Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diverticulitis
Uploaded by
Mary GiuntiniOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diverticulitis
Uploaded by
Mary GiuntiniCopyright:
Available Formats
Exemplar - Diverticulitis
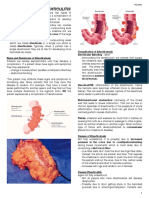
Basic Patho: Diverticulitis is generally extraluminal, occurring on the outside of the colon, and is often referred
to as an outpouching. Diverticulosis is the presence of diverticula that are noninflamed. Many patients with
diverticulosis are asymptomatic and may not even know they have the condition. Diverticulitis is an
inflammation and/or infected diverticula. Diverticulitis most often occurs in the colon, particularly the sigmoid
colon.
Manifestations Labs/Diagnostics
Ab pain over the area that is involved, Plain flat-plate ab x-ray and a CT
usually the sigmoid colon. scan.
May experience fever, or leukocytosis WBC are monitored for elevations r/t
(too many WBCs). inflammation and possible infection,
Often a palpable mass is felt over the but should decrease w/ tx.
involved area. Urinalysis (should show a few RBCs
Increased flatus if the ureter is near a perforated
Anorexia diverticulum.)
Ab bloating/distention
Diarrhea/constipation
Stools may contain mucus/blood
The first sign that may appear in the
older adult is a change in mental Teaching
status.
Avoid laxatives and enemas because
Baseline temp is often decreased from
they increase intestinal motility.
normal in the older adult. (may
Dietary recommendations (increasing
present w/ s/s of sepsis)
fibers from raw fruits and veggies in
their diets. W/o adequate fiber, more
Treatments/Interventions water is absorbed from the stool. This
slows transit time and makes it more
Broad-spectrum antibiotics difficult for the stool to pass through
Consume a clear liquid diet until the colon causing constipation and
symptoms subside. (the diet should be straining which is thought to lead to
advanced slowly as tolerated) the formation of diverticula).
May receive an NG tube for bowel Weight reduction (obesity has been
decompression and will receive linked to increased intra-abdominal
parenteral antibiotics. pressure, which is a risk factor for
Pain meds may be given PRN. diverticulitis).
If pts develop complications such as Complete antibiotic therapy as
perforation, hemorrhage, obstruction, prescribed.
or abscess, they may require surgery
to remove the diseased portion of the
colon. (may have temporary ostomy)
You might also like
- Bowel ObstructionDocument46 pagesBowel ObstructionAhmadNurwanto100% (1)
- Urolithiasis (Renal Calculi)Document12 pagesUrolithiasis (Renal Calculi)jhodane100% (1)
- Intestinal ObstructionDocument59 pagesIntestinal ObstructionGeorge GuruNo ratings yet
- Metab II DiverticulosisDocument94 pagesMetab II DiverticulosisEthel Lourdes Cornejo AmodiaNo ratings yet
- All CCS Platforms ListsDocument4 pagesAll CCS Platforms ListsRamanpreet Kaur MaanNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Gastritis and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Gastritis and Related ConditionsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Diverticular Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandDiverticular Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Williams Gynecology PDFDriveDocument25 pagesWilliams Gynecology PDFDriveKawaii Rjen-chanNo ratings yet
- Intussusception: Dr. Narendra Singh Shekhawat Assistant Professor Department of Shalya TantraDocument21 pagesIntussusception: Dr. Narendra Singh Shekhawat Assistant Professor Department of Shalya TantrakhushbuNo ratings yet
- PeritonitisDocument9 pagesPeritonitismardsz100% (4)
- Small Bowel: Alaa MaaliDocument78 pagesSmall Bowel: Alaa MaaliHalima AssiNo ratings yet
- Large Bowel Obstruction by Nic MDocument42 pagesLarge Bowel Obstruction by Nic MRisky OpponentNo ratings yet
