Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ewrweoiroqi
Uploaded by
smagasipaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ewrweoiroqi
Uploaded by
smagasipaCopyright:
Available Formats
/*
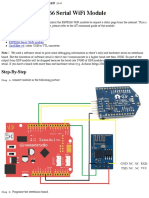
This sketch connects to the Cayenne server using an ESP8266 WiFi module as a shield
connected via a hardware serial to an Arduino.
The CayenneMQTT Library is required to run this sketch. If you have not already
done so you can install it from the Arduino IDE Library Manager.
Steps:
1. Install the ESP8266SerialLibrary.zip library via the Arduino IDE (Sketch-
>Include Library->Add .ZIP Library) from the Cayenne extras/libraries
folder (e.g. My Documents\Arduino\libraries\CayenneMQTT\extras\libraries) to
compile this example.
2. Connect the ESP8266 as a shield to your Arduino. This example uses the Serial1
hardware serial pins available on the Mega. You can also try
using a software serial, though it may be less stable.
3. Set the Cayenne authentication info to match the authentication info from the
Dashboard.
4. Set the network name and password.
5. Compile and upload the sketch.
6. A temporary widget will be automatically generated in the Cayenne Dashboard. To
make the widget permanent click the plus sign on the widget.
NOTE: This code requires ESP8266 firmware version 1.0.0 (AT v0.22) or later.
*/
//#define CAYENNE_DEBUG // Uncomment to show debug messages
#define CAYENNE_PRINT Serial // Comment this out to disable prints and save space
#include <CayenneMQTTESP8266Shield.h>
#include "max6675.h"
int thermoDO = 4;
int thermoCS = 5;
int thermoCLK = 6;
MAX6675 thermocouple(thermoCLK, thermoCS, thermoDO);
// WiFi network info.
char ssid[] = "ssid";
char wifiPassword[] = "wifiPassword";
// Cayenne authentication info. This should be obtained from the Cayenne Dashboard.
char username[] = "MQTT_USERNAME";
char password[] = "MQTT_PASSWORD";
char clientID[] = "CLIENT_ID";
// Set ESP8266 Serial object. In this example we use the Serial1 hardware serial
which is available on boards like the Arduino Mega.
#define EspSerial Serial1
ESP8266 wifi(&EspSerial);
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
delay(10);
// Set ESP8266 baud rate
EspSerial.begin(115200);
delay(10);
Cayenne.begin(username, password, clientID, wifi, ssid, wifiPassword);
}
void loop()
{
Cayenne.loop();
}
// Default function for sending sensor data at intervals to Cayenne.
// You can also use functions for specific channels, e.g CAYENNE_OUT(1) for sending
channel 1 data.
CAYENNE_OUT_DEFAULT()
{
// Write data to Cayenne here. This example just sends the current uptime in
milliseconds on virtual channel 0.
Cayenne.virtualWrite(0, millis());
Cayenne.celsiusWrite(1, thermocouple.readCelsius());
//Cayenne.virtualWrite(2, thermocouple.readFahrenheit());
}
// Default function for processing actuator commands from the Cayenne Dashboard.
// You can also use functions for specific channels, e.g CAYENNE_IN(1) for channel
1 commands.
