Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sifat Optis Mineral PDF
Sifat Optis Mineral PDF
Uploaded by
Wisnu Saputra AjiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sifat Optis Mineral PDF
Sifat Optis Mineral PDF
Uploaded by
Wisnu Saputra AjiCopyright:
Available Formats
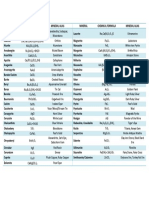
APATITE
General Formula: System:
Sample: PT-10C
Ca5(PO4)3(F,OH,Cl) Hexagonal
Hexagonal and elongated
Hexagonal and
Apatite needles
elongated Apatite
The hexagonal grains are
needles
cross sections of apatite
Fine grained hexagonal
needles, cut perpendicular
and elongated needles Block diagram showing the
to the long axis which also
of apatite included in relationship between the
corresponds to the c
plagioclase and crystallographic axes and the indicatrix
crystallographic axis and
clinopyroxene within an axes.
the optic axis, thus the
olivine diabase.
needles appear black.
The long axis of the
The long axis of the image
image is 0.9 mm, plane
is 0.9 mm,crossed polar
light view
view
Optical Properties
Colour usually colourless Form small euhedral to
Pleochroism non pleochroic in thin subhedral elongate
section prismatic crystals with
hexagonal cross sections
are most common, also
found as anhedral grains
and granular or columnar
aggregates
Relief/ moderate high Cleavage poor basal and prismatic,
RI positive not readily visible in thin
nw = 1.633-1.667 section
ne = 1.629-1.665
Birefringence 0.001 - 0.007 Twinning rare
Interference first order grey
Colours
Interference uniaxial Optic elongate sections show
Figure negative Orientation parallel extinction and are
Optic Sign length fast
2V
Composition widest variation in Alteration stable in most geologic
composition is environments
associated with the
hydroxyl site, e.g. F
for OH for Cl
Occurrence present as an Distinguishing moderate to high relief,
accessory in a wide Features low birefringence and
variety of igneous and uniaxial character
metamorphic rocks
and as detrital grains
in sedimentary rocks
CALCITE
General Formula: System:
Sample: M-24
CaCO3 Hexagonal (trigonal)
Calcite
Calcite
Irregular calcite crystals within
Extreme inteference
a marble. Note the Block diagram showing the
colours of calcite and the
rhombohedral cleavage relationship between the
presence of twinning in
displayed by the grain just left crystallographic axes and the
the top right grain.
of center. indicatrix axes.
Field of View = 2.7 mm,
Field of View = 2.7 mm, plane
crossed polars
light
Optical Properties
Colour colourless Form variety of habits, but
Pleochroism non pelochroic usually coinsist of
scalenohedron and
rhombohedron
combinations. In most
rocks calcite forms
anhedral grains or grain
aggregates
Relief moderate negative to Cleavage perfect rhombohedral
RI high positive, marked cleavage, angle between
change with stage cleavages 74°57'
rotation
nw = 1.658
ne = 1.486
Birefringence 0.172 Twinning lamellar twins parallel to
Interference extreme, creamy high one edge of the cleavage
Colours order colours rhomb or along the long
diagonal of the rhomb
Interference uniaxial Optic extinction is inclined or
Figure negative Orientation symmetrical to cleavage
Optic Sign traces, the fast ray is
2V parallel to the short
diagonal of the
rhombohedral faces
Composition dominantly CaCO3, Alteration altered to dolomite
but substitution of Mg, during diagenesis,
Fe, Mn, or Zn and calcite is soluble in
minor Sr and Ba natural waters and may
be removed by solution
Occurrence common and Distinguishing cleavage, variable relief,
widespread as a major Features extreme interference
mineral in limestones, colours
and an accessory in
igneous, metamorphic
and sedimentary rocks
NEPHELINE
General Formula: Sample: System:
Na3K(Al4Si4O16) Nepheline Syenite Hexagonal
TITLE TITLE Block diagram showing the relationship
DESCRIPTION DESCRIPTION between the crystallographic axes and the
SCALE SCALE indicatrix axes.
Optical Properties
Colour colourless Form anhedral to sudhedral in
Pleochroism non pleochroic intrusive rocks, subhedral
to euhedral in extrusive
rocks
Relief low negative to low Cleavage rarely seen in thin section,
RI positive irregular fractures
nw = 1.529-1.546
ne = 1.526-1.544
Birefringence 0.003 - 0.005 Twinning not observed
Interference first order grey
Colours
Interference uniaxial Optic longitudinal sections
Figure negative Orientation through euhedral crystals
Optic Sign as length fast, with
2V parallel extinction
Composition most nepheline has a Alteration alters to clay minerals,
3:1 ratio of Na:K. At analcime, sodalite,
high temperatures calcite, and cancrinite
complete solid solution
exists between pure
nepheline (100% Na)
and kalsilite (100% K)
Occurrence common in syenite, Distinguishing low relief, looks like
nepheline syenite and Features quartz but may be altered
related alkalic rocks. and is uniaxial negative
Nepehiline is never
associated with
primary quartz.
