Professional Documents
Culture Documents
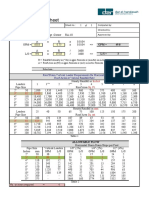
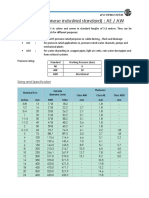
Downspout Sizing Chart Table 10.2. Sizing Roof Drain, Leaders, and Vertical Rainwater Piping (IAPMO, 2000)
Uploaded by
ASHOK SUTHAROriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Downspout Sizing Chart Table 10.2. Sizing Roof Drain, Leaders, and Vertical Rainwater Piping (IAPMO, 2000)
Uploaded by
ASHOK SUTHARCopyright:
Available Formats
Downspout Sizing Chart
Table 10.2. Sizing roof drain, leaders, and vertical rainwater piping (IAPMO, 2000).
Drain, leader, Maximum allowable horizontal projected roof areas in
Flow
or pipe size square feet at various rainfall rates
Inches gpm 1 in./hr 2 in./hr 3 in./hr 4 in./hr 5 in./hr 6 in./hr
2 23 2,176 1,088 725 544 435 363
3 67 6,440 3,220 2,147 1,610 1,288 1,073
4 144 13,840 6,920 4,613 3,460 2,768 2,307
5 261 25,120 12,560 8,373 6,280 5,024 4,187
6 424 40,800 20,400 13,600 10,200 8,160 6,800
8 913 88,000 44,000 29,333 22,000 17,600 14,667
25 50 75 100 125 150
Millimeters L/S
mm/hr mm/hr mm/hr mm/hr mm/hr mm/hr
50 1.5 202 101 67 51 40 34
80 4.2 600 300 200 150 120 100
100 9.1 1,286 643 429 321 257 214
125 16.5 2,334 1,117 778 583 467 389
150 26.8 3,790 1,895 1,263 948 758 632
200 57.6 8,175 4,088 2,725 2,044 1,635 1,363
Notes: 1. The sizing data for vertical conductors, leaders, and drains is based on the pipes flowing
7/24 full. 2. For rainfall rates not listed, determine the allowable roof area by dividing the area
given in the 1 inch/hour (25 mm/hour) column by the desired rainfall rate. 3. Vertical piping may
be round, square, or rectangular. A square pipe should be sized to enclose its equivalent round
pipe. A rectangular pipe should have at least the same cross-sectional area as its equivalent round
pipe, except that the ratio of its side dimensions should not exceed 3 to 1.
These charts originally appeared in a Texas A&M AgriLife publication, B-6240, Rainwater
Harvesting: System Planning (2010), By Justin Mechell, Billy Kniffen, Bruce Lesikar, Douglas
Kingman, Fouad Jaber, Rachel Alexander, and Brent Clayton. The full publication is available
in print at AgriLifeBookstore.org.
You might also like
- British Commercial Computer Digest: Pergamon Computer Data SeriesFrom EverandBritish Commercial Computer Digest: Pergamon Computer Data SeriesNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation Sheet: Roof Drain Vertical Leader Requirements For Horizontal Roof Areas at Various Rainfall RateDocument1 pageDesign Calculation Sheet: Roof Drain Vertical Leader Requirements For Horizontal Roof Areas at Various Rainfall RateAhmed Handy 911No ratings yet
- Chilled Water Flow, Pipe SizeDocument3 pagesChilled Water Flow, Pipe SizeSatya N.GNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation Sheet (Rain Water Pipe Sizing)Document1 pageDesign Calculation Sheet (Rain Water Pipe Sizing)Anonymous VEqJ96RNo ratings yet
- RainwaterDocument6 pagesRainwaterKarthy Ganesan100% (1)
- Metering Pumps: Models A and BDocument5 pagesMetering Pumps: Models A and Bbmanojkumar16No ratings yet
- Brosur ITU - AHU CS Type Aug-2016Document4 pagesBrosur ITU - AHU CS Type Aug-2016Yudhi YudadmokoNo ratings yet
