Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Enzyme Notes pdf1 PDF
Enzyme Notes pdf1 PDF
Uploaded by
N.NityainiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Enzyme Notes pdf1 PDF
Enzyme Notes pdf1 PDF
Uploaded by
N.NityainiCopyright:
Available Formats
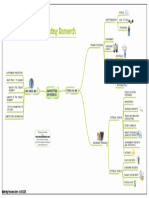
1. Intracellular enzymes www.sureshkumarbio.wordpress.
com
-formed and used within the cell
Example Proteins which act as biological
DEFINITION
-the enzyme inside the erythrocyte: catalyst that speed up
Carbonic anhydrase TYPES biochemical reactions in the
CO2 + H2O H2CO3 cell.
2. Extracellular enzymes
-produced in the cell and used outside the cell 1. Temperature
Example ENZYME FACTORS -low temperature: enzymes not
-the enzyme that digest starch in the mouth: THAT AFFECT active
Salivary amylase -high temperature, above 40 ͦC,
Starch maltose enzymes not active as bonds
startto break
1. made of protein
USES -above 60 ͦC, enzyme molecule
GENERAL bonds break completely.
2. produced in living cells
CHARACTERISTICS Enzymes denature.
3. only required in small quantities
4. not changed at the end of reaction
1. Protease 5. Trypsin 2. pH
5. not damaged at the end of reaction
-tenderisation of meat in meat -pre digests baby food -enzymes are sensitive to the
6. specific: usually one enzyme for one
Industries changes in pH values
substrate
2. Lipase 6. Pectinase -different enzymes have
7. substrate: the molecule that enzyme
-removal of organic stains in -clarifies fruit juices different
reacts with
biological detergents optimum pH values.
8.can react in two direction
3. Ligninase 7. Amylase Example:
Example:
-removal of lignin from pulp in -converts starch into Amylase………..nearly neutral
amylase
paper industries glucose and various Pepsin and Rennin…….acidic
Starch maltose
syrups Trypsin……….alkaline
9. name usually ends with ‘ase’ 4. Rennin 8. Cellulase
-coagulant in cheese production -used to break cell wall 3. Enzyme concentration
Example: sucrose, maltase, lipase
in dairy industries of the sea weeds to -if enzyme concentration is more
But some do not, example rennin,
extract agar than substrate concentration:
pepsin, trypsin
Rate of reaction increases
5. .Substrate concentration
Known as Lock and Key Hypothesis -if substrate concentration is
Enzyme Substrate Enzyme –substrate complex Enzyme Products more than enzyme
ACTION concentration: Rate of reaction
MECHANISM decreases
You might also like
- FLOWCHARTDocument1 pageFLOWCHARTPatrick FormosoNo ratings yet
- K Sembulingam Essentials of Medical Physiology 6th 008Document7 pagesK Sembulingam Essentials of Medical Physiology 6th 008Hajara Abubakari SadiqNo ratings yet
- Module 6 in BiochemistryDocument19 pagesModule 6 in BiochemistryjeromeNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of Tuberculosis (TB) Infection - LabCE - Com, Laboratory Continuing EducationDocument2 pagesPathogenesis of Tuberculosis (TB) Infection - LabCE - Com, Laboratory Continuing Educationshrish chandra pandeyNo ratings yet
- Anterior Uveitis: Ophthalmology Management TreeDocument2 pagesAnterior Uveitis: Ophthalmology Management TreeSandro PandurevicNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument7 pagesEnzymesYoni Lacanilao100% (1)
- Nattuvangam SyllabusDocument1 pageNattuvangam SyllabusRajah PriyankaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument41 pagesRespiratory SystemNikkiAbbaNiColeCartagenaNo ratings yet
- General PhysiotherapyDocument6 pagesGeneral Physiotherapysomebody_maNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation Management For Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients 2Document19 pagesRehabilitation Management For Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients 2Jothiprasanna KNo ratings yet
