Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fluency Calculation
Uploaded by
alun tyasOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fluency Calculation
Uploaded by
alun tyasCopyright:
Available Formats
In speech rate, the pruned syllables and all disfluencies are excluded in the
measurement. To calculate speech rate the number of all syllables is divided by the
total time required to produce the speech sample in seconds. Then the result is
multiplied by 60 to find syllables per minute. To give the standard of normal
speaking rate in syllables, the Tennessee Department of Education Fluency Resource
Packet (2009:24) sets 162�230 is the number of syllables adolescent or adult
normally could produce per minute.
On Pause Rate, the total number of pauses and filled pauses such as uhm, err, emm
including corrections and repetitions are divided by the total amount of time
expressed in seconds and then multiplied by 100.
Disfluent syllables is calculated by subtracting the number of pruned syllables
from the number of total syllables in the sample. Pruned syllables include fillers,
errors, and repetitions. The result is the number of disfluent syllables which is
then divided by 230 as the highest normal number of syllable per minute and
multiplied by the total time in seconds.
Mean length of run between pauses measures the average number of syllables produced
in runs of speech between pauses and other disfluencies to give an idea how much is
said without interruption. Mean length of runs is calculated by subtracting the
total number of syllables by the times of pauses above 0.3 seconds and other
disfluencies then divided by the normal amount of syllables per minutes for the set
time of speech sample that is 2 minutes.
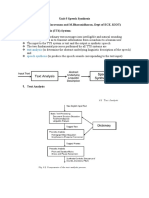
To get the fluency level, the mean score of the four components is matched with the
table which is adapted from the Fluency Scale Ordinate by Jong and Hulstjin
(2009:47-48) to the preferred implementable form used in this research. The scale
proposed as Fluency Scale Ordinate Corporation in Jong and Hulstijn (2009:47-48) is
as shown in the appendix.
You might also like
- All About IELTS: Step by Step Practical Guide to Crack IELTSFrom EverandAll About IELTS: Step by Step Practical Guide to Crack IELTSRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Transcription Style GuideDocument15 pagesTranscription Style GuideIvan G. KišNo ratings yet
- Speech Synthesis in Indian Languages: AbstractDocument4 pagesSpeech Synthesis in Indian Languages: AbstractEr Paramjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Complexity of Speech in Televisual Media and Its Influence On Language AcquisitionDocument6 pagesComplexity of Speech in Televisual Media and Its Influence On Language Acquisitionj_subraNo ratings yet
- Effect of Windowing On The Calculation of MFCC Statistical Parameter For Different Gender in Hindi SpeechDocument5 pagesEffect of Windowing On The Calculation of MFCC Statistical Parameter For Different Gender in Hindi SpeechNishant WadhawanNo ratings yet
- 1337 Chon Hee CheongDocument5 pages1337 Chon Hee CheongdinadinicNo ratings yet
- Text-to-Speech (TTS) SystemDocument11 pagesText-to-Speech (TTS) Systemkumar aniketNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Kannada Text-To-Speech (KTTS) SystemDocument5 pagesEvaluation of Kannada Text-To-Speech (KTTS) Systemeditor_ijarcsseNo ratings yet
- Removal of Spectral Discontinuity in ConcatenatedSpeech WaveformDocument5 pagesRemoval of Spectral Discontinuity in ConcatenatedSpeech WaveformJitendra DhimanNo ratings yet
- RoughDocument2 pagesRoughMuzakkir siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Speech ProcessingDocument12 pagesUnit 5 Speech ProcessingV Saravanan ECE KIOTNo ratings yet
- Speech ProductionDocument8 pagesSpeech ProductionGokulNo ratings yet
- Identification of Hindi Dialects.Document5 pagesIdentification of Hindi Dialects.Saurabh BhardwajNo ratings yet
- CBM Sed 345 1Document1 pageCBM Sed 345 1api-374117005No ratings yet
- Ijaiem 2013 07 02 132Document5 pagesIjaiem 2013 07 02 132editorijaiemNo ratings yet
- Notes On Phonological Based Drunken Detection Algorithm: Adel RahimiDocument5 pagesNotes On Phonological Based Drunken Detection Algorithm: Adel RahimiAli AzgarNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On A Time-Varying Convergence Parameter For The LMS Algorithm in The Presence of White Gaussian NoiseDocument63 pagesA Project Report On A Time-Varying Convergence Parameter For The LMS Algorithm in The Presence of White Gaussian NoisesrujaNDHARNo ratings yet
- As R TutorialDocument16 pagesAs R TutorialjeysamNo ratings yet
- BleuDocument5 pagesBleuSowjanya VakkalankaNo ratings yet
- Spoken Production.Document4 pagesSpoken Production.brettymel.nuiqueNo ratings yet
- Tech Review With ScreenshotsDocument5 pagesTech Review With Screenshotsapi-252881959No ratings yet
- Demos 008Document8 pagesDemos 008music2850No ratings yet