- Polycab LT Cables Pricelist 2017Document2 pagesPolycab LT Cables Pricelist 2017Rajaa The greatNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Technical ManualDocument32 pagesWastewater Technical ManualagonzalezcordovaNo ratings yet
- Sound AttenuatorDocument4 pagesSound AttenuatorFareethAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Hjda 2009-2 R1 (Jar)Document2 pagesHjda 2009-2 R1 (Jar)Anonymous ciu3QEjuSNo ratings yet
- ACME Threads PDFDocument2 pagesACME Threads PDFfarshid jamshidi50% (2)
- Butterfly Valve B7GDocument3 pagesButterfly Valve B7GJorgeCabreraCoronelNo ratings yet
- British Steel European Sections Product RangeDocument9 pagesBritish Steel European Sections Product Rangemdakhan679No ratings yet
- Specification Sheet ANSI B16.5 RTJ Weld Neck - Class 1500 or 2500 Precision Tube Series ModelDocument1 pageSpecification Sheet ANSI B16.5 RTJ Weld Neck - Class 1500 or 2500 Precision Tube Series ModelDhong888No ratings yet
- PIPE Vs FLOWDocument3 pagesPIPE Vs FLOWmanoNo ratings yet
- Bowen™ Overshot Make Up Torques & StrengthsDocument1 pageBowen™ Overshot Make Up Torques & Strengthscatalin calin100% (2)
- Tablice Armature Sipki I Mreza 2020Document3 pagesTablice Armature Sipki I Mreza 2020Aco ZbiljaneznamstadanapisemNo ratings yet
- Standard Pipe Schedule 40 ASTM A 53 Grades A and BDocument1 pageStandard Pipe Schedule 40 ASTM A 53 Grades A and BKelvin RojasNo ratings yet
- Size of Down SpoutDocument1 pageSize of Down SpoutjoNo ratings yet
- 3516 ProductInformation 31-03-2020Document46 pages3516 ProductInformation 31-03-2020adewunmi olufemiNo ratings yet
- Katalog MKM Acsr AsDocument1 pageKatalog MKM Acsr Ascampua.aduak1No ratings yet
- VAM ACE Rev (1) .3 - 07-2005Document8 pagesVAM ACE Rev (1) .3 - 07-2005frankslwslee59No ratings yet
- Appendix C Overhead Line ImpedancesDocument12 pagesAppendix C Overhead Line ImpedancesHermis Escandell MedinaNo ratings yet
- D009R0Document1 pageD009R0quality staffordNo ratings yet
- Ramill Tech Toolkit 3Document9 pagesRamill Tech Toolkit 3moddysNo ratings yet
- Worldwide Fastener Standard: Printed Copies Are UncontrolledDocument2 pagesWorldwide Fastener Standard: Printed Copies Are UncontrolledRasatja Yongskulrote100% (1)
- Campbell Chain PDFDocument46 pagesCampbell Chain PDFrisiana_limuriaNo ratings yet
- Bermad Turbo-BarDocument4 pagesBermad Turbo-BarAngel BarrantesNo ratings yet
- Welded Wiremesh: BRC West Indies Limited, Cane Garden, St. Thomas, BarbadosDocument29 pagesWelded Wiremesh: BRC West Indies Limited, Cane Garden, St. Thomas, BarbadosEngrDebashisMallickNo ratings yet
- 2.2 - Details of Shell & Tube H.EDocument110 pages2.2 - Details of Shell & Tube H.ENader GaafarNo ratings yet
- Heavy Hex Nuts Dimensions, Weight Imperial Metric SizesDocument5 pagesHeavy Hex Nuts Dimensions, Weight Imperial Metric SizesEnyNo ratings yet
- Confinement Check d0Document15 pagesConfinement Check d0Srishti Project ConsultantsNo ratings yet
- SD Reinforcing Mesh Q131Document12 pagesSD Reinforcing Mesh Q131Mohand EliassNo ratings yet
- SD Reinforcing Mesh Q131Document12 pagesSD Reinforcing Mesh Q131Mohand EliassNo ratings yet
- Acsr SPLN 41-7 PDFDocument2 pagesAcsr SPLN 41-7 PDFDharta Wira100% (1)
- Spec44140 CablesDocument2 pagesSpec44140 CablesCarlos LozanoNo ratings yet
- NEW VAM Rev (1) .3 - 07-2005Document8 pagesNEW VAM Rev (1) .3 - 07-2005frankslwslee59No ratings yet
