Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Table of Oral Diseases
Uploaded by
Radwa MohamedOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Table of Oral Diseases
Uploaded by
Radwa MohamedCopyright:
Available Formats
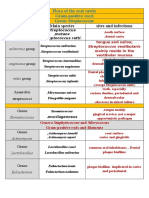
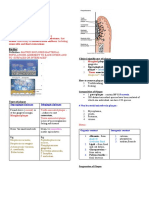
eas Dental Caries Periodontal disease Dentoalveolar abscess Periodontal abscess Ludwig's angina Osteomyelitis
Dis
e
Dental caries is a chronic condition where tissues Infection around apices occur in patients with bilateral infection of rare infection.
infection of enamel or of the periodontium are of the roots of teeth, established periodontal the sublingual and sub- inflammation of the
dentine in which the infected by bacteria following necrosis of the pockets mandibular spaces medullary cavity of
Defination
microbial agents are causing inflammatory pulp. bone, but it usually
members of the normal responses to the tissues remain localized within spreads to involve the
commensal flora. the alveolar bone.or cortical bone and
open into the soft tissue periosteum as well.
thedemineralization of breakdown of the intra- or extra-oral welling, redness and cellulitis of the fascial infected necrotic
enamel or dentine by periodontium resulting swelling or in potentially tenderness of the spaces, bone
Representation
acids produced by in loss of tissue dangerous spread of overlying gingiva brawny oedema with
/shape
plaque microorganisms attachment and infection through fascial elevation of the
as they metabolize destruction of the planes. tongue, airway
dietary carbohydrates alveolar bone. obstruction and very
little pus.
tooth, saliva, 1.Host tissues
supragingival plaque, 2.Microbes
Aetiological
Factors
the diet (especially 3.Immune defense
sucrose intake) and the system
time necessary for
caries development
Streptococcus mutans Porphyromonas streptococci (S. anaerobic Gram- staphylococci, anaerobic Gram-
Microbiology/c
Lactobacilli gingivalis anginosus, S. negative rods, streptococc negative rods
organism
ausative
intermedium and S. alpha haemolytic anaerobic Gram- anaerobic
constellatus) aerobic streptococci negative bacilli streptococci
spirochaetes. anaerobic streptococci,
You might also like
- Perio Micro 2nd YrDocument33 pagesPerio Micro 2nd Yrsoni bistaNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Oral Microbiology: From Healthy Microflora to DiseaseFrom EverandAtlas of Oral Microbiology: From Healthy Microflora to DiseaseXuedong ZhouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- 5-Plaque and CalculusDocument174 pages5-Plaque and CalculusAJPEDO LIFE100% (1)
- Sites and Infections Main Species Group: Flora of The Oral Cavity Gram-Positive Cocci Genus StreptococcusDocument3 pagesSites and Infections Main Species Group: Flora of The Oral Cavity Gram-Positive Cocci Genus StreptococcusEhab qasimNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0165247814001874 Main PDFDocument17 pages1 s2.0 S0165247814001874 Main PDFIonela MadalinaNo ratings yet
- Atypical Ulcer Palate Terciary Syphilis Ooo2019Document6 pagesAtypical Ulcer Palate Terciary Syphilis Ooo2019DIEGO MAURICIO PAZ GARCIANo ratings yet
- L25 Microbiology in EndodonticsDocument57 pagesL25 Microbiology in Endodonticselle70503No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - CariologyDocument4 pagesLesson 2 - Cariologymkpkqc4j4hNo ratings yet
- Gut Recovery Program: A New Approach To Treating Chronic Gastrointestinal InfectionsDocument47 pagesGut Recovery Program: A New Approach To Treating Chronic Gastrointestinal Infectionsautismone100% (3)
- Dental Plaque As A Biofilm: PD Marsh and DJ BradshawDocument7 pagesDental Plaque As A Biofilm: PD Marsh and DJ BradshawTasha FarahNo ratings yet
- Quizlet Hygienist ComputerDocument5 pagesQuizlet Hygienist ComputerCamila FreitasNo ratings yet
- Peridontal Pocket PerioDocument29 pagesPeridontal Pocket PerioFourthMolar.comNo ratings yet
- Lesson 36Document13 pagesLesson 36Abdelraouf ElmanamaNo ratings yet
- اندو مايكروDocument9 pagesاندو مايكروMahmoud HamamrehNo ratings yet
- Recent Concepts in Plaque Formation: Section TwoDocument3 pagesRecent Concepts in Plaque Formation: Section TwoLaura RăschipNo ratings yet
- Nematodes 1Document6 pagesNematodes 1Ericsson CarabbacanNo ratings yet
- Endodontic Microbiology Final PPT PresentationDocument80 pagesEndodontic Microbiology Final PPT PresentationAnji Satsangi100% (2)
- Glossary of Periodontal Terms PDFDocument56 pagesGlossary of Periodontal Terms PDFCarlos Gilberto Guillaumin EsparzaNo ratings yet
- Pathway of PulpDocument120 pagesPathway of PulpTanuj Singh100% (1)
- Normal FloraDocument8 pagesNormal FloraGhina RizwanNo ratings yet
- The History of Caries The History of CariesDocument39 pagesThe History of Caries The History of CariesBob Permana SimanungkalitNo ratings yet
- Infection M2 PathogensDocument8 pagesInfection M2 PathogensArjelyn LungcayNo ratings yet
- Endo. MicrobiologyDocument7 pagesEndo. MicrobiologyzaheerbdsNo ratings yet
- Role of The Oral Microflora in HealthDocument9 pagesRole of The Oral Microflora in HealthIceu EstuNo ratings yet
- Endodontic MicrobiologyDocument9 pagesEndodontic MicrobiologySarah KahilNo ratings yet
- Bacteroides Spp. Porphyromonas Spp. Fusobacterium Spp. Prevotella SPPDocument2 pagesBacteroides Spp. Porphyromonas Spp. Fusobacterium Spp. Prevotella SPPAbcd ReyesNo ratings yet
- ActinomycetesDocument39 pagesActinomyceteshengkitanjung100% (1)
- BACTE (Quizlet)Document4 pagesBACTE (Quizlet)Allyssa AniNo ratings yet
- Fish Gut Microbiota Factors Affecting Fish Gut Microbome and Their Physiological Role in FishDocument29 pagesFish Gut Microbiota Factors Affecting Fish Gut Microbome and Their Physiological Role in FishSathishkumar.G TNFUNo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology: Dr. Tasnim Hamdan Graduated From University of ValenciaDocument160 pagesOral Pathology: Dr. Tasnim Hamdan Graduated From University of ValenciaMariam Abd ElhadiNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases of The SkinDocument5 pagesInfectious Diseases of The SkinKate LagundiNo ratings yet
- Imunologi Jar Perio, Blok 9Document46 pagesImunologi Jar Perio, Blok 9Naviatul UlfaNo ratings yet
- Dental Plaque As A BiofilmDocument34 pagesDental Plaque As A BiofilmAishwarya JoshiNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Odontogenic Infection - Principles of Management - Dental Ebook & Lecture Notes PDF Download (Studynama - Com - India's Biggest Website For BDS Study Material Downloads)Document17 pagesPrevention of Odontogenic Infection - Principles of Management - Dental Ebook & Lecture Notes PDF Download (Studynama - Com - India's Biggest Website For BDS Study Material Downloads)Vinnie SinghNo ratings yet
- 4-Australian Dental Journal - 2008 - Figdor - A Big Role For The Very Small Understanding The Endodontic Microbial FloraDocument14 pages4-Australian Dental Journal - 2008 - Figdor - A Big Role For The Very Small Understanding The Endodontic Microbial Florakyrillos killineyNo ratings yet
- Symbiotic Relations and Microbes Normal MicrofloreDocument32 pagesSymbiotic Relations and Microbes Normal MicrofloreAndulile Francis MwaigwisyaNo ratings yet
- Study GuideDocument7 pagesStudy GuideFurtipopNo ratings yet
- Dental Disease in Pet Rabbits 3 Jaw AbscessesDocument11 pagesDental Disease in Pet Rabbits 3 Jaw AbscessesBrvo CruzNo ratings yet
- A Review On The Human Oral MicrofloraDocument5 pagesA Review On The Human Oral MicrofloraRiya KvNo ratings yet
- Micro MicrobiotaDocument7 pagesMicro MicrobiotaJustinNo ratings yet
- ANCYLOSTOMA DUODENALE Old World HookwormDocument2 pagesANCYLOSTOMA DUODENALE Old World HookwormScarlet AdolfoNo ratings yet
- Etiology of Periodontal DiseaseDocument3 pagesEtiology of Periodontal DiseaseKelly YeowNo ratings yet
- Etiology of Periodontal DiseaseDocument3 pagesEtiology of Periodontal DiseaseKelly YeowNo ratings yet
- Normal Oral Microbial FloraDocument17 pagesNormal Oral Microbial FloraNeeraj Rajendra MehtaNo ratings yet
- Based On Belizario:: Fasciolopsis BuskiDocument6 pagesBased On Belizario:: Fasciolopsis BuskimaqmmNo ratings yet
- Infection 2021Document32 pagesInfection 2021noor.albseerawiNo ratings yet
- Beneficial Bacteria of The Periodontium PDFDocument11 pagesBeneficial Bacteria of The Periodontium PDFSrivani PeriNo ratings yet
- Pulp and Periradicular MicrobiologyDocument8 pagesPulp and Periradicular MicrobiologyدرالجمانNo ratings yet
