0% found this document useful (0 votes)
491 views42 pagesClass 9 NCERT Tissues Overview
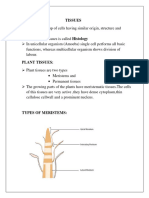
This document discusses the different types of plant tissues. It defines tissue as a group of cells performing a specific function. There are four main types of plant tissues: meristematic tissue which facilitates growth, permanent tissues including simple tissues like parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma and complex tissues like xylem and phloem that transport water and nutrients. Xylem transports water and minerals upwards while phloem transports food materials throughout the plant.
Uploaded by
JoshiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
Topics covered
- Tissue Definition,
- Tissue Coordination,
- Root Structure,
- Plant Transport Systems,
- Plant Anatomy,
- Cellular Organization,
- Plant Cell Types,
- Cell Structure,
- Plant Growth Regions,
- Lateral Meristem
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
491 views42 pagesClass 9 NCERT Tissues Overview
This document discusses the different types of plant tissues. It defines tissue as a group of cells performing a specific function. There are four main types of plant tissues: meristematic tissue which facilitates growth, permanent tissues including simple tissues like parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma and complex tissues like xylem and phloem that transport water and nutrients. Xylem transports water and minerals upwards while phloem transports food materials throughout the plant.
Uploaded by
JoshiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
Topics covered
- Tissue Definition,
- Tissue Coordination,
- Root Structure,
- Plant Transport Systems,
- Plant Anatomy,
- Cellular Organization,
- Plant Cell Types,
- Cell Structure,
- Plant Growth Regions,
- Lateral Meristem