Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Syphilitic Chancre of The Tongue: Images in Clinical Medicine
Uploaded by
drfmentOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Syphilitic Chancre of The Tongue: Images in Clinical Medicine
Uploaded by
drfmentCopyright:
Available Formats
The n e w e ng l a n d j o u r na l of m e dic i n e
images in clinical medicine
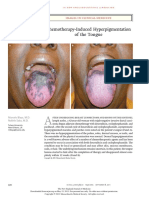
Syphilitic Chancre of the Tongue
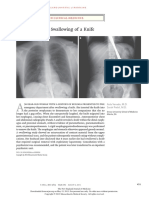
A B
A
41-year-old man presented with a 6-week history of a painful, Konrad Staines, B.Ch.D.
nonhealing lesion on the dorsum of his tongue. Examination revealed an Philip Sloan, B.D.S., Ph.D.
ulcer with a raised, indurated margin (Panel A). Malignancy and other infec- Newcastle Dental School
tions were considered in the differential diagnosis. There was no lymphadenopathy Newcastle upon Tyne, United Kingdom
on examination. A chronic inflammatory infiltrate with mature plasma cells and a
granulomatous component was evident on incisional biopsy. Immunohistochemi-
cal staining for Treponema pallidum identified spirochetes in the granulation tissue
overlying the ulcer, as well as in the walls and lumen of the capillaries at its margin
(Panel B, arrows). A strongly positive treponemal antibody absorption test and par-
ticle agglutination assay (titer ≥1:1280) and a second-line enzyme immunoassay
confirmed these findings. The tongue ulcer was diagnosed as a primary syphilitic
chancre. The results of screening tests for the human immunodeficiency virus,
chlamydia, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae were negative, and the patient was referred to
public health officials for sexual-contact tracing. Standard treatment with a single
intramuscular injection of benzathine penicillin G resulted in rapid pain relief and
complete resolution of the chancre over a 3-week period.
Copyright © 2011 Massachusetts Medical Society.
n engl j med 365;5 nejm.org august 4, 2011 e11
The New England Journal of Medicine
Downloaded from nejm.org on May 15, 2013. For personal use only. No other uses without permission.
Copyright © 2011 Massachusetts Medical Society. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- 1953-The Double ShuffleDocument216 pages1953-The Double ShuffledrfmentNo ratings yet
- The Fast BuckDocument111 pagesThe Fast Buckdrfment100% (1)
- 2006 FRACP Written Examination Paediatrics & ChildDocument27 pages2006 FRACP Written Examination Paediatrics & ChildMedicEdNo ratings yet
- Rheumatology 2012 MrcppassDocument131 pagesRheumatology 2012 MrcppassRaouf Ra'fat Soliman100% (5)
- Nej Mic M 1009319Document1 pageNej Mic M 1009319drfmentNo ratings yet
- Nej Mic M 1010983Document1 pageNej Mic M 1010983drfmentNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis of The Mandible in A Six-Year-Old ChildDocument0 pagesCase Report: Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis of The Mandible in A Six-Year-Old ChildElvina Agnestin HarianjaNo ratings yet
- Nej Mic M 1009305Document1 pageNej Mic M 1009305Abdalla Mohammed AliNo ratings yet
- AteneoDocument8 pagesAteneofabiandionisioNo ratings yet
- Clinical and Pathologic Analyses of Tuberculosis in The Oral Cavity: Report of 11 CasesDocument8 pagesClinical and Pathologic Analyses of Tuberculosis in The Oral Cavity: Report of 11 CasesMaria Lozano Figueroa 5to secNo ratings yet
- Nejmcpc 2107352Document11 pagesNejmcpc 2107352Fábio MenesesNo ratings yet
- Oral Findings of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus-A Grand Round CaseDocument5 pagesOral Findings of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus-A Grand Round CaseIntanNo ratings yet
