Professional Documents
Culture Documents
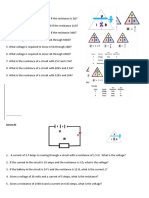
WS1 - Conversion
Uploaded by
shiva nayakCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
WS1 - Conversion
Uploaded by
shiva nayakCopyright:
Available Formats
Conversion IGCSE
Powers of Ten
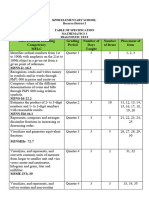
Common Name Billionth Millionth Thousandth Hundred Thousand Million Billion Trillion
Symbol n μ m c k M G T
Prefix Nano Micro Milli Centi Kilo Mega Giga Tera
Multiple 10-9 10 -6
10-3
10-2
103 106 109 1012
This table shows the names of the most common prefixes we meet in physics.
For example 1 kilometre is equal to 1 000 metres, and 1 microgram is equal to
1/1000th of a gram. Use the table to convert the following.
1. Convert the following into metres:
a. 10 cm _____________________________________________
b. 5 mm _____________________________________________
c. 1 Mm _____________________________________________
2. Convert the following into kilograms:
a. 2000 g _____________________________________________
b. 1 μg _____________________________________________
c. 3 mg _____________________________________________
3. Convert the following into newtons:
a. 2.3 kN _____________________________________________
b. 20 GN _____________________________________________
c. 300 mN _____________________________________________
4. Convert the following into watts:
a. 60 kW _____________________________________________
b. 45 MW _____________________________________________
c. 0.1 GW _____________________________________________
5. Convert the following:
a. 0.3 kJ into joules. ____________________________________
b. 90 mA into amps. ____________________________________
c. 800 kHz into hertz. ____________________________________
d. 1 nC into coulombs. ____________________________________
Conversion IGCSE
Squares and Cubes
The above method works perfectly for most of the situations we come across in
physics. When we meet squares and cubes, however, we have to be careful.
Example: How many square centimetres are there in one square metre?
1m
The box shows a 1 m x 1 m square, i.e. 1 m2.
We know 1 m is equal to 100 cm, so the box is also
1m 100 cm 100 cm x 100 cm, i.e. 10 000 cm2.
Therefore, 1 m2 is equal to 10 000 cm2.
100 cm
6. Convert the following into square centimetres:
a. 5 m2 _____________________________________________
b. 0.5 m2 _____________________________________________
7. Convert the following into square metres:
a. 100 cm2 _____________________________________________
b. 30 cm2 _____________________________________________
Example: How many cubic centimetres are there in one cubic metre?
1m
The box shows a 1 m x 1 m x 1 m cube, i.e. 1 m3.
1m
We know 1 m is equal to 100 cm, so the box is also
100 cm 100 cm x 100 cm x 100 cm, i.e. 1 000 000 cm3.
1m
100 cm Therefore, 1 m3 is equal to 1 000 000 cm3.
100 cm
8. Convert the following into cubic centimetres:
a. 2 m3 _____________________________________________
b. 50 m3 _____________________________________________
9. Convert the following into cubic metres:
a. 500 cm3 _____________________________________________
b. 1 cm3 _____________________________________________
10. How many cubic millimetres would fit in 1 m3?
Conversion IGCSE
Powers of Ten
Common Name Billionth Millionth Thousandth Hundred Thousand Million Billion Trillion
Symbol n μ m c k M G T
Prefix Nano Micro Milli Centi Kilo Mega Giga Tera
Multiple 10-9 10 -6
10-3
10-2
103 106 109 1012
This table shows the names of the most common prefixes we meet in physics.
For example 1 kilometre is equal to 1 000 metres, and 1 microgram is equal to
1/1000th of a gram. Use the table to convert the following.
