0% found this document useful (0 votes)
127 views2 pagesBiocoach Activity Concept 4: Dermal Tissues
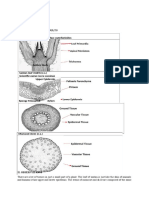
The dermal tissue system protects plants and controls interactions with the environment. The epidermis is usually a single layer of cells covering younger parts of a plant. It secretes a waxy cuticle that inhibits water loss. The epidermis contains several cell types like guard cells that regulate gas exchange, epidermal hairs that lower water loss, and glandular hairs that prevent herbivory. In older stems and roots, the epidermis may be replaced by periderm which allows gas exchange and protection.
Uploaded by
Mea Aprilia MaheswariCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
127 views2 pagesBiocoach Activity Concept 4: Dermal Tissues
The dermal tissue system protects plants and controls interactions with the environment. The epidermis is usually a single layer of cells covering younger parts of a plant. It secretes a waxy cuticle that inhibits water loss. The epidermis contains several cell types like guard cells that regulate gas exchange, epidermal hairs that lower water loss, and glandular hairs that prevent herbivory. In older stems and roots, the epidermis may be replaced by periderm which allows gas exchange and protection.
Uploaded by
Mea Aprilia MaheswariCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd