Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DS
DS
Uploaded by
Ali Longasa Cortez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesOriginal Title
DS.doc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesDS
DS
Uploaded by
Ali Longasa CortezCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
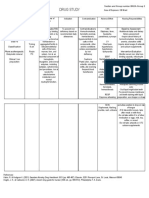
Name of
Medications
Classifications Pharmacodynamics Indications Containdications Ad
Generic
or
(Brand Name)
Mode of Action
1. Nalbuphine Pharmacologic Analgesia is believed It is used for: Contraindicated in
Hydrochloride classification: to result from action patients
(Nubain) narcotic agonist- of drug at opiate Moderate to hypersensitive to
severe pain
antagonist, opioid receptor sites in the drug. Use cautiously
Supplement to
partial agonist CNS, relieving in patients with
anesthesia
moderate to severe history of drug abuse,
Therapeutic pain. The narcotic emotional instability,
classification: antagonist effect may head injury,
analgesic, adjunct result from increased intracranial
to anesthesia competitive inhibition pressure, impaired
at opiate receptors. ventilation, MI
Like other opioids, accompanied by
nalbuphine causes nausea and vomiting,
respiratory upcoming biliary
depression, sedation, surgery, hepatic or
and miosis. In patients renal disease, and in
with coronary artery patients with a sulfite
disease or MI, it sensitivity.
appears to produce no
substantial changes in
heart rate, pulmonary
artery or wedge
pressure, left
ventricular end-
diastolic pressure,
pulmonary vascular
resistance, or cardiac
index.
2. Bisacodyl Pharmacologic Bisacodyl has a direct It is used for: Contraindicated in
(Correctol, classification: stimulant effect on the patients
Dulcolax, Fleet diphenylmethane colon, increasing Constipation, hypersensitive to
Laxative, derivative peristalsis and preparation drug; in patients with
for childbirth,
Modane) enhancing bowel abdominal pain,
Therapeutic surgery, or
evacuation. nausea, vomiting, or
classification: rectal or other symptoms of
stimulant laxative bowel appendicitis or acute
examination
surgical abdomen;
and in patients with
rectal bleeding,
gastroenteritis, or
intestinal
obstruction.
3. Oxytocin Pharmacologic Oxytocin increases the It is used for: Contraindicated in
classification: sodium permeability patients
(Pitocin, exogenous of uterine myofibrils, Induction of hypersensitive to
Syntocinon) labor
hormone indirectly stimulating drug and in those
Augmentation
the contraction of with severe toxemia,
Therapeutic of labor
uterine smooth hypertonic uterine
classification: Reduction of
muscle. The threshold patterns, total
oxytocic, lactation postpartum
for response is placenta previa, and
stimulant bleeding after
lowered when vasoprevia. Also
expulsion of
estrogen levels are contraindicated when
placenta
high. Uterine response To induce cephalopelvic
increases with the abortion disproportion is
length of the Oxytocin present; when
pregnancy and challenge test delivery requires
increases further conversion, as in
to assess fetal
during active labor. distress in transverse lie; in fetal
Response mimics high-risk distress when
labor contractions. pregnancies of delivery isn’t
greater than imminent; and in
31 weeks’ prematurity and
gestation other obstetric
emergencies.
4. Cefuroxime Pharmacologic Cefuroxime is It is used for: Contraindicated in
axetil classification: primarily bactericidal; patients
second-generation it also may be Serious lower hypersensitive to
(Ceftin) respiratory,
cephalosporin bacteriostatic. Activity cefuroxime or other
depends on the urinary tract, cephalosporins. Use
Therapeutic skin, and skin-
organism, tissue cautiously in breast-
Cefuroxime classification: penetration, dosage, structure feeding women and
sodium antibiotic infections;
and rate of organism in patients with
bone and joint
multiplication. It acts impaired renal
(Kefurox, infections;
by adhering to function or penicillin
Zinacef) septicemia;
bacterial penicillin- allergy.
binding proteins, meningitis
thereby inhibiting cell caused by
wall synthesis. susceptible
organisms.
Pharyngitis,
tonsillitis,
lower
respiratory
tract infection,
urinary tract
infection
Otitis media,
impetigo
Perioperative
prophylaxis
Gonorrhea
(urethral,
endocervical,
rectal)
Lyme disease
(erythema
migrans)
5. Ibuprofen Pharmacologic Mechanisms of action It is used for: Contraindicated in
classification: are unknown; patients
(Advil, NSAID ibuprofen is thought Arthritis, gout, hypersensitive to
Children’s and
to inhibit drug or in those who
Advil, Therapeutic prostaglandin postextrac- have the syndrome of
Medipren, classification: tion dental
synthesis. nasal polyps,
Motrin, nonnarcotic pain angioedema, and
Primary
MotrinIB, analgesic, bronchospastic
Nuprin, antipyretic, anti- dysmeno-
reaction to aspirin or
Pediacare inflammatory rrhea
other NSAIDs.
Fever, Rufen, Mild to
Contraindicated
Trendar) moderate
during the last
pain,
trimester of
headache,
pregnancy because it
backache and
may cause problems
minor aches
with the fetus or
associated
complications during
with the
delivery.
common cold
Juvenile Use cautiously in
arthritis patients with
Fever
impaired renal or
reduction
hepatic function, GI
disorders, peptic
ulcer disease, cardiac
decompensation,
hypertension, or
coagulation defects.
Because chewable
tablets contain
aspartame, use
cautiously in patients
with
phenylketonuria.
6. Terraferron Vitamins and Terraferron works by It is used for: Contraindicated in
minerals completing the need patients with a
Ferrous of iron in the body; Improving the known
sulfate; folic Antianemics acting on nutritional hypersensitivity to
acid; vitamin status of
megaloblastic bone any of the
B-complex; marrow to produce a patient with ingredients.
Vitamin C; iron deficiency
normoblastic marrow. Hemochromatosis
Nicotinamide 1 For the
and hemosiderosis
capsule prevention
are contraindications
and treatment
to iron therapy.
of anemias
due to folic
acid and
vitamin B12
deficiencies,
also from
nutritional
deficiency of
vitamin B
complex.
You might also like
- Drug Study: Davao Doctors College General Malvar ST., Davao City Nursing ProgramDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Davao Doctors College General Malvar ST., Davao City Nursing ProgramJear RomeroNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-Med WardDocument2 pagesDrug Study-Med WardErnest Brian FernandezNo ratings yet
- ARI Control ProgrammeDocument13 pagesARI Control ProgrammeArun George44% (9)
- Drug Card PhenytoinDocument5 pagesDrug Card PhenytoinGifther JohnNo ratings yet
- Tramadol Drug StudyDocument4 pagesTramadol Drug StudyJust A Nsg StudentNo ratings yet
- LoperamideDocument5 pagesLoperamideErick TriardiantoNo ratings yet
- ProgesteroneDocument1 pageProgesteroneAGUIRANG, Crystal Joyce R.No ratings yet
- DRUG Plasil (Metoclopra Mide)Document2 pagesDRUG Plasil (Metoclopra Mide)rholiboi0% (1)
- Omeprazole 2018: Newborn Use OnlyDocument5 pagesOmeprazole 2018: Newborn Use OnlyHengky AntonNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - AmoebiasisDocument7 pagesDRUG STUDY - AmoebiasisErika NicaNo ratings yet
- AzithromycinDocument1 pageAzithromycinGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CefuroximeDocument2 pagesDrug Study CefuroximeSiafei RabeNo ratings yet
- Total Abdominal Hysterectomy Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy (Tahbso) Nursing Responsibilities Rationale Pre-OperativeDocument4 pagesTotal Abdominal Hysterectomy Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy (Tahbso) Nursing Responsibilities Rationale Pre-OperativeMiar QuestNo ratings yet
- Mycophenolate Mofetil (Cellcept) and Mycophenolate Sodium (Myfortic)Document3 pagesMycophenolate Mofetil (Cellcept) and Mycophenolate Sodium (Myfortic)Riksan RiksanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HepatitisDocument7 pagesDrug Study HepatitisKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyStephannie MirandaNo ratings yet
- Activity 6 - Drug StudyDocument14 pagesActivity 6 - Drug StudyAl-Mujib TanogNo ratings yet
- DelavirdineDocument2 pagesDelavirdineRosher Deliman JanoyanNo ratings yet
- Acyclovir (Acycloguanosi Ne) : Systemic Administration History: AllergyDocument3 pagesAcyclovir (Acycloguanosi Ne) : Systemic Administration History: AllergyAnnahNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- Celecoxib CelebrexDocument1 pageCelecoxib CelebrexBeverly Ann de LeonNo ratings yet
- Ranitidine Tramadol Ketorolac Ampicillin Paracetamol Drug StudyDocument10 pagesRanitidine Tramadol Ketorolac Ampicillin Paracetamol Drug StudyMarco MoralesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CHDCDocument1 pageDrug Study CHDCIannBlancoNo ratings yet
