Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Detailed
Uploaded by
L Deepanti PunjabanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Detailed
Uploaded by
L Deepanti PunjabanCopyright:
Available Formats
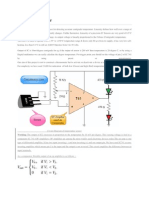
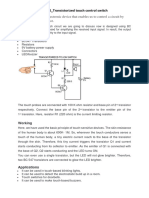
Working Explanation:
Working of this Smoke Detector Alarm Circuit is explained here. In this project, we have used
transistor operating properties to work this circuit as a smoke detector. As we already know that we
have used a BC547 NPN transistor which will turn on whenever it gets least 0.70v at its base terminal.
So, we have applied a Voltage Divider Circuit at its base. The voltage divider circuit consists of a
potentiometer and the LDR sensor. Ideally, whenever there is no smoke in the detector unit, the
forward bias applied to the transistor is grounded due to low resistance of LDR, as the light from the
LED makes internal resistance low of LDR. We’ve adjusted the potentiometer so that whenever there
is any smoke in the detector unit, the forward bias of the transistor triggers the next transistor that in
turn makes the buzzer sound.
Also, we’d used multimeter to set and correct the voltages applied to the base of first transistor, to
which sensor is attached.
Use of second transistor is to amplify the input signal (due to Darlington pair effect) and to switch
on/off buzzer. Although we may use single transistor but the sensitivity may also be decreased and
enough smoke has to be there for switching on/off transistor and to amplify the signal.
Regarding assembling of the project,
First, we need a cardboard, onto which we attached a printout of the circuit. Then, we mount the
components specified in the circuit diagram and make connections on the back side using jumper
wires. Then, we connect the battery and test/correct the voltages as described earlier, such that when
no smoke is there the buzzer doesn’t sounds and when traces of smoke enters the unit, the buzzer
sounds.
You might also like
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- Name: Muhammad Usama Reg: 796-FET/BSME/F18 Assignment Week 11 Course Title: Electronics Engineering (Ee-201)Document10 pagesName: Muhammad Usama Reg: 796-FET/BSME/F18 Assignment Week 11 Course Title: Electronics Engineering (Ee-201)Usama GulzarNo ratings yet
- EEE 111 ProjectsDocument8 pagesEEE 111 ProjectsAnik Saha Toni 1912619643No ratings yet
- Arduino Magnet LevitationDocument7 pagesArduino Magnet LevitationlorenaNo ratings yet
- Fire Alarm With Siren SoundDocument2 pagesFire Alarm With Siren Soundmanjeet kumarNo ratings yet
- Temperature SensorDocument5 pagesTemperature SensorAbhinav Madheshiya100% (1)
- Fire Alarm Circuit at Low CostDocument14 pagesFire Alarm Circuit at Low CostBRAHMA AAKUMAIIA0% (1)
- Color SensorDocument14 pagesColor SensorKarl Reinier Villadiego EraNo ratings yet
- Fire Detection Alarm SystemDocument5 pagesFire Detection Alarm Systemsmartxdigital marketNo ratings yet
- Et LR-1Document6 pagesEt LR-1idreesaqib12No ratings yet
- Report of IR Sensor ProjectDocument13 pagesReport of IR Sensor ProjectHammad Umer0% (2)
- Non-Contact AC Voltage Detector Using TransistorsDocument28 pagesNon-Contact AC Voltage Detector Using TransistorsH Aries OñaNo ratings yet
- Stereo VU MeterDocument3 pagesStereo VU Metersarantapodarusa4009No ratings yet
- Automatic Traffic Light Control SystemDocument4 pagesAutomatic Traffic Light Control SystemRajaMandapatiNo ratings yet
- Wireless DoorbellDocument20 pagesWireless Doorbellmujahed1987No ratings yet
