Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Understanding the IS-LM Model for Macroeconomic Equilibrium
Uploaded by
KashfiaKamalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Understanding the IS-LM Model for Macroeconomic Equilibrium
Uploaded by
KashfiaKamalCopyright:
Available Formats
What is the IS-LM Model?
The IS-LM model, which stands for "investment-savings" (IS) and "liquidity preference-money
supply" (LM) is a Keynesian macroeconomic model that displays how the market for economic
goods (IS) interacts with the loanable funds market (LM) or money market. It is embodied as a
graph in which the IS and LM curves intersect to show the short-run equilibrium between
interest rates and output.
The IS-LM model describes how aggregate markets for real goods and financial markets
interact to balance the rate of interest and total output in the macro economy.
IS-LM was devised as a formal graphic representation of Keynesian economic theory.
IS-LM can be used to describe how changes in market preferences alter the equilibrium
levels of GDP and market interest rates, but the model lacks the precision and realism to
be a useful prescription tool for economic policy.
Understanding IS-LM Model
British economist John Hicks first introduced the IS-LM model in 1937, just one year after
fellow British economist John Maynard Keynes published The General Theory of Employment,
Interest, and Money.
You might also like
- The Mundell-Fleming Economic Model: A crucial model for understanding international economicsFrom EverandThe Mundell-Fleming Economic Model: A crucial model for understanding international economicsNo ratings yet
- ResumDocument4 pagesResumPedroNo ratings yet
- Summary Of "Keynes & The New Role Of The State" By Unknown Author: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESFrom EverandSummary Of "Keynes & The New Role Of The State" By Unknown Author: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNo ratings yet
- Working of IS-LM Modal ASS4 PDFDocument25 pagesWorking of IS-LM Modal ASS4 PDFSanu BoseNo ratings yet
- Classical Political Economics and Modern Capitalism: Theories of Value, Competition, Trade and Long CyclesFrom EverandClassical Political Economics and Modern Capitalism: Theories of Value, Competition, Trade and Long CyclesNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Interest Rates Investment Saving Liquidity Preference Money Supply National Income Aggregate Demand CurveDocument1 pageMacroeconomic Interest Rates Investment Saving Liquidity Preference Money Supply National Income Aggregate Demand CurveMzee KodiaNo ratings yet
- Hicks-Hansen Model (1) JozaDocument2 pagesHicks-Hansen Model (1) JozaHenrikBanficNo ratings yet
- IS-LM Model DefinitionDocument6 pagesIS-LM Model Definitionselozok1No ratings yet
- Equilibrium in Goods and Money MarketDocument16 pagesEquilibrium in Goods and Money MarketSamia GhafoorNo ratings yet
- ISLM Model Derivation: Keynes vs Classics Debate on Fiscal and Monetary PolicyDocument13 pagesISLM Model Derivation: Keynes vs Classics Debate on Fiscal and Monetary PolicyVinit SonawaneNo ratings yet
- The Assets-Augmented System, ISLMDocument35 pagesThe Assets-Augmented System, ISLMVinit SonawaneNo ratings yet
- IS-LM ModelDocument6 pagesIS-LM ModelAnand Kant JhaNo ratings yet
- Modern Theory of Interest RateeDocument9 pagesModern Theory of Interest RateeAppan Kandala VasudevacharyNo ratings yet
- Macro Bagian m3 Chap 11Document2 pagesMacro Bagian m3 Chap 11Tri WidyastutiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document178 pagesChapter 11andrew myintmyatNo ratings yet
- Week 6 The is-LM ModelDocument32 pagesWeek 6 The is-LM ModelBiswajit DasNo ratings yet
- Marco-Economics Assignment: Topic: Is-Lm ModelDocument6 pagesMarco-Economics Assignment: Topic: Is-Lm ModelVishwanath Sagar100% (1)