- CEFUROXIMEDocument1 pageCEFUROXIMECarl Julienne MasangcayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-ClindamycinDocument3 pagesDrug Study-ClindamycinDUMANGENG ELLAINE D.100% (1)
- C. Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesC. Nursing Care PlanJonna Mae TurquezaNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Rifadin RifampinDocument4 pagesCollege of Nursing: Rifadin RifampinAnika PleñosNo ratings yet
- OB Drug StudyDocument12 pagesOB Drug StudyCj AttoNo ratings yet
- Sal But AmolDocument2 pagesSal But AmolCalimlim KimNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Patient With Musculoskeletal InjuryDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Patient With Musculoskeletal InjuryKyla ToledoNo ratings yet
- Crisis Management .Document9 pagesCrisis Management .jeromeNo ratings yet
- Antimalarial DrugsDocument7 pagesAntimalarial DrugsHilmanNo ratings yet
- JM Drug Study CaseDocument4 pagesJM Drug Study CaseMilky Lescano LargozaNo ratings yet
- Piperacillin Tazobactam (Zosynpiperacillin)Document1 pagePiperacillin Tazobactam (Zosynpiperacillin)ENo ratings yet
- Metoclopramide (Reglan)Document1 pageMetoclopramide (Reglan)ENo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Brokenshire CollegeDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Brokenshire CollegeJai GoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study and NCP For Eamc Ob-Gyne Ward Case PresDocument4 pagesDrug Study and NCP For Eamc Ob-Gyne Ward Case PresvirnzrobzNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyLeah Reese VersonNo ratings yet
- Module V ActDocument3 pagesModule V ActQueencess hayoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - IbuprofenDocument3 pagesDrug Study - IbuprofenThalia UyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument21 pagesDrug StudyShyla Garnace JavillonarNo ratings yet
- Domperidone-Oral: Generic Name: Domperidone - Oral (Dom-Pair-Eh-Doan)Document7 pagesDomperidone-Oral: Generic Name: Domperidone - Oral (Dom-Pair-Eh-Doan)Pusparasmi Mas Ayu SuprabhaNo ratings yet
- Cephalexin Drug Study RNpedia ComDocument2 pagesCephalexin Drug Study RNpedia ComTaraKyleUyNo ratings yet
- OmeprazoleDocument2 pagesOmeprazoleKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Primaxin (Imipenem - Cilistatin)Document2 pagesPrimaxin (Imipenem - Cilistatin)ENo ratings yet
- Javier, Jomar A. BSN121 Group 83 Nursing Care Plan (Pediatric Patient)Document7 pagesJavier, Jomar A. BSN121 Group 83 Nursing Care Plan (Pediatric Patient)Julie AnnNo ratings yet
- AnastrozoleDocument2 pagesAnastrozoleAnonymous FgT04krgymNo ratings yet
- ZoladexDocument2 pagesZoladexمحمد الزناتيNo ratings yet
- Esomeprazole (Nexium)Document4 pagesEsomeprazole (Nexium)Roderick AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument16 pagesDrug StudygabbyNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MetoprololDocument2 pagesDrug Study MetoprololHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- DRUG NAME: Hydroxyurea: Synonym (S) : Common Trade Name (S) : ClassificationDocument7 pagesDRUG NAME: Hydroxyurea: Synonym (S) : Common Trade Name (S) : ClassificationDewinta AbutNo ratings yet
- JM DrugDocument3 pagesJM DrugVerdie B. NgayanNo ratings yet
- Name of The DrugDocument2 pagesName of The DrugSistine Rose LabajoNo ratings yet
- Spinal Anes Drug StudyDocument12 pagesSpinal Anes Drug StudyNicosia Mae FerrerNo ratings yet
- Gentamicin _ a Drug Study Presented to the Faculty of the Nursing Department Mrs. Mylahrose Jovita N. Acaba, RN, MN _ in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements in NCM 209-RLE INTEGRATED MANAGEMENT of CHILDHOON (1)Document6 pagesGentamicin _ a Drug Study Presented to the Faculty of the Nursing Department Mrs. Mylahrose Jovita N. Acaba, RN, MN _ in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements in NCM 209-RLE INTEGRATED MANAGEMENT of CHILDHOON (1)allkhusairy6tuansiNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementNathanielle Keith PENASONo ratings yet