1. Convert the following into metres:
a. 10 cm 0.1 m
b. 5 mm 0.005 m or 5x10-3 m
c. 1 Mm 1 000 000 m or 1x106 m
2. Convert the following into kilograms:
a. 2000 g 2 kg
b. 1 μg 0.000001 kg or 1x10-6 kg
c. 3 mg 0.003 kg or 3x10-3 kg
3. Convert the following into newtons:
a. 2.3 kN 2300 N
b. 20 GN 20 000 000 000 N or 20x109 N
c. 300 mN 0.3 N or 300x10-3 N
4. Convert the following into watts:
a. 60 kW 60 000 W or 60x103 W
b. 45 MW 45 000 000 W or 45x106 W
c. 0.1 GW 100 000 000 W or 1.0x108 W
5. Convert the following:
a. 0.3 kJ into joules. 300 J
b. 90 mA into amps. 0.090 A or 90x10-3 A
c. 800 kHz into hertz. 800 000 Hz or 800x103 Hz
d. 1 nC into coulombs. 0.000 000 001 C or 1.0x10-9 C
Conversion IGCSE
Squares and Cubes
The above method works perfectly for most of the situations we come across in
physics. When we meet squares and cubes, however, we have to be careful.
Example: How many square centimetres are there in one square metre?
1m
The box shows a 1 m x 1 m square, i.e. 1 m2.
We know 1 m is equal to 100 cm, so the box is also
1m 100 cm 100 cm x 100 cm, i.e. 10 000 cm2.
Therefore, 1 m2 is equal to 10 000 cm2.
100 cm
6. Convert the following into square centimetres:
a. 5 m2 50 000 cm2
b. 0.5 m2 5 000 cm2
7. Convert the following into square metres:
a. 100 cm2 0.01 m2
b. 30 cm2 0.003 m2
Example: How many cubic centimetres are there in one cubic metre?
1m
The box shows a 1 m x 1 m x 1 m cube, i.e. 1 m3.
1m
We know 1 m is equal to 100 cm, so the box is also
100 cm 100 cm x 100 cm x 100 cm, i.e. 1 000 000 cm3.
1m
100 cm Therefore, 1 m3 is equal to 1 000 000 cm3.
100 cm
8. Convert the following into cubic centimetres:
a. 2 m3 2 000 000 m3
b. 50 m3 50 000 000 m3
9. Convert the following into cubic metres:
a. 500 cm3 0.0005 m3 or 5x10-4 m3
b. 1 cm3 0.000 001 m3 or 1x10-6 m3
10. How many cubic millimetres would fit in 1 m3? 1000 x 1000 x 1000
= 1 000 000 000 mm3
You might also like
- 0455 Example Candidate Responses Paper 2 IGCSEDocument41 pages0455 Example Candidate Responses Paper 2 IGCSEwaihon.pang2011No ratings yet
- EfficiencyDocument2 pagesEfficiencyDanielGuimarãesCosta100% (1)
- Computer Science P2Document16 pagesComputer Science P2Farhan HossainNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/02Document18 pagesCambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/02Dhrisha GadaNo ratings yet
- Organisation of Cells (2.1.2) CIE IGCSE Biology Revision Notes 2023 Save My Exams 6Document1 pageOrganisation of Cells (2.1.2) CIE IGCSE Biology Revision Notes 2023 Save My Exams 6Ruchika Jha100% (1)
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/22Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/22jad obaidNo ratings yet
- Lights atDocument22 pagesLights atantonylukNo ratings yet
- Ss 1 Further Mathematics Vectors Lesson 7Document2 pagesSs 1 Further Mathematics Vectors Lesson 7Adio Babatunde Abiodun Cabax100% (1)
- Worksheet Work 11 JanuaryDocument6 pagesWorksheet Work 11 JanuaryPaul BugejaNo ratings yet
- Unit 14 (Final) PDFDocument7 pagesUnit 14 (Final) PDFआई सी एस इंस्टीट्यूटNo ratings yet
- Measuring Instruments & Significant FiguresDocument16 pagesMeasuring Instruments & Significant FiguresPraphul MalolNo ratings yet
- Ial WPH05 01 Nov19 PDFDocument28 pagesIal WPH05 01 Nov19 PDFNovado San CafayreNo ratings yet
- Probability & Statistics 1: Cambridge International AS & A Level MathematicsDocument122 pagesProbability & Statistics 1: Cambridge International AS & A Level Mathematicsmh874sw6zpNo ratings yet
