0% found this document useful (0 votes)
166 views8 pagesELEC2100 Homework 1 Solutions
This document contains the suggested solutions to homework 1 questions for the ELEC2100 course. It involves solving problems related to signals and systems, including:
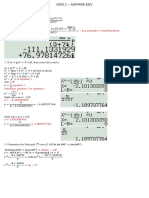
1) Analyzing complex exponential signals
2) Decomposing signals into even and odd parts
3) Determining properties of linear time-invariant systems
4) Convolving and correlating signals
5) Analyzing causal and stable systems
The problems cover topics like complex numbers, Fourier analysis, convolution, correlation, and system properties.
Uploaded by
FL SoloCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
166 views8 pagesELEC2100 Homework 1 Solutions
This document contains the suggested solutions to homework 1 questions for the ELEC2100 course. It involves solving problems related to signals and systems, including:
1) Analyzing complex exponential signals
2) Decomposing signals into even and odd parts
3) Determining properties of linear time-invariant systems
4) Convolving and correlating signals
5) Analyzing causal and stable systems
The problems cover topics like complex numbers, Fourier analysis, convolution, correlation, and system properties.
Uploaded by
FL SoloCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd