is considered to be the primary cause of LS.
Cities like Venice, Mexico, and Bangkok have shown cumulative subsidence in the order of 10m
due to the exploitation of groundwater hence causing huge economic and human life loss.
Calcutta (India) has also shown some of the visible impacts of Land subsidence like cracks,
tilting of the building and subsoil flow due to metro construction. The mean subsidence rate
estimated in the city is 10.83 mm/year (Sahu and Sikdar, 2011).
There is a high probability of Land Subsidence in North Indian regions due to similar soil as that
of Kolkata and unmindful mining of groundwater especially in Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, and
Haryana.
Land Subsidence can be measured using techniques like aquifer compaction, GPS
measurements, and pressure of groundwater in aquifers. However, the phenomenon can be
studied more accurately using remote sensing techniques such as Differential Interferometric
SAR(DInSAR).
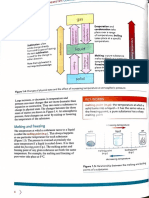
DInSAR Interferogram is a product of two SAR images acquired at a different time with
topographic surface removed using DEM. The generated interferogram gives the information
about phase difference which can be further converted to path difference in order to generate
deformation map at millimeter level of accuracy.
Research Proposal:
The proposed work aims at
You might also like
- Impact of Underground Space Construction On Water EnvironmentDocument11 pagesImpact of Underground Space Construction On Water EnvironmentPiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering: Professor: Takashi TsuchidaDocument5 pagesDepartment of Civil and Environmental Engineering: Professor: Takashi TsuchidaSoveasna ChanNo ratings yet
- Land SubsidiesDocument15 pagesLand SubsidiesSoveasna ChanNo ratings yet
- Impact of Urbanization On Groundwater Recharge and Disharge (In Reference To Kathmandu Valley)Document6 pagesImpact of Urbanization On Groundwater Recharge and Disharge (In Reference To Kathmandu Valley)Ashkimas DreamerNo ratings yet
- Urban FloodsDocument14 pagesUrban Floodsvenu manikanta100% (1)
- Water ResourcesDocument8 pagesWater ResourcesVibhore jainNo ratings yet
- Problem Description Dayeuhkolot - FTSL ITBDocument11 pagesProblem Description Dayeuhkolot - FTSL ITBTeguh TriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document20 pagesChapter 2Bhavya MewadaNo ratings yet
- AR DhakaDocument7 pagesAR DhakaImranuzzaman ImranNo ratings yet
- STS 11 EssayDocument6 pagesSTS 11 EssayKISHA MICHA LUMIKID100% (1)
- Anthropogenic Drivers of Relative Sea-Level Rise IDocument16 pagesAnthropogenic Drivers of Relative Sea-Level Rise ITrong Khiem HoangNo ratings yet
- An Economic Evaluation of The Health and AgricultuDocument26 pagesAn Economic Evaluation of The Health and AgricultuSecretario SigmaNo ratings yet
- Soil Erosion (HSP)Document11 pagesSoil Erosion (HSP)api-3731257100% (1)
- WaterDocument21 pagesWaterNawir SyarifNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument8 pagesSummaryfirdhaNo ratings yet
- B Urbanization & Environmental DegradationDocument16 pagesB Urbanization & Environmental Degradationrizwan_habibNo ratings yet
- CVL 820: Case Study 1aDocument1 pageCVL 820: Case Study 1aRavi Kumar MahawarNo ratings yet
- About Chennai Water ShortageDocument4 pagesAbout Chennai Water ShortageRocking RamNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering (Hydrology and Water Resources)Document20 pagesCollege of Engineering (Hydrology and Water Resources)Esra AljabriNo ratings yet
- Artificial Kidneys of SoilDocument23 pagesArtificial Kidneys of SoilChithira P UNo ratings yet