QUARTZ
General Formula: System:
Sample: M-20
SiO2 Hexagonal (trigonal)
Orthoquartzite
Subrounded quartz
Orthoquartzite
grains cemented in
Note the variety of
a matrix of silica.
orientations present Block diagram showing the
The grain
in the randomly relationship between the
boundaries are
oriented quartz crystallographic axes and the
clearly marked by
grains. indicatrix axes.
the fine grained
Field of View 2.7
inclusions.
mm, crossed polars
Field of View 2.7
mm, plane light
Optical Properties
Colour colourless Form typically anhedral to
Pleochroism non-pleochroic highly irregular in
igneous and
metamorphic rocks.
Detritial grains are
are more or less
equant.
Relief/ low positive relief Cleavage not observed
RI nw = 1.544
ne = 1.553
Birefringence 0.009 Twinning non observed
Interference Maximum interference
Colours colour range up to first
order white, with a tinge
of yellow
Interference unixial positive, but Optic optic axis is the c
Figure/ strained displaying Orientation axis. Elongate
Optic Sign undulatory extinction may crystals cut from end
2V show a biaxial to end are length
interference figure with a slow.
small separation of the
isogyres.
Composition essentially pure SiO2, Alteration not readily altered
although trace amounts of and is very stable in
Ti, Fe, Mn, Al may be weathering
present. environments.
Occurrence one of the most widely Distinguishing low relief, low
abundant minerals, Features birefringence, lack of
present in a wide variety cleavage, uniaxial
of environments. positive.
TOURMALINE
System:
General Formula:
Sample: PT-123 Hexagonal
Na(Mg,Fe,Li,Al)3Al6(Si6O18)(BO3)3(OH,F)4
(trigonal)
Radiating Tourmaline
Radiating Tourmaline
The extinction of the
The range of pleochroic colours displayed Block diagram
individual grains varies
by the radiating tourmaline crystals is showing the
across the grain
evident. Note that the grains exhibit their relationship
aggregate, when the
lightest and darkest pleochroic colour when between the
long axis is parallel to
the long axis is parallel and perpendicluar, crystallographic
the polars the grain is
respectively, to the lower polar vibration axes and the
extinct.
direction (N-S). indicatrix axes.
Field of View 2.7 mm,
Field of View 2.7 mm, plane light
crossed polars
Optical Properties
Colour highly variable, blue, Form euhedral, stubby
Pleochroism green, pink, yellow columnar to acicular
stongly pleochroic with crystals with a
w > e, basal sections are rounded triangular
uniformly dark. to crudely hexagonal
cross section
Relief moderate to high positive Cleavage poorly developed,
RI nw = 1.631-1.968 fractures are
ne = 1.610-1.675 conchoidal
Birefringence 0.015-0.035 Twinning rare
Interference Colours up to upper second order,
but commonly masked
by mineral's colour
Interference Figure uniaxial Optic longitudinal sections
Optic Sign negative Orientation show parallel
2V extinction and are
length fast
Composition highly variable, RI and Alteration fairly stable in
birefringence increase weathering
generally with increasing environments
Fe
Occurrence characteristic mineral in Distinguishing crystal habit, distinct
granites and related Features pleochrosm.
rocks, in schists, gneisses Tourmaline exhibits
and phyllites and as a its darkest
detrital mineral pleochroic colour
when the long axis
of the grain is
aligned
perpendicular to the
lower polar.
ZIRCON
General Formula: System:
Sample: GB 12
ZrSiO4 Tetragonal
Zircon
Zircon
The same image as that on
Euhedral zircon grain within
the left, the high
a granitic gneiss. Note the Block diagram showing the
interference colours of the
highly fractured nature of relationship between the
zircon grain are not
the grain and the very strong crystallographic axes and the
readily evident in this
relief. indicatrix axes.
