0% found this document useful (0 votes)
182 views3 pagesCircuit Analysis: Req and Current I
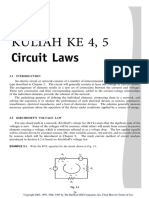
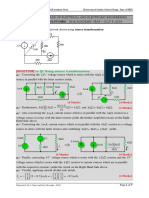
(1) The resistances are combined through series and parallel transformations to find the equivalent resistance Req between terminals a and b, which is calculated to be 2.43R.
(2) Using Req, the current I is determined to be 0.41V0/R.
(3) Nodal analysis is applied to determine the node voltages, from which the same current I=0.41V0/R is obtained, verifying the solution.
Uploaded by
cucabeludoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
182 views3 pagesCircuit Analysis: Req and Current I
(1) The resistances are combined through series and parallel transformations to find the equivalent resistance Req between terminals a and b, which is calculated to be 2.43R.
(2) Using Req, the current I is determined to be 0.41V0/R.
(3) Nodal analysis is applied to determine the node voltages, from which the same current I=0.41V0/R is obtained, verifying the solution.
Uploaded by
cucabeludoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd