Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RBT Saq
RBT Saq
Uploaded by
Relangi SrinivasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
RBT Saq
RBT Saq
Uploaded by
Relangi SrinivasCopyright:
Available Formats
ROBOTICS IV B.
Tech I Sem (MECH) R15
UNIT I
1. Define a Robot?
RIA defines a robot as a “programmable, multifunction manipulator designed to Move
materials, parts, tools or special devices through variable programmed motions for the
performance of the variety of task”.
2. What is mean by automation?
Automation is a technology that is concerned with the use of electronic mechanical and
computer based system in the operation control and production.
3. What is a robot?
Robot is an
Electro-mechanical device
Perform various task
May be human controlled or automated.
It finds its uses in all aspects of our life
4. What are the rules of robot?
Do not harm being
Obey human being
Protects itself from harm.
5. Why a robot used?
a. To reduce production cost
Fast
Accurate
Difficulties in human nature
b. To avoid 3-D jobs
Dirty
Dangerous
Difficult
6. What is meant by robot anatomy?
Robot anatomy means study of structure of robot. Manipulator is constructed of a series of joints &
links. A joint provides relative motion between the input link and the output link. Each joint provides
the robot with one degree of freedom.
7. Name the commonly used robot configuration system?
The commonly used robot configuration systems are
Cartesian coordinate system
Cylindrical coordinate system
Polar or spherical coordinate system
Revolute coordinate system
8. What are the types of automation?
Fixed automation
Programmable automation
Flexible automation
Malla Reddy College of Engineering and Technology (MRCET) Page 1
ROBOTICS IV B.Tech I Sem (MECH) R15
9. Write are the Benefits of industrial automation?
Improved product quality
Improved safety
Increased manufacturing flexibility
Improved operation reliability
Improved decision making
10. List the different types of robots?
Robotic Manipulator
Wheeled Mobile Robots
Legged Robots
Underwater Robots
Flying Robots
Robot Vision
Artificial Intelligence
Industrial Automation
11. Write Asimov’s laws of robotics?
Three rules written by science fiction author Isaac Asimov and later expanded upon. These
rules are built in to almost all positronic robots appearing in his fiction and cannot be bypassed.
The rules are introduced in his 1942 short story Runaround although they were foreshadowed in
a few earlier stories.
The Three Laws of Robotics are as follows:
I. A robot may not injure a human being or, through inaction, allow a human being to
come to harm.
II. A robot must obey any orders given to it by human beings, except where such orders
would conflict with the First Law.
III. A robot must protect its own existence as long as such protection does not conflict
with the First or Second Law.
12. What is mean by workspace?
The space in which the end point of the robot arm is capable of operating is called as a workspace in
other words reachabillity of robot arm is known as workspace.
13. What is mean by work volume?
The volume of the space swept by the robot arm is called work volume
14. What is meant by work envelop?
The work envelop is described by the surface of the workspace.
15. What is meant by a accuracy of robot?
The robot’s ability to reach a reference point within the robot’s full work volume is
known as accuracy of robot.
Malla Reddy College of Engineering and Technology (MRCET) Page 2
ROBOTICS IV B.Tech I Sem (MECH) R15
16. What is meant by pay load capacity of robot?
The maximum load which can be carried by the manipulator at low or normal speed
17. What is meant by precision of robot?
It is the smallest increment of motion for which the robot can be controlled
18. What is repeatability of robot?
Repeatability refers to robot’s ability to return to the programmed point when it is
commanded to do so.
19. What is meant by quality of robot?
A robot is said to be high quality when the precision and accuracy is more
20. Classify the motion control of Robot arm?
Limited sequence control
Point to point control
Continuous path control
Intelligent control
21. What are the Subsystems of industrial robot?
Actuators
Transmission systems
Power supplies & power storage system
Sensors
Microprocessors & controllers
Algorithms & softwares (higher level & lower level)
22. What is meant Degrees Of Freedom?
It is described as one of the variables required to define the motion of a body in
space. Each joint in a robotic system gives the robot one degree of freedom.
23. How much encoder need for measure 45 degree of freedom?
45 encoders
24. What are the Advantages and disadvantages of robot?
Advantages
Greater flexibility, reprogrammability, adjustable kinematics dexterity
Greater response time to inputs than humans
Improved product quality
Maximize capital intensive equipment in multiple work shifts.