- Oral Prophylaxis Perio Prelim Notes 2Document4 pagesOral Prophylaxis Perio Prelim Notes 2Bea YmsnNo ratings yet
- Fasciolopsis Buski - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsDocument13 pagesFasciolopsis Buski - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsRadeat GetiyeNo ratings yet
- MRSA - Prevention and ControlDocument105 pagesMRSA - Prevention and ControlShajahan SideequeNo ratings yet
- Dentalplaque Part1 161112155549Document54 pagesDentalplaque Part1 161112155549Alankrita Singh100% (1)
- Dental Plaque As A BiofilmDocument103 pagesDental Plaque As A BiofilmShivangi sharmaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology of Root Canal Infections: Marjut Sakko, Leo Tjäderhane, Riina Rautemaa-RichardsonDocument6 pagesMicrobiology of Root Canal Infections: Marjut Sakko, Leo Tjäderhane, Riina Rautemaa-Richardsonmarisolporto87No ratings yet
- Bacte RIA Virus Proto ZOA Fungu S: MicroorganismsDocument1 pageBacte RIA Virus Proto ZOA Fungu S: Microorganismssathiah2802No ratings yet
- Dental Plaque: By:-Raina J. P. Khanam Post Graduate 2 Year Dept. of Periodontics and ImplantologyDocument69 pagesDental Plaque: By:-Raina J. P. Khanam Post Graduate 2 Year Dept. of Periodontics and ImplantologyAtul KoundelNo ratings yet
- Medical WritingDocument4 pagesMedical WritingRAO NABEEL AKRAMNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiofilmsDocument41 pagesIntroduction To BiofilmsOmeyya TanveerNo ratings yet
- Dental Plaque As A Biofilm - Dr. PriyaDocument103 pagesDental Plaque As A Biofilm - Dr. PriyaDr. Priya PatelNo ratings yet
- DBM MangalaDocument49 pagesDBM MangalaRadwa MohamedNo ratings yet
- 7 HMP Shunt Pathway RO PDF v1Document9 pages7 HMP Shunt Pathway RO PDF v1Radwa MohamedNo ratings yet
- AmelogenisisDocument3 pagesAmelogenisisRadwa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Glia - WikipediaDocument8 pagesGlia - WikipediaRadwa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous System - WikipediaDocument3 pagesPeripheral Nervous System - WikipediaRadwa MohamedNo ratings yet
- 2 D A of Carbohydrate PDFDocument16 pages2 D A of Carbohydrate PDFRadwa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates CehmistryDocument18 pagesCarbohydrates CehmistryRadwa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Microbes and Oral DiseasesDocument40 pagesMicrobes and Oral DiseasesRadwa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Dentin - WikipediaDocument5 pagesDentin - WikipediaRadwa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Antonio Nanci - Ten Cate's Oral Histology - Development, Structure, and Function (2017, Elsevier) - Part6 PDFDocument2 pagesAntonio Nanci - Ten Cate's Oral Histology - Development, Structure, and Function (2017, Elsevier) - Part6 PDFRadwa Mohamed100% (1)
- Antonio Nanci - Ten Cate's Oral Histology - Development, Structure, and Function (2017, Elsevier) - Part3 PDFDocument3 pagesAntonio Nanci - Ten Cate's Oral Histology - Development, Structure, and Function (2017, Elsevier) - Part3 PDFRadwa Mohamed100% (1)
- Xiaomi Technology Co.: Growth Via Online Channels: Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesXiaomi Technology Co.: Growth Via Online Channels: Page 1 of 2Radwa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Contributors: Florin Amzica PHDDocument3 pagesContributors: Florin Amzica PHDRadwa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Developing Originality Update 051112 PDFDocument2 pagesDeveloping Originality Update 051112 PDFRadwa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Antonio Nanci - Ten Cate's Oral Histology - Development, Structure, and Function (2017, Elsevier) - Part2 PDFDocument7 pagesAntonio Nanci - Ten Cate's Oral Histology - Development, Structure, and Function (2017, Elsevier) - Part2 PDFRadwa Mohamed0% (1)
- Go-Jek in IndonesiaDocument3 pagesGo-Jek in IndonesiaRadwa MohamedNo ratings yet
- How To Write Good Journal PublicationDocument49 pagesHow To Write Good Journal PublicationRadwa Mohamed100% (1)
- Walmart Case StudyDocument4 pagesWalmart Case StudyRadwa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument46 pagesLiterature ReviewRadwa Mohamed80% (5)