- Wireless DoorbellDocument8 pagesWireless DoorbellnicklingatongNo ratings yet
- EEE202H Group4 (179-183) Project ReportDocument9 pagesEEE202H Group4 (179-183) Project ReportShamsul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Automatic Room Light Controller With Bidirectional Visitor CounterDocument24 pagesAutomatic Room Light Controller With Bidirectional Visitor CounterDANIEL WELDAYNo ratings yet
- Turn On Led Using LDRDocument5 pagesTurn On Led Using LDRNikhil KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Project in Industrial Electronics: Prepared By: Norvel Hez P. Chiu Adham Jay C. Taborada Jaime A. Tracarol JRDocument9 pagesProject in Industrial Electronics: Prepared By: Norvel Hez P. Chiu Adham Jay C. Taborada Jaime A. Tracarol JRRyan CireraNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document6 pagesPresentation 2Anik Saha Toni 1912619643No ratings yet
- Experiment: Title:-IR BlockerDocument14 pagesExperiment: Title:-IR BlockerOisin MaguireNo ratings yet
- Wireless DoorbellDocument7 pagesWireless DoorbellSuneel KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Fire Alarms 497Document6 pagesFire Alarms 497MohanNo ratings yet
- DISCUSSIONDocument3 pagesDISCUSSIONHarsha MadushanNo ratings yet
- CMPE 30094 - BSCPE 3-1: Logic Circuits and Design (Laboratory)Document7 pagesCMPE 30094 - BSCPE 3-1: Logic Circuits and Design (Laboratory)AngelicaNo ratings yet
- Wireless DoorbellDocument7 pagesWireless DoorbellAgnes NagyNo ratings yet
- Circuitpages Light Dark Activated RelayDocument14 pagesCircuitpages Light Dark Activated Relayalexwongks6118No ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 Block Diagram and Component DiscriptionDocument7 pagesChapter - 3 Block Diagram and Component DiscriptionHika TarikuNo ratings yet
- Building Sensors and Motors For The Handy Board: Connector Wiring TechniqueDocument8 pagesBuilding Sensors and Motors For The Handy Board: Connector Wiring Techniquepiyushji125No ratings yet
- Simple Emergency Light Circuit DiagramDocument20 pagesSimple Emergency Light Circuit DiagramHENRY SINGCOLNo ratings yet
- Automatic Street Light Control SystemDocument7 pagesAutomatic Street Light Control SystemAnjali SharmaNo ratings yet
- DidiDocument2 pagesDidiMercyNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 - L-9 - Touch Control Switch and LDR Based Relay CircuitDocument7 pagesUnit-2 - L-9 - Touch Control Switch and LDR Based Relay Circuitwebip33713No ratings yet
- University of Management and Technology Lahore School of Engineering Electrical Engineering DepartmentDocument9 pagesUniversity of Management and Technology Lahore School of Engineering Electrical Engineering DepartmentHammad ImranNo ratings yet
- ICL8038 Function GeneratorDocument6 pagesICL8038 Function Generatorvali dNo ratings yet
- Minor Project LPG Gas SensorDocument18 pagesMinor Project LPG Gas SensorHimanshu kumarNo ratings yet
- Touch Lamp Control DimmerDocument2 pagesTouch Lamp Control DimmerJoey TorresNo ratings yet
- Laporan 4 Simple Audio Amplifier PDFDocument9 pagesLaporan 4 Simple Audio Amplifier PDFAzman HanafiahNo ratings yet
- Electronics ProjectDocument9 pagesElectronics Projectlevi'cNo ratings yet
- Thermistor Temperature Sensing AlarmDocument2 pagesThermistor Temperature Sensing AlarmDark RiderNo ratings yet
- Thermistor Temperature Sensing AlarmDocument2 pagesThermistor Temperature Sensing AlarmPorkkodi SugumaranNo ratings yet
- Laser Light Door BellDocument16 pagesLaser Light Door Bellsahila sadafNo ratings yet
