Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Review of Related Literature Chapter 2
Uploaded by
Vanessa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views6 pagesHow to prepare RRL
Original Title
RRL.pdfx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHow to prepare RRL
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views6 pagesReview of Related Literature Chapter 2
Uploaded by
VanessaHow to prepare RRL
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Inquiries, Investigations
& Immersion Review of
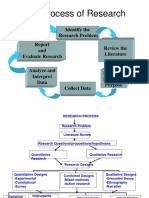
RESEARCH PROJECT
Related Literature
Chapter 2
Review of Related Literature Review of Related Literature
• introductory section • is a systematic process that requires
• involves the systematic identification, careful and perceptive reading and
location and analysis of documents attention to detail.
containing information related to the • The researcher attempts to gather
research problem. information relevant to the research
problem at hand.
Selecting, Citing and Synthesizing Functions of RRL
Literature
• serves as to tie together what others • convinces your reader that your research will
have done and what you plan to do. make a significant and substantial
contribution to the literature
• The review is supposed to lead
somewhere---your own research and its • demostrates your knowledge of the research
problem
justification
• demonstrates your understanding of the
theoretical and reserch issues related to your
research question
Functions of RRL The process centers on three questions:
• ensures that you are not "reinventing the wheel"
• gives credits to those who have laid the • Where is the information found?
groundwork for your research
• What should be done with information
• indicates your ability to integrate and synthesize
the existing literature after it has been found?
• provides new theoretical insights or develops new • What is made of the information?
model as the conceptual framework for your
research.
• shows your ability to critically evaluate relevant
literature information
Where is the information found? What should be done with
information after it has been found?
• Specific sources • information is assembled and
•both electronic and hard copy summarized
• Give examples. • in other words, SYNTHESIZED.
What is made of the information? How to organize your RRL?
• a critical analysis •make use of subheadings
•theoretical models
•measuring instruments
•cross-cultural and gender
differences
What to avoid? Most students' literature reviews
suffer from the following problems:
• Avoid repetitive sentences such as • Being repetitive and verbose
"According to Bueno(2013)..." • citing irrelevant or trivial references
"According to Bueno(2014)..." • depending too much on secondary sources
or • failing to cite influential papers
"Matriano (2015) found that..." • failing to keep up with recent developments
"Almazan (2011) found that..." • lacking focus, unity and coherence
• lacking organization and structure
Selective Review of Literature Selective Review of Literature
• The needed review for Chapter 1 is a •Main purpose:
selective, not comprehensive, review of the • to sharpen your preliminary considerations
literature regarding your topic of study, method, and
data source
•What to review:
• other studies that focused on similar topics
or used a similar data collection method
• studies that have used similar or perhaps
even the same sources
Comprehensive Review How to Review
• For Chapter 2: Comprehensive review • The main topic of the study, including the
issues/questions being addressed by the study;
• It aims to bring together what is known on a
• The data collection method, including the
particular topic, possibly highlighting
extent of the data collection (e.g., the
controversial or disparate lines of thinking or
number of people interviewed in an interview
even the progress over time in cumulating
knowledge about a subject. study, or the length and breadth of fieldwork
in a participant-observer study);
How to Review
• The study’s main findings, including the
specific data used to represent the findings;
• The study’s main conclusions; and APA Citation
• Your own comments about the strengths
and weaknesses of the study—and the full
bibliographic details for citing the study.