image,
Field of View 1 mm, plane
Field of View 1 mm,
light
crossed polars
Optical Properties
Colour colourless to pale Form euhedral to sudhedral
Pleochroism brown tetragonal crystals with
weakly pleochroic pyramidal terminations
Relief very high positive Cleavage not usually seen in thin
RI nw = 1.920-1.960 section
ne = 1.967-2.015
Birefringence 0.036-0.065 Twinning not twinned
Interference up to third or fourth
Colours order
Interference uniaxial Optic elongate grains are
Figure positive Orientation length slow with
Optic Sign parallel extinction
2V
Composition significant Hf for Zr Alteration does not readily alter
and minor U and Th
Occurrence common accessory Distinguishing small, high-relief grains
mineral in felsic rocks Features with bright interference
and less common in colours
mafic rocks, common in
metamorphic rocks
derived from clastic
sediments, common
detritial mineral
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Manual Epithermal & Porphyry - G.corbett 2018Document207 pagesManual Epithermal & Porphyry - G.corbett 2018roberto andia100% (2)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Ceklis Sistem Utilitas OkDocument3 pagesCeklis Sistem Utilitas Okgemc99No ratings yet
- Pengkajian PasienDocument19 pagesPengkajian Pasiengemc99No ratings yet
- Personal Letter For The Best Friends: Dear LucyDocument10 pagesPersonal Letter For The Best Friends: Dear Lucygemc99No ratings yet
- Daftar Obat Sidang Jemaat Gereja Maranatha TeminabuanDocument2 pagesDaftar Obat Sidang Jemaat Gereja Maranatha Teminabuangemc99No ratings yet
- Silverchair Without YouDocument4 pagesSilverchair Without Yougemc99No ratings yet
- ARD Test HandbookDocument42 pagesARD Test HandbookEddie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Mississippi Valley Type DepositDocument25 pagesMississippi Valley Type DepositBonjovi Verdejo100% (2)
- Naming Metamorphic Rocks IUGSDocument3 pagesNaming Metamorphic Rocks IUGSMaMtNo ratings yet
- Quartz FamilyDocument4 pagesQuartz FamilySORIANO, JEZEREEL JOYCE A.No ratings yet
- Mineral Alias & FormulasDocument1 pageMineral Alias & FormulasKatrina BucudNo ratings yet
- EASC 101 Lab 2 Minerals Part 2 (50 Marks) : Instructions Marked Lab 1 Assignment and Lectures 1 & 2 (If Needed)Document7 pagesEASC 101 Lab 2 Minerals Part 2 (50 Marks) : Instructions Marked Lab 1 Assignment and Lectures 1 & 2 (If Needed)Jason SuNo ratings yet
- FeldsparDocument18 pagesFeldsparPauliina 'VrmzNo ratings yet
- Igneous Petrology Part 4Document1 pageIgneous Petrology Part 4Anuj SinghNo ratings yet
- Minerals 06 00121Document23 pagesMinerals 06 00121Mohammad Gulam KibriahNo ratings yet
- Genesis of VertisolsDocument35 pagesGenesis of VertisolsRam Prasad Sharma100% (1)
- Dana-S Textbook of Mineralogy PDFDocument912 pagesDana-S Textbook of Mineralogy PDFimamjuandaNo ratings yet
- Earth Materials and ProcessesDocument1 pageEarth Materials and ProcessesJemarjo SalandananNo ratings yet
- Classification and Definitions of Textures and Mineral Structures in OresDocument27 pagesClassification and Definitions of Textures and Mineral Structures in OresMaria Alejandra Suarez Garcia100% (1)
- Knittel1989 Cordon GFD PDFDocument11 pagesKnittel1989 Cordon GFD PDFRene BautistaNo ratings yet
- X ICSE Geography 02Document126 pagesX ICSE Geography 02mandar sawant84% (19)
- A Petrographical Review of Metamorphic Rocks From Ciletuh Complex, in West Java and Their Related Metamorphism in Central Indonesia RegionDocument10 pagesA Petrographical Review of Metamorphic Rocks From Ciletuh Complex, in West Java and Their Related Metamorphism in Central Indonesia RegionMeutia FildzahNo ratings yet
- Orogenic Gold Deposits - GrovesDocument21 pagesOrogenic Gold Deposits - GrovesSuta Vijaya100% (1)
- Geology P2 ReviewerDocument4 pagesGeology P2 ReviewerJohn Aldrin Santiago PalaganasNo ratings yet
- GG 2019Document14 pagesGG 2019Ranjith kumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The School of RocksDocument54 pagesChapter 2 - The School of RocksCecilia Q. UyNo ratings yet
- GEOS Question PaperDocument3 pagesGEOS Question PaperPiyush Pasari100% (1)
- Extractive Metallurgy First PDFDocument22 pagesExtractive Metallurgy First PDFDerek Jensen100% (8)
- Porphyry Deposits Sinclair, W.D.)Document14 pagesPorphyry Deposits Sinclair, W.D.)Manael Ridwan100% (2)
- Ore Forming Minerals-1Document42 pagesOre Forming Minerals-1MD ASAD KHANNo ratings yet
- The Surface Chemistry of Soils PDFDocument245 pagesThe Surface Chemistry of Soils PDFRisely Ferraz100% (1)
- Landscape Yang Terbentuk Oleh Proses DenudasionalDocument40 pagesLandscape Yang Terbentuk Oleh Proses DenudasionalipungjiNo ratings yet
- H. H. Read F.R.S. (Auth.) - Rutley's Elements of Mineralogy (1970, Springer Netherlands) PDFDocument566 pagesH. H. Read F.R.S. (Auth.) - Rutley's Elements of Mineralogy (1970, Springer Netherlands) PDFsaurabh shuklaNo ratings yet
- Ageing Phenomena of CelluloseDocument9 pagesAgeing Phenomena of CellulosedchyNo ratings yet
- Magnesia GlossaryDocument22 pagesMagnesia GlossaryPanos AntonakopoulosNo ratings yet