Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ILT Notes
ILT Notes
Uploaded by
AlexandraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ILT Notes
ILT Notes
Uploaded by
AlexandraCopyright:
Available Formats
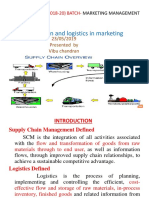
Logistics
- The movement of product from point of origin (Factory / Manufacturer) to the point of
consumption.
- i.e: Car – how the car move from the manufacturer to consumer.
Logistics Management
- Delivering to the customer the desired level of services and quality at the lowest affordable
costs.
- Design & administration of system to control the flow of materials throughout a corporation.
- How you handle the logistics activities. / Activity involved in / happen in between logistics.
Logistics activities
1. Transportation 4. Inventory management 7. Customer services
2. Warehousing 5. Information management 8. Customer order processing
3. Packaging 6. Material handling 9. Location analysis
Types of logistics
1. Reverse logistics / Product recall.
- A process of moving goods from their place of use, back to the place of manufacturer for
reprocessing, repair, recycling @ disposal.
- 2 situations:
- direct from customers to manufacturer
- from customers to retailers/suppliers back to manufacturer
2. Inbound logistics
- The movement of raw materials and parts from suppliers to manufacturer.
- Refers to the transport, storage, and delivery of goods coming into manufacturer.
- i.e: Car. raw material – rubber
- Supplier send the rubber to vehicle manufacturer for producing tyre.
3. Outbound logistics
- The movement of finished goods from manufacturer to customers / point of consumption.
- The process of storing, transporting and distributing goods to customers.
- 2 situations:
- Direct from manufacturer to customers.
- From manufacturer to retailer/supplier then to customers.
- i.e: IKEA delivery the furniture to customers.
4. Third party logistics (3PL)
- A third party logistics providers provides outsourcing logistics services of transportation only
for companies.
- Outside agency helps manufacturer to do movement of products for delivering to customers.
- i.e: UPS, GDex, DHL, Fedex.
5. Fourth party logistics (4PL)
- Refers to complete outsourcing of manufacturing and logistics functions including selection of
3PL.
- 4PL providers also manufacture the product, decide the 3PL, packaging, warehousing functions
and so on.
Importance of logistics
1. Products may reach globally
- all other countries can use a pro with help of DHL, GDex, and UPS.
2. Increase profits
3. Cost savings
- the more units of product u send, the more cost u can save.
4. Increase customer satisfaction
- manufacturer get a well shipper that can provide fast, accurate & quality services,
- customer demand for better services – product delivered them asap (timely manner).
5. Warehouse management
- avoid storing the goods for too long
- maximize storage capacity of warehouse
- increase the efficiency cash turnover
- inventory management / reduction.
Objectives of logistics
1. Inventory reductions
- reduce the stock as much as possible.
- avoid to store the product too long
2. Minimum product damages
- product damages increase the logistics costs.
- reasons for product damages :
- improper logistical packaging
- poor handling
3. Ensure maximum customer satisfaction
- get good review & feedback from customer
4. Lower logistics costs
5. Reliable & consistent delivery performance
- a good logistic should provide better, quality, timely, and accurate service to customer
- no delay in delivery, no sending wrong product or damage
You might also like
- Summary Logistics Principles and Practice Visser Van GoorDocument38 pagesSummary Logistics Principles and Practice Visser Van GoorParbatty Arjune100% (1)
- Meaning of Logistics & Market Logistics DecisionDocument41 pagesMeaning of Logistics & Market Logistics Decisionyuktichauhan07100% (2)
- A Study of Warehouse ManagementDocument30 pagesA Study of Warehouse ManagementAnoop Duvey100% (1)
- Logistic NotesDocument16 pagesLogistic NotesFatima AliNo ratings yet
- 2011 LSCM Lesson1 Logistics PDFDocument83 pages2011 LSCM Lesson1 Logistics PDFAnkita Agarwal67% (3)
- LogisticsDocument6 pagesLogisticsVy LinhNo ratings yet
- Logistics Management What Is Logistics?: Ways To Increase ProfitsDocument9 pagesLogistics Management What Is Logistics?: Ways To Increase ProfitssidharthNo ratings yet
- Logistics EnglishDocument27 pagesLogistics EnglishI'malookIube100% (1)
- Supply ChainDocument9 pagesSupply ChainUynn LêNo ratings yet
- Logistics 1.7 1.8Document6 pagesLogistics 1.7 1.8Mia KhalifaNo ratings yet
- POB Logistics and Supply ChainDocument59 pagesPOB Logistics and Supply Chainmalindabissoon312No ratings yet
- C - Intro To LogisticsDocument36 pagesC - Intro To LogisticsGigi De JoyaNo ratings yet
- Elements of Logistics Management NotesDocument59 pagesElements of Logistics Management Notesaksr27100% (5)
- Physical Distribution SystemDocument20 pagesPhysical Distribution SystemSubha RudraNo ratings yet
- Definition of LogisticsDocument31 pagesDefinition of LogisticsArun Narayanan100% (1)
- Elements of Logistics Management NotesDocument52 pagesElements of Logistics Management NotesKamauWafulaWanyamaNo ratings yet
- C CC CCC CC CCC CCDocument4 pagesC CC CCC CC CCC CCRohan AdhiyaNo ratings yet
- Physical DistributionDocument21 pagesPhysical DistributionulkasolankiNo ratings yet
- Project On Logistic Management and SCM: Unit 2Document46 pagesProject On Logistic Management and SCM: Unit 2Salman KhanNo ratings yet
- Dimensions of Logistics (Cont.) : Micro DimensionDocument3 pagesDimensions of Logistics (Cont.) : Micro DimensioncristianaNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain and Logistics in Marketing - CDocument20 pagesSupply Chain and Logistics in Marketing - CvibuNo ratings yet
- Marketing Logistics and Supply Chain ManagementDocument25 pagesMarketing Logistics and Supply Chain ManagementShashi KantNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Logistics ManagementDocument6 pagesUnit 4 Logistics Managementadityasaraswat704No ratings yet
- Logistics and Supply ChainDocument36 pagesLogistics and Supply ChainCamila Pérez SanabriaNo ratings yet
- Definition of LogisticsDocument44 pagesDefinition of LogisticsPooja TripathiNo ratings yet
- Definition ListDocument16 pagesDefinition Listhuseyinova747No ratings yet
- Section 7 - Logistics and Supply ChainDocument14 pagesSection 7 - Logistics and Supply Chainhsomia873No ratings yet
- Abdul Moiz Shakeel 22348 3rd Class ActivityDocument4 pagesAbdul Moiz Shakeel 22348 3rd Class ActivityMoizShakeelNo ratings yet
- Concept of LogisticsDocument38 pagesConcept of LogisticsSoham100% (1)
- Logistics23 B6 - Day2 - Logistics in BusinessDocument21 pagesLogistics23 B6 - Day2 - Logistics in BusinessmartinrecileNo ratings yet
