Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Circularity and Cylindricity
Uploaded by
daniel_sasikumarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Circularity and Cylindricity
Uploaded by
daniel_sasikumarCopyright:
Available Formats
Circularity and Cylindricity|
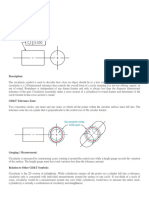
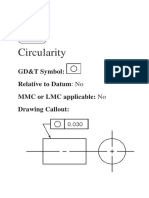
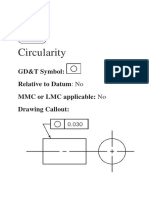
Circularity: Every circular cross section of the part must lie between two concentric circles spaced the
‘circularity’ distance apart. In this example, the circularity is 0.25 mm. All cross sections (like A-A and B-
B in the figure) must lie within two circles 0.25 mm apart. Circularity is 2-dimensional. You are only
checking to see if the cross sections are OK, not whether their centres lie on a straight line.
Cylindricity: Every circular cross section of the cylinder must lie between two concentric cylinders
spaced the ‘cylindricity’ distance apart. In this example, the cylindricity is 0.03 mm. All cross sections
(like A-A and B-B in the figure) must lie within these two cylinders 0.03 mm apart. Cylindricity is 3-
dimensional. You are checking to see if the cross sections are ok AND that they lie on a straight line.
The rod in the picture below might be OK for circularity, but will not be OK for cylindricity.
Circularity can also apply to spheres and cones, while cylindricity applies only to cylinders.
You might also like
- Band Saw (Missing Shop Manual): The Tool Information You Need at Your FingertipsFrom EverandBand Saw (Missing Shop Manual): The Tool Information You Need at Your FingertipsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mathmitering FinalDocument10 pagesMathmitering FinalhungphammanhNo ratings yet
- Concentricity & Coaxiality (GD&T)Document12 pagesConcentricity & Coaxiality (GD&T)Kishor kumar Bhatia88% (8)
- MECHANICAL DESIGN ENGINEERING - Geometrical Dimensioning and Tolerancing - What Is The CYLINDRICITY Tolerance?Document7 pagesMECHANICAL DESIGN ENGINEERING - Geometrical Dimensioning and Tolerancing - What Is The CYLINDRICITY Tolerance?Sathya DharanNo ratings yet
- Cylindricity DefinitionDocument3 pagesCylindricity DefinitionMuhd Rifdi Che AbRahimNo ratings yet
- SEM 2 Prismatic Compass Survey Practical CC4PDocument17 pagesSEM 2 Prismatic Compass Survey Practical CC4PVin Diesel100% (1)
- Drawing PracticesDocument60 pagesDrawing Practicespverma02No ratings yet
- CNC Ball ScrewDocument2 pagesCNC Ball ScrewJatin KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Mazhar Hussain - Bt13Mec045 Sahil Mishra - Bt13Mec046 N.Siva Prasad - Bt13Mec047Document12 pagesMazhar Hussain - Bt13Mec045 Sahil Mishra - Bt13Mec046 N.Siva Prasad - Bt13Mec047pankajNo ratings yet
- Laying Out ToolsDocument9 pagesLaying Out ToolscaliNo ratings yet
- Circularity GD & TDocument2 pagesCircularity GD & Tath-harNo ratings yet
- RoundnessDocument7 pagesRoundnessjacobian1810No ratings yet
- 2006 Mathematics Extension 1 NotesDocument68 pages2006 Mathematics Extension 1 Notesacid_starsNo ratings yet
- Form TolerancesDocument4 pagesForm Tolerancesvskumar4uNo ratings yet
- GD&T PosterDocument1 pageGD&T Posterssaramail100% (1)
- Straightness, Circularity, CylindricityDocument18 pagesStraightness, Circularity, CylindricityKarthik Ram0% (1)
- Cylindricity (GD&T)Document10 pagesCylindricity (GD&T)Kishor kumar Bhatia100% (1)
- Boston Gear Helical GearsDocument14 pagesBoston Gear Helical GearssandchiNo ratings yet
- MDM15B036 Assignment2 QI&PVDocument7 pagesMDM15B036 Assignment2 QI&PVBMSNo ratings yet
- 6.0 Chain DrivesDocument9 pages6.0 Chain DrivesMaggy IrunguNo ratings yet
- Exp.2 Angular MeasurementsDocument10 pagesExp.2 Angular MeasurementsG. Dancer GhNo ratings yet
- CNC SYSTEMS Mechanical ComponentsDocument2 pagesCNC SYSTEMS Mechanical ComponentsRajendra Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Understanding Vernier Calliper Screw Gauge and SpherometerDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Vernier Calliper Screw Gauge and SpherometerAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- EMG 2402 Metrology - Notes 2022 Lecture 3 - 01022022Document16 pagesEMG 2402 Metrology - Notes 2022 Lecture 3 - 01022022Glenn GatibaNo ratings yet
- Unit1-Properties and ShapesDocument10 pagesUnit1-Properties and ShapesMacha NuttsNo ratings yet
- G1975 - Instruction ManualDocument36 pagesG1975 - Instruction ManualLeon GalindoNo ratings yet
- Angle Measurement 2Document7 pagesAngle Measurement 2Jonathan Da Costa100% (1)
- Coms SurDocument28 pagesComs SurAnkit GargNo ratings yet
- Screw Gauge TauseefDocument4 pagesScrew Gauge TauseefMuhammad Tauseef ZafarNo ratings yet
- Survey Whole Circle BearingDocument19 pagesSurvey Whole Circle BearingVin GaragiNo ratings yet
- Chopper Frame Plans Drawing Advantage SummaryDocument12 pagesChopper Frame Plans Drawing Advantage Summarycustomchoppersguide100% (2)
- Chapter 3: Angular Measurements: Definition of AngleDocument10 pagesChapter 3: Angular Measurements: Definition of AngleMohsin Munawar100% (1)
- Runout & Concentricity 2Document1 pageRunout & Concentricity 2Grimmo1979No ratings yet
- Acceptance of MC Tool 123 PDFDocument24 pagesAcceptance of MC Tool 123 PDFakshayNo ratings yet
- Chain DrivesDocument13 pagesChain DrivesnattydreadfathelahNo ratings yet
- Unit No. 04: Angular MeasurementDocument9 pagesUnit No. 04: Angular MeasurementKrishna NikamNo ratings yet
- Mod-3. Spur GearDocument18 pagesMod-3. Spur GearSharthak GhoshNo ratings yet
- GD&T Form and Position TolerancesDocument1 pageGD&T Form and Position TolerancesSaulo TrejoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Measurement of Angles and DirectionDocument72 pagesLecture 6 Measurement of Angles and DirectionAli SandsNo ratings yet
- GD &T CircularityDocument5 pagesGD &T CircularityrahulNo ratings yet
- Cam MechDocument24 pagesCam MechmarcglebNo ratings yet
- Circularity: GD&T Symbol: Relative To Datum MMC or LMC Applicable: Drawing CalloutDocument5 pagesCircularity: GD&T Symbol: Relative To Datum MMC or LMC Applicable: Drawing CalloutrahulNo ratings yet
- Unit IiDocument19 pagesUnit IiGaneshNo ratings yet
- Brochure Roundness BookletDocument12 pagesBrochure Roundness BookletImm Yoon-AhNo ratings yet
- Cycloidal CurvesDocument9 pagesCycloidal CurvesSri DNo ratings yet
- CHP 4 ESDocument30 pagesCHP 4 ESMurtaza Muhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Intersection of SolidsDocument13 pagesIntersection of SolidsSuneel Kumar Meena0% (1)
- Metrology Laboratory: Experiment No. 1Document5 pagesMetrology Laboratory: Experiment No. 1Mitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit III NewDocument21 pagesUnit III NewsathiaNo ratings yet
- Plastic Injection Mold Design for Toolmakers - Volume II: Plastic Injection Mold Design for Toolmakers, #2From EverandPlastic Injection Mold Design for Toolmakers - Volume II: Plastic Injection Mold Design for Toolmakers, #2No ratings yet
- Kinematic Differential Geometry and Saddle Synthesis of LinkagesFrom EverandKinematic Differential Geometry and Saddle Synthesis of LinkagesNo ratings yet
- Suggestion ProgramDocument2 pagesSuggestion Programdaniel_sasikumarNo ratings yet
- Bzad Capa FormDocument1 pageBzad Capa Formdaniel_sasikumarNo ratings yet
- Handing Over FormDocument1 pageHanding Over Formdaniel_sasikumarNo ratings yet
- Calculating Whether or Not A Hole Is in Spec With Bonus ToleranceDocument1 pageCalculating Whether or Not A Hole Is in Spec With Bonus Tolerancedaniel_sasikumarNo ratings yet
- .013-00-Checking AidsDocument3 pages.013-00-Checking Aidsdaniel_sasikumarNo ratings yet
- Process Flow ChartDocument4 pagesProcess Flow Chartdaniel_sasikumarNo ratings yet
- IAS AnswersDocument3 pagesIAS Answersdaniel_sasikumarNo ratings yet
- Order Process: Annexure - CDocument1 pageOrder Process: Annexure - Cdaniel_sasikumarNo ratings yet
- Month June 2018 100 50 July 2018 40 10 Aug 2018 No of Enquiries Received No of Enquiries Converted Into OrdersDocument2 pagesMonth June 2018 100 50 July 2018 40 10 Aug 2018 No of Enquiries Received No of Enquiries Converted Into Ordersdaniel_sasikumarNo ratings yet
- 5 5 3 First Aid Box Fire Extinguisher Emergency Exit Machine ShopDocument2 pages5 5 3 First Aid Box Fire Extinguisher Emergency Exit Machine Shopdaniel_sasikumarNo ratings yet
- Alpha Drives: Vendor RatingDocument10 pagesAlpha Drives: Vendor Ratingdaniel_sasikumarNo ratings yet
- LM25 Aluminium Casting Alloy (Al - Si7Mg) : Chemical CompositionDocument3 pagesLM25 Aluminium Casting Alloy (Al - Si7Mg) : Chemical Compositiondaniel_sasikumarNo ratings yet