Disadvantages
Replacement of human labour
More unemployment
Significant retraining costs for both unemployed and users of new technology
Advertising technology does not always disclose some of the hidden disadvantages
Malla Reddy College of Engineering and Technology (MRCET) Page 3
ROBOTICS IV B.Tech I Sem (MECH) R15
25. What are the limitations of robot?
Assembly dexterity does not match that of human beings, particularly where eye-
hand coordination required.
Payload to robot weight ratio is poor, often less than 5%
Robot structural configurations often constrain joint limits and thus the work volume
Work volume can be constrained even further when parts of substantial size are
picked up when tooling/sensors added to the robot
The robot repeatability and/or accuracy can constrain the range of potential
application
26. Write about the origin of Robot ?
In 1495, Leonardo da Vinci drew up plans for a mechanical man, and the Byzantine Emperor,
suggested the poet W.B. Yeats, possessed a tree in whose golden branches artificial birds were
rumored to sing .
Only in this century did the word robot see its advent. Its etymology can be traced to the
Czech robota, meaning drudgery or slave labor, first used to describe artificial workers in the
1920’s play, Rossum’s Universal Robots, by Karel Capek [3]. Created to help humans, the robots
eventually take over the world. Another early rendition of robots was Fritz Lang’s Weimar
film, Metropolis.
A similar theme emerges in Isaac Asimov’s I, Robot, a series of short stories exploring the
possibilities of robot consciousness and their interactions with humans. Surprisingly forward-
seeing for 1950, the book ends with the eerie sense that the giant electronic brains the robots
eventually construct are somehow extrapolating and channeling human destiny
27. Name the important specifications of an industrial robot.
Accuracy
Repeatability
Degree of Freedom
Resolution
Envelope
28. Define base and tool Coordinate system.
A tool coordinates definition system capable of easily obtaining a transformation matrix for
defining a tool coordinates system of a robot. The tool coordinates system at the 0° position of the
robot is rotated around each axis so that the tool coordinates system becomes parallel to a base
coordinates system.
Malla Reddy College of Engineering and Technology (MRCET) Page 4
ROBOTICS IV B.Tech I Sem (MECH) R15
29. Define an Industrial Robot.
An industrial robot is an automatically controlled, reprogrammable, multipurpose manipulator
programmable in three or more axes. A programmable mechanical device that is used in place of
a person to perform dangerous or repetitive tasks with a high degree of accuracy.
30. What are the three degrees of freedom associated with the arm and body motion?
Right (or) left movement (X-axis motion)
In and out movement (Y-axis motion)
Vertical movement (Z-axis motion)
31. What is meant by pitch, yaw and roll?
Pitch is rotation around the X axis, yaw is around the Y axis, and roll is around the Z axis. Yaw is
side to side swinging around an axis. Pitch is up and down movement about an axis and roll is
rotatory motion about an axis.
32. Explain the types of rotary joint notations
Rotational joint (type R)
Twisting joint (type T)
Revolving joint (type V)
Translational
UNIT II
1. Name the important parts of harmonic drive?
The important parts of harmonic drive are
Rigid circular spline with internal teeth
Flex spline with external teeth
Elliptical wave generation
2. State the advantages and limitation of a hydraulic drive?
Advantages:
It gives greater speed and strength
It gives highest power to weight ratio
It is used for heavy pay loads
It can be used for large working envelope
It is safe and reliable to work in wet and dirty conditions
It can be used in hazardous environment.
Disadvantages
It occupies more space
Maintenance should be done regularly
Malla Reddy College of Engineering and Technology (MRCET) Page 5
ROBOTICS IV B.Tech I Sem (MECH) R15
3. What are the types of hydraulic actuator?
The types of hydraulic actuators are
Linear hydraulic actuator
I. Single acting cylinder
II. Double acting cylinder
III. Double acting double rod cylinder
Hydraulic rotary actuator
I. Gear motor
II. Vane motor
III. Piston motor
4. What are the types of encoder?
I. Linear encoder
II. Rotary encoder
Absolute encoder
Incremental encoder
5. What is frame grabber?
It is hardware device used to capture and store the digital image.