- STS11 Module 4Document21 pagesSTS11 Module 4John Dave BantayanNo ratings yet
- Hari Ilam - Floods in IndiaDocument8 pagesHari Ilam - Floods in IndiaAlga FariNo ratings yet
- English 2nd Edition Land SubsidenceDocument14 pagesEnglish 2nd Edition Land SubsidenceReginald SkibbaNo ratings yet
- Ground Water Regulation in IndiaDocument4 pagesGround Water Regulation in Indiapintu ramNo ratings yet
- Human Activity On Drainage BasinDocument6 pagesHuman Activity On Drainage BasinMalia DamitNo ratings yet
- JGR Solid Earth - 2018 - Gebremichael - Assessing Land Deformation and Sea Encroachment in The Nile Delta A RadarDocument17 pagesJGR Solid Earth - 2018 - Gebremichael - Assessing Land Deformation and Sea Encroachment in The Nile Delta A RadarAswathiNo ratings yet
- The Many Things I Picked Up in My Economic Geography ClassDocument2 pagesThe Many Things I Picked Up in My Economic Geography ClassTanveer SohelNo ratings yet
- Hillslope ProcessesDocument16 pagesHillslope Processesgeography13No ratings yet
- Water Wealth: A Briefing Paper On The State of Groundwater Management in BangladeshDocument19 pagesWater Wealth: A Briefing Paper On The State of Groundwater Management in BangladeshTanvir Mahmood KamalNo ratings yet
- 5.surface WaterDocument12 pages5.surface WaterzeonmiccuNo ratings yet
- How Different Activities of Human Affects The QualityDocument7 pagesHow Different Activities of Human Affects The QualityJenny-Lyn DuranNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Liquefaction Potential Hazard of Chennai City, India: Using Geological and Geomorphological CharacteristicsDocument14 pagesEvaluation of Liquefaction Potential Hazard of Chennai City, India: Using Geological and Geomorphological Characteristicsanon_158809066No ratings yet
- The Effects of Urbanization and Industrialization: Land Clearance and Reclama TionDocument17 pagesThe Effects of Urbanization and Industrialization: Land Clearance and Reclama TionGrace WongNo ratings yet
- The Big Apple BarricadeDocument21 pagesThe Big Apple BarricadeSandra delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Liquefaction Potential Hazard of Chennai City, India: Using Geological and Geomorphological CharacteristicsDocument14 pagesEvaluation of Liquefaction Potential Hazard of Chennai City, India: Using Geological and Geomorphological CharacteristicsDivya SankarNo ratings yet
- Geophysics and GroundwaterDocument22 pagesGeophysics and GroundwaterKateNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE Geography Student's Book AnswersDocument34 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Geography Student's Book AnswersAvrinox88% (8)
- Urban Flood Management A Case Study of CDocument9 pagesUrban Flood Management A Case Study of Cdivya100% (1)
- Unit 12 Land Degradation: StructureDocument14 pagesUnit 12 Land Degradation: Structuretarakesh17No ratings yet
- Paul2019 Article GeospatialAnalysisOfTheDepletiDocument13 pagesPaul2019 Article GeospatialAnalysisOfTheDepletiapple_51210079No ratings yet
- Understand Societal Implications For Wetland Transformation: Riverine SystemDocument8 pagesUnderstand Societal Implications For Wetland Transformation: Riverine SystemMizanur Rahman SarkerNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2214790X21001866 MainDocument15 pages1 s2.0 S2214790X21001866 MainMarcos Fernandes de OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Impact of UrbanizationDocument11 pagesImpact of UrbanizationZama Mahmood100% (1)
- Impact of Mining Activity On Water Resource: An Overview StudyDocument8 pagesImpact of Mining Activity On Water Resource: An Overview StudyAmbika BedasurNo ratings yet