- Chapter08 Deformation of Solids SsDocument6 pagesChapter08 Deformation of Solids SseltytanNo ratings yet
- Properties of Matter and Materials WorksheetDocument16 pagesProperties of Matter and Materials Worksheetrashmi_harryNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits 2 QPDocument12 pagesElectric Circuits 2 QPAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: 2048/12 Religious Studies (Bible Knowledge)Document4 pagesCambridge O Level: 2048/12 Religious Studies (Bible Knowledge)Ammar FaisalNo ratings yet
- Igcse Business Studies Exam Practice Questions AnswersDocument2 pagesIgcse Business Studies Exam Practice Questions AnswersJasnika kaur SethiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/42Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/42Desire KandawasvikaNo ratings yet
- Pendulum ProblemsDocument2 pagesPendulum ProblemsLavander Blush100% (1)
- 0625 Igcse Physics 22Document237 pages0625 Igcse Physics 22Vinod R100% (1)
- Answers To End-Of-Chapter QuestionsDocument2 pagesAnswers To End-Of-Chapter QuestionsAjay LakshmananNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Biology revision worksheetDocument3 pagesGrade 7 Biology revision worksheetRenee DisaNo ratings yet
- O.level Human Bio Edexcel Past Papers Paper 1 2019 - 2020Document68 pagesO.level Human Bio Edexcel Past Papers Paper 1 2019 - 2020Tamer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Answers To End-Of-Chapter QuestionsDocument2 pagesAnswers To End-Of-Chapter Questionsjn hgvhvhnmNo ratings yet
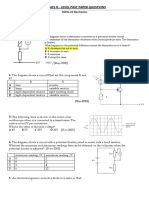
- Level Past Paper Questions - Physics O: TOPIC-22 Electronics PAPER-1 Multiple ChoiceDocument10 pagesLevel Past Paper Questions - Physics O: TOPIC-22 Electronics PAPER-1 Multiple Choiceelty TanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1.2bDocument5 pagesWorksheet 1.2bNurulAinMatAron100% (1)
- Z Notes Maths 2023-25Document16 pagesZ Notes Maths 2023-25Ali AsifNo ratings yet
- GCSE Percentages Exercise 2 - Determining percentages as fractions of amountsDocument4 pagesGCSE Percentages Exercise 2 - Determining percentages as fractions of amountsSally VakhtangishviliNo ratings yet
- Upper and Lower Bounds: Exam-Type Questions A1 A2 A3 A4Document2 pagesUpper and Lower Bounds: Exam-Type Questions A1 A2 A3 A4Nayem Hossain Hemu100% (1)
- English Language: 8700/2 - Paper 2 Writers' Viewpoints and Perspectives Mark SchemeDocument17 pagesEnglish Language: 8700/2 - Paper 2 Writers' Viewpoints and Perspectives Mark SchemeT SolomonNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Introduction To Rate Law StudentDocument6 pages5.2 Introduction To Rate Law StudentSyed RazaNo ratings yet
- Energy Stores PowerpointDocument17 pagesEnergy Stores PowerpointT. Christabel Vijitha100% (1)
- Upper and Lower Bounds 112594Document12 pagesUpper and Lower Bounds 112594Moamen ElkayalNo ratings yet
- Sets & Venn Diagrams Question Paper 1Document10 pagesSets & Venn Diagrams Question Paper 1Mohamed GamilNo ratings yet
- Body Systems Worksheet Grade 4Document3 pagesBody Systems Worksheet Grade 4Rabab KashifNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE / IGCSE (9-1) First Language English 0500 / 0990Document7 pagesCambridge IGCSE / IGCSE (9-1) First Language English 0500 / 0990Amalia ZabalaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Paper 4 PracticeDocument27 pagesIGCSE Physics Paper 4 PracticealfaazmcsNo ratings yet