- Oral Findings of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus - A Grand Round CaseDocument6 pagesOral Findings of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus - A Grand Round CaseArditya Dwi YudistiraNo ratings yet
- Bégon 2010Document2 pagesBégon 2010pamela queirozNo ratings yet
- Nejmicm 2301685Document1 pageNejmicm 2301685Feliep MontoyaNo ratings yet
- NeurosyphilisDocument8 pagesNeurosyphilisl1o2stNo ratings yet
- Nej Mic M 1009351Document1 pageNej Mic M 1009351dr.raziNo ratings yet
- Nickel: Periodontal Status and Blood Parameters in Allergic Orthodontic PatientsDocument5 pagesNickel: Periodontal Status and Blood Parameters in Allergic Orthodontic PatientsPae Anusorn AmtanonNo ratings yet
- Wolvius 1996Document3 pagesWolvius 1996pamela queirozNo ratings yet
- Childhood OLPDocument6 pagesChildhood OLPNurul Andika Virginia PutriNo ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary Syphilis: Images in Clinical MedicineDocument1 pagePrimary and Secondary Syphilis: Images in Clinical MedicineTha Vila Le ColloNo ratings yet
- Nej Mic M 1014268Document1 pageNej Mic M 1014268drfmentNo ratings yet
- 53 FullDocument6 pages53 Fullmuhammad HaseebNo ratings yet
- Case 32 2021A 14 Year Old GirlDocument10 pagesCase 32 2021A 14 Year Old GirlSohana IslamNo ratings yet
- JurnalDocument9 pagesJurnalRifqi FathendraNo ratings yet
- "Thumb Sign" of Epiglottitis: Images in Clinical MedicineDocument1 page"Thumb Sign" of Epiglottitis: Images in Clinical MedicineRian YupitaNo ratings yet
- A. B. C. D. E.: Clos Tridium Botulinum: Diplopia, Speech Disturbance, andDocument27 pagesA. B. C. D. E.: Clos Tridium Botulinum: Diplopia, Speech Disturbance, andPrashant SinghNo ratings yet
- Maxilla Unilateral Swelling As The First Diagnostic Symptom of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Relapse: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesMaxilla Unilateral Swelling As The First Diagnostic Symptom of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Relapse: A Case ReportTayta UmayuqNo ratings yet
- Caso 1Document14 pagesCaso 1Luanna DávilaNo ratings yet
- Childhood Oral Lichen Planus: Report of Two CasesDocument5 pagesChildhood Oral Lichen Planus: Report of Two CasesFuad HasanNo ratings yet
- Comninos 2019Document4 pagesComninos 2019Priscilla GeraldineNo ratings yet
- Case 20-2010 A 32-Year-Old Woman With Oligomenorrhea Ang Infertility PDFDocument9 pagesCase 20-2010 A 32-Year-Old Woman With Oligomenorrhea Ang Infertility PDFOrlando CuellarNo ratings yet
- Tongue Necrosis in Giant-Cell Arteritis: Images in Clinical MedicineDocument1 pageTongue Necrosis in Giant-Cell Arteritis: Images in Clinical MedicineMr. LNo ratings yet
- WCM2018 ABSTRACTS Microcirculation JournalDocument97 pagesWCM2018 ABSTRACTS Microcirculation JournalalbertwolandNo ratings yet
- Img 20211223 0023Document1 pageImg 20211223 0023dudaNo ratings yet
- Quiste Del Conducto NasopalatinoDocument3 pagesQuiste Del Conducto NasopalatinoYhamile Elizabeth Machaca PereyraNo ratings yet
- Images in Emergency Medicine: 0196-0644/$-See Front MatterDocument2 pagesImages in Emergency Medicine: 0196-0644/$-See Front Matterkhayan delfinoNo ratings yet
- Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Diagnosed From Oral LesionsDocument5 pagesTuberous Sclerosis Complex Diagnosed From Oral LesionsJoão Paulo Versiani LadeiaNo ratings yet
- A Head Shot: Images in Clinical MedicineDocument1 pageA Head Shot: Images in Clinical MedicinedrfmentNo ratings yet
- Swetman 2012Document3 pagesSwetman 2012Priyaa DharshiniNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Cysts - A Descriptive Clinicopathological StudyDocument6 pagesOdontogenic Cysts - A Descriptive Clinicopathological StudyAvif PutraNo ratings yet