- Concept Map SeizuresDocument1 pageConcept Map SeizuresMary GiuntiniNo ratings yet
- Diverticulitis Cure: The Ultimate Diverticulitis Diet: Diverticulitis Recipes: Your Ultimate Diverticulitis CookbookFrom EverandDiverticulitis Cure: The Ultimate Diverticulitis Diet: Diverticulitis Recipes: Your Ultimate Diverticulitis CookbookNo ratings yet
- Dysphagia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandDysphagia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Apendice Maingots Abdominal Operations 12th EditionDocument26 pagesApendice Maingots Abdominal Operations 12th EditionSimonGonzalezAponteNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis and CholelithiasisDocument19 pagesCholecystitis and CholelithiasisChristine Salimbagat100% (1)
- Concept Map PDDocument1 pageConcept Map PDMary GiuntiniNo ratings yet
- Small Bowel Obstruction &post Operative IleusDocument62 pagesSmall Bowel Obstruction &post Operative IleusMamanya Fadhil HaniNo ratings yet
- Summary For Acute AppendicitisDocument13 pagesSummary For Acute AppendicitisFemale calmNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Obstruction in Paediatrics - James GathogoDocument21 pagesIntestinal Obstruction in Paediatrics - James GathogoMalueth Angui100% (1)
- Ascites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAscites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Obstruction FinalDocument10 pagesIntestinal Obstruction FinalAmlan jyoti thanapatiNo ratings yet
- Common Health Problems That Develop During Infancy MPNDocument14 pagesCommon Health Problems That Develop During Infancy MPNShaii Whomewhat GuyguyonNo ratings yet
- AppendectomyDocument6 pagesAppendectomyapi-3797941100% (10)
- Lecture Colon 2016Document186 pagesLecture Colon 2016Mr AANo ratings yet
- Case Study AppendectomyDocument39 pagesCase Study AppendectomyHomework Ping100% (1)
- Diverticulosis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandDiverticulosis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Chapter 38 - Management of Patients With Intestinal and Rectal DisordersDocument7 pagesChapter 38 - Management of Patients With Intestinal and Rectal DisordersMichael BoadoNo ratings yet
- Diverticulitis Diet: A 3-Week Step-by-Step Guide for Women, With Curated Recipes and a Sample Meal PlanFrom EverandDiverticulitis Diet: A 3-Week Step-by-Step Guide for Women, With Curated Recipes and a Sample Meal PlanNo ratings yet
- Concept Map StrokeDocument1 pageConcept Map StrokeMary GiuntiniNo ratings yet
- What Is Intestinal ObstructionDocument5 pagesWhat Is Intestinal ObstructionmatrixtrinityNo ratings yet
- The Ideal Acute Pancreatitis Diet Cookbook; The Superb Diet Guide To Manage And Treat Pancreatitis And Reduce Inflammation With Nutritious RecipesFrom EverandThe Ideal Acute Pancreatitis Diet Cookbook; The Superb Diet Guide To Manage And Treat Pancreatitis And Reduce Inflammation With Nutritious RecipesNo ratings yet
- The Perfect Ic Diet Cookbook The Complete Nutrition Guide To Healing Chronic Pelvic Pain And Managing Symptoms Of Interstitial Cystitis With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesFrom EverandThe Perfect Ic Diet Cookbook The Complete Nutrition Guide To Healing Chronic Pelvic Pain And Managing Symptoms Of Interstitial Cystitis With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesNo ratings yet
- Diverticular Disease Ed Patient Factsheet April 2016Document2 pagesDiverticular Disease Ed Patient Factsheet April 2016minerva-larasatiNo ratings yet
- Diverticular Disease and Intestinal ObstructionDocument31 pagesDiverticular Disease and Intestinal ObstructionPauLa Cheneree Peña ÜNo ratings yet
- Cause: Diverticular DiseaseDocument4 pagesCause: Diverticular DiseaseJANELLE GIFT SENARLONo ratings yet
- 22 Manuscript Intestinal ObstructionDocument8 pages22 Manuscript Intestinal Obstructionkint manlangitNo ratings yet