CAYENNE_IN_DEFAULT()
{
CAYENNE_LOG("Channel %u, value %s", request.channel, getValue.asString());
//Process message here. If there is an error set an error message using
getValue.setError(), e.g getValue.setError("Error message");
}
You might also like
- Build your own Blockchain: Make your own blockchain and trading bot on your pcFrom EverandBuild your own Blockchain: Make your own blockchain and trading bot on your pcNo ratings yet
- Build your own dashboard to control devices remotely with aRESTDocument7 pagesBuild your own dashboard to control devices remotely with aRESTAroob ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Esp8266 V10Document22 pagesEsp8266 V10lalonaderNo ratings yet
- # Cayenne MQTT ESPDocument2 pages# Cayenne MQTT ESPsridhar kolurNo ratings yet
- Login Page by Arduino & Esp8266 Imp: Electropeak'S Official WebsiteDocument10 pagesLogin Page by Arduino & Esp8266 Imp: Electropeak'S Official WebsiteDamir SpahićNo ratings yet
- Network Security All-in-one: ASA Firepower WSA Umbrella VPN ISE Layer 2 SecurityFrom EverandNetwork Security All-in-one: ASA Firepower WSA Umbrella VPN ISE Layer 2 SecurityNo ratings yet
- Getting Started in ESP826 As An IOTDocument25 pagesGetting Started in ESP826 As An IOTmallikharjunag100% (5)
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3From EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3No ratings yet
- XC3802 ManualmainDocument2 pagesXC3802 ManualmainCodieNo ratings yet
- Tutorial For Esp8266 Serial Wifi ModuleDocument3 pagesTutorial For Esp8266 Serial Wifi ModuleRajaAtifNo ratings yet
- Tutorial For Esp8266 Serial Wifi ModuleDocument3 pagesTutorial For Esp8266 Serial Wifi ModuleRRTRTNo ratings yet
- ESP8266 JQuery and AJAX Web ServerDocument4 pagesESP8266 JQuery and AJAX Web ServersaravananNo ratings yet
- Build a Wi-Fi Controlled 4-Channel Switch for IoTDocument8 pagesBuild a Wi-Fi Controlled 4-Channel Switch for IoTShrinivasNo ratings yet
- How to Set an ESP32 as an Access Point for Web Server ProjectsDocument9 pagesHow to Set an ESP32 as an Access Point for Web Server ProjectsPerez Geovanni100% (1)
- WiFi Serial Transceiver Module - WikiDocument6 pagesWiFi Serial Transceiver Module - WikiAlbert SuwandhiNo ratings yet
- Wemos ESP32 Lolin32 Board BOOK ENGLISHDocument22 pagesWemos ESP32 Lolin32 Board BOOK ENGLISHDima KnyaNo ratings yet
- IoTAssignment 2Document7 pagesIoTAssignment 2Ashitosh KurheNo ratings yet
- ESP8266+Arduino Workshop Shows How to Use Small, Powerful, Cheap WiFi Module for IoT ProjectsDocument31 pagesESP8266+Arduino Workshop Shows How to Use Small, Powerful, Cheap WiFi Module for IoT ProjectsRaj Kumar82% (11)
- Malesia EspDocument344 pagesMalesia EsppensamemuchoNo ratings yet
- Light Intensity Monitor Using WebapiDocument5 pagesLight Intensity Monitor Using WebapiAlexander SupertrampNo ratings yet
- Dfrobot Wifi Shield V2.1 Arduino Tutorial: by Frikkie Du ToitDocument8 pagesDfrobot Wifi Shield V2.1 Arduino Tutorial: by Frikkie Du Toitvn6994100% (1)
- Tutorial For ESP8266 Serial WiFi ModuleDocument4 pagesTutorial For ESP8266 Serial WiFi ModuleGîrdianu Alex0% (1)
- How To Use ESP8266 With PCF8574 - 4 Input and 4 Output: Step 1: ComponentsDocument5 pagesHow To Use ESP8266 With PCF8574 - 4 Input and 4 Output: Step 1: ComponentsedermadrugaNo ratings yet
- Write-Read Data ThingspeakDocument8 pagesWrite-Read Data ThingspeakDimasNo ratings yet
- Controlling Two Led or Relays With Blynk An ESP 8266Document10 pagesControlling Two Led or Relays With Blynk An ESP 8266ferNo ratings yet
- Home Automation in The Cloud With The Esp8266 and Adafruit IoDocument12 pagesHome Automation in The Cloud With The Esp8266 and Adafruit IoAhmed WadeNo ratings yet
- How To Get Data From URL VariableDocument2 pagesHow To Get Data From URL VariablePakai UmumNo ratings yet
- Components RequiredDocument16 pagesComponents RequiredmacashNo ratings yet
- Build An ESP8266 Web ServerDocument21 pagesBuild An ESP8266 Web Serverpinguino2820100% (1)
- ESP8266-01 - USB-Stick ENGDocument9 pagesESP8266-01 - USB-Stick ENGali azila100% (2)
- Laporan Sementara 3 - Kelompok 5 - BM5ADocument13 pagesLaporan Sementara 3 - Kelompok 5 - BM5AFARHAN YUSWA BIYANTONo ratings yet