- Note On Three-Pane ModelDocument6 pagesNote On Three-Pane ModelTanay Pandey50% (4)
- Is-Lm: Investment Equilibrium of The Market Goods Real Output John R. HicksDocument5 pagesIs-Lm: Investment Equilibrium of The Market Goods Real Output John R. HicksPulasthi Prabashana KuruppuarachchiNo ratings yet
- IS/LM Model: HistoryDocument6 pagesIS/LM Model: Historyhimanshu_ymca01No ratings yet
- The General Equilibrium Model ExplainedDocument11 pagesThe General Equilibrium Model ExplainedAkshay PatilNo ratings yet
- Is - LM ModelDocument20 pagesIs - LM ModelTimothy AveryNo ratings yet
- What is the IS-LM ModelDocument6 pagesWhat is the IS-LM ModelKINGS GroupNo ratings yet
- Lectura Q3Document16 pagesLectura Q3RodrigoNo ratings yet
- CH 18 - Policy Under Fixed Exchange Rates PDFDocument40 pagesCH 18 - Policy Under Fixed Exchange Rates PDFamrith vardhanNo ratings yet
- IS-LM Intersection Explained in Keynesian Macroeconomics ModelDocument3 pagesIS-LM Intersection Explained in Keynesian Macroeconomics ModelJose Jestin GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics: Sana BashirDocument13 pagesMacroeconomics: Sana BashirAbdullah AliNo ratings yet
- Limitations of the IS-LM model and how it is affectedDocument1 pageLimitations of the IS-LM model and how it is affectedRai JiNo ratings yet
- Monetary Theory Course Notes After Mid Ch20Document19 pagesMonetary Theory Course Notes After Mid Ch20Muhammad ButtNo ratings yet
- What Is The Neoclassical SynthesisDocument5 pagesWhat Is The Neoclassical SynthesisTayyeba Shoaib100% (1)
- Macroeconomics Notes Unit 2Document9 pagesMacroeconomics Notes Unit 2Eshaan GuruNo ratings yet
- Economics Final2014-1Document36 pagesEconomics Final2014-1world_warNo ratings yet
- MacroeconomicsDocument2 pagesMacroeconomicsayeshanoor1354No ratings yet
- DoccDocument1 pageDoccFatoumata KoïtaNo ratings yet
- SamuelsonDocument2 pagesSamuelsonV.R RameswarNo ratings yet
- IS-LM (Macroeconomics)Document11 pagesIS-LM (Macroeconomics)GETinTOthE SySteMNo ratings yet
- An Alternative Model to Teach MacroeconomicsDocument50 pagesAn Alternative Model to Teach MacroeconomicsProveedor Iptv EspañaNo ratings yet
- Modern Interest TheoryDocument10 pagesModern Interest TheoryAppan Kandala VasudevacharyNo ratings yet
- Horwitz - Capital Theory, Inflation, and Deflation The Austrians and Monetary Disequilibrium Theory ComparedDocument32 pagesHorwitz - Capital Theory, Inflation, and Deflation The Austrians and Monetary Disequilibrium Theory ComparedGina IoanNo ratings yet
- Module 6 is - LM ModelDocument50 pagesModule 6 is - LM ModelHetvi JasaniNo ratings yet
- Modern Theory of Interest or IsDocument6 pagesModern Theory of Interest or IsAppan Kandala Vasudevachary100% (4)
- Chapter 3Document25 pagesChapter 3HayamnotNo ratings yet
- Romer D Keynesian Macroeconomics Without The LM CurveDocument33 pagesRomer D Keynesian Macroeconomics Without The LM CurveSuikouskyNo ratings yet
- Macr Chapter 1Document10 pagesMacr Chapter 1Surafel BefekaduNo ratings yet
- Is-LM Model With Rational ExpectationsDocument17 pagesIs-LM Model With Rational Expectationssmart__petea9423No ratings yet
- Monetarist Counter-Revolution PDFDocument25 pagesMonetarist Counter-Revolution PDFreader22No ratings yet
- Assignment On Intermediate Macro Economic (ECN 303) - USEDDocument6 pagesAssignment On Intermediate Macro Economic (ECN 303) - USEDBernardokpeNo ratings yet
- 4 IS-LM ModelDocument29 pages4 IS-LM ModelKoeNo ratings yet
- 2. History of EconomicsDocument3 pages2. History of EconomicsTOMY PERIKOROTTE CHACKONo ratings yet
- 7663-Article Text-25717-1-10-20230619Document10 pages7663-Article Text-25717-1-10-20230619wimarwahyu1No ratings yet
- Sitedata Temp Turnitintool 592372239. 6458 1417615254 3051Document8 pagesSitedata Temp Turnitintool 592372239. 6458 1417615254 3051Tayyeba ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document20 pagesModule 3Pranav AsharNo ratings yet
- IS-LM Model - Close and Open Economy - Class 17&20 PDFDocument8 pagesIS-LM Model - Close and Open Economy - Class 17&20 PDFDebabrattaNo ratings yet
- Navigation Map Izmir 01 2014Document36 pagesNavigation Map Izmir 01 2014Stephan SchulmeisterNo ratings yet
- Classical Theory of EconomicsDocument13 pagesClassical Theory of EconomicsmohitNo ratings yet
- Understand Macroeconomics with the IS-LM ModelDocument6 pagesUnderstand Macroeconomics with the IS-LM ModelTalat KhanamNo ratings yet
- The Adaptive Markets Hypothesis: Market Efficiency From An Evolutionary PerspectiveDocument33 pagesThe Adaptive Markets Hypothesis: Market Efficiency From An Evolutionary PerspectiveMark JonhstonNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Demand and Supply Chapter From Wollo University Economics TextDocument14 pagesAggregate Demand and Supply Chapter From Wollo University Economics TextShalom FikerNo ratings yet
- Eco Basics PDFDocument57 pagesEco Basics PDFHalley KalyanNo ratings yet
- Macro Economics ReportDocument21 pagesMacro Economics ReportbilmsyedNo ratings yet
- Reading Passage IELTSDocument5 pagesReading Passage IELTSKashfiaKamalNo ratings yet
- Ielts 6th August 2021Document1 pageIelts 6th August 2021KashfiaKamalNo ratings yet
- An Amoeba Is UnicellularDocument1 pageAn Amoeba Is UnicellularKashfiaKamalNo ratings yet
- Book Review Amatun HossainDocument1 pageBook Review Amatun HossainKashfiaKamalNo ratings yet
- Ielts PassageDocument3 pagesIelts PassageKashfiaKamalNo ratings yet
- Ielts Reading QuestionsDocument1 pageIelts Reading QuestionsKashfiaKamalNo ratings yet
- State One Advantage For Stem Cells in Medical ScienceDocument2 pagesState One Advantage For Stem Cells in Medical ScienceKashfiaKamalNo ratings yet
- What Is Meant by EcosystemDocument3 pagesWhat Is Meant by EcosystemKashfiaKamalNo ratings yet
- 2011 Dotted CalendarsDocument12 pages2011 Dotted CalendarsPenny WaddinghamNo ratings yet
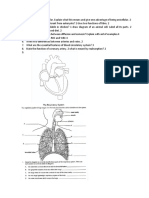
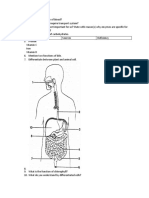
- Explain How Double Circulation Takes PlaceDocument2 pagesExplain How Double Circulation Takes PlaceKashfiaKamalNo ratings yet
- IntroDocument1 pageIntroKashfiaKamalNo ratings yet
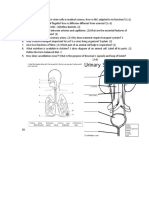
- What Is The Difference Between Excretion and EgestionDocument1 pageWhat Is The Difference Between Excretion and EgestionKashfiaKamalNo ratings yet
- What Is The Function of BloodDocument1 pageWhat Is The Function of BloodKashfiaKamalNo ratings yet
- Spot PriceDocument1 pageSpot PriceKashfiaKamalNo ratings yet
- Mission and Vision StatementsDocument3 pagesMission and Vision StatementsKashfiaKamalNo ratings yet
- NameDocument1 pageNameKashfiaKamalNo ratings yet
- (Holiday Letter) Merry Christmas in Hand-Painted 02-WPS OfficeDocument1 page(Holiday Letter) Merry Christmas in Hand-Painted 02-WPS OfficeKashfiaKamalNo ratings yet
- Pala EmpireDocument5 pagesPala EmpireKashfiaKamalNo ratings yet
- The Goal of Working Capital DraftDocument2 pagesThe Goal of Working Capital DraftKashfiaKamalNo ratings yet
- Imgtopdf Generated 0711171709006Document1 pageImgtopdf Generated 0711171709006KashfiaKamalNo ratings yet
- University of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingFrom EverandUniversity of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (97)
- The War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesFrom EverandThe War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- A History of the United States in Five Crashes: Stock Market Meltdowns That Defined a NationFrom EverandA History of the United States in Five Crashes: Stock Market Meltdowns That Defined a NationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- The Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumFrom EverandThe Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (12)
