Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Toxic Immune
Toxic Immune
Uploaded by
rahini balu0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesOriginal Title
toxic immune.doc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesToxic Immune
Toxic Immune
Uploaded by
rahini baluCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Normal function of the immune system requires participation
by many components, and disruption of any of these could conceivably result in
impaired capability.
If impairment is sufficient, the individual is at increased risk of infection and
cancer
This has been clearly demonstrated by patients on immunosuppressive therapy
(e.g, transplant patients) and in
animal studies involving a variety of chemicals.
Although there are few clear examples of immunosuppression from occupational
or environmental exposure in humans, there is no reason to expect that
this effect cannot occur under these circumstances as well
3. Causing or Exacerbating
Autoimmune Disease.
By producing a dysregulation of the immune system, drugs and
chemicals are capable of causing the immune system to attack
normal body constituents.
This has been clearly demonstrated for several drugs, and a
number of reports suggest that it may also occur from
occupational and environmental exposures.
Metals
Metals have been associated with various types of hypersensitivity reactions.
Beryllium, nickel, chromium, cadmium, silver, and zirconium have all been
found to produce contact dermatitis.
Nearly 10 percent of women and 2 percent of men have sensitivity to nickel,
and may develop rashes upon contact with nickel in jewelry, coins, and clothing
fasteners. Sensitive individuals may also respond to chromium in tanned leather
products.
Metals are also associated with pulmonary hypersensitivity reactions and
occupational asthma.
One of the most serious of these diseases is berylliosis, a delayed hypersensitivity
(type IV) reaction thought to result from beryllium acting as a hapten. Acutely,
hypersensitivity to beryllium is manifested as pneumonitis and pulmonary
edema.
Suppressing effect in the immune
system
Arsenic was used in the early twentieth century to treat some
inflammatory diseases, and currently appears to have some efficacy in
treating leukemia
Patients treated with arsenicals were reported to have a relatively high
incidence of the viral disease herpes zoster, suggesting some impairment
of the immune system
A number of studies have reported increased or unusual autoantibodies
in association with exposure to some metals in the workplace,
suggesting potential autoimmune toxicity. For example:
there is evidence of immune complex glomerulonephritis in nephrotoxicity
from cadmium and mercury
Iodine and lithium have been linked to autoimmune thyroid disease
chromium and gold have been associated with systemic lupus erythematosus
like disease
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus PathophysiologyDocument8 pagesSystemic Lupus Erythematosus Pathophysiologykathy92% (24)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Blueprints QA Pediatrics For Step 3 1Document59 pagesBlueprints QA Pediatrics For Step 3 1Moataz Trabeh100% (2)
- Management and Discharge PlanDocument2 pagesManagement and Discharge PlanZenny Marie B Dureza0% (1)
- NEET PG Pathology Pearls 1 PDFDocument272 pagesNEET PG Pathology Pearls 1 PDFAchyuth kattupalli100% (3)
- 09.cutaneous Manifestations of Systemic DiseasesDocument51 pages09.cutaneous Manifestations of Systemic DiseasesMohamed Rikarz Ahamed RikarzNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Diseases and Types PDFDocument24 pagesAutoimmune Diseases and Types PDFBaqar ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions: A Collective Arrangement by The Chapter Editors, Associate Editors, and CD-ROM Editor of 2005Document38 pagesSample Questions: A Collective Arrangement by The Chapter Editors, Associate Editors, and CD-ROM Editor of 2005Jennifer Schymick100% (2)
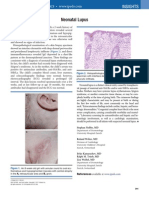
- Lupus NeonatalDocument2 pagesLupus NeonatalFer45No ratings yet
- AIA PCP Eng FA 20140605 HKDocument6 pagesAIA PCP Eng FA 20140605 HKJosephQuentinNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Canine Claw Disease - A Prospective Study of 24 DogsDocument9 pagesDiagnosis of Canine Claw Disease - A Prospective Study of 24 DogsjenNo ratings yet
- 10 Steps To Reverse Autoimmune Disease - DRDocument11 pages10 Steps To Reverse Autoimmune Disease - DROCanadian100% (1)
- BFKT Test 1Document1 pageBFKT Test 1Laurus AdiaNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Diseases: Dr. Ansar Uddin Ahmed Asst. Prof and Head Dept. of Periodontology and Oral PathologyDocument13 pagesAutoimmune Diseases: Dr. Ansar Uddin Ahmed Asst. Prof and Head Dept. of Periodontology and Oral PathologyTas DidNo ratings yet
- SLE Patogenesis & Patofisiologi PDFDocument8 pagesSLE Patogenesis & Patofisiologi PDFRIZQI IRFANSYAH100% (1)
- Morbid Anxiety As A Risk Factor in Patients With Somatic Diseases A Review of Recent FindingsDocument9 pagesMorbid Anxiety As A Risk Factor in Patients With Somatic Diseases A Review of Recent FindingsAdelina AndritoiNo ratings yet
- Goljan RR - ImmunopathologyDocument13 pagesGoljan RR - ImmunopathologyShaz ChindhyNo ratings yet
- Psychoimmunology Essay by DR Romesh Senewiratne-Alagaratnam (MD)Document32 pagesPsychoimmunology Essay by DR Romesh Senewiratne-Alagaratnam (MD)Dr Romesh Arya Chakravarti100% (2)
- HypersensitivityDocument6 pagesHypersensitivitykuldip.biotech100% (1)
- Lect.12 - Immunologic and Endocrine Alterations in ChildrenDocument61 pagesLect.12 - Immunologic and Endocrine Alterations in ChildrenlouradelNo ratings yet
- Spot DiagnosisDocument77 pagesSpot DiagnosisRapid Medicine100% (3)
- Pregnancy in Women With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus - UpToDateDocument25 pagesPregnancy in Women With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus - UpToDateKarla GonzalezNo ratings yet
- AUPH R&D Day FinalDocument163 pagesAUPH R&D Day FinalmedtechyNo ratings yet
- RheumatologyDocument28 pagesRheumatologyOanaroxana Varsa100% (2)
- Antinuclear AntibodiesDocument99 pagesAntinuclear Antibodiesdudapaskas100% (1)
- Protein Losing EnteropathyDocument9 pagesProtein Losing EnteropathyrajibNo ratings yet
- Comp Predictor Quizlet Study GuideDocument20 pagesComp Predictor Quizlet Study GuideJennifer Vicioso100% (9)
- To Whom So Ever It May Concer12Document18 pagesTo Whom So Ever It May Concer12vijay kumarNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Pathogenesis and Clinical FeaturesDocument30 pagesSystemic Lupus Erythematosus: Pathogenesis and Clinical FeaturesOrion JohnNo ratings yet
- Oral Disease (Handbook)Document106 pagesOral Disease (Handbook)lulud astikaNo ratings yet
- Physical - Hard To PenetrateDocument13 pagesPhysical - Hard To PenetrateCriselle Ruth Orendain Lardizabal0% (1)