- Shield WiFi 802.11b PDFDocument8 pagesShield WiFi 802.11b PDFmilenyNo ratings yet
- Avaya Asterisk LoggerDocument15 pagesAvaya Asterisk LoggerArcangelo Di BattistaNo ratings yet
- Arduino Activity Web Server GuideDocument7 pagesArduino Activity Web Server GuideArdian Ramadita SugaraNo ratings yet
- IoT Monitoring Temperature Data on ServerDocument15 pagesIoT Monitoring Temperature Data on ServerfaishalNo ratings yet
- Firmata WIFIDocument37 pagesFirmata WIFIsoo chiNo ratings yet
- Getting Started With ESP8266Document10 pagesGetting Started With ESP8266Julpan Ongly Pangaribuan100% (1)
- Home Automation in The Cloud With The Esp8266 and Adafruit IoDocument16 pagesHome Automation in The Cloud With The Esp8266 and Adafruit IoBhaumik VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Esp8266 To Find IP AddressDocument6 pagesEsp8266 To Find IP AddressAlroy AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- ESP8266 DHT11 Humidity Temperature Data LoggerDocument6 pagesESP8266 DHT11 Humidity Temperature Data LoggersaravananNo ratings yet
- Configure and Setup Squid Cache Proxy Server On Fedora CoreDocument11 pagesConfigure and Setup Squid Cache Proxy Server On Fedora CorejbonNo ratings yet
- Arduino Uno Proximity 2022Document4 pagesArduino Uno Proximity 2022dream angelNo ratings yet
- LABSEC-2020 ASA 8.3 (Or Higher) Lab Guide PDFDocument11 pagesLABSEC-2020 ASA 8.3 (Or Higher) Lab Guide PDFRiadh MadhourNo ratings yet
- Iot Minor DegreeDocument51 pagesIot Minor DegreeKevin ModiNo ratings yet
- ESP8266 Tutorial - How To Control Anything From The Internet! - DIY HackingDocument8 pagesESP8266 Tutorial - How To Control Anything From The Internet! - DIY HackingjayarajanNo ratings yet
- Wifi Weather Station Esp 8266Document7 pagesWifi Weather Station Esp 8266MoogNo ratings yet
- Home Automation in The Cloud With The Esp8266 and Adafruit Io PDFDocument14 pagesHome Automation in The Cloud With The Esp8266 and Adafruit Io PDFJeffsor100% (2)
- ESP32 Weather Station With BM280Document15 pagesESP32 Weather Station With BM280CahyaDsnNo ratings yet
- IOT1Document23 pagesIOT1thesoulmatecreationNo ratings yet
- MQTT Adafruit LibraryDocument21 pagesMQTT Adafruit LibraryrogerlawNo ratings yet
- SD Card Reader Module With Arduino TutorialDocument8 pagesSD Card Reader Module With Arduino TutorialJunior ElimeelogodavejuniorNo ratings yet
- Cisco Router Password Recovery - PDocument6 pagesCisco Router Password Recovery - PEddie C. LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Password Recovery Procedure For The Cisco 806, 827, and 837 RoutersDocument8 pagesPassword Recovery Procedure For The Cisco 806, 827, and 837 Routersnineor10100% (1)
- GrafanaCon LA IoT Workshop PDFDocument30 pagesGrafanaCon LA IoT Workshop PDFThe FannyNo ratings yet
- IoT & Observability Monitoring our world with GrafanaDocument30 pagesIoT & Observability Monitoring our world with GrafanaThe FannyNo ratings yet
- Importing digital code block into Cadence AMSDocument6 pagesImporting digital code block into Cadence AMSMostafa M. SamiNo ratings yet
- SBC ESP01 RM - ManualDocument7 pagesSBC ESP01 RM - ManualivucixNo ratings yet
- Secu Gen Hamster Pro 20Document2 pagesSecu Gen Hamster Pro 20Ashish GusainNo ratings yet
- Javelin Mobility Ability 2.0 GuideDocument36 pagesJavelin Mobility Ability 2.0 Guideroham25156No ratings yet
- Pruebas de Certificación Lingüística in - B1 - Ce - Sol - J - 2015 Answer Key - JUNE 2015 Task 1Document2 pagesPruebas de Certificación Lingüística in - B1 - Ce - Sol - J - 2015 Answer Key - JUNE 2015 Task 1Jeru SierraNo ratings yet
- The Separation of Coherent and Incoherent Compton X-Ray ScatteringDocument8 pagesThe Separation of Coherent and Incoherent Compton X-Ray ScatteringFaisal AmirNo ratings yet
- My Demo DemoDocument19 pagesMy Demo DemoAlex LopezNo ratings yet
- Summary G.E 9 Rizal Works (Chapter 1-13)Document23 pagesSummary G.E 9 Rizal Works (Chapter 1-13)Erwin Jay CabantacNo ratings yet
- G.raju Reddy Resume (PDF1) PDFDocument3 pagesG.raju Reddy Resume (PDF1) PDFanon_708469687No ratings yet
- Top Answers to Mahout Interview QuestionsDocument6 pagesTop Answers to Mahout Interview QuestionsPappu KhanNo ratings yet