- Elements of Logistics Management NotesDocument45 pagesElements of Logistics Management NotesSujata Mansukhani93% (27)
- Summary IntermediateDocument16 pagesSummary IntermediateW.M. AukemaNo ratings yet
- LSCM NotesDocument55 pagesLSCM NotesNikhil KhobragadeNo ratings yet
- Logistics NotesDocument5 pagesLogistics NotesShabana IbrahimNo ratings yet
- LOGISTICSDocument11 pagesLOGISTICSKritika AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Logistics ManagementDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Logistics ManagementFaisal Tanwar100% (1)
- Logestic 1Document30 pagesLogestic 1wahid mohdNo ratings yet
- Warehousing ElmerDocument107 pagesWarehousing ElmerJolina LuceroNo ratings yet
- Class Notes SlidesDocument27 pagesClass Notes SlidesanitasndNo ratings yet
- Logistics NotesDocument33 pagesLogistics NotesMustafa SoniNo ratings yet
- Repaso Final LogisticaDocument9 pagesRepaso Final Logisticaaaxel0702No ratings yet
- Zagadnienia Na Egzamin Z AngielskiegoDocument37 pagesZagadnienia Na Egzamin Z AngielskiegomamusiazeskorkiNo ratings yet
- BSCM 1Document14 pagesBSCM 1Bambang NuryantoNo ratings yet
- Role of Logistics in SCMDocument2 pagesRole of Logistics in SCMshashi singhNo ratings yet
- AttachmentDocument102 pagesAttachmentmark kamauNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 I.logisticsDocument14 pagesUnit 3 I.logisticsBeverly Diane P. De Luna-AngioNo ratings yet
- Logistics Mgt.-Lesson 1Document7 pagesLogistics Mgt.-Lesson 1marianbuenaventura03No ratings yet
- TSCM Eq SolutionDocument104 pagesTSCM Eq Solutionch0c018No ratings yet
- LOGSTICSDocument56 pagesLOGSTICSEng RaniaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21Document19 pagesChapter 21Fire BoltNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Lesson 1 Logistics NotesDocument6 pagesUnit 7 Lesson 1 Logistics Notesanmitchell586No ratings yet
- Logistic NotesDocument42 pagesLogistic NotesMansur Shaikh100% (1)
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument80 pagesSupply Chain ManagementIrene PonticelliNo ratings yet
- Logistics PlanningDocument20 pagesLogistics PlanningJoginder GrewalNo ratings yet
- Log Revision 6.1 Procurement ProcessDocument13 pagesLog Revision 6.1 Procurement ProcessA - SIB1728 - Aliff HaiqalNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document2 pagesActivity 3Steffane Mae SasutilNo ratings yet
- Name: Mukami Sharon ADMISSION:18M01APSO42 Unit: Transport Management and Logistics Unit Code: PSM 316 Lecturer: Mr. S.K NdonyeDocument3 pagesName: Mukami Sharon ADMISSION:18M01APSO42 Unit: Transport Management and Logistics Unit Code: PSM 316 Lecturer: Mr. S.K NdonyeSharon ZweiNo ratings yet
- LogisticsDocument7 pagesLogisticsShanthiniVmsNo ratings yet
- Procedure and Documentation in Supply Chain Management: Business strategy books, #1From EverandProcedure and Documentation in Supply Chain Management: Business strategy books, #1No ratings yet
- The French AlphabetDocument1 pageThe French AlphabetAlexandraNo ratings yet
- ThaiDocument1 pageThaiAlexandraNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Financial Accounting and Management AccountingDocument2 pagesDifferences Between Financial Accounting and Management AccountingAlexandra100% (1)
- Bùhǎo Means 'Not Good'. ("Bu" Means 'No' or 'Not'.) ChineseDocument3 pagesBùhǎo Means 'Not Good'. ("Bu" Means 'No' or 'Not'.) ChineseAlexandraNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Trends NetworkDocument11 pagesModule 2 Trends NetworkBianca TaganileNo ratings yet
- Well-Developed Oral and Written Communication SkillsDocument3 pagesWell-Developed Oral and Written Communication Skillslyca_limNo ratings yet