- Paralytic Ileus: Prepared By: Laurence A. Adena, ManDocument43 pagesParalytic Ileus: Prepared By: Laurence A. Adena, ManJanah Beado PagayNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocument9 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasiamardsz100% (1)
- Dr. Pankaj Kumar Assistant Professor Surgical GastroenterologyDocument39 pagesDr. Pankaj Kumar Assistant Professor Surgical GastroenterologyIlham Suryo Wibowo AntonoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans: Cholecystitis CholelithiasisDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plans: Cholecystitis CholelithiasisAnnisa Fitriani NasutionNo ratings yet
- 9 Intestinal ObstructionDocument7 pages9 Intestinal ObstructionMAH pedNo ratings yet
- CHOLECYSTITIS With CHOLECYSTOLITHIASISDocument2 pagesCHOLECYSTITIS With CHOLECYSTOLITHIASISkennice_nereaNo ratings yet
- Pathology of The Digestive System: Presentation by Rowell AngelesDocument25 pagesPathology of The Digestive System: Presentation by Rowell AngelesZEESHAN YOUSUFNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) : Free Nursing LecturesDocument8 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) : Free Nursing Lecturesmeshael_29No ratings yet
- RLQ PainDocument20 pagesRLQ PainBEATRICE SOPHIA PARMANo ratings yet
- Mechanical Causes of Intestinal ObstructionDocument5 pagesMechanical Causes of Intestinal ObstructionKimberly Subade MandilagNo ratings yet
- PancreatitisDocument12 pagesPancreatitismardsz100% (5)
- Small Bowel Obstruction Vs IleusDocument63 pagesSmall Bowel Obstruction Vs IleusKamalesh MurariNo ratings yet
- What Are Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis?Document8 pagesWhat Are Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis?Zilvia EhrlichNo ratings yet
- PancreatitisDocument12 pagesPancreatitisapi-3797941100% (2)
- Intestinal Obstruction PDFDocument4 pagesIntestinal Obstruction PDFKiiza AloysiusNo ratings yet
- PancreatitisDocument12 pagesPancreatitisjhodane100% (4)
- MS Diverticulosis & DiverticulitisDocument2 pagesMS Diverticulosis & DiverticulitisRachelle Ann CarilloNo ratings yet
- UROLITHIASISDocument9 pagesUROLITHIASISmardsz100% (13)
- Lecture 7 Intussusception 2016Document8 pagesLecture 7 Intussusception 2016Nuukelo ShimbomeNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document5 pagesWeek 2Maica LectanaNo ratings yet
- Bowel ObstructionDocument8 pagesBowel ObstructionJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Open Access Textbook of General Surgery: Large Bowel Obstruction A BoutallDocument6 pagesOpen Access Textbook of General Surgery: Large Bowel Obstruction A BoutallDian FikriNo ratings yet
- An Approach To Small Bowel ObstructionDocument3 pagesAn Approach To Small Bowel ObstructionHardik JeenaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Gastro Intestinal Problem 2Document20 pagesNursing Management of Gastro Intestinal Problem 2wyneNo ratings yet
- Small Bowel Obstruction - Clinical Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument11 pagesSmall Bowel Obstruction - Clinical Diagnosis and TreatmentVigariooNo ratings yet
- Small Bowel Obstruction: Bowel Obstruction (Or Intestinal Obstruction) Is A Mechanical or FunctionalDocument4 pagesSmall Bowel Obstruction: Bowel Obstruction (Or Intestinal Obstruction) Is A Mechanical or FunctionaljazzshaneNo ratings yet
- Gi DistressDocument3 pagesGi DistressSushil ShindeNo ratings yet
- Gastric Outlet Obstruction, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandGastric Outlet Obstruction, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Constipation: How To Treat Constipation: How To Prevent Constipation: Along With Nutrition, Diet, And Exercise For ConstipationFrom EverandConstipation: How To Treat Constipation: How To Prevent Constipation: Along With Nutrition, Diet, And Exercise For ConstipationNo ratings yet