Activity
• Make a citation for the following reference
materials
• epubs.scu.edu.au/theses/351/
• Journal of Comparative Neurology
In-text Citation
You might also like
- Review of Related Literature Review: Chapter 2 - FINALSDocument4 pagesReview of Related Literature Review: Chapter 2 - FINALSBiya MacunteNo ratings yet
- Writing Research ArticleDocument2 pagesWriting Research ArticleAiman ZafarNo ratings yet
- 3 Chapter The Research ProcessDocument6 pages3 Chapter The Research ProcessHannah Wynzelle AbanNo ratings yet
- Lec 4-Literature ReviewDocument15 pagesLec 4-Literature ReviewIsha KhalidNo ratings yet
- Conducting and Writing: Literature ReviewDocument36 pagesConducting and Writing: Literature Reviewleserdrac333No ratings yet
- Literature Review 2023Document13 pagesLiterature Review 2023Dynamic ClothesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Establishing The Theoretical and Empirical Basis of The ResearchDocument16 pagesLesson 3 - Establishing The Theoretical and Empirical Basis of The ResearchMarkNo ratings yet
- The Literature Review: A Critical Component of ResearchDocument52 pagesThe Literature Review: A Critical Component of ResearchMimeroseNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: Review of Literature in ResearchDocument41 pagesChapter Three: Review of Literature in ResearchAliyan AmanNo ratings yet
- Good Literature Review Poor Literature ReviewDocument4 pagesGood Literature Review Poor Literature ReviewJean BelciñaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review - PurposeDocument7 pagesLiterature Review - PurposemanjackNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Literature ReviewDocument26 pagesChapter 3 Literature Reviewabraha gebruNo ratings yet
- Carrying Out A Literature ReviewDocument41 pagesCarrying Out A Literature ReviewPashaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Review of LiteratureDocument28 pagesChapter Two Review of LiteratureHenok FikaduNo ratings yet
- Research Course OutlineDocument5 pagesResearch Course OutlineCaroline AyuyaNo ratings yet
- Research Process in Flow ChartDocument40 pagesResearch Process in Flow ChartEmmanuel EliyaNo ratings yet
- PR 2Document32 pagesPR 2hariethgray216No ratings yet
- PADM 312 - SU 3Document11 pagesPADM 312 - SU 3honwanaamanda1No ratings yet
- Literature Review Part-BDocument22 pagesLiterature Review Part-BMuhammad Faisal AfzalNo ratings yet
- W5 - Related StudiesDocument68 pagesW5 - Related StudiesAndreve john RebuciasNo ratings yet
- AUJAYEB Literature ReviewDocument27 pagesAUJAYEB Literature ReviewNeha MunneeNo ratings yet
- Ch03 Literature ReviewDocument22 pagesCh03 Literature ReviewAlice LowNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document31 pagesChapter 3Abreham AwokeNo ratings yet
- Writing Literature ReviewDocument6 pagesWriting Literature ReviewNikki Alquino100% (1)
- Phases of Nursing Research ReviewerDocument6 pagesPhases of Nursing Research ReviewerElizabeth IdananNo ratings yet
- PR G2 RRLDocument14 pagesPR G2 RRLDuruthe MabanagNo ratings yet
- Reviewing Literature and Research DesignDocument15 pagesReviewing Literature and Research DesignYaha RewNo ratings yet
- Research - Literature ReviewDocument42 pagesResearch - Literature ReviewHamiduNo ratings yet
- RM Unit Ii - RM (Ajs)Document30 pagesRM Unit Ii - RM (Ajs)mdkatak1002No ratings yet
- Literature Review Importance and StepsDocument8 pagesLiterature Review Importance and StepsDavis MulengaNo ratings yet
- RRL Chapter 2Document4 pagesRRL Chapter 2Adiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- BRM Part IiDocument349 pagesBRM Part Iimolalign tekalignNo ratings yet
- RECAPPS Checklist For Research PaperDocument1 pageRECAPPS Checklist For Research Paperzuo shanshanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - III Literature SurveyDocument28 pagesCHAPTER - III Literature SurveyMeseret YirgaNo ratings yet