- Exam PapersDocument32 pagesExam PapersCraft CityNo ratings yet
- Hooke's Law QPDocument10 pagesHooke's Law QPNurulAinMatAronNo ratings yet
- Momentum QPDocument6 pagesMomentum QPXandws -IOS tips and trick and gamingNo ratings yet
- 9225 International Gcse Business Question Paper 1 v1.0Document24 pages9225 International Gcse Business Question Paper 1 v1.0Kenny Kwok100% (1)
- 10 ElectricityDocument22 pages10 Electricity이다연No ratings yet
- Week 5 AS 11gr HomeworkDocument4 pagesWeek 5 AS 11gr Homeworkaisaverdieva04No ratings yet
- CRPF PUBLIC SCHOOL FINAL TERM MATHEMATICS EXAM CLASS 3Document6 pagesCRPF PUBLIC SCHOOL FINAL TERM MATHEMATICS EXAM CLASS 3RajivNo ratings yet
- Pressure 2022-2023 18.2Document7 pagesPressure 2022-2023 18.2JAKE PAULNo ratings yet
- 86342059-IGCSE-Physics-Density 1Document12 pages86342059-IGCSE-Physics-Density 1Vedant NavaniNo ratings yet
- Revision NotesDocument45 pagesRevision NotesDalia SaqqaNo ratings yet
- Physics Alternative To Practical (5054) OCT-NOV 2008Document12 pagesPhysics Alternative To Practical (5054) OCT-NOV 2008PEACE_29100% (4)
- S3 - Waves Revision GuideDocument2 pagesS3 - Waves Revision GuideLix FNNo ratings yet
- Transformation NotesDocument12 pagesTransformation NotespapersculptorNo ratings yet
- Second Language UrduDocument5 pagesSecond Language Urdumstudy123456No ratings yet
- Upper and Lower Bounds Higher GCSE Exam Style QuestionsDocument1 pageUpper and Lower Bounds Higher GCSE Exam Style Questionsdanexxo100% (1)
- Electric Circuits QPDocument12 pagesElectric Circuits QPishaNo ratings yet
- WS - Unit ConversionsDocument5 pagesWS - Unit Conversionsvictoria kairooNo ratings yet
- Physics Worksheet AS Level - ConversionDocument4 pagesPhysics Worksheet AS Level - ConversionHolly Maria Casson0% (1)
- Chapter 26 - MeasuresDocument24 pagesChapter 26 - MeasuresJMGNo ratings yet
- 1 To Study Various Factors On Which The Internal resistanceEMF of A Cell Depends.Document11 pages1 To Study Various Factors On Which The Internal resistanceEMF of A Cell Depends.shiva nayak100% (4)
- 11 A CTDocument1 page11 A CTshiva nayakNo ratings yet
- 11 A CTDocument1 page11 A CTshiva nayakNo ratings yet
- Comparing FieldsDocument9 pagesComparing Fieldsshiva nayakNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1shiva nayakNo ratings yet
- JAHSGcfuqav WFYI3Document1 pageJAHSGcfuqav WFYI3shiva nayakNo ratings yet
- Motion in A CircleDocument5 pagesMotion in A Circleshiva nayakNo ratings yet
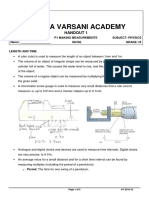
- Surya Varsani Academy: WorksheetDocument4 pagesSurya Varsani Academy: Worksheetshiva nayakNo ratings yet
- Final Exam TT Cbse 2019-20Document6 pagesFinal Exam TT Cbse 2019-20shiva nayakNo ratings yet
- Forces and Moments EquilibriumDocument4 pagesForces and Moments Equilibriumshiva nayakNo ratings yet
- Motion in A CircleDocument5 pagesMotion in A Circleshiva nayakNo ratings yet
- Surya Varsani Academy: Circular MotionDocument1 pageSurya Varsani Academy: Circular Motionshiva nayakNo ratings yet
- p2 Describing MotionDocument5 pagesp2 Describing Motionshiva nayakNo ratings yet
- Surya Varsani Academy: Worksheet 1 OscillationsDocument7 pagesSurya Varsani Academy: Worksheet 1 Oscillationsshiva nayakNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1shiva nayakNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work - Science Stage 9: Term 1 Term 2 Term 3Document52 pagesScheme of Work - Science Stage 9: Term 1 Term 2 Term 3shiva nayakNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work Science Stage 9.v1 Tcm143 353968Document50 pagesScheme of Work Science Stage 9.v1 Tcm143 353968shiva nayakNo ratings yet