6. What is the common imaging device used for robot vision system?
Block and White vidicon camera, charge coupled devices, solid state camera, charge injection
device.
7. What is pixel?
Picture elements are also known as pixels.
8. What is the frame of the vision data?
The digital image of the camera is called frame of the vision data
9. What is segmentation?
Segmentation is the method to group area of an image having similar characteristics or
features into distinct entities representing part of the image.
10. What is thresholding?
Thresholding is a binary conversion technique in which each pixel is converted into a binary
value either black or white.
11. What is region growing?
Region growing is collection of segmentation techniques in which pixels are grouped in
regions called grid elements based on attribute similarities
12. What are the functions of machine vision system?
Sensing and digitizing image data
Image processing and analysis
Application
Malla Reddy College of Engineering and Technology (MRCET) Page 6
ROBOTICS IV B.Tech I Sem (MECH) R15
13. What is application of machine vision system?
Inspection
Identification
Visual servoing and navigation
14. What is sensor?
A sensor is an electrical device that transfers a physical phenomenon into an electrical signal.
Sensors in robotics are used for both the internal feedback control and external interaction with
the outside environment
15. What is transducer?
Transducer is a device which converts the one form of the energy into another form without
changing the information content.
16. What are the basic classifications of sensors?
Tactile sensors
Proximity sensors
Range sensors
Voice sensors etc
17. What are the desirable features of sensors? Nov/Dec-2013
1. Good Accuracy, 2. High Precision, 3. Wide operating range, 4. Instant speed of response,
5. Good Repealibility, 6. Low cost,
and easy in operation
18. What is the tactile sensor? May/june2013 Nov/Dec-2013
Tactile sensor is a device which indicates the contact between themselves and some other
solid objects.
19. List the different type of tactile sensor?
Digital(Touch) sensor
Analogue (force) sensor
20. What is touch sensor?
Sensor which senses the presence or absence of the object by having physical contact
between the object
21. List the component of the force wrist?
Metallic frame
Bracket for tool mounting
Strain gauges
Malla Reddy College of Engineering and Technology (MRCET) Page 7
ROBOTICS IV B.Tech I Sem (MECH) R15
22. What is a tactile array sensor?
Tactile array sensor is a special type of force sensor composed of a matrix of force sensing
elements.
23. What is the proximity sensor?
Sensor which senses the presence or absence of the object without having physical contact
between the object
24. What are the classifications of a proximity sensor?
Inductive sensor
Capacitive sensor
Ultrasonic sensor
Magnetic sensor
25. What is a range sensor?
Sensor which sense the range of the object
26. What is a voice sensor?
It is advanced sensor system used to communicate commands or information orally to robot.
27. What is a vision sensor?
It is a advanced sensor system used in conjunction with pattern reorganization and other
technique to view and interpret event occurring in the robot work space.
28. What is potentiometer?
Potentiometer is an electrical meter to measure the unknown voltage.
29. What is inspection?
It is quality control operation in which the checking of part assembly or products for
conformance to certain criteria is specifying by the design engineering department.
30. What is meant by quantisation?
Each sampled discrete time voltage level is assigned to a finite no of amplitude levels. These
amplitude levels correspond to gray scale used in the system. The predefined amplitude levels are
characteristic to a particular A to D converter and consist of discrete values of voltage levels is
defined by
Number of quantisation levels = 2 power n
Where n is the no of bits of the A/D converter
31. What is meant by encoding?
Encoding is defined as the representation of an amplitude level by a binary digit sequence.
32. What is meant by sampling?
The given analog signal is sampled periodically to obtained a series of discrete signals.
Malla Reddy College of Engineering and Technology (MRCET) Page 8
ROBOTICS IV B.Tech I Sem (MECH) R15
33. What is the function of Gearing in a Robot?
To vary the speed of manipulator motion driven by actuating systems
34. What are the advantages of fiber optics?
Speed of transmitting data will be high
Loss of data is reduced
35. Compare Hydraulic and Puematic drives .
36. What is gear ratio?
Ratio of No of teeth driven gear by no of teeth driving gear
37. Classified different types of stepper motor?
Variable reluctance motors ( soft steel rotor)
Permanent Magnet (PM) stepper motor
Hybrid Stepper Motor
UNIT III
Two marks
1. Define End effector:
End effector is a device that is attached to the end of the wrist arm to perform specific task.
