0% found this document useful (0 votes)
116 views2 pagesDynamometer
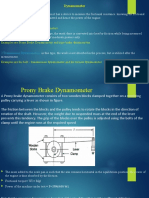
A dynamometer is a machine that measures the torque and rotational speed of an engine or other rotating shaft to determine its power output. It works by absorbing the engine's power, which is transformed into heat, allowing the dynamometer to indirectly measure the absorbed power. There are two main types: absorption dynamometers, which use friction brakes like Prony or rope brakes to absorb power, and transmission dynamometers, which transmit power through the dynamometer to other machines where it can be measured.
Uploaded by
Muhammad RehanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
116 views2 pagesDynamometer
A dynamometer is a machine that measures the torque and rotational speed of an engine or other rotating shaft to determine its power output. It works by absorbing the engine's power, which is transformed into heat, allowing the dynamometer to indirectly measure the absorbed power. There are two main types: absorption dynamometers, which use friction brakes like Prony or rope brakes to absorb power, and transmission dynamometers, which transmit power through the dynamometer to other machines where it can be measured.
Uploaded by
Muhammad RehanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd