Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Uppp2 Sem 3 2017
Uppp2 Sem 3 2017
Uploaded by
John LiapCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Uppp2 Sem 3 2017
Uppp2 Sem 3 2017
Uploaded by
John LiapCopyright:
Available Formats
CONFIDENTIAL* 2
SECTION A [15 marks]
Answer all questions in this section. Indicate the correct answer on the space provided in page 5
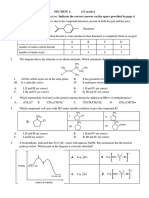
1. The structural formula of an organic compound is shown below. Which is correct about the
number of sp2 and sp3 hybridised C atoms in the molecule?
sp2 sp3
A 5 5
B 4 5
C 5 4
D 6 4
2. What is the correct name of the molecule with the skeletal formula shown?
A. 5-hydroxy-2,3-dimethylhex-2-ene B. 2-hydroxy4,5-dimethylhex-4-ene
C. 2,3-dimethyl-2-hexen-5-ol D. 4,5-dimethyl-4-hexen-2-ol
3. The diagram shows the structure of 1,3-butadiene.
The addition reaction between 1,3-butadiene and two molecules of hydrogen bromide, HBr,
can produce three structurally isomeric products. How many of these products have at least
one chiral centre?
A. 0 B. 1 C. 2 D. 3
4. When heated with chlorine under ultraviolet, the hydrocarbon 2,2-dimethylbutane undergoes
free radical substitution. In a propagation step a free radical X• is formed.
How many different structures of X• are possible?
A. 2 B. 3 C. 4 D. 5
5. Which of the following reaction schemes can be used for the preparation of benzoic acid?
962 / 3 - CHEMISTRY PAPER 3
TRIAL EXAMINATION STPM SMK TASEK UTARA
CONFIDENTIAL* 3
6. The reaction between boiling methylbenzene and chlorine takes place in a number of steps to
give several products. Which of the following could be one of the steps?
7. A reaction pathway diagram is shown.
The four reactions that follow are all exothermic. Which reaction would not have such a
pathway?
8. Haloalkanes show trends in their physical and chemical properties. Which properties steadily
increase from C2H5Cl to C2H5Br to C2H5I ?
I. the polarity of the carbon-halogen bond
II. the boiling point of the haloalkane
III. the rate of reaction of the haloalkane with nucleophiles
IV. the preference to undergoes SN2 mechanism
A. I and IV B. II and III
C. I and II D. III and IV
962 / 3 - CHEMISTRY PAPER 3
TRIAL EXAMINATION STPM SMK TASEK UTARA
CONFIDENTIAL* 4
9. Y gives product Z after mild oxidation. Z gives a positive result with Tollens’ reagent and with
2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine reagent. What could be the identity of Y?
A. pentan-1-ol B. pentan-2-ol C. pentan-2,3-diol D. pentanal
10. A sample of butan-2-one is treated with lithium tetrahydridoaluminate(III) and then with
concentrated sulphuric acid at 180°C. Which of the following could not apply to the product
formed?
A. It shows optical isomerism.
B. It undergoes nucleophilic addition reaction.
C. It reacts with sodium metal to give hydrogen.
D. It decolourises acidified solution of potassium manganate(VII)
11. Which reagent cannot be used to distinguish between ethanal and propanone?
A. acidified sodium dichromate(VI) solution
B. alkaline aqueous iodine
C. cold acidified potassium manganate(VII) solution
D. Fehling’s reagent
12. The structural formulae of two compounds A and B are shown below.
Which statements about these compounds are correct?
I. The two compounds are structural isomers of each other.
II. The empirical formula of both compounds is C3H6O.
III. Both compounds are carboxylic acids.
IV. Both compounds can undergoes hydrolysis.
A. I and IV B. II and III
C. I and II D. I, III and IV
13. The ester CH3CH2CH2COOCH2CH(CH3)2 was hydrolysed under acidic conditions. What are
the organic products of this hydrolysis?
A. butanoic acid and 2-methylpropan-1-ol
B. butanoic acid and 2-methylpropan-2-ol
C. butan-1-ol and 2-methylpropanoic acid
D. propanoic acid and 2-methylpropan-1-ol
962 / 3 - CHEMISTRY PAPER 3
TRIAL EXAMINATION STPM SMK TASEK UTARA
CONFIDENTIAL* 5
14. The following reaction between phenol and a compound X produces an orange dye
Which reagents can be used to produce X?
15. GABA is a neuro-transmitter released by red algae which encourages shellfish larvae to settle
on the ocean bed.
H2NCH2CH2CH2COOH GABA
In what way does GABA differ from amino acids obtained by the hydrolysis of protein?
A It does not form a zwitterion. B It is not soluble in water.
C It is not a 2-aminocarboxylic acid. D It does not form a polyamide linkage
962 / 3 - CHEMISTRY PAPER 3
TRIAL EXAMINATION STPM SMK TASEK UTARA
CONFIDENTIAL* 6
SMK TASEK UTARA, JOHOR BAHRU
UJIAN PENILAIAN PRA-PENTAKSIRAN (2) SEM 3 2017
SUBJECT : CHEMISTRY
Name : ____________________________________ Tingkatan : UPPER 6 ____________
Section A [15 marks]
1 6 11
2 7 12
3 8 13
4 9 14
5 10 15
Section B [15 marks]
Answer all questions in this section
16. A reaction sequence based on propan-1-ol is shown.
(a) Suggest a reagent and condition for reaction 1 and reaction 2 to occur : [2 marks]
Reaction 1 : ……………………………………………………………………………
Reaction 2 : ……………………………………………………………………………
(b) Complete the reaction sequence by filling the molecular structure of A and B in the boxes
provided. [2 marks]
(c) Suggest a chemical test that can be used to distinguish ethanoic acid from compound B
proposed in (b) [3 marks]
………………………………………………………………………………………………....
………………………………………………………………………………………………....
………………………………………………………………………………………………....
………………………………………………………………………………………………....
962 / 3 - CHEMISTRY PAPER 3
TRIAL EXAMINATION STPM SMK TASEK UTARA
CONFIDENTIAL* 7
17. Glutamic acid is one of the natural amino acid found naturally in kombu broth, a type of
seaweed, which eventually, can be used to produce monosodium glutamate (MSG). The
molecular structure of glutamic acid is given below
(a) Give the IUPAC name of glutamic acid. [1 mark]
………………………………………………………………………………………………....
(b) When two glutamic acid reacted, it can form dipeptide that is bonded by peptide linkage.
(i) Define the term peptide linkage [1 mark]
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(ii) Draw the structures of dipeptide that can be formed by reacting two glutamic acid
[2 marks]
(c) Glutamic acid shows variation in chemical properties due to the presence of carboxyl group
and amino group. Draw the molecular structure of the product formed when glutamic acid
react with the following compound [2 marks]
(i) dilute hydrochloric acid (ii) methanol with concentrated sulphuric acid
under reflux.
(d) Write the chemical equation for the reaction between glutamic acid with sodium hydroxide
to produce monosodium glutamate (MSG) and state one of its application in our daily life
Equation : [2 marks]
Application : …………………………………………………………………………………………
962 / 3 - CHEMISTRY PAPER 3
TRIAL EXAMINATION STPM SMK TASEK UTARA
CONFIDENTIAL* 8
Section C [30 marks]
Answer any two of the three questions below
18. Compound E, with molecular mass, MR = 106.5, is an optically active primary haloalkane has
the following composition by mass - 56.34% of carbon ; 10.33% of hydrogen and 33.33 % of
chlorine.
(a) Calculate the empirical formula and molecular formula of E [4 marks]
(b) When compound E react with aqueous sodium hydroxide under reflux to form compound F.
F decolourised hot acidified potassium dichromate(VI) to produce a compound G which
reacts with potassium hydroxide to form salt and water. Compound E can also react with
magnesium in dry ether to form compound H and H further react with propanone followed
by acidic hydrolysis to form compound J.
(i) Deduce the molecular structure of E, F, G, H and J [5 marks]
(ii) Write all the equations for the reactions that occurred. [6 marks]
19. Paracetamol is commonly used as modern medicine to treat mild fever and headache. The
structure of paracetamol is given below
(a) Using suitable reagents and conditions, propose a reaction scheme to synthesis paracetamol
starting from phenol. [5 marks]
(b) Draw the molecular structure of the products for the reaction of paracetamol with
(i) hydrochloric acid under reflux [2 marks]
(ii) sodium hydroxide under reflux [2 marks]
(c) When paracetamol is treated with aniline under suitable condition, it may be use to produce
a yellow colour type of paracetamol which enhance the appearances suitable for children to
consume. The reaction scheme for reaction of paracetamol and aniline is describe below
Based on the reaction scheme above
(i) State the reagents and conditions for x and y [3 marks]
(ii) Draw the molecular structure of M and N [2 marks]
(iii) State the type of reaction occur from M to form N [1 mark]
962 / 3 - CHEMISTRY PAPER 3
TRIAL EXAMINATION STPM SMK TASEK UTARA
CONFIDENTIAL* 9
20. An optically active ester, P, with the molecular formula C5H10O2 undergoes acidic hydrolysis
to form compound Q and an optical active compound R. Both Q and R react with acidified
potassium manganate (VII), however only organic compound S is formed from either Q and R,
where S can react with both 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine and iodoform test.
(a) Explain the above observations using suitable equations and write the structural formulae of
P, Q, R and S [10 marks]
(b) Compound T is an optically active carboxylic acid that is an isomer of ester P.
(i) Name compound T. [1 mark]
(ii) Compare and explain the boiling point of compound P and T. [4 marks]
=================== END OF QUESTION PAPER ===================
962 / 3 - CHEMISTRY PAPER 3
TRIAL EXAMINATION STPM SMK TASEK UTARA
You might also like
- Organic Chemistry Question IB Chem SLDocument40 pagesOrganic Chemistry Question IB Chem SLAarav Verma100% (1)
- Cabbage and Caviar. History of Food in Rusia - Alison K. SmithDocument413 pagesCabbage and Caviar. History of Food in Rusia - Alison K. SmithLuis Felipe La Corte CastroNo ratings yet
- Hem Actsheet: Redox Equilibria IV - Redox TitrationsDocument3 pagesHem Actsheet: Redox Equilibria IV - Redox TitrationsAya ZhNo ratings yet
- Basic Culinary Math - PptsDocument39 pagesBasic Culinary Math - PptsfugaperuNo ratings yet
- CH13 Hydrocarbons Shobhit NirwanDocument58 pagesCH13 Hydrocarbons Shobhit NirwanpujaNo ratings yet
- Taste of Sea Food - Taste of Sea Food Morocco - 2023Document58 pagesTaste of Sea Food - Taste of Sea Food Morocco - 2023Petra MaizácNo ratings yet
- Organic C CCCC CCCCDocument88 pagesOrganic C CCCC CCCCKugan KishurNo ratings yet
- Ingredients:: Print SaveDocument3 pagesIngredients:: Print SaveDany MelNo ratings yet
- Culinary Arts A Guide To The LiteratureDocument34 pagesCulinary Arts A Guide To The LiteratureOmar MakkiNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Questions on NougatFrom EverandThe Little Book of Questions on NougatRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- CHM 361 Experiment 2 and 3Document22 pagesCHM 361 Experiment 2 and 3dayang100% (2)
- Easy Spaghetti BologneseDocument5 pagesEasy Spaghetti BologneseNurul Aini100% (1)
- Texas Jack's Famous Pumpkin & Pumpkin Seed Recipes: (36 Recipes For Delectable Pumpkin & Pumpkin Seed Treats)From EverandTexas Jack's Famous Pumpkin & Pumpkin Seed Recipes: (36 Recipes For Delectable Pumpkin & Pumpkin Seed Treats)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Alejandro (1984) The Flavor of AsiaDocument264 pagesAlejandro (1984) The Flavor of AsiaSmir Tola100% (1)
- Restaurant: EstablishmentDocument4 pagesRestaurant: EstablishmentNial HoerunNo ratings yet
- Iodine Thiosulfate Titration QuestionsDocument13 pagesIodine Thiosulfate Titration QuestionsWeb Books100% (1)
- Cookery and Dining in Imperial RomeFrom EverandCookery and Dining in Imperial RomeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- How Does The Shape of An Ice Cube Affect How Fast It MeltsDocument2 pagesHow Does The Shape of An Ice Cube Affect How Fast It Meltsobx4everNo ratings yet
- Maeb ThesisDocument52 pagesMaeb ThesisEmma CatindoyNo ratings yet
- EDTA Titration LabDocument16 pagesEDTA Titration LabJosef Hilton67% (3)
- Radioactivity Notes 1 PDFDocument6 pagesRadioactivity Notes 1 PDFBOSS BOSS100% (2)
- About Cake: First IcingDocument58 pagesAbout Cake: First IcingGinalyn BenitezNo ratings yet
- French Cuisine: A Brief HistoryDocument32 pagesFrench Cuisine: A Brief HistoryPinoy DeveloperNo ratings yet
- Coffee Basics - The Difference Between Arabica and RobustaDocument20 pagesCoffee Basics - The Difference Between Arabica and RobustaMaru PabloNo ratings yet
- Culinary Math SkillsDocument59 pagesCulinary Math SkillsReghEllorimo33% (3)
- Italian Style Poultry and Game Dishes - A Selection of Classic and Authentic Italian Recipes (Italian Cooking Series)From EverandItalian Style Poultry and Game Dishes - A Selection of Classic and Authentic Italian Recipes (Italian Cooking Series)No ratings yet
- RecipesDocument31 pagesRecipesMa Christine Giangan BarbaNo ratings yet
- Dangmaingoc TramDocument73 pagesDangmaingoc TramPrince arbert FuentesNo ratings yet
- Green Breakroom ProductsDocument1 pageGreen Breakroom ProductsExecutive Computer Products100% (1)
- Entrepreneurship Group ProjectDocument13 pagesEntrepreneurship Group ProjectBibu JohnyNo ratings yet
- Chemi Sem 3Document6 pagesChemi Sem 3Max NgNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions in This Section. Indicate The Correct Answer On The Space Provided in Page 2Document5 pagesAnswer All Questions in This Section. Indicate The Correct Answer On The Space Provided in Page 2seanNo ratings yet
- SMJK Chung Ling Pulau Pinang Peperiksaan Percubaan STPM 2019 Semester 3 Chemistry Upper 6Document4 pagesSMJK Chung Ling Pulau Pinang Peperiksaan Percubaan STPM 2019 Semester 3 Chemistry Upper 6AlyciaLeeNo ratings yet
- CHE 232 Test 1Document11 pagesCHE 232 Test 1moatlhodiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry STPM Sem 3 MSAB Pre-Trial QuestionDocument6 pagesChemistry STPM Sem 3 MSAB Pre-Trial QuestionKenneth Chan43% (7)
- Che 232 Test 1b 2016 AnsDocument12 pagesChe 232 Test 1b 2016 AnsBONOLO RANKONo ratings yet
- Acfrogbyyb W54zpzfswkn8k3vq0clq6et8mk Ne Px62hvrlk5chrlql9xx83xtq2sr0dqcuhrswcoglr Ueky068cras4ph7jxkmy 143kq0wnhekbynbh 4 Eq1p0kvslajoriecir6ikqqswDocument8 pagesAcfrogbyyb W54zpzfswkn8k3vq0clq6et8mk Ne Px62hvrlk5chrlql9xx83xtq2sr0dqcuhrswcoglr Ueky068cras4ph7jxkmy 143kq0wnhekbynbh 4 Eq1p0kvslajoriecir6ikqqswThanh Hằng NgôNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Chemistry QPDocument4 pagesClass Xii Chemistry QPRiya JasuNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Sample Paper-15: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 14Document14 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Sample Paper-15: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 14Allen Neal JonesNo ratings yet
- Cblechpu 07Document6 pagesCblechpu 07Yash PatelNo ratings yet
- Write Your Name and ID No On The Question Papers. All Questions Are CompulsoryDocument8 pagesWrite Your Name and ID No On The Question Papers. All Questions Are CompulsoryAPOORVA OJHANo ratings yet
- Confidential : (Malacca High School Estd.1826)Document9 pagesConfidential : (Malacca High School Estd.1826)ThilagaNo ratings yet
- 12 Lyp Chemistry s1 PDFDocument7 pages12 Lyp Chemistry s1 PDFBT De0pA PUBG MOBILENo ratings yet
- CHE 232 Test 1 2015 AnsDocument12 pagesCHE 232 Test 1 2015 AnsBONOLO RANKONo ratings yet
- Sample Paper For ChemistryDocument23 pagesSample Paper For ChemistryAmit joshiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Test - 12th Science-ChemistryDocument7 pagesChemistry Test - 12th Science-ChemistryAishley ChalametNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Sample Paper 2Document6 pagesChemistry Sample Paper 2Koushiki Chakraborty 10 f 27No ratings yet
- Do Not Open This Booklet Until Told To Do SoDocument18 pagesDo Not Open This Booklet Until Told To Do SoNasyaNo ratings yet
- BINA ITEM 2023 P3 KIMIA QUESTION EditedDocument12 pagesBINA ITEM 2023 P3 KIMIA QUESTION EditedFazliawati MahayuddinNo ratings yet
- S.NO. Unit VSA SAI Saii LA Total (1 Mark) (2 Marks) (3 Marks) (5 Marks)Document6 pagesS.NO. Unit VSA SAI Saii LA Total (1 Mark) (2 Marks) (3 Marks) (5 Marks)api-243565143No ratings yet
- Chemistry SQP XII PDFDocument14 pagesChemistry SQP XII PDFIshikaGuptaNo ratings yet
- Class12 QP Workshop RoorkeeDocument232 pagesClass12 QP Workshop RoorkeeSoumya JoshiNo ratings yet
- Gerak Gempur 3 Term 3 With AnswersDocument11 pagesGerak Gempur 3 Term 3 With AnswersShima SenseiiNo ratings yet
- Trial p3 2016 Q (Johor-Sekolah Tinggi Muar)Document8 pagesTrial p3 2016 Q (Johor-Sekolah Tinggi Muar)Chan Yek FungNo ratings yet
- AkcDocument4 pagesAkcGirishmaNo ratings yet