- I4-2017!6!307 On The Way From Industry 4.0 To Industry 5.0 - From Digital Manufacturing To Digital SocietyDocument5 pagesI4-2017!6!307 On The Way From Industry 4.0 To Industry 5.0 - From Digital Manufacturing To Digital SocietyRadwa MohamedNo ratings yet
- NOKIA The Rise and FallDocument3 pagesNOKIA The Rise and FallRadwa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Content Learning Resources: TLE6HE - 0b - 3 TLE6HE - 0b - 4Document1 pageContent Learning Resources: TLE6HE - 0b - 3 TLE6HE - 0b - 4Hannah Nerika Sasil Abucayan - AbolocNo ratings yet
- Module-5-Rising Towards The Reality of My Dreams-Karen SantiagoDocument45 pagesModule-5-Rising Towards The Reality of My Dreams-Karen SantiagoKaren SantiagoNo ratings yet
- IU Campus Bus Route OverviewsDocument7 pagesIU Campus Bus Route OverviewsIUBCampusBusNo ratings yet
- Admission For F.Y.B.Com (2019-20) Outsiders (1st Merit List) & Sindhi Minority Students PDFDocument14 pagesAdmission For F.Y.B.Com (2019-20) Outsiders (1st Merit List) & Sindhi Minority Students PDFAniket TiwariNo ratings yet
- Inclusive Talent Development As A Key Talent ManagementDocument23 pagesInclusive Talent Development As A Key Talent Managementdevi susanto sibagariangNo ratings yet
- 4as LESSON PLAN - TEMPLATEDocument6 pages4as LESSON PLAN - TEMPLATEAljohn LumapasNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study Lays and KurkureDocument6 pagesComparative Study Lays and KurkureANKIT SHARMANo ratings yet
- EEL 6892-Virtual Computers FigueiredoDocument5 pagesEEL 6892-Virtual Computers FigueiredoLuciNo ratings yet
- Post ObservationDocument2 pagesPost Observationapi-225785152No ratings yet
- Intelligent Fault Detection Scheme For Microgrids With Wavelet-Based Deep Neural NetworksDocument10 pagesIntelligent Fault Detection Scheme For Microgrids With Wavelet-Based Deep Neural NetworksJaimeNo ratings yet
- II SemDocument11 pagesII SemmuniNo ratings yet
- Vcs Sapwebas InstallDocument98 pagesVcs Sapwebas Installjaleelpeace9157No ratings yet
- The Power of Positive AttitudeDocument3 pagesThe Power of Positive AttitudeSiyaa Singh100% (1)
- Philosophy CVDocument3 pagesPhilosophy CVapi-547566221No ratings yet
- Raisin in The SunDocument11 pagesRaisin in The SunMery Joy Cabeza ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Caries Patterns in Primary Dentition in 3-To 5-Year-Old Children. Medellín, ColombiaDocument10 pagesCaries Patterns in Primary Dentition in 3-To 5-Year-Old Children. Medellín, ColombiaLuis Gonzaga Lopez BNo ratings yet
- USA Student Visa Sample Questions and Interview TipsDocument3 pagesUSA Student Visa Sample Questions and Interview TipsTitu KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Background and Its InformationDocument9 pagesBackground and Its InformationJm Jeffrey MarceloNo ratings yet
- Integration of Task-Based Approaches in A TESOL CourseDocument13 pagesIntegration of Task-Based Approaches in A TESOL CourseAlexDomingoNo ratings yet
- GiangtranDocument1 pageGiangtranapi-711059807No ratings yet
- Cycle 2-Annotated Bibliography 1Document4 pagesCycle 2-Annotated Bibliography 1api-343815626100% (1)
- Code Simplicity Open Source DesignDocument27 pagesCode Simplicity Open Source DesignVaibhav MuleNo ratings yet
- Sparsely Constrained NNDocument6 pagesSparsely Constrained NNAman JalanNo ratings yet
- Theory and Theorists: Michael G. MooreDocument28 pagesTheory and Theorists: Michael G. MooreMohamad Siri Muslimin100% (1)
- Algetb 22Document4 pagesAlgetb 22sonaraghavanNo ratings yet
- My Diagram in A DrumDocument2 pagesMy Diagram in A DrumJeah mae TauleNo ratings yet
- Programming Skills For Data Science: Start Writing Code To Wrangle, Analyze, and Visualize Data With R (Addison-Wesley Data & Analytics Series) - Michael FreemanDocument5 pagesProgramming Skills For Data Science: Start Writing Code To Wrangle, Analyze, and Visualize Data With R (Addison-Wesley Data & Analytics Series) - Michael FreemanryzyloweNo ratings yet
- First Grade Science Seasons LessonDocument10 pagesFirst Grade Science Seasons Lessonapi-273149494100% (2)
- LC 31Document3 pagesLC 31JT SaguinNo ratings yet
- Letter of RecommendatioProfessionalDocument2 pagesLetter of RecommendatioProfessionalUzair Maqbool KhanNo ratings yet