- Taplin O. Pots and PlaysDocument322 pagesTaplin O. Pots and PlaysLuciana Jazmín Fernández Bernardez100% (2)
- English Investigatory ProjectDocument16 pagesEnglish Investigatory ProjectViplavNo ratings yet
- Motor Learning Theory: References: Cole & Tufano, Chapter 19 Reserve Article: Mathiowetz & Bass Haugen (1994) AJOTDocument23 pagesMotor Learning Theory: References: Cole & Tufano, Chapter 19 Reserve Article: Mathiowetz & Bass Haugen (1994) AJOTEdwin BedfordNo ratings yet
- 302-1006-003 Make-Up750ml MEK-United States - ADITIVO PDFDocument8 pages302-1006-003 Make-Up750ml MEK-United States - ADITIVO PDFAlexander MamaniNo ratings yet
- Full Download Business Analytics 3rd Edition Cam Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Business Analytics 3rd Edition Cam Solutions Manualwyattcgkzc100% (41)
- Jacques Derrida - Given Time - I Counterfeit MoneyDocument91 pagesJacques Derrida - Given Time - I Counterfeit MoneyLasha KharaziNo ratings yet
- Asia Medical Devices Report - Q2 2019Document41 pagesAsia Medical Devices Report - Q2 2019Ân THiênNo ratings yet
- POWER8 Overview v50 PDFDocument262 pagesPOWER8 Overview v50 PDFJohansen LeeNo ratings yet
- PG 511 B 1 B 1: Ordering Code Series PGP/PGM511Document7 pagesPG 511 B 1 B 1: Ordering Code Series PGP/PGM511Zoran JankovNo ratings yet
- Silencerco Catalog 2011Document28 pagesSilencerco Catalog 2011Mario LopezNo ratings yet
- History and Working Principle of CNC MachinesDocument308 pagesHistory and Working Principle of CNC MachinesYash IngleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Dissertation SmokingDocument8 pagesNursing Dissertation SmokingCustomPapersOnlineSingapore100% (1)
- 151005#LinkDesign20220821-203024Document5 pages151005#LinkDesign20220821-203024jemal yahyaaNo ratings yet
- Bukh DV 36 SmeDocument5 pagesBukh DV 36 SmeTullio OpattiNo ratings yet
- Power Management GuideDocument101 pagesPower Management GuideDiego MenegazziNo ratings yet
- Sebahat Elif Olgun Sebahat Elif Olgun Essay Final Draft 38263 18290098Document2 pagesSebahat Elif Olgun Sebahat Elif Olgun Essay Final Draft 38263 18290098api-433221820No ratings yet
- Act-06-Possessive AdjectivesDocument1 pageAct-06-Possessive Adjectivesconscientious.citizen29No ratings yet
- Geometry Practice Test 7 - ACT PROBLEMSDocument7 pagesGeometry Practice Test 7 - ACT PROBLEMSCarlos OrtizNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary TestDocument20 pagesVocabulary TesttimenetsolutionsNo ratings yet
- GM Repertoire 1A The Catalan PDFDocument794 pagesGM Repertoire 1A The Catalan PDFYoSoyDavidNo ratings yet
- Present ContinuousDocument2 pagesPresent ContinuouseditfotiNo ratings yet
- Steel TemperingDocument2 pagesSteel TemperingSalem GarrabNo ratings yet
- Release NotesDocument61 pagesRelease NotesThunder StormNo ratings yet
- 8th Grade Lesson 1 - Tectonic Plates - EarthquakesDocument2 pages8th Grade Lesson 1 - Tectonic Plates - EarthquakesKerwin SoriaoNo ratings yet
- IOSA Standards Manual: ORG 3.7.8 ORG 3.7.8 ORG 3.7.9 ORG 3.7.9 Table 1.2Document12 pagesIOSA Standards Manual: ORG 3.7.8 ORG 3.7.8 ORG 3.7.9 ORG 3.7.9 Table 1.2frankNo ratings yet
- A Review of The Outpatient Treatment Methods For COVID-19: A Special Interview With Dr. Pierre KoryDocument41 pagesA Review of The Outpatient Treatment Methods For COVID-19: A Special Interview With Dr. Pierre KoryJan Willem van BorselenNo ratings yet
- Progress Record TemplateDocument12 pagesProgress Record TemplatenickcnNo ratings yet
- BedZED Housing, Sutton, London BILL DUNSTER ARCHITECTS PDFDocument3 pagesBedZED Housing, Sutton, London BILL DUNSTER ARCHITECTS PDFflavius00No ratings yet