- DMS 411: Business Research Methods Literature ReviewDocument31 pagesDMS 411: Business Research Methods Literature ReviewWycliff OtengNo ratings yet
- NRes1 Course Unit 4Document5 pagesNRes1 Course Unit 4Giselle EstoquiaNo ratings yet
- Research Methods OverviewDocument28 pagesResearch Methods OverviewJewel DanNo ratings yet
- The Process of ResearchDocument15 pagesThe Process of ResearchJacob VisuwaNo ratings yet
- The Critical Literature ReviewDocument17 pagesThe Critical Literature ReviewAkram ALhamadNo ratings yet
- Literature Review: Politeknik Negeri Semarang 2018Document58 pagesLiterature Review: Politeknik Negeri Semarang 2018Ardi JunNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument19 pagesLiterature Reviewnono85No ratings yet
- Module 2Document41 pagesModule 2AnithaNo ratings yet
- Conducting Research (1) : Dr. Rasha SalamaDocument39 pagesConducting Research (1) : Dr. Rasha SalamaIVLNo ratings yet
- Designing Research Band Literature SearchDocument57 pagesDesigning Research Band Literature SearchNatalie FernandezNo ratings yet
- Basic Steps of ResearchDocument28 pagesBasic Steps of ResearchsamikshaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Content 1Document15 pagesUnit 2 Content 1[5013] Dorathi ChristineNo ratings yet
- HRM First Assignment and Guide On Article ReviewDocument19 pagesHRM First Assignment and Guide On Article ReviewNaod FekedeNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Ms. Jenny Sobrevega, IS FacultyDocument15 pagesPrepared By: Ms. Jenny Sobrevega, IS FacultyEryn LacsaNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument51 pagesLiterature Reviewየማርያም ልጅ ነኝNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Business and Management ResearchDocument54 pagesThe Nature of Business and Management ResearchSan Thida SweNo ratings yet
- ABR - Qualitative Analysis of Data InsightsDocument32 pagesABR - Qualitative Analysis of Data InsightsSaroosh ZahidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document24 pagesChapter 2Harsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Identifying Problems & Research Gap: Week 2 Metodologi RisetDocument51 pagesIdentifying Problems & Research Gap: Week 2 Metodologi RisetshldhyNo ratings yet
- 1 Research Preparation - 124018Document23 pages1 Research Preparation - 124018Mikhoy RiveralNo ratings yet
- Overview of Related Literature 1Document7 pagesOverview of Related Literature 1Kc BaniagaNo ratings yet
- Conducting Research1Document40 pagesConducting Research1IKMDITA EKA PRATIWINo ratings yet
- Library Workshop - Literature Review - NTU URECA - AY2019-20Document30 pagesLibrary Workshop - Literature Review - NTU URECA - AY2019-20steven wangNo ratings yet
- Nursing Research Chapter 2Document3 pagesNursing Research Chapter 2mac_jerichoNo ratings yet
- PPT Chapter 3 LiteratureDocument17 pagesPPT Chapter 3 LiteratureJaatooNo ratings yet
- Capstone Lec 1Document24 pagesCapstone Lec 1VanessaNo ratings yet
- Capstone Lec 3Document16 pagesCapstone Lec 3VanessaNo ratings yet
- Capstone Lec 1Document24 pagesCapstone Lec 1VanessaNo ratings yet
- APA 6 BGS Qualitative Research Paper August 20142Document46 pagesAPA 6 BGS Qualitative Research Paper August 20142Jacq Calaycay100% (2)
- Activity Sheet No 1 IIIDocument1 pageActivity Sheet No 1 IIIVanessaNo ratings yet
- Frog Activity SheetsDocument1 pageFrog Activity SheetsVanessaNo ratings yet
- Bugeted Lesson Physics 2Document3 pagesBugeted Lesson Physics 2VanessaNo ratings yet
- Capability Brown - Landscape PDFDocument94 pagesCapability Brown - Landscape PDFDushyantNo ratings yet
- SBSC Self Study Report Final PDFDocument451 pagesSBSC Self Study Report Final PDFArjun Arjun0% (1)