- Ijcet: International Journal of Computer Engineering & Technology (Ijcet)Document9 pagesIjcet: International Journal of Computer Engineering & Technology (Ijcet)IAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Feature Based Classification of Dysfluent and Normal Speech: P.Mahesha D.S.VinodDocument4 pagesFeature Based Classification of Dysfluent and Normal Speech: P.Mahesha D.S.VinodPadmini PalliNo ratings yet
- Speech Acoustics ProjectDocument22 pagesSpeech Acoustics Projectyeasir089No ratings yet
- Icsps10 WindowDocument4 pagesIcsps10 WindowkondaraNo ratings yet
- Data Collection MethodsDocument10 pagesData Collection Methods6ybczp6t9bNo ratings yet
- Static Dictionary For Pronunciation ModelingDocument5 pagesStatic Dictionary For Pronunciation ModelingesatjournalsNo ratings yet
- Standardising Shorthand Speed Tests PDFDocument12 pagesStandardising Shorthand Speed Tests PDFSomnath MandiNo ratings yet
- OromignaDocument19 pagesOromignazerihun nanaNo ratings yet
- How Voice WorksDocument3 pagesHow Voice WorksetbalanseNo ratings yet
- Erlang - A Unit of TrafficDocument1 pageErlang - A Unit of TrafficArinze OkemefunaNo ratings yet
- Lab9: Speech SynthesisDocument13 pagesLab9: Speech SynthesisMichel OlveraNo ratings yet
- Speech and Audio Processing and CodingDocument52 pagesSpeech and Audio Processing and CodingSatishNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Bangla Spelling CheckerDocument8 pagesA Comprehensive Bangla Spelling CheckerxaqibNo ratings yet
- End-to-End Evaluation in Simultaneous TranslationDocument9 pagesEnd-to-End Evaluation in Simultaneous TranslationMarco TrujilloNo ratings yet
- A New Silence Removal and Endpoint Detection Algorithm For Speech and Speaker Recognition ApplicationsDocument5 pagesA New Silence Removal and Endpoint Detection Algorithm For Speech and Speaker Recognition ApplicationsEng SmsmaNo ratings yet
- Febrer 98 ADocument4 pagesFebrer 98 A22SUPS01 ASWIN KNo ratings yet
- Robust End-Of-Utterance Detection For Real-Time Speech Recognition ApplicationsDocument4 pagesRobust End-Of-Utterance Detection For Real-Time Speech Recognition ApplicationsvinaynsitNo ratings yet
- Darpa96 H4Document6 pagesDarpa96 H4Amelia Putri DiandraNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3: Theory of TTSDocument26 pagesChapter-3: Theory of TTSBoby JosephNo ratings yet
- PEER Stage2 10.1016/j.specom.2007.01.001Document31 pagesPEER Stage2 10.1016/j.specom.2007.01.001Myagmarbayar NerguiNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Noise Removal and Echo Cancellation For Audio SignalsDocument3 pagesComparison of Noise Removal and Echo Cancellation For Audio SignalsamiglaniNo ratings yet
- Confidence IntervalDocument12 pagesConfidence IntervalObuli KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Real Time AnalysisDocument9 pagesReal Time AnalysisNeny M. DjamarisNo ratings yet
- Static Dictionary For Pronunciation ModelingDocument5 pagesStatic Dictionary For Pronunciation ModelingInternational Journal of Research in Engineering and TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Time Frequency Analysis and Wavelet Transform Tutorial Time-Frequency Analysis For Voiceprint (Speaker) RecognitionDocument22 pagesTime Frequency Analysis and Wavelet Transform Tutorial Time-Frequency Analysis For Voiceprint (Speaker) RecognitionCan AlptekinNo ratings yet
- Some Refelexions and Results About Adeqaute Speech Denoising Technique According To Desired QualityDocument4 pagesSome Refelexions and Results About Adeqaute Speech Denoising Technique According To Desired QualityAnis Ben AichaNo ratings yet
- Assesment of StutteringDocument12 pagesAssesment of StutteringASMAA NOORUDHEENNo ratings yet
- Speech Enhancement Using LPC Analysis-A ReviewDocument6 pagesSpeech Enhancement Using LPC Analysis-A ReviewInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Voice Conversion by Prosody and Vocal Tract Modification: K. Sreenivasa Rao B. YegnanarayanaDocument6 pagesVoice Conversion by Prosody and Vocal Tract Modification: K. Sreenivasa Rao B. Yegnanarayanaleonunes80No ratings yet
- Acoustical Design of Rooms For Speech: by J.S. BradleyDocument6 pagesAcoustical Design of Rooms For Speech: by J.S. BradleystesagNo ratings yet
- Subword Unit Concatenation For Malay Speech Synthesis: KeywordsDocument7 pagesSubword Unit Concatenation For Malay Speech Synthesis: KeywordsSab SabrinaNo ratings yet
- English Transcribing RegulatinsDocument9 pagesEnglish Transcribing RegulatinsMary Gold Ferolino CabralesNo ratings yet
- Redaction HTK Amazigh SpeechDocument15 pagesRedaction HTK Amazigh Speechhhakim32No ratings yet
- Zhao & Jurafsky - 2005 - A Preliminary Study of Mandarin Filled PausesDocument4 pagesZhao & Jurafsky - 2005 - A Preliminary Study of Mandarin Filled PausesShuang SongNo ratings yet
- Pauses and The Temporal Structure of Speech: Brigitte ZellnerDocument23 pagesPauses and The Temporal Structure of Speech: Brigitte Zellner123kantriNo ratings yet
- Language ThesisDocument14 pagesLanguage Thesisneskic86No ratings yet