- Second Class: How the Elites Betrayed America's Working Men and WomenFrom EverandSecond Class: How the Elites Betrayed America's Working Men and WomenNo ratings yet
- Vulture Capitalism: Corporate Crimes, Backdoor Bailouts, and the Death of FreedomFrom EverandVulture Capitalism: Corporate Crimes, Backdoor Bailouts, and the Death of FreedomNo ratings yet
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyFrom EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (227)
- Narrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic EventsFrom EverandNarrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic EventsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (94)
- The Trillion-Dollar Conspiracy: How the New World Order, Man-Made Diseases, and Zombie Banks Are Destroying AmericaFrom EverandThe Trillion-Dollar Conspiracy: How the New World Order, Man-Made Diseases, and Zombie Banks Are Destroying AmericaNo ratings yet
- The Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationFrom EverandThe Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (46)
- Kleptopia: How Dirty Money Is Conquering the WorldFrom EverandKleptopia: How Dirty Money Is Conquering the WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (25)
- Look Again: The Power of Noticing What Was Always ThereFrom EverandLook Again: The Power of Noticing What Was Always ThereRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Nudge: The Final Edition: Improving Decisions About Money, Health, And The EnvironmentFrom EverandNudge: The Final Edition: Improving Decisions About Money, Health, And The EnvironmentRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (92)
- The Genius of Israel: The Surprising Resilience of a Divided Nation in a Turbulent WorldFrom EverandThe Genius of Israel: The Surprising Resilience of a Divided Nation in a Turbulent WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)
- Principles for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailFrom EverandPrinciples for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (237)
- Economics 101: From Consumer Behavior to Competitive Markets—Everything You Need to Know About EconomicsFrom EverandEconomics 101: From Consumer Behavior to Competitive Markets—Everything You Need to Know About EconomicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- This Changes Everything: Capitalism vs. The ClimateFrom EverandThis Changes Everything: Capitalism vs. The ClimateRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (349)
- The Finance Curse: How Global Finance Is Making Us All PoorerFrom EverandThe Finance Curse: How Global Finance Is Making Us All PoorerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- The Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetFrom EverandThe Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetNo ratings yet
- Financial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassFrom EverandFinancial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassNo ratings yet
- The Lords of Easy Money: How the Federal Reserve Broke the American EconomyFrom EverandThe Lords of Easy Money: How the Federal Reserve Broke the American EconomyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (69)
- Kaizen: The Ultimate Guide to Mastering Continuous Improvement And Transforming Your Life With Self DisciplineFrom EverandKaizen: The Ultimate Guide to Mastering Continuous Improvement And Transforming Your Life With Self DisciplineRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (36)