- Tok Presentation Script IdeaDocument5 pagesTok Presentation Script IdeaAashna pandyaNo ratings yet
- Visual Text Analysis in Digital Humanities: ForumDocument25 pagesVisual Text Analysis in Digital Humanities: ForumGizliustaNo ratings yet
- The Kohler Effect: A Motivational Strategy For Strength and ConditioningDocument6 pagesThe Kohler Effect: A Motivational Strategy For Strength and ConditioningPrecision Wellness Precision WellnessNo ratings yet
- Kelling Et Al. (1974) - The Kansas City Preventive Patrol ExperimentDocument56 pagesKelling Et Al. (1974) - The Kansas City Preventive Patrol ExperimentPoliceFoundationNo ratings yet
- Maritime Student Resume - John Michael O. GarciaDocument2 pagesMaritime Student Resume - John Michael O. GarciaMichael AngeloNo ratings yet
- Shining Student's Engagement Skills Via Mobile LearningDocument6 pagesShining Student's Engagement Skills Via Mobile LearningguanyitorNo ratings yet
- Customer Satisfaction With Career Guidance: A Literature ReviewDocument17 pagesCustomer Satisfaction With Career Guidance: A Literature ReviewRohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Mobile Ethics and Awareness Among UsersDocument18 pagesMobile Ethics and Awareness Among UsersBhaskar BhushanNo ratings yet
- ENG 151-4 Fall 2021 SyllabusDocument7 pagesENG 151-4 Fall 2021 SyllabusPj TuavaoNo ratings yet
- H - LRTT2Document32 pagesH - LRTT2ROGEN KATE AZARCONNo ratings yet
- Research 8 Quarter 1 Module 4Document17 pagesResearch 8 Quarter 1 Module 4marvielseNo ratings yet
- # 2 CnoDocument16 pages# 2 Cnoleizt_13No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Related Literature and StudiesDocument27 pagesChapter 2 Related Literature and StudiesJohn Bryll Puebla AgbayNo ratings yet
- NP 5223 SLR1 PDFDocument246 pagesNP 5223 SLR1 PDFJuan Emanuel VenturelliNo ratings yet
- Puting and Applications Advanced Techniques For Clinical DentistryDocument407 pagesPuting and Applications Advanced Techniques For Clinical DentistryKyaw Swe Shin MyintNo ratings yet
- High-Impact Succession Management: Executive SummaryDocument18 pagesHigh-Impact Succession Management: Executive SummaryLorena Garcia100% (1)
- Storyboard Kyle Goss Sociology2Document6 pagesStoryboard Kyle Goss Sociology2api-471003412No ratings yet
- BSC (Hons) BT (PS) 19 PDFDocument16 pagesBSC (Hons) BT (PS) 19 PDFRaja Vamsi MavuduruNo ratings yet
- A Review of Major Causes of Delay in Road Construction Projects-Ijaerdv05i0944008 PDFDocument5 pagesA Review of Major Causes of Delay in Road Construction Projects-Ijaerdv05i0944008 PDFkelil Gena komichaNo ratings yet
- Research Problem and ObjectivesDocument10 pagesResearch Problem and ObjectivesMarkNo ratings yet
- Coping With Sexual HarassmentDocument17 pagesCoping With Sexual HarassmentEhtisham HassanNo ratings yet
- SOP CaltechDocument2 pagesSOP CaltechAndy Ho40% (5)
- Anti-Racism in STEM FinalDocument27 pagesAnti-Racism in STEM FinalJuan PobleteNo ratings yet
- Customer Experiences in The Age of Artificial IntelligenceDocument14 pagesCustomer Experiences in The Age of Artificial Intelligencedaksh gupta100% (1)
- Effect of Cash Management On The Financial Performance of Cooperative Banks in Rwanda: A Case of Zigma CSSDocument11 pagesEffect of Cash Management On The Financial Performance of Cooperative Banks in Rwanda: A Case of Zigma CSSjournalNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Big Data Ecosystem A Systematic Literature ReviewDocument20 pagesManufacturing Big Data Ecosystem A Systematic Literature ReviewLeonardo SanchezNo ratings yet
- CuasiexperimentDocument33 pagesCuasiexperimentBrenda RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Industry 4.0Document20 pagesIndustry 4.0SHASHANK CHOUDHARY 22No ratings yet