- Nejmcpc 1102202Document10 pagesNejmcpc 1102202FrinkooFrinkoBNo ratings yet
- Case 14-2020: A 37-Year-Old Man With Joint Pain and Eye RednessDocument9 pagesCase 14-2020: A 37-Year-Old Man With Joint Pain and Eye RednessWho's Alewii?No ratings yet
- Letters To The Editors: Primary Sjögren's Syndrome As Paraneoplastic Disorder: A Case ReportDocument1 pageLetters To The Editors: Primary Sjögren's Syndrome As Paraneoplastic Disorder: A Case ReportDarian AngNo ratings yet
- Referensi 6Document3 pagesReferensi 6Nurul Rezki Fitriani AzisNo ratings yet
- Tumefactive Demyelinating Lesions: Nine Cases and A Review of The LiteratureDocument9 pagesTumefactive Demyelinating Lesions: Nine Cases and A Review of The LiteraturePS NeuroNo ratings yet
- Piis0002713809601151 PDFDocument6 pagesPiis0002713809601151 PDFLuwinda SariNo ratings yet
- Congenital Insensitivity To Pain and Anhydrosis (CIPA) Syndrome A Report of 4 CasesDocument6 pagesCongenital Insensitivity To Pain and Anhydrosis (CIPA) Syndrome A Report of 4 CasesAhmad DiazNo ratings yet
- Come Monitorare? Dallo Swan Ganz Al Pulse Contour.: Alessandro LocatelliDocument47 pagesCome Monitorare? Dallo Swan Ganz Al Pulse Contour.: Alessandro LocatelliAttilio Del RossoNo ratings yet
- Differences in Clinical and Laboratory Findings Between Group D and Non-Group D Non-TyphoidalDocument10 pagesDifferences in Clinical and Laboratory Findings Between Group D and Non-Group D Non-TyphoidalBana NanaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal PedetDocument6 pagesJurnal PedetDesna Datu RaraNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 002Document9 pagesJurnal 002Nadila FaatinNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Joen 2020 01 011 PDFDocument8 pages10 1016@j Joen 2020 01 011 PDFDaniela Paulina Riveros DonosoNo ratings yet
- Non-Traumatic Rupture of Spleen Can Splenectomy BeDocument3 pagesNon-Traumatic Rupture of Spleen Can Splenectomy Beysh_girlNo ratings yet
- Ileal-Lymphoid-Nodular Hyperplasia, Non-Specific Colitis, and Pervasive Developmental Disorder in ChildrenDocument11 pagesIleal-Lymphoid-Nodular Hyperplasia, Non-Specific Colitis, and Pervasive Developmental Disorder in ChildrenEmmanuelLeidiNo ratings yet
- Case 34-2021: A 38-Year-Old Man With Altered Mental Status and New Onset of SeizuresDocument9 pagesCase 34-2021: A 38-Year-Old Man With Altered Mental Status and New Onset of Seizuresskrv99No ratings yet
- Glomus Tympanicum: Images in Clinical MedicineDocument1 pageGlomus Tympanicum: Images in Clinical MedicinedrfmentNo ratings yet
- Case 14-2020: A 37-Year-Old Man With Joint Pain and Eye RednessDocument9 pagesCase 14-2020: A 37-Year-Old Man With Joint Pain and Eye RednessGénesis LeónNo ratings yet
- Literatür 1Document6 pagesLiteratür 1Oguzhan KumNo ratings yet
- Huntingtons ChoreaDocument2 pagesHuntingtons ChoreamaryNo ratings yet
- Nej Mic M 1014268Document1 pageNej Mic M 1014268drfmentNo ratings yet
- Nej Mic M 1010669Document1 pageNej Mic M 1010669drfmentNo ratings yet
- A Head Shot: Images in Clinical MedicineDocument1 pageA Head Shot: Images in Clinical MedicinedrfmentNo ratings yet
- Glomus Tympanicum: Images in Clinical MedicineDocument1 pageGlomus Tympanicum: Images in Clinical MedicinedrfmentNo ratings yet
- Nej Mic M 1008826Document1 pageNej Mic M 1008826drfmentNo ratings yet
- Case 2-2013: A 20-Year-Old Man With Recurrent Ear Pain, Fever, and HeadacheDocument11 pagesCase 2-2013: A 20-Year-Old Man With Recurrent Ear Pain, Fever, and HeadachedrfmentNo ratings yet
- Nej M CPC 1209935Document9 pagesNej M CPC 1209935drfmentNo ratings yet