2. What is meant by manipulator?
Manipulator is a machine has a function similar to those of the human upper limbs and moves an
object spatially from one location to another.
Malla Reddy College of Engineering and Technology (MRCET) Page 9
ROBOTICS IV B.Tech I Sem (MECH) R15
3. Compare Electronic and pneumatic manipulator
ELECTRONIC PNEUMATIC
High precision Low precision
Speed of response is quick Slow response
Compact in size Huge size hence space occupied is large
Low cost less maintenance Maintenance is required often
4. What is Repeatabilty
It is the ability of a robot to achieve the target point after the process completes for cyclic process
5. Sketch and name the parts of manipulator
6. Give some example of robot End effector:
Gripper
Tools
Welding equipment’s
End of arm tooling(EOAT)
7. What is meant by gripper?
Gripper is a End effector which can hold or grasp the object
8. What are the types of gripper?
Magnetic gripper
Mechanical gripper
Hooking gripper
Vacuum gripper
9. What is a stripping device?
A device used to remove workspace from the magnetic gripper
Malla Reddy College of Engineering and Technology (MRCET) Page 10
ROBOTICS IV B.Tech I Sem (MECH) R15
10. What are the types of mechanism gripper?
Linkage actuation gripper
Gear and rack actuation gripper
Cam actuation gripper
Screw actuation gripper
11. What are the advantages and disadvantages of magnetic gripper? Advantages
Pickup time very fast
Variation in part size can be tolerated. The gripper do not have to be designed for one
particular work part
They have ability to handle metal parts with holes
They require only one surface for gripping
Disadvantages
Residual magnetism
Side slippage
More than one sheet will be lifted by magnet from a stack
12. Write different types of magnetic gripper?
There are two of magnetic gripper
Electromagnetic gripper
Permanent magnet gripper
13. What is Adhesive gripper?
Adhesive gripper in which an adhesive substance performs the grasping action for handling
fabrics and other lightweight material are called adhesive gripper
14. Limitation of Adhesive gripper?
Adhesive substance losses his tackiness on repeated usage
Reliability is diminished with successive operations
15. List the advantages and features of suction cup gripper?
Require only one surface of the part for grasping
Applies uniform pressure distribution on the surface of the part
Relatively a lightweight gripper
Applicable to a variety of different material.
16. Give some examples of tool as robot End effector
Shop welding tools
Arc welding tools
Spray painting nozzle
Water jet cutting tool
Malla Reddy College of Engineering and Technology (MRCET) Page 11
ROBOTICS IV B.Tech I Sem (MECH) R15
17. What is transfer function?
The transfer function relates the Laplace transformation of the system output to the Laplace
transformation of the system input.
18. What is controller?
Controller is information processing device whose input are both desired and measurement
position, velocity (or) other pertinent variables in a process and whose outputs are drive signals
to a motor (or) actuators.
19. Write control techniques of robot?
All industrial robots are either servo or non-servo controlled
Non servo (open loop) control
Servo (closed loop) control
20. What is actuator?
They convert the electrical energy into meaningful mechanical work
Mechanical output can be rotational or linear
Motor provide motion
Electromagnets provide linear motion
21. What is summing junction
Summing junctions may have any number of arrows entering but only one leaving
22. What is a take point?
Take of point permit signals and variables to be shared among more than a single component
23. What is a functional block?
Function block represents one of the components of the system and contains the transfer
function for the component.
24. What is a single arrow?
Single arrow indicates the direction of variables and signals in the diagram.
25. Name some feedback device used in Robotics?
Potentiometer
Resolver
Encoder
26. List the various actuating mechanism used in mechanical gripper?
Linkage actuation gripper
Gear and rack actuation gripper
Cam actuation gripper
Screw actuation gripper
Malla Reddy College of Engineering and Technology (MRCET) Page 12
ROBOTICS IV B.Tech I Sem (MECH) R15
27. Which type of robot is commonly used for pick and place operation?
Cylindrical coordinate robot is commonly used for pick and place operation
28. What do you meant by material transfer application?
Material transfer application are defined as operation in which the primary objective is move
a part from one location to another location
29. What is pick and place operation?
Pick and place operation involved tasks in which the robot picks the part at one location and
move it another location
30. What is meant by PID control?
The PID controller produces an output signal consisting of three terms-one proportional to
error signal, another one proportional to integral of error signal and the third one proportional to
derivative of error signal.