- Fundamental and Derived PositionDocument47 pagesFundamental and Derived PositionAmbusam Anita100% (1)
- Vasoactive Intestinal PeptideDocument2 pagesVasoactive Intestinal PeptidebournvilleeaterNo ratings yet
- GastrointestinalDocument39 pagesGastrointestinalالمسوول الاعلاميNo ratings yet
- Care of The Patient With Anterior Uveitis: Quick Reference GuideDocument4 pagesCare of The Patient With Anterior Uveitis: Quick Reference GuideAkicaNo ratings yet
- Types of Lasers - Solid State Laser, Gas Laser, Liquid Laser & Semiconductor LaserDocument4 pagesTypes of Lasers - Solid State Laser, Gas Laser, Liquid Laser & Semiconductor LaserRUPAM GHOSH100% (1)
- A Practical Physiotherapy Approach in Intensive Care Unit: April 2019Document12 pagesA Practical Physiotherapy Approach in Intensive Care Unit: April 2019NSSNS BALAJINo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System (Gi Tract) - I. General Organization, Esophagus and StomachDocument10 pagesGastrointestinal System (Gi Tract) - I. General Organization, Esophagus and StomacharaneyaNo ratings yet
- 4 I Morpho - Reversible Cell InjuryDocument21 pages4 I Morpho - Reversible Cell InjuryKartikey MishraNo ratings yet
- Radial Nerve PalsyDocument61 pagesRadial Nerve PalsyDenoson PalsonNo ratings yet
- BPH First Year Curriculum of Purbanchal UniversityDocument48 pagesBPH First Year Curriculum of Purbanchal Universityseo167No ratings yet
- Urinary Tract DisorderDocument63 pagesUrinary Tract DisorderShivaranjan KsNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic DrugsDocument44 pagesCholinergic Drugskhuzaima9100% (1)
- Didynamic+Current+Lecture GOODDocument16 pagesDidynamic+Current+Lecture GOODkrishnamoorthy abiramanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Response Ni FinalDocument35 pagesEndocrine Response Ni FinalSaktriawan ArifNo ratings yet
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Power Point PresentationDocument6 pagesCarpal Tunnel Syndrome Power Point Presentationapi-237061134No ratings yet
- In The Name of Allah The Most Beneficent and Most Merciful: Sports Clinic & Physiotherapy CentreDocument30 pagesIn The Name of Allah The Most Beneficent and Most Merciful: Sports Clinic & Physiotherapy CentreShahid Ahmed Heera100% (1)
- Arterial Blood Gases - PhysiopediaDocument2 pagesArterial Blood Gases - PhysiopediaKim BadillesNo ratings yet
- List of Physiology PracticalsDocument2 pagesList of Physiology PracticalsSeerat Ul irfanNo ratings yet
- Acid Peptic DisordersDocument67 pagesAcid Peptic DisordersTheop AyodeleNo ratings yet
- OedemaDocument23 pagesOedemaTavleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Physiological Mechanism of RegulationDocument11 pagesPhysiological Mechanism of Regulationmonster40lbsNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular Junction by Dr. RoomiDocument20 pagesNeuromuscular Junction by Dr. RoomiMudassar Roomi100% (1)
- The Structure, Function and Organisation of The Human BodyDocument28 pagesThe Structure, Function and Organisation of The Human BodyGemma WhitehouseNo ratings yet
- Joint, Connective Tissue, and Bone Disorders and ManagementDocument47 pagesJoint, Connective Tissue, and Bone Disorders and ManagementAmbreen TariqNo ratings yet
- Principles of Anatomy and Physiology: 14 EditionDocument62 pagesPrinciples of Anatomy and Physiology: 14 EditionWilliam C Chisha100% (1)
- Mechanism of Gastric SecretionDocument11 pagesMechanism of Gastric Secretionmulya ningsihNo ratings yet
- Physiotherapy For Stroke Patients - Physiotherapy Remedies For Victims of StrokeDocument9 pagesPhysiotherapy For Stroke Patients - Physiotherapy Remedies For Victims of StrokeHumaira RahmanNo ratings yet
- Neuro ProformaDocument20 pagesNeuro ProformaPraneetha NouduriNo ratings yet
- Skeletal TBDocument30 pagesSkeletal TBShashidhar Bk100% (4)