- Transistor Intercom System CircuitDocument8 pagesTransistor Intercom System CircuitchaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Aim of The Project To Make An Door AlarmDocument7 pagesAim of The Project To Make An Door Alarmpawan dhingraNo ratings yet
- Report of Project-1Document12 pagesReport of Project-103061341753 03061341753No ratings yet
- Alternating Current DetectorDocument5 pagesAlternating Current DetectorNeeraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Automatic Street LightDocument2 pagesAutomatic Street LightsaiNo ratings yet
- Railway Gate Control...............Document52 pagesRailway Gate Control...............sknagarNo ratings yet
- Clap Switching PDFDocument13 pagesClap Switching PDFSurendra UppariNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: Introduction: Figure 1.1: Block Diagram of Applaud SwitchDocument9 pagesChapter-1: Introduction: Figure 1.1: Block Diagram of Applaud SwitchGaurav MishraNo ratings yet
- That You Read All The Background Information of This Laboratory BEFORE Proceding With The ExperimentDocument14 pagesThat You Read All The Background Information of This Laboratory BEFORE Proceding With The ExperimentRajith MohananNo ratings yet
- BuzzerDocument6 pagesBuzzerKENEDY MWALUKASANo ratings yet
- Reg-Sv: Light Dimming RegulationDocument8 pagesReg-Sv: Light Dimming Regulationkaushik4endNo ratings yet
- A Simple Technique To Measure The Light Intensity Using Arduino and LDRDocument2 pagesA Simple Technique To Measure The Light Intensity Using Arduino and LDRLuis DiazNo ratings yet
- K 48Document5 pagesK 48Aydin BatmazNo ratings yet
- Voltage Detector Using Any 555 ICDocument8 pagesVoltage Detector Using Any 555 ICPiyush chaudhari100% (2)
- Automatic Pump ONDocument5 pagesAutomatic Pump ONVijay KrishnaNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument14 pagesReportAkash SiboNo ratings yet
- Photo-Coupler and Touch Alarm Switch: Experiment #9Document10 pagesPhoto-Coupler and Touch Alarm Switch: Experiment #9Taha Khan 4ANo ratings yet
- EL001Document3 pagesEL001L Deepanti PunjabanNo ratings yet
- POTAINDocument2 pagesPOTAINL Deepanti PunjabanNo ratings yet
- Automatic BrakingDocument50 pagesAutomatic BrakingL Deepanti PunjabanNo ratings yet
- Mech 2019Document2 pagesMech 2019Anil TandonNo ratings yet
- CS ProjectsDocument1 pageCS ProjectsL Deepanti PunjabanNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1L Deepanti PunjabanNo ratings yet
- RPi Walking StickDocument4 pagesRPi Walking StickL Deepanti PunjabanNo ratings yet
- RB 1Document3 pagesRB 1L Deepanti PunjabanNo ratings yet
- Automatic BrakingDocument50 pagesAutomatic BrakingL Deepanti PunjabanNo ratings yet
- French SymbolsDocument2 pagesFrench SymbolsL Deepanti PunjabanNo ratings yet
- Automatic BrakingDocument50 pagesAutomatic BrakingL Deepanti PunjabanNo ratings yet
- Biogas PlantDocument3 pagesBiogas PlantL Deepanti PunjabanNo ratings yet
- Automatic BrakingDocument50 pagesAutomatic BrakingL Deepanti PunjabanNo ratings yet
- DetailedDocument1 pageDetailedL Deepanti PunjabanNo ratings yet
- Bottle Filling Station Using PLC AutomationDocument4 pagesBottle Filling Station Using PLC AutomationL Deepanti PunjabanNo ratings yet
- Automatic BrakingDocument50 pagesAutomatic BrakingL Deepanti PunjabanNo ratings yet
- Automatic BrakingDocument50 pagesAutomatic BrakingL Deepanti PunjabanNo ratings yet
- The Papermaking ProcessDocument4 pagesThe Papermaking ProcessL Deepanti PunjabanNo ratings yet
- IOT Air PollutionDocument15 pagesIOT Air PollutionL Deepanti PunjabanNo ratings yet
- AxisDocument3 pagesAxisL Deepanti PunjabanNo ratings yet