- Drug Study Quinine SulfateDocument7 pagesDrug Study Quinine SulfateKathlyn_Matic_6376No ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- DRUG STUDY-1st BatchDocument27 pagesDRUG STUDY-1st BatchCanny CańasNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudycandiceannetarangcoNo ratings yet
- CEFRADINEDocument2 pagesCEFRADINEAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Postnatal Assessment: Name Date: Age: D.O.A: Sex: Hospital: Marital Status: IP .NoDocument11 pagesPostnatal Assessment: Name Date: Age: D.O.A: Sex: Hospital: Marital Status: IP .NoRadha SriNo ratings yet
- Ob Gyn Blueprints: Study Online atDocument17 pagesOb Gyn Blueprints: Study Online atMiko VargasNo ratings yet
- HEMOPTYSISDocument21 pagesHEMOPTYSISYeny WijayantiNo ratings yet
- Referensi Obat Kronis 2019Document59 pagesReferensi Obat Kronis 2019tutikNo ratings yet
- Ferrous SulfateDocument2 pagesFerrous SulfateRoseben SomidoNo ratings yet
- Daftar Nama Obat Dan PengencernyaDocument15 pagesDaftar Nama Obat Dan PengencernyaMeta SuryantiNo ratings yet
- Lo MastitisDocument12 pagesLo MastitisRaul MooreNo ratings yet
- MisoprostolDocument6 pagesMisoprostolMitchel Córdova LoaizaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - DoxycylineDocument3 pagesDrug Study - DoxycylineHaifi Hun100% (1)
- Temperature Monitoring SheetDocument3 pagesTemperature Monitoring SheetVijayGowthamanNo ratings yet
- No Nomor Kartu Nama Nomor SJP Poli Tujuan SJP Nama FKTPDocument3 pagesNo Nomor Kartu Nama Nomor SJP Poli Tujuan SJP Nama FKTPklinik dktNo ratings yet
- Gonorrhea: Clap Flores Blancas Gleet Leus Venereal Morbus Gallicus Sy Bad Blood Disease Chlamydia InfectionDocument2 pagesGonorrhea: Clap Flores Blancas Gleet Leus Venereal Morbus Gallicus Sy Bad Blood Disease Chlamydia InfectionWiljohn de la CruzNo ratings yet
- West Visayas State University COLLEGE of NURSING La Paz, IloiloDocument2 pagesWest Visayas State University COLLEGE of NURSING La Paz, IloilopircanoNo ratings yet
- Magnesium SulphateDocument9 pagesMagnesium SulphateNatália A. OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Lembar Kerja Penyimpanan ObatDocument6 pagesLembar Kerja Penyimpanan ObatfaizadeaNo ratings yet
- Form P (Weekly Reporting Format - IDSP) : Oriana Hospital PVT - LTDDocument2 pagesForm P (Weekly Reporting Format - IDSP) : Oriana Hospital PVT - LTDRavi ParmarNo ratings yet
- HIV AIDS Opportunistic InfectionsDocument26 pagesHIV AIDS Opportunistic InfectionsLaylee ClareNo ratings yet
- MCQ On MeaslesDocument27 pagesMCQ On Measlesnikhil75% (12)
- RX Protocol by DR - Anwarul Azim PDFDocument120 pagesRX Protocol by DR - Anwarul Azim PDFGB Majumder100% (1)
- ChemotherapyDocument47 pagesChemotherapySara EhabNo ratings yet
- ScabiesDocument2 pagesScabiesyulia_azzahra5523No ratings yet
- Hypertension Urinary Tract Infection: Blood-Pressure/default - HTMDocument1 pageHypertension Urinary Tract Infection: Blood-Pressure/default - HTMRiand Marie TeodoroNo ratings yet
- Morning Report: Tim Jaga:Dm Farizan, DM Meyta, Dmnanda, Dmdian Pembimbing Dr. Nanizaitun, SP - PDDocument14 pagesMorning Report: Tim Jaga:Dm Farizan, DM Meyta, Dmnanda, Dmdian Pembimbing Dr. Nanizaitun, SP - PDFarizan hasyim Hari prathamaNo ratings yet
- Annex A1 - KonSulTa Meds PDFDocument4 pagesAnnex A1 - KonSulTa Meds PDFEric Monte de RamosNo ratings yet
- Graves BrochureDocument2 pagesGraves BrochureSussy ListiarsasihNo ratings yet
- Dr. Reckweg FormulaeDocument4 pagesDr. Reckweg FormulaeSatyendra RawatNo ratings yet
- 7.antiviral To MalariaDocument48 pages7.antiviral To MalariaSalih IntajNo ratings yet