- Conditions For The Emergence of Life On The Early Earth: Summary and ReflectionsDocument15 pagesConditions For The Emergence of Life On The Early Earth: Summary and Reflectionsapi-3713202No ratings yet
- S-H Polarimeter Polartronic-532 Eng - 062015 PDFDocument2 pagesS-H Polarimeter Polartronic-532 Eng - 062015 PDFSuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Notes GoodDocument21 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Notes GoodAnitesh DharamNo ratings yet
- THC124 - Lesson 1. The Impacts of TourismDocument50 pagesTHC124 - Lesson 1. The Impacts of TourismAnne Letrondo Bajarias100% (1)
- Project management software enables collaborationDocument4 pagesProject management software enables collaborationNoman AliNo ratings yet
- BCG ReportDocument9 pagesBCG Reportjlgjlj ljglkhNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 of EthicsDocument110 pagesUnit 1 of EthicsAbhinav kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- LAWO PI - MADI - SRC - enDocument2 pagesLAWO PI - MADI - SRC - enfjavierpoloNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in (Teaching Science)Document8 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in (Teaching Science)Evan Jane Jumamil67% (3)
- Instant Download Ebook PDF Building Construction Handbook 11th Edition PDF ScribdDocument41 pagesInstant Download Ebook PDF Building Construction Handbook 11th Edition PDF Scribdthomas.bilal255100% (38)
- The Secret Science of Shaktipat - Guide To Initiation 13 September 2020Document77 pagesThe Secret Science of Shaktipat - Guide To Initiation 13 September 2020Patrick JenksNo ratings yet
- WET - AT - AT - 003 - ENG - Manuale Di Istruzione Tenute LubrificateDocument15 pagesWET - AT - AT - 003 - ENG - Manuale Di Istruzione Tenute LubrificateNadia WilsonNo ratings yet
- Confined Space: Hole Watch TrainingDocument36 pagesConfined Space: Hole Watch TrainingMalik JunaidNo ratings yet
- St. Augustine School of Nursing: Republic of The Philippines Department of Education SASN - Las PiñasDocument2 pagesSt. Augustine School of Nursing: Republic of The Philippines Department of Education SASN - Las PiñasCarl Joseph MasujerNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Practice 1Document3 pagesVocabulary Practice 1Phuong AnhNo ratings yet
- Monologue Speech in A Foreign Language LessonDocument3 pagesMonologue Speech in A Foreign Language LessonResearch ParkNo ratings yet
- SHSHA Report PresentationDocument27 pagesSHSHA Report PresentationPatrick JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Advanced Guide To Digital MarketingDocument43 pagesAdvanced Guide To Digital MarketingArpan KarNo ratings yet
- The Life of The Last Pharaoh of EgyptDocument16 pagesThe Life of The Last Pharaoh of EgyptShanelle BarrilNo ratings yet
- Material 01 - Human-Computer InteractionDocument8 pagesMaterial 01 - Human-Computer InteractionIlangmi NutolangNo ratings yet
- Reaction Order and Rate Law Expression Worksheet KeyDocument5 pagesReaction Order and Rate Law Expression Worksheet KeyLyra GurimbaoNo ratings yet
- Azure DevOps Engineer: Exam AZ-400: Azure DevOps Engineer: Exam AZ-400 Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps SolutionsFrom EverandAzure DevOps Engineer: Exam AZ-400: Azure DevOps Engineer: Exam AZ-400 Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Kali Linux - An Ethical Hacker's Cookbook - Second Edition: Practical recipes that combine strategies, attacks, and tools for advanced penetration testing, 2nd EditionFrom EverandKali Linux - An Ethical Hacker's Cookbook - Second Edition: Practical recipes that combine strategies, attacks, and tools for advanced penetration testing, 2nd EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Hackers & Painters: Big Ideas from the Computer AgeFrom EverandHackers & Painters: Big Ideas from the Computer AgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Linux for Beginners: Linux Command Line, Linux Programming and Linux Operating SystemFrom EverandLinux for Beginners: Linux Command Line, Linux Programming and Linux Operating SystemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Linux: The Ultimate Beginner's Guide to Learn Linux Operating System, Command Line and Linux Programming Step by StepFrom EverandLinux: The Ultimate Beginner's