- 1-C AL 15kV 220 NLEPR 133 Percent SIMpull PVC MV-105.specDocument2 pages1-C AL 15kV 220 NLEPR 133 Percent SIMpull PVC MV-105.specFrancisco Zanin FernandesNo ratings yet
- Technical Details of ACSR CablesDocument2 pagesTechnical Details of ACSR CablesGustavo AguiarNo ratings yet
- Flanges: Figure 71 Flange Adapter (ANSI Class 125/150)Document2 pagesFlanges: Figure 71 Flange Adapter (ANSI Class 125/150)Mina MagdyNo ratings yet
- Coaxial Cable Characteristics and DataDocument6 pagesCoaxial Cable Characteristics and Dataadel agustiNo ratings yet
- Aplisens PEM-1000Document4 pagesAplisens PEM-1000CalcRodVerNo ratings yet
- JIS Pipe Catalogue For Jis StandardsDocument1 pageJIS Pipe Catalogue For Jis StandardsTeguh PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Polycab HT Cables 2017 Pricelist PDFDocument1 pagePolycab HT Cables 2017 Pricelist PDFjuga2013No ratings yet
- Gaon Cable Catalogue (Eng.)Document54 pagesGaon Cable Catalogue (Eng.)harry jangNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Protection: ValvesDocument15 pagesPipeline Protection: ValvesMaqsood NishatNo ratings yet
- Covalence S1301-M Epoxy Primer: DescriptionDocument4 pagesCovalence S1301-M Epoxy Primer: DescriptionJuan Carlos Contreras CherresNo ratings yet
- Acsr Al Bare-Rev 04Document1 pageAcsr Al Bare-Rev 04Ae SuwaphanNo ratings yet
- Power Cables & Wires Technical Manual: Table A23. Minimum Wire-Bending Space at TerminalsDocument77 pagesPower Cables & Wires Technical Manual: Table A23. Minimum Wire-Bending Space at Terminalsbharatsehgal00@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Tacsr Jec 3406 PDFDocument1 pageTacsr Jec 3406 PDFomar_cohen_1No ratings yet
- AVK Gate Valves TADocument1 pageAVK Gate Valves TAAleksandarSashaStankovichNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Wire StrandDocument18 pagesCatalogue Wire StrandbronsenwijayaNo ratings yet
- Kap 20 Technical-InformationDocument13 pagesKap 20 Technical-InformationAngelo PereiraNo ratings yet
- Permanent Strand Anchor System: Main StandardsDocument7 pagesPermanent Strand Anchor System: Main StandardsGopu RNo ratings yet
- JKR Jba SpecDocument1 pageJKR Jba SpecYvonne NiamNo ratings yet
- PDS DM8233 01 GS Epg 9018303Document2 pagesPDS DM8233 01 GS Epg 9018303Geovanny SanJuanNo ratings yet
- Roof Drain Pipe SizingDocument1 pageRoof Drain Pipe SizingRolandNo ratings yet
- Warehouse ManagementDocument31 pagesWarehouse ManagementASHOK SUTHARNo ratings yet
- Predictable VariabilityDocument14 pagesPredictable VariabilityASHOK SUTHAR100% (1)
- Demand ForecastingDocument34 pagesDemand ForecastingASHOK SUTHARNo ratings yet
- Inventory ManagementDocument46 pagesInventory ManagementASHOK SUTHARNo ratings yet
- Outsourcing Make Vs BuyDocument27 pagesOutsourcing Make Vs BuyASHOK SUTHARNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Planning in Supply ChainDocument27 pagesAggregate Planning in Supply ChainASHOK SUTHARNo ratings yet
- CurvesDocument19 pagesCurvesASHOK SUTHARNo ratings yet
- SE Prod FM CH 3 Flow in Pipes NumericalsDocument23 pagesSE Prod FM CH 3 Flow in Pipes NumericalsASHOK SUTHARNo ratings yet
- DME-II Gears&RCB VJTI PDFDocument17 pagesDME-II Gears&RCB VJTI PDFASHOK SUTHARNo ratings yet
- Trigger Sprayer Dynamic Systems ModelDocument5 pagesTrigger Sprayer Dynamic Systems ModelLTE002No ratings yet
- Vse 2 Plugin ManualDocument4 pagesVse 2 Plugin ManualConst VassNo ratings yet
