Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 7 Application in Class PDF
Uploaded by
Anonymous xUb9GnoFOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 7 Application in Class PDF
Uploaded by
Anonymous xUb9GnoFCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 7 Application See D2L week 4 – Practice
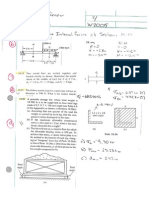
Graph 1
Equilibrium
P: $1,300
Q: 100 computers
Total Revenue
TR= P x Q = $1,300 x 100 = $130,000
Consumer Surplus
WTP: $2,000
P: $1,300
Cs = WTP - P = $2,000 - $1,300
Cs= $700 Gain from exchange
Total Consumer Surplus
TCs = 1/2 x Q x (WTP - P) = 1/2 x 100 x $700
TCs = $35,000 Gain from exchange
Producer Surplus
WTS: $500 (OC)
P: $1,300
Ps = (P received - C) or (P received - WTS)
Ps = $800 Gain from exchange
Total Producer Surplus
TPs = 1/2 x Q x (p - WTS)
PPs = 1/2 x 100 x $800
TPs = $40,000 Gain from exchange
Market Efficiency
TCS + TPS = $35,000 + $40,000 = $75,000
The total gain from the free market is
maximize
Chapter 1
Rational People decision making is based on the Marginal
Benefits (D) vs Marginal Costs (S).
Chapter 13
MB > MC: Purchase
MB = MC: Equilibrium and S = D
MB < MC:
MB is the willingness to pay for that extra units will provide
and on how many units that already possess. MB is the next
unit being consumed or acquired.
MB = D = Downward slope demonstrates the diminishing
return when people acquire an additional good.
Graph 2
Equilibrium
P: $1,000
Q: 150 computers
Calculate Total Revenue?
Calculate Consumer Surplus?
Calculate Total Consumer Surplus?
Calculate Producer Surplus?
Calculate Total Producer Surplus?
Calculate Total Market Surplus or Efficiency?
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Stock Arket Agic - TradeWins PublishingDocument159 pagesStock Arket Agic - TradeWins PublishingK P LoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Bond Prices and Yields (Slide)Document104 pagesChapter 14 Bond Prices and Yields (Slide)Giang Nguyễn LêNo ratings yet
- SMC Online Trading PurchasedDocument69 pagesSMC Online Trading PurchasedShivangi Jaiswal100% (1)
- Entrepreneurship ExamDocument3 pagesEntrepreneurship ExamCindy JauculanNo ratings yet
- IKEA Case StudyDocument20 pagesIKEA Case StudyAbinash Sabat100% (2)
- Principles of Macroeconomics Practice AssignmentDocument4 pagesPrinciples of Macroeconomics Practice AssignmentAnonymous xUb9GnoFNo ratings yet
- Kinetics of ReactionsDocument119 pagesKinetics of ReactionsAnonymous xUb9GnoFNo ratings yet
- ENCH 501 Midterm Cheat SheatDocument1 pageENCH 501 Midterm Cheat SheatAnonymous xUb9GnoFNo ratings yet
- ECON203Summer2019Assignment1 (Answer) PDFDocument4 pagesECON203Summer2019Assignment1 (Answer) PDFAnonymous xUb9GnoFNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium NotesDocument11 pagesEquilibrium NotesAnonymous xUb9GnoFNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium NotesDocument11 pagesEquilibrium NotesAnonymous xUb9GnoFNo ratings yet
- SMTL246 E01 Review QuestionsDocument6 pagesSMTL246 E01 Review QuestionsAnonymous xUb9GnoFNo ratings yet
- 2015 ENGG317 Assignment2Document2 pages2015 ENGG317 Assignment2Anonymous xUb9GnoFNo ratings yet
- Sample Engineering Dynamcs AssignmentDocument2 pagesSample Engineering Dynamcs AssignmentAnonymous xUb9GnoFNo ratings yet
- Blue Pelican JavaDocument543 pagesBlue Pelican JavaAnonymous xUb9GnoFNo ratings yet
- 810002Document2 pages810002jigneshparmarNo ratings yet
- T - Proc - Notices - Notices - 085 - K - Notice - Doc - 80312 - 443033651Document28 pagesT - Proc - Notices - Notices - 085 - K - Notice - Doc - 80312 - 443033651Enamul HaqueNo ratings yet
- International Financial Management 5Document53 pagesInternational Financial Management 5胡依然100% (1)
- Lipo FifoDocument4 pagesLipo FifoJAS 0313No ratings yet
- EvaluateDocument5 pagesEvaluateFlorence BamugyeNo ratings yet
- IFR Definitive GuideDocument257 pagesIFR Definitive Guidehussaisz100% (1)
- Brand BooksDocument123 pagesBrand BooksANo ratings yet
- Ibs Sitiawan 1 30/06/23Document2 pagesIbs Sitiawan 1 30/06/23KISHANTHNI A/P MURUGAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Kirana TradeDocument6 pagesKirana Tradekanshou87No ratings yet
- Societal Marketing ConceptDocument3 pagesSocietal Marketing ConceptNadia TariqNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics in Modules Economics in ModulesDocument21 pagesMicroeconomics in Modules Economics in ModulesFarhan AbrarNo ratings yet
- Kirt C Butler Multinational Finance 4e 2008Document4 pagesKirt C Butler Multinational Finance 4e 2008Abhishek AnandNo ratings yet
- College of Computer Studies: Entrepreneurial MindDocument2 pagesCollege of Computer Studies: Entrepreneurial MindJE TCNo ratings yet
- Tugas CMA Soal 8-45 Dan 8-46 Richard Andrew - 8312419003 Fix PDFDocument12 pagesTugas CMA Soal 8-45 Dan 8-46 Richard Andrew - 8312419003 Fix PDFsNo ratings yet
- Showrooming at Best Buy: Case AnalysisDocument4 pagesShowrooming at Best Buy: Case AnalysisAnubhavChauhanNo ratings yet
- FormulebladDocument5 pagesFormulebladwdqkj.nsd,ndsNo ratings yet
- Procter & Gamble: Delivering Goods: (2004-07-01) - Contributed by Tom Steinert-ThrelkeldDocument4 pagesProcter & Gamble: Delivering Goods: (2004-07-01) - Contributed by Tom Steinert-ThrelkeldArjun AnpatNo ratings yet
- Global ProductDocument13 pagesGlobal ProductBalli VermaNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing Consumers' Convenience Shopping of Industrial Products: A Study of Kinondoni DistrictDocument11 pagesFactors Influencing Consumers' Convenience Shopping of Industrial Products: A Study of Kinondoni DistrictFuadNo ratings yet
- Practice Homework CH 5 FA21Document5 pagesPractice Homework CH 5 FA21Thomas TermoteNo ratings yet
- Production of 100% Organic Dry Fish in BangladeshDocument52 pagesProduction of 100% Organic Dry Fish in BangladeshAbu NayeemNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Finance: Quo Vadis?Document15 pagesBehavioral Finance: Quo Vadis?Igor MartinsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 8 EDDocument47 pagesChapter 6 8 EDMonir HossainNo ratings yet
- Volume Is What Drives The MarketDocument1 pageVolume Is What Drives The MarketHendra SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Accounting Slides Income StatmentDocument20 pagesAccounting Slides Income StatmentEdouard Rivet-BonjeanNo ratings yet