UNIT IV
Two marks
1. What is kinematics?
Kinematics will enable us to calculate what each joint variable must be if we desire the hand
to be located at a particular point and have a particular orientation.
2. Define statics.
Statics deals with force which acts on the various parts which are assumed to be rest.
3. What is link?
A link may be defined as a member (or) a combination of member of mechanism connecting
other members and having motion to them.
Link of machine may transfer both power and motion
4. What is forward kinematics?
It is a scheme to determine joint angle by robot knowing its position in the world coordinate
system
5. What is reverse kinematics?
It is a scheme to determine the position of the robot in the world coordinate system by
knowing the joint angles and the link parameter of the robot.
6. Define manipulator kinematics.
Manipulator kinematics is connected with the position and orindation of the robot’s end of
arm or end effector attached to it as a function of time but without regard for the effects of force
(or) mass.
Malla Reddy College of Engineering and Technology (MRCET) Page 13
ROBOTICS IV B.Tech I Sem (MECH) R15
7. Write about transformation.
Transformation of frames introduced to make modelling the relocation of object
easier.
An object is described with respect to a frame located in the object, and this frame is
reloaded with transformation.
8. Explain kinematic model.
Before a robot can move its hand to an object must be located relative to it. There is
currently no simple method for measuring the location of the robot hand.
Most robot calculated the position of their hand using kinematic model of their arm.
9. Write steps to drive kinematics model?
1) Assign D-H coordination frame
2) Find link parameter
3) Transformation matrices of adjacent joints
4) Calculate kinematic matrix
5) When necessary, Euler angle representation
10. Give a method to salve forward kinematic problems?
Denavid-Hartenberg conversion
11. Give a method to salve inverse kinematic problems?
Closed form (or) Analytical solutions
numerical solutions
12. What is the principle of vacuum cup?
The principle used in vacuum pump and venture
13. What are the methods of robot programming?
Lead through methods
Texual robot languages
Mechanical programming
14. What are ways of accomplishing lead through programming?
Power lead through
Manual lead through
15. What is teach pendent?
The teach pendant is usually a small handheld control box with combinations of toggle
switches, dials and buttons to regulate the robot’s physical movements and program capabilities.
16. What are the methods of teaching?
Joint movement
X-Y-Z coordinate motions
Tool coordinate motion
Malla Reddy College of Engineering and Technology (MRCET) Page 14
ROBOTICS IV B.Tech I Sem (MECH) R15
17. What are the basic mechanisms of legged robot?
Slider
Liver
18. What are the benefits that can be obtained with a legged robot?
Better mobility
Better stability on the platform
Better energy efficiency
Smaller impact on the ground
19. What is APAS?
Adaptable programmable system was developed by national science foundation & westing
house Electric Corporation. The purpose was to advance the state of the art in automated batch
assembly.
20. Write the different type of kinematics analysis of mechanism?
Graphical Position Analysis Method
Algebraic Position Analysis of Linkages
Complex Algebra Method for Position Analysis
21. When a robot singularity will occurs?
A robot singularity occurs when robot axes are redundant (more axes then necessary to cause
the same motion) or when the robot is in certain configurations that require extremely high joint
rates to move at some nominal speed in Cartesian space
22. Write the two modes of lead through programming?
Teach mode
Run mode
23. Write end effector command
OPEN
CLOSE
OPEN I
CLOSED I
24. List out basic modes of operation in robot language structure.
The three basic modes of operations are
Monitor mode
Run mode
Edit mode
Malla Reddy College of Engineering and Technology (MRCET) Page 15
ROBOTICS IV B.Tech I Sem (MECH) R15
25. State that robot language element.
Constant, variables
Motion command
End effector and sensor command
Computation and operations.
UNIT V
Two marks
1. What is meant by SCARA?
SCARA is a robot – This also has a cylindrical work space. RRP main body. Such robots were
used to assemble the SONY Walkman
2. What is meant by robot cell ?
A robot cell is a complete system that includes the robot, controller, and other peripherals such
as a part positioner and safety environment. Robot cells are sometimes referred to as workcells.