- Resume of Bijo MathewDocument6 pagesResume of Bijo MathewBijo Mathew100% (1)
- Important Short Questions & Answers: Human Anatomy & Physiology HAP 20114Document12 pagesImportant Short Questions & Answers: Human Anatomy & Physiology HAP 20114Kunal DangatNo ratings yet
- Genanat D&R AgamDocument51 pagesGenanat D&R AgamWitty GreenNo ratings yet
- LAB - Lung CapacityDocument5 pagesLAB - Lung CapacityWinnie LeeNo ratings yet
- Basic Immunology Introduction:: Hypersensitivity ReactionsDocument10 pagesBasic Immunology Introduction:: Hypersensitivity ReactionsRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Institutes Approved For Pharmacy Technicians Lahore: Aiman Institute of Pharmacy Technician 40+40Document4 pagesInstitutes Approved For Pharmacy Technicians Lahore: Aiman Institute of Pharmacy Technician 40+40Omer FarooqNo ratings yet
- DM PhysioDocument24 pagesDM Physiodwi astutiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cell PhysiologyDocument149 pagesIntroduction To Cell PhysiologyAlysaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes and Their Importance in Plants and AnimalsDocument4 pagesEnzymes and Their Importance in Plants and Animalsanili50% (2)
- A&P - 7. Shoulder Girdle & Upper Limb Detailed Anatomy (42p)Document42 pagesA&P - 7. Shoulder Girdle & Upper Limb Detailed Anatomy (42p)andreeaNo ratings yet
- Various Clinical Consideration of Sira: Anatomical Considerations, Sira Vedhan and Sira Gata VataDocument3 pagesVarious Clinical Consideration of Sira: Anatomical Considerations, Sira Vedhan and Sira Gata VataRaptor EaglesNo ratings yet
- Annavaha SrotasDocument12 pagesAnnavaha SrotasBiswajit DuttaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System NotesDocument10 pagesDigestive System NotesArchanna VyassNo ratings yet
- Jaundice 03Document24 pagesJaundice 03kuldeep sainiNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Examination PromptDocument4 pagesNervous System Examination PromptaeyousefNo ratings yet
- The Cockroach (Periplaneta Americana, L.): An Introduction to Entomology for Students of Science and MedicineFrom EverandThe Cockroach (Periplaneta Americana, L.): An Introduction to Entomology for Students of Science and MedicineRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Enzyme Notes PDFDocument1 pageEnzyme Notes PDFHannah NazriNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical BiochemistryDocument52 pagesPharmaceutical BiochemistryCherryl ValeraNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Biology - Unit 2 Summary NotesDocument10 pagesAQA GCSE Biology - Unit 2 Summary NotesRajashree MuNo ratings yet
- Folio Biology EnzymeDocument10 pagesFolio Biology EnzymeIzZati YazidNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Objectives and StrategiesDocument14 pagesHuman Resource Objectives and StrategiesNathiyaaNo ratings yet
- Judge Making LawDocument7 pagesJudge Making LawNathiyaaNo ratings yet
- The Economic ConflictDocument6 pagesThe Economic ConflictNathiyaaNo ratings yet
- Business Studies A - LEVELDocument7 pagesBusiness Studies A - LEVELNathiyaaNo ratings yet
- Economics CrosswordsDocument1 pageEconomics CrosswordsNathiyaaNo ratings yet
- Preparing A Wet Mount - ExperimentDocument7 pagesPreparing A Wet Mount - ExperimentNathiyaaNo ratings yet
- Eco-Marketing ResearchDocument1 pageEco-Marketing ResearchNathiyaaNo ratings yet
- Marketing CrosswordDocument1 pageMarketing CrosswordNathiyaaNo ratings yet
- f5 Mid Term Physics Paper 1 SMKRPK 2007Document12 pagesf5 Mid Term Physics Paper 1 SMKRPK 2007NathiyaaNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4 CartoonDocument9 pagesPhysics Form 4 CartoonYi YuenNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY SPMDocument81 pagesCHEMISTRY SPMNathiyaaNo ratings yet