- Set 1 STPM Biology 2022 Kelantan (Soalan)Document9 pagesSet 1 STPM Biology 2022 Kelantan (Soalan)Dharani RavindranNo ratings yet
- Honors Chem 1st Semester Exam Study Guide Fall 2010Document5 pagesHonors Chem 1st Semester Exam Study Guide Fall 2010Aref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems Set 5Document3 pagesPractice Problems Set 5Kishwer NishatNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Anions IDocument5 pagesReactions of Anions IChrysler SteveNo ratings yet
- Distillation Apparatus-USER MANUALDocument40 pagesDistillation Apparatus-USER MANUALebalideNo ratings yet
- CHEM 209 Chapter 04 Fall 2020 002 SQ UpdatedDocument119 pagesCHEM 209 Chapter 04 Fall 2020 002 SQ UpdatedTaanzNo ratings yet
- Hi-Flo 6 Hi-Flo 9 Twin Hi-Flo 6 Twin Hi-Flo 9 Filters 1999 LineDocument34 pagesHi-Flo 6 Hi-Flo 9 Twin Hi-Flo 6 Twin Hi-Flo 9 Filters 1999 LineДмитрий ЧерныхNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced Hydrocarbons Important QuestionsDocument21 pagesJEE Advanced Hydrocarbons Important QuestionsSai SreyanNo ratings yet
- Transition Metals Lanthanides & ActinidesDocument26 pagesTransition Metals Lanthanides & ActinidesNatish JaglanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 22: Properties of AlcoholsDocument17 pagesLaboratory 22: Properties of AlcoholsElvis BartingeiNo ratings yet
- Reaction Between Manganate (VII) and Ethanedioate - InstructionsDocument3 pagesReaction Between Manganate (VII) and Ethanedioate - InstructionsLeelaSreeNo ratings yet
- Kappa Number Determination Using SpectrosDocument9 pagesKappa Number Determination Using SpectrosAnkit MaharshiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - IA DraftDocument8 pagesChemistry - IA DraftwolfcroissantNo ratings yet
- Selected Form 6 ExperimentsDocument26 pagesSelected Form 6 ExperimentsVanessa ChanNo ratings yet
- 2.3F: Visualizing TLC Plates: Visualization SummaryDocument13 pages2.3F: Visualizing TLC Plates: Visualization SummaryLina Al KhalidiNo ratings yet
- RedoxDocument2 pagesRedoxRay AribatoNo ratings yet
- For JEE Aspirants: Complete Inorganic Chemistry ReactionsDocument56 pagesFor JEE Aspirants: Complete Inorganic Chemistry ReactionsLakshmi AnandNo ratings yet
- Volumetric AnalysisDocument8 pagesVolumetric AnalysisJanumathy.H SVVVNo ratings yet
- Understanding Market Channels and Alternatives For Commercial Catfish Farmers (PDFDrive)Document95 pagesUnderstanding Market Channels and Alternatives For Commercial Catfish Farmers (PDFDrive)AmiibahNo ratings yet
- ASTM D888 - 12 Medición de Oxígeno DisueltoDocument14 pagesASTM D888 - 12 Medición de Oxígeno DisueltoElias100% (1)
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Class 10 Science Chapter 1Document18 pagesNCERT Exemplar Solution Class 10 Science Chapter 1JenifarNishaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practical XIIDocument26 pagesChemistry Practical XIISuyash ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Exp 40 Redox TitrationDocument2 pagesExp 40 Redox TitrationCherylNo ratings yet
- Ibrahim Poultry Traders Training ReportDocument53 pagesIbrahim Poultry Traders Training ReportHassnain KhanNo ratings yet
- D & f-BLOCK ELEMENTS MARKSWISE QUESTIONSDocument9 pagesD & f-BLOCK ELEMENTS MARKSWISE QUESTIONSSachin GuptaNo ratings yet
- Short Notes: Form 5 Chemistry: Rate or ReactionDocument15 pagesShort Notes: Form 5 Chemistry: Rate or ReactionShivaani ParamasivamNo ratings yet
- eALOM Chemistry Practical HandbookDocument148 pageseALOM Chemistry Practical HandbookElizabeth GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: Shahjalal University of Science & Technology, SylhetDocument5 pagesLab Report: Shahjalal University of Science & Technology, SylhetMd Afif AbrarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry VivaDocument16 pagesChemistry VivakritikaNo ratings yet