Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basis&Steps LinearRegressionAnalysis
Uploaded by
KevinVittoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basis&Steps LinearRegressionAnalysis
Uploaded by
KevinVittoCopyright:
Available Formats
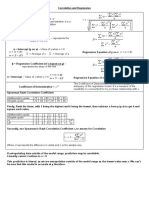
ASSOCIATIVE/CAUSAL/EXPLANATORY MODELS
Linear Regression Analysis
Slope-Intercept Form of a Linear Equation: 𝒚 = 𝒂 + 𝒃𝒙
Where:
𝒚 = dependent variable; demand or sales
𝒙 = independent variable; any variable that affects demand or sales;
e.g. time, price, population, household income, advertising exp.
𝒂 = y-intercept of the line; value of 𝒚 when 𝒙 = 0.
∆𝒚
𝒃 = slope of the line =
∆𝒙
Step 1: Gather data
x y
x1 y1
x2 y2
x3 y3
: :
xn yn
Step 2: Confirm that there’s indeed a strong linear relationship between 𝒙 and𝒚.
Calculate the correlation coefficient, 𝒓.
n xy x y
r ; if 𝒓 ≥ 𝟎. 𝟕𝟎, there’s strong linear
n x x n y y
2 2 2 2
relationship between 𝒙 and𝒚 and
Linear Regression Analysis may be
Step 3: Calculate the slope, 𝒃: used to forecast 𝒚 given 𝒙.
n xy x y
b
n x 2 x
2
Step 4: Calculate the y-intercept, 𝒂:
a
y b x
n
Step 5: Derive the Linear Regression Equation Step 6. Forecast 𝒚 given 𝒙.
𝒚 = 𝒂 + 𝒃𝒙
You might also like
- Statistics Formulas CheatsheetDocument3 pagesStatistics Formulas CheatsheetCarmen Bl100% (1)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Regression AnalysisDocument12 pagesRegression Analysispravesh1987No ratings yet
- Regression Analysis MCQDocument15 pagesRegression Analysis MCQsakshi tyagiNo ratings yet
- Regression AnalysisDocument43 pagesRegression AnalysisRàmèsh RôdálbáñdîNo ratings yet
- Booking: ConfirmationDocument1 pageBooking: ConfirmationKevinVittoNo ratings yet
- BasisSteps LinearRegressionAnalysisDocument1 pageBasisSteps LinearRegressionAnalysisEzrah Kiel VillezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11 Simple Regression PDFDocument6 pagesLesson 11 Simple Regression PDFMarrick MbuiNo ratings yet
- Regression AnalysisDocument28 pagesRegression AnalysisSneha SofatNo ratings yet
- Regression SummaryDocument2 pagesRegression SummarySiobhan GriffinNo ratings yet
- Regression Analysis: Basic StatisticsDocument26 pagesRegression Analysis: Basic StatisticsDr. Arunava MookherjeeNo ratings yet
- Case Study Chapter 9Document8 pagesCase Study Chapter 9Alex HenryNo ratings yet
- Regression - Definition, Formula, Derivation, Application - EmbibeDocument10 pagesRegression - Definition, Formula, Derivation, Application - EmbibeSrishti ShivangNo ratings yet
- IV. (B) RegressionDocument6 pagesIV. (B) RegressionShamima AkterNo ratings yet
- Bat-604 QTM Unit 2 FinalDocument22 pagesBat-604 QTM Unit 2 FinalAditi MittalNo ratings yet
- Regression AnalysisDocument21 pagesRegression Analysismanisha61981No ratings yet
- Unit 6Document8 pagesUnit 6Mahesh GandikotaNo ratings yet
- CH 17 Correlation Vs RegressionDocument17 pagesCH 17 Correlation Vs RegressionDottie KamelliaNo ratings yet
- Topic:-Regression: Name: - Teotia Nidhi Class: - M.SC BiotechnologyDocument11 pagesTopic:-Regression: Name: - Teotia Nidhi Class: - M.SC Biotechnologynidhi teotiaNo ratings yet
- Simple RegressionDocument8 pagesSimple RegressionDlo PereraNo ratings yet
- Statistical Analysis: Linear RegressionDocument36 pagesStatistical Analysis: Linear RegressionDafter KhemboNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document9 pagesUnit 6satish kumarNo ratings yet
- IV. (A) CorrelationDocument3 pagesIV. (A) CorrelationShamima AkterNo ratings yet
- Regression AnalysisDocument65 pagesRegression AnalysisLiliNo ratings yet
- 2.linear RegressionDocument49 pages2.linear Regressionkoleti vikasNo ratings yet
- Regression Analysis MCQDocument15 pagesRegression Analysis MCQsakshi tyagiNo ratings yet
- J. K.Shah Classes Regression AnalysisDocument15 pagesJ. K.Shah Classes Regression AnalysisHassaan KhanNo ratings yet
- Topic:-Regression: Name: - Teotia Nidhi Class: - M.SC BiotechnologyDocument10 pagesTopic:-Regression: Name: - Teotia Nidhi Class: - M.SC Biotechnologynidhi teotiaNo ratings yet
- Production Planning and ControlDocument44 pagesProduction Planning and ControlShanu ShaNo ratings yet
- 169 Ch13 Regression AnalysisDocument15 pages169 Ch13 Regression Analysisshaik sonuNo ratings yet