- How Advertising Differs A Content Analysis of Traditional Print Advertising and Online Media ModelsDocument71 pagesHow Advertising Differs A Content Analysis of Traditional Print Advertising and Online Media Modelsobserverbg@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Training and Development in Indigo AirlinesDocument95 pagesTraining and Development in Indigo Airlinesbhartisuman75% (4)
- Airpods Pro Service Program For Sound IssuesDocument1 pageAirpods Pro Service Program For Sound Issuesmarkanapier100% (1)
- Work Measurement 3Document16 pagesWork Measurement 3Miguel HernandezNo ratings yet
- Sidebyside Audio CD DownloadDocument4 pagesSidebyside Audio CD DownloadAngel Leuris0% (3)
- Catalogue Air Dryer ARXDocument8 pagesCatalogue Air Dryer ARXtrantrunghoa1984No ratings yet
- English Proficiency Test OkDocument19 pagesEnglish Proficiency Test OkNoelle Mendes100% (5)
- A Four Element Rectangular Dielectric Resonator Antenna Array For Wireless ApplicationsDocument4 pagesA Four Element Rectangular Dielectric Resonator Antenna Array For Wireless ApplicationsSubhanjali MyneniNo ratings yet
- Exp 01Document8 pagesExp 01MohamedElSayedNo ratings yet
- Acse RailsDocument96 pagesAcse RailsZain UddinNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current: Theory and Exercise BookletDocument31 pagesAlternating Current: Theory and Exercise BookletMD CHHIMPANo ratings yet
- Market Research Company in IndiaDocument8 pagesMarket Research Company in Indiaaditya adityaNo ratings yet
- Kaizen Masaakiimai 090701152003 Phpapp01Document48 pagesKaizen Masaakiimai 090701152003 Phpapp01Shaikh Haseeb UR Rehman100% (2)
- SIRAJGANJDocument98 pagesSIRAJGANJAfiat KhanNo ratings yet
- Hyperautomation: Hyperautomation and AI Security Are Two Technologies That Are Most Likely ToDocument9 pagesHyperautomation: Hyperautomation and AI Security Are Two Technologies That Are Most Likely Torammanohar22No ratings yet
- ECE 6313 Neural Networks SyllabusDocument4 pagesECE 6313 Neural Networks SyllabusSose ManukNo ratings yet
- GE Range JGB735SP1SS Parts ListDocument2 pagesGE Range JGB735SP1SS Parts ListMuller SolimanNo ratings yet
- LEXE0047-02 Data SheetDocument4 pagesLEXE0047-02 Data Sheetsklm123No ratings yet
- Setting Up The System in BODSDocument21 pagesSetting Up The System in BODSPayal MohantyNo ratings yet
- Requirements For Azure Information Protection - AIP - Microsoft DocsDocument2 pagesRequirements For Azure Information Protection - AIP - Microsoft DocssjmpakNo ratings yet
- IP Morocco 2014Document2 pagesIP Morocco 2014Wahbi SoufianeNo ratings yet
- Controls: Instruction ManualDocument32 pagesControls: Instruction Manualmarvin17No ratings yet
- RST Instruments: C109 Pneumatic Readout Instruction ManualDocument25 pagesRST Instruments: C109 Pneumatic Readout Instruction ManualarywimNo ratings yet
- C++ LabDocument9 pagesC++ LabtnssbhaskarNo ratings yet
- Actuator Catalogue CompleteDocument22 pagesActuator Catalogue Completeprashantsingh0450% (2)
- Hayman Industries Utility Poles 178785 PDFDocument8 pagesHayman Industries Utility Poles 178785 PDFvcockscribdNo ratings yet
- HRD536C Hrd536cki HRD536C2Document82 pagesHRD536C Hrd536cki HRD536C2David ThijsNo ratings yet
- How To Play The Violin-Key SignaturesDocument3 pagesHow To Play The Violin-Key SignaturesMichael SchallockNo ratings yet