- PancreatitisDocument2 pagesPancreatitisMary GiuntiniNo ratings yet
- Hyper GlycemiaDocument1 pageHyper GlycemiaMary GiuntiniNo ratings yet
- Exemplar - Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseDocument1 pageExemplar - Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseMary GiuntiniNo ratings yet
- Colorectal CancerDocument1 pageColorectal CancerMary GiuntiniNo ratings yet
- Exemplar - Hypoglycemia: If Blood Glucose Levels Continue To Drop.Document1 pageExemplar - Hypoglycemia: If Blood Glucose Levels Continue To Drop.Mary GiuntiniNo ratings yet
- Exemplar - Protein-Calorie MalnutritionDocument1 pageExemplar - Protein-Calorie MalnutritionMary GiuntiniNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument1 pagePeptic Ulcer DiseaseMary GiuntiniNo ratings yet
- Exemplar - Obesity/BMI: Energy ExpenditureDocument1 pageExemplar - Obesity/BMI: Energy ExpenditureMary GiuntiniNo ratings yet
- AppendicitisDocument1 pageAppendicitisMary GiuntiniNo ratings yet
- Laparoscopic Colon Surgery: Past, Present and FutureDocument31 pagesLaparoscopic Colon Surgery: Past, Present and FutureprivedNo ratings yet
- May 2022Document47 pagesMay 2022SOMANATHAN UMAHSUTHANNo ratings yet
- Acute Colonic Diverticulitis: Annals of Internal MedicineDocument16 pagesAcute Colonic Diverticulitis: Annals of Internal MedicineOscar F RojasNo ratings yet
- DiseasesDocument8 pagesDiseasesBulcio Reed NaxilaNo ratings yet
- GastrointestinalDocument16 pagesGastrointestinalCelestial, Maybelle MarieNo ratings yet
- Peritonits: - Peritonitis:Is An Inflammation (Irritation) of The Peritoneum, TheDocument20 pagesPeritonits: - Peritonitis:Is An Inflammation (Irritation) of The Peritoneum, TheManish SapkotaNo ratings yet
- GIT NursingDocument8 pagesGIT NursingBasa, Rica Mae P.No ratings yet
- Colon, Rectum & AnusDocument6 pagesColon, Rectum & AnusLeikkaNo ratings yet
- DR Sanjay Adusumilli Divertic DiseaseDocument46 pagesDR Sanjay Adusumilli Divertic DiseaseVanyieldNo ratings yet
- Abdomen & Pelvis Pathology - CT-scanDocument53 pagesAbdomen & Pelvis Pathology - CT-scanKeithKam100% (1)
- Surgical Approach To Peritonitis and Abdominal Sepsis - Background, Preoperative Preparation, Considerations For Surgical ManagementDocument8 pagesSurgical Approach To Peritonitis and Abdominal Sepsis - Background, Preoperative Preparation, Considerations For Surgical ManagementCiubuc AndrianNo ratings yet
- Diverticulitis: Clinical PracticeDocument10 pagesDiverticulitis: Clinical PracticeZilvia EhrlichNo ratings yet
- Pemicu 4 GIT DevinDocument94 pagesPemicu 4 GIT DevinDevin AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Week 11: Nursing Care of Patients With Intestinal and Rectal Disorders Abnormalities of Fecal EliminationDocument9 pagesWeek 11: Nursing Care of Patients With Intestinal and Rectal Disorders Abnormalities of Fecal Eliminationeliza luisNo ratings yet
- B. Belingon - Notes From Case Session Slides, Anna's Notes (Dr. Esterl), Becky's Notes (Dr. Nguyen)Document11 pagesB. Belingon - Notes From Case Session Slides, Anna's Notes (Dr. Esterl), Becky's Notes (Dr. Nguyen)lizzy596No ratings yet
- Nurseslabs Gi Diseases Nursing Quiz 4Document6 pagesNurseslabs Gi Diseases Nursing Quiz 4Yenny PepitoNo ratings yet
- DiverticulitisDocument8 pagesDiverticulitisjennifer.hd.mfNo ratings yet
- Acute AbdomenDocument5 pagesAcute Abdomenhappylife100% (1)
- Exploratory LaparotomyDocument25 pagesExploratory Laparotomywinai13No ratings yet
- 10 Foods To Avoid For Diverticulitis Diet - 10FAQDocument5 pages10 Foods To Avoid For Diverticulitis Diet - 10FAQRay ManzanillaNo ratings yet
- DiverticulitaDocument6 pagesDiverticulitaoxichinolinNo ratings yet
- Imaging in Diverticulitis of The ColonDocument7 pagesImaging in Diverticulitis of The ColonHaryo Chandra KusumosariNo ratings yet