- J. K.Shah Classes Regression AnalysisDocument21 pagesJ. K.Shah Classes Regression AnalysisLloyd SebastianNo ratings yet
- Correlation and RegressionDocument48 pagesCorrelation and RegressionGabrielle Anne San GabrielNo ratings yet
- Blue Data Statistics Facebook Cover - 20230911 - 132020 - 0000Document9 pagesBlue Data Statistics Facebook Cover - 20230911 - 132020 - 0000SalwahNo ratings yet
- 07 - Correlation and Regression Analysis-1Document13 pages07 - Correlation and Regression Analysis-1Harshit SodhiNo ratings yet
- 17 Regression AnalysisDocument10 pages17 Regression AnalysisDeepakNo ratings yet
- Simple Regression Model: Conference PaperDocument10 pagesSimple Regression Model: Conference PaperVigneshwari MahamuniNo ratings yet
- Extra Notes On RegressionDocument4 pagesExtra Notes On RegressionLuciano EbangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 CORRELATION AND REGRESSIONDocument28 pagesChapter 5 CORRELATION AND REGRESSIONWerty Gigz DurendezNo ratings yet
- CorrelationDocument18 pagesCorrelationanandNo ratings yet
- Simple Linear Regression and CorrelationDocument31 pagesSimple Linear Regression and CorrelationMohammed KashoobNo ratings yet
- Simple and Multiple Regression (LEC-6)Document56 pagesSimple and Multiple Regression (LEC-6)sh TanvirNo ratings yet
- Lesson 13Document21 pagesLesson 13JACINDA MYRTLE MALINAO ALCIDNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - 6 7-8 Regression Bias VarianceDocument51 pagesLecture 5 - 6 7-8 Regression Bias VarianceSaikat DasNo ratings yet
- Modified CorrelationDocument53 pagesModified CorrelationHazel HeridaNo ratings yet
- Correlation and Regression Bi-Variate Data: Let (XDocument11 pagesCorrelation and Regression Bi-Variate Data: Let (XBharat Kul RatanNo ratings yet
- Statistics 3 NotesDocument90 pagesStatistics 3 Notesnajam u saqibNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Simple Correlation and Regression Analysis1Document16 pagesUnit 3 Simple Correlation and Regression Analysis1Rhea MirchandaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Seventeen: Correlation & Regression AnalysisDocument17 pagesChapter - Seventeen: Correlation & Regression AnalysisRahul AGJNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 - Regression AnalysisDocument51 pagesTopic 8 - Regression AnalysisBass Lin3No ratings yet
- Correlation and Simple RegressionDocument5 pagesCorrelation and Simple RegressionMarjorie HouNo ratings yet
- Looking at Data: Relationships: Least-Squares RegressionDocument23 pagesLooking at Data: Relationships: Least-Squares RegressioncrutiliNo ratings yet
- Corr and RegressDocument61 pagesCorr and Regresskamendra chauhanNo ratings yet
- Regression (Autosaved) (Autosaved)Document80 pagesRegression (Autosaved) (Autosaved)DishaNo ratings yet
- X X X X y 0 y y y y X 0: InterceptsDocument6 pagesX X X X y 0 y y y y X 0: InterceptsGan J XinNo ratings yet
- Corr and RegDocument48 pagesCorr and Regkailash_123No ratings yet
- 12 - Correlation and RegressionDocument18 pages12 - Correlation and RegressionLony PatalNo ratings yet
- Regression: by Vijeta Gupta Amity UniversityDocument15 pagesRegression: by Vijeta Gupta Amity UniversityAnkita GuptaNo ratings yet
- RegressionDocument6 pagesRegressionMansi ChughNo ratings yet
- Tristanm Sethn Spencerb Alg-2 pr6 pw5Document6 pagesTristanm Sethn Spencerb Alg-2 pr6 pw5api-357616428No ratings yet
- Correlation and Regression-1Document32 pagesCorrelation and Regression-1KELVIN ADDONo ratings yet
- Rubric For Evaluating Reflection Papers & The Culminating ProductDocument38 pagesRubric For Evaluating Reflection Papers & The Culminating ProductKevinVittoNo ratings yet
- Nurturing and Developing Spirituality Is Essential Especially in This World That Increasingly Leaning Toward Materialism and SecularismDocument2 pagesNurturing and Developing Spirituality Is Essential Especially in This World That Increasingly Leaning Toward Materialism and SecularismKevinVittoNo ratings yet
- CFEDocument4 pagesCFEKevinVittoNo ratings yet
- Interview With EntrepreneursDocument5 pagesInterview With EntrepreneursKevinVittoNo ratings yet
- Literary Critic Mystery Macabre Romanticism Detective Fiction Science FictionDocument1 pageLiterary Critic Mystery Macabre Romanticism Detective Fiction Science FictionKevinVittoNo ratings yet