Guide to Learn Linux Operating System, Command Line and Linux Programming Step by StepRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Windows 11 Manual For Seniors: A Beginners Guide to Navigate Your Computer with Step-by-Step InstructionsFrom EverandWindows 11 Manual For Seniors: A Beginners Guide to Navigate Your Computer with Step-by-Step InstructionsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Java Professional Interview Guide: Learn About Java Interview Questions and Practise Answering About Concurrency, JDBC, Exception Handling, Spring, and HibernateFrom EverandJava Professional Interview Guide: Learn About Java Interview Questions and Practise Answering About Concurrency, JDBC, Exception Handling, Spring, and HibernateNo ratings yet
- The Linux Command Line Beginner's GuideFrom EverandThe Linux Command Line Beginner's GuideRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- Python Programming Illustrated For Beginners & Intermediates“Learn By Doing” Approach-Step By Step Ultimate Guide To Mastering Python: The Future Is Here!From EverandPython Programming Illustrated For Beginners & Intermediates“Learn By Doing” Approach-Step By Step Ultimate Guide To Mastering Python: The Future Is Here!Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- The Ultimate Kali Linux Book - Second Edition: Perform advanced penetration testing using Nmap, Metasploit, Aircrack-ng, and EmpireFrom EverandThe Ultimate Kali Linux Book - Second Edition: Perform advanced penetration testing using Nmap, Metasploit, Aircrack-ng, and EmpireNo ratings yet
- COBOL Basic Training Using VSAM, IMS and DB2From EverandCOBOL Basic Training Using VSAM, IMS and DB2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Kali Linux Intrusion and Exploitation CookbookFrom EverandKali Linux Intrusion and Exploitation CookbookRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Powershell: The ultimate beginner's guide to Powershell, making you a master at Windows Powershell command line fast!From EverandPowershell: The ultimate beginner's guide to Powershell, making you a master at Windows Powershell command line fast!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Mac Terminal Reference and Scripting PrimerFrom EverandThe Mac Terminal Reference and Scripting PrimerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Excel : The Ultimate Comprehensive Step-By-Step Guide to the Basics of Excel Programming: 1From EverandExcel : The Ultimate Comprehensive Step-By-Step Guide to the Basics of Excel Programming: 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Hacking with Kali Linux: A Step by Step Guide to Learn the Basics of Linux Penetration. What A Beginner Needs to Know About Wireless Networks Hacking and Systems Security. Tools Explanation IncludedFrom EverandHacking with Kali Linux: A Step by Step Guide to Learn the Basics of Linux Penetration. What A Beginner Needs to Know About Wireless Networks Hacking and Systems Security. Tools Explanation IncludedNo ratings yet
- Make Your PC Stable and Fast: What Microsoft Forgot to Tell YouFrom EverandMake Your PC Stable and Fast: What Microsoft Forgot to Tell YouRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- CompTIA Linux+/LPIC-1: Training and Exam Preparation Guide (Exam Codes: LX0-103/101-400 and LX0-104/102-400)From EverandCompTIA Linux+/LPIC-1: Training and Exam Preparation Guide (Exam Codes: LX0-103/101-400 and LX0-104/102-400)No ratings yet
- HACKING: Social Engineering Attacks, Techniques & PreventionFrom EverandHACKING: Social Engineering Attacks, Techniques & PreventionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Ubuntu Linux Toolbox: 1000+ Commands for Power UsersFrom EverandUbuntu Linux Toolbox: 1000+ Commands for Power UsersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Kali Linux for Beginners: A Step-by-Step Guide to Learn the Basics of Hacking and Security TestingFrom EverandKali Linux for Beginners: A Step-by-Step Guide to Learn the Basics of Hacking and Security TestingNo ratings yet
- Ubuntu 22.04 Essentials: A Guide to Ubuntu 22.04 Desktop and Server EditionsFrom EverandUbuntu 22.04 Essentials: A Guide to Ubuntu 22.04 Desktop and Server EditionsNo ratings yet