Turnkey cells are fully integrated, pre-configured solutions. They install in minimal time and
offer the advantage of proven success.
Custom cells are built to customer specifications and allow for the limitations and challenges
often found in an industrial setting.They are ideal for applications a standard workcell would not
be able to perform.
3. What are the functions of work cell control ?
It is used to monitor the sequence of robot function for particular task
4. What are the parameters to be considered for selecting a robot
Degree of freedom
Weight of object to be lifted
Speed of response
Type of gripper
5. Name few non manufacturing application of robot
Space Mission
Toys
Educational Robots
Domestically application
6. Write some industrial application of robot?
a). Material handling application
Material transfer application
Machine loading/unloading application
b). Processing application
Welding
Painting
Malla Reddy College of Engineering and Technology (MRCET) Page 16
ROBOTICS IV B.Tech I Sem (MECH) R15
Assembly
Inspection
7. What are the benefits of industrial robot?
Industrial robot offers the following benefits
Increase productivity
Improve product quality
More consistent product quality
Reduce scrap and waste
Reduce reworking costs
Reduce raw goods inventory
Direct labour cost saving
Saving in overhead cost such as lighting, heating and cooling
8. What is palletizing?
Palletizing is the operation in which the robot picks cartons from conveyor and places them
on to a pallet
9. What is depalletizing?
Depalletizing operation is the reverse of palletizing operation in which the robot removes
cartons from the pallet and places them on to conveyor or other location
10. What are the different types of material handling operation? Nov/Dec2013
Picking and placing
Palletizing and depalletizing
Machine loading and unloading
Parts feeding , storage and retrival
Sorting of the parts from conveyors
11. What are the gantry robots?
If the robots are mounted over head they are called gentry robots
12. How the workpieces are fed to the robot by some mechanical feeding device?
The workpieces are fed to the robot by some mechanical feeding device or conveyor in a
known location and orientation
13. What is the interpretation of manufacturing system?
Manufacturing system is defined as the system which converts the input into a ` suitable
output
14. What are the technologies used in manufacturing system?
Computer aided design/computer aided manufacturing
FMS
CIM
AGILE
LEAN
Malla Reddy College of Engineering and Technology (MRCET) Page 17
ROBOTICS IV B.Tech I Sem (MECH) R15
15. Define the term “CIM”
The term CIM denotes the use of computer pervasive use of computer system to design the
product, plan the product, control the operations and perform the various business related
function
16. Write down some elements of CIM?
LAN, Database, FEM, QC, CNC, TOOL DESIGN, MARKETING, COMPUTER AIDED
DESIGN, ANALYSIS, ROBOT SCHEDULING
17. What are parts feeding, storage and retrieval process?
Parts feeding means feeding the part to the machine
Storage means storing different types of object in the pallet
Retrieval is the process of taking the object from the pallet
18. What is pallet?
Pallet is a storage area which consists of a number of cells to store workpiece of different size
19. Differentiate palletizing and depalletizing
Palletizing Depallatizing
a. The pickup point is constant a. The pickup point is different
b. The delivery point is different b. The delivery point is constant
20. Application of robot in loading and unloading?
Die casting
Injection moulding
Forming, stamping
Trimming process
21. What is assembly?
The term assembly is defined to mean the fitting of two or more discrete parts to form
a new subassembly
22. Defined part presentation.
In order to perform an assembly task the part that is to be assembled must be presented to
robot this is part presentation
23. Explain bowl feeders?
Bowl feeders are devices used for feeding and orienting small parts in automated assembly