- A Study On Soil Erosion and Its Impacts On Floods and SedimentationDocument9 pagesA Study On Soil Erosion and Its Impacts On Floods and SedimentationInternational Journal of Research in Engineering and TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Drainage Problems Related To Irrigation in MaharashtraDocument17 pagesDrainage Problems Related To Irrigation in MaharashtraDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENo ratings yet
- Remotesensing 12 03822 v2Document23 pagesRemotesensing 12 03822 v2Netra Bahadur KatuwalNo ratings yet
- Groundwater Rise Problem and Risk Evaluation in Major Cities of Arid Lands - Jedddah Case in Kingdom of Saudi ArabiaDocument18 pagesGroundwater Rise Problem and Risk Evaluation in Major Cities of Arid Lands - Jedddah Case in Kingdom of Saudi ArabiaEsra AljabriNo ratings yet
- Evs AssignmentDocument6 pagesEvs AssignmentYash GargNo ratings yet
- Subject-Irrigation Engineering: Water-LoggingDocument22 pagesSubject-Irrigation Engineering: Water-LoggingMorshed Bin Alam FervvezNo ratings yet
- STS11 Module 4Document21 pagesSTS11 Module 4marjoralyn.esganaNo ratings yet
- Coarse and Fine Aggregates: Future of KeralaDocument11 pagesCoarse and Fine Aggregates: Future of KeralaDrThrivikramji KythNo ratings yet
- The Large Scale Mekong Sand MiningDocument3 pagesThe Large Scale Mekong Sand MiningpraharshithaNo ratings yet
- 2018 Herrera-León EtalDocument12 pages2018 Herrera-León EtalgeochuyNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science and Engineering: 20BSCY201Document8 pagesEnvironmental Science and Engineering: 20BSCY201HARSHITHA M SEC 2020No ratings yet
- He Effect of River Flow and Land Use Land Cover Dynamics On Reservoir Sedimentation in A Small ASAL Tropical Basin in KenyaDocument14 pagesHe Effect of River Flow and Land Use Land Cover Dynamics On Reservoir Sedimentation in A Small ASAL Tropical Basin in KenyaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- The Large Dams - Their Disadvantages and Objections To Their Construction by Aid Giving AgenciesDocument5 pagesThe Large Dams - Their Disadvantages and Objections To Their Construction by Aid Giving AgenciesVukasin MilcanovicNo ratings yet
- Caso Subsidencia Japon PDFDocument10 pagesCaso Subsidencia Japon PDFCesar Felipe Jimenez SantiagoNo ratings yet
- HTO: Toronto's Water from Lake Iroquois to Lost Rivers and Low-flow ToiletsFrom EverandHTO: Toronto's Water from Lake Iroquois to Lost Rivers and Low-flow ToiletsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry States of MatterDocument24 pagesChemistry States of MatterSahil BakliwalNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Chap 2 ChemDocument15 pagesAtomic Structure Chap 2 ChemSahil BakliwalNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Worksheet PressureDocument2 pagesGrade 8 Worksheet PressureSahil Bakliwal100% (3)
- Measurements and Statistics TestDocument6 pagesMeasurements and Statistics TestSahil BakliwalNo ratings yet
- Advanced Mechanics of Reinforced Concrete Slot 1Document1 pageAdvanced Mechanics of Reinforced Concrete Slot 1Sahil BakliwalNo ratings yet
- Aman Mehta MasterCardDocument1 pageAman Mehta MasterCardSahil BakliwalNo ratings yet
- Statistics: 2. The Mean of 6, 8, X + 2, 10, 2x - 1, and 2 Is 9. Find The Value of XDocument2 pagesStatistics: 2. The Mean of 6, 8, X + 2, 10, 2x - 1, and 2 Is 9. Find The Value of XSahil BakliwalNo ratings yet
- Literature/case Study/ This Study Is Important For India: Formatted: Font: BoldDocument5 pagesLiterature/case Study/ This Study Is Important For India: Formatted: Font: BoldSahil BakliwalNo ratings yet
- Nitish Exercise3Document4 pagesNitish Exercise3Sahil BakliwalNo ratings yet