- Particle Arrangement and MovementDocument4 pagesParticle Arrangement and Movementshiva nayakNo ratings yet
- Particle Arrangement and MovementDocument4 pagesParticle Arrangement and Movementshiva nayakNo ratings yet
- p1 Making MeasurementsDocument2 pagesp1 Making Measurementsshiva nayakNo ratings yet
- ConstructorDocument23 pagesConstructorrina mahureNo ratings yet
- Stenography Module ContentDocument15 pagesStenography Module ContentIrish OccenoNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument112 pagesUnit IrajanNo ratings yet
- CSEC IT Workshop Part 2 - ADocument20 pagesCSEC IT Workshop Part 2 - ATeck Ismael0% (2)
- MAPEH 5 Variations of TempoDocument10 pagesMAPEH 5 Variations of TempoLea SanchezNo ratings yet
- Laporan Modul 3Document12 pagesLaporan Modul 3IqbalNo ratings yet
- HSBC Bank Message Implementation GuideDocument60 pagesHSBC Bank Message Implementation GuideKe Rong ChoiNo ratings yet
- C SharpDocument21 pagesC SharpNaveen ReignsNo ratings yet
- Fractions Decimals PercentageDocument91 pagesFractions Decimals PercentageDaniel PendonNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 4 Maths Revision Worksheet (124) - Metric MeasuresDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 4 Maths Revision Worksheet (124) - Metric MeasuresGiridhar Ragavasimhan67% (3)
- Compiler Construction Chapter 6Document111 pagesCompiler Construction Chapter 6HammadHussainNo ratings yet
- List of Jōyō KanjiDocument138 pagesList of Jōyō KanjiitsnaptimeleviNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic MathDocument7 pagesDiagnostic MathArdelina CorcueraNo ratings yet
- Trace N PDFDocument15 pagesTrace N PDFFilip MicleaNo ratings yet
- Assambly ch03Document33 pagesAssambly ch03Mypdfsite100% (1)
- Arrays and StringsDocument56 pagesArrays and StringsAAsfawNo ratings yet
- Principle of Programming Language: Biyani's Think TankDocument154 pagesPrinciple of Programming Language: Biyani's Think Tanksunita sainiNo ratings yet
- Natural Disasters PunctuationDocument2 pagesNatural Disasters Punctuationகவிதா வேலுNo ratings yet
- Particella 04 - Corno InglésDocument4 pagesParticella 04 - Corno InglésJose SuñerNo ratings yet
- Writing Numbers Rules PDFDocument3 pagesWriting Numbers Rules PDFGurpreet MaanNo ratings yet
- ASME Conference 2011 Worksheets & FlashcardsDocument12 pagesASME Conference 2011 Worksheets & FlashcardsWoobly100% (1)
- J S S 1 Maths 1st Term E-Note 2017Document39 pagesJ S S 1 Maths 1st Term E-Note 2017preciousNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Form 1 - Chapter 1Document47 pagesMathematics Form 1 - Chapter 1SABARIVAASAN A/L SEELAN Moe100% (1)
- Lab 04 - Classes and Object C#Document7 pagesLab 04 - Classes and Object C#Muhammad AnasNo ratings yet
- Allegro Appassionato For Euphonium (Recital)Document17 pagesAllegro Appassionato For Euphonium (Recital)Blott2000100% (3)
- MIT6 004s09 Tutor01 SolDocument13 pagesMIT6 004s09 Tutor01 SolAbhijith RanguduNo ratings yet
- HTML and Css ManualDocument157 pagesHTML and Css ManualFS20IF015No ratings yet
- MCA1020 Programming With CDocument5 pagesMCA1020 Programming With CrakeshNo ratings yet
- Oops ConceptDocument55 pagesOops ConceptSiddharthSharmaNo ratings yet