operations. They are made two main components
The bowl
24. The vibrating baseWhat are the types of assembly operation?
Parts mating
Parts joining
Malla Reddy College of Engineering and Technology (MRCET) Page 18
ROBOTICS IV B.Tech I Sem (MECH) R15
25. Basic configuration of assembly systems?
A single workstation assembly
A series of work station assembly
Combination of both
26. Explain designing for robot assembly.
Certain assembly tasks are very difficult for the robot to perform than others. If
possible this difficulty factor should be consider in the design of product
Another consideration in the design of an assembly is the direction in which the parts
are to be added in the assembly operation
Malla Reddy College of Engineering and Technology (MRCET) Page 19
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Soben BA25Document2 pagesSoben BA25choisoominNo ratings yet
- Automation in Industrial Applications: Izabella GEAPANA, Toader SERETAN October 09, 2020Document83 pagesAutomation in Industrial Applications: Izabella GEAPANA, Toader SERETAN October 09, 2020Ștefan KișNo ratings yet
- Automatic Control Systems (Fifth Edition) : ReviewerDocument2 pagesAutomatic Control Systems (Fifth Edition) : Reviewer2020EEP006 DEBANJAN DHARANo ratings yet
- Adaptive PID Controller Using For Speed Control of The BLDC MotorDocument4 pagesAdaptive PID Controller Using For Speed Control of The BLDC MotorAKU BUKAN SIAPA-SIAPANo ratings yet
- Optimal Control TheoryDocument12 pagesOptimal Control TheoryThomas TyrellNo ratings yet
- Rme40002 Le 2-1Document32 pagesRme40002 Le 2-1Mai NguyenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PID Controllers - Theory Tuning and Application To Frontier AreasDocument270 pagesIntroduction To PID Controllers - Theory Tuning and Application To Frontier AreasSchreiber_Dieses100% (6)
- Nonlinear Control of Induction Motor: Z. KrzeminskiDocument6 pagesNonlinear Control of Induction Motor: Z. KrzeminskiWs KenheiNo ratings yet
- How To Design IIR FilterDocument11 pagesHow To Design IIR FilterJignesh PrajapatiNo ratings yet
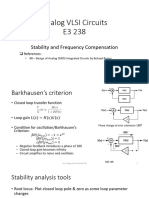
- Stability and Frequency CompensationDocument18 pagesStability and Frequency Compensationbommena vishwa tejaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ProductDocument18 pagesIntroduction To ProductYokuhoNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Speed Control Using PID ControllerDocument7 pagesDC Motor Speed Control Using PID ControllerEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 Train UML ExampleDocument35 pagesChapter1 Train UML ExampleSanthoshreddy GogulaNo ratings yet
- 199999914506-Electrical Engineering - Chauhan Niravkumar AshokkumarDocument14 pages199999914506-Electrical Engineering - Chauhan Niravkumar AshokkumarNirav ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Fluidsim5 EnusDocument652 pagesFluidsim5 EnusNiran JanNo ratings yet
- Suzuki Et Al IEEE ICCA 2000 x1Document6 pagesSuzuki Et Al IEEE ICCA 2000 x1Denis Constantin Ilie-AblachimNo ratings yet
- 4G Strategic Activity - Closed Loop MIMO - ExpandTrial - 20170301Document25 pages4G Strategic Activity - Closed Loop MIMO - ExpandTrial - 20170301Arif AlamsyahNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of B.tech Hons Electrical TechnologyDocument48 pagesSyllabus of B.tech Hons Electrical Technologyumarsaleem069No ratings yet
- Mechatronic PDFDocument245 pagesMechatronic PDFBurak ÖzcanNo ratings yet
- GEE338 Problem Set #4 Compensators and PID PDFDocument3 pagesGEE338 Problem Set #4 Compensators and PID PDFAkram KhorsheidNo ratings yet
- Kaizen TheoryDocument29 pagesKaizen TheorySahar Alam BarbhuiyaNo ratings yet
- Farid ArvaniDocument6 pagesFarid ArvaniDasuki FahmiNo ratings yet
- Labview Based Three Phase Induction Motor Speed Control: 1 Literature SurveyDocument68 pagesLabview Based Three Phase Induction Motor Speed Control: 1 Literature Surveyhardikrananjay100% (1)
- Pneumatics Basic Level: Workbook TP 101Document44 pagesPneumatics Basic Level: Workbook TP 101Asia Ct100% (1)
- Final Project Report On Mimo SystemDocument30 pagesFinal Project Report On Mimo SystemDebayan Sen100% (1)
- Automatic Air ConditionerDocument45 pagesAutomatic Air Conditioneryibeltal mequanint0% (2)
- Fuel System Design For The More Electric EngineDocument8 pagesFuel System Design For The More Electric EngineSon Pham VanNo ratings yet
- Coupled Tank - MPCDocument6 pagesCoupled Tank - MPCMutiara PurnamaNo ratings yet
- PSD4 PDFDocument37 pagesPSD4 PDFaswardiNo ratings yet