Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction of Linux, Unix, Windows
Uploaded by
sanya garg0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views3 pagesOriginal Title
introduction of linux,unix,windows
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views3 pagesIntroduction of Linux, Unix, Windows
Uploaded by
sanya gargCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
LINUX
Linux is one of popular version of UNIX operating System. It is open source
as its source code is freely available. It is free to use. Linux was designed
considering UNIX compatibility. Its functionality list is quite similar to that
of UNIX.
Components of Linux System
Linux Operating System has primarily three components
Kernel − Kernel is the core part of Linux. It is responsible for all major
activities of this operating system. It consists of various modules and it
interacts directly with the underlying hardware. Kernel provides the required
abstraction to hide low level hardware details to system or application
programs.
System Library − System libraries are special functions or programs using
which application programs or system utilities accesses Kernel's features.
These libraries implement most of the functionalities of the operating system
and do not requires kernel module's code access rights.
System Utility − System Utility programs are responsible to do specialized,
individual level tasks.
Kernel Mode vs User Mode
Kernel component code executes in a special privileged mode
called kernel mode with full access to all resources of the computer. This
code represents a single process, executes in single address space and do
not require any context switch and hence is very efficient and fast. Kernel
runs each processes and provides system services to processes, provides
protected access to hardware to processes.
Support code which is not required to run in kernel mode is in System
Library. User programs and other system programs works in User
Mode which has no access to system hardware and kernel code. User
programs/ utilities use System libraries to access Kernel functions to get
system's low level tasks.
Basic Features
Following are some of the important features of Linux Operating System.
Portable − Portability means software can works on different types of
hardware in same way. Linux kernel and application programs supports their
installation on any kind of hardware platform.
Open Source − Linux source code is freely available and it is community
based development project. Multiple teams work in collaboration to enhance
the capability of Linux operating system and it is continuously evolving.
Multi-User − Linux is a multiuser system means multiple users can access
system resources like memory/ ram/ application programs at same time.
Multiprogramming − Linux is a multiprogramming system means multiple
applications can run at same time.
Hierarchical File System − Linux provides a standard file structure in which
system files/ user files are arranged.
Shell − Linux provides a special interpreter program which can be used to
execute commands of the operating system. It can be used to do various types
of operations, call application programs. etc.
Security − Linux provides user security using authentication features like
password protection/ controlled access to specific files/ encryption of data.
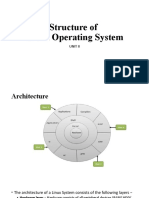
Architecture The following illustration shows the architecture of a
Linux system −
The architecture of a Linux System consists of the following layers −
Hardware layer − Hardware consists of all peripheral devices (RAM/ HDD/
CPU etc).
Kernel − It is the core component of Operating System, interacts directly with
hardware, provides low level services to upper layer components.
Shell − An interface to kernel, hiding complexity of kernel's functions from
users. The shell takes commands from the user and executes kernel's
functions.
Utilities − Utility programs that provide the user most of the functionalities of
an operating systems.
You might also like
- Linux Kernel Explained: Components, Modes and FeaturesDocument3 pagesLinux Kernel Explained: Components, Modes and FeaturesjagruthimsNo ratings yet
- Linux System Components Kernel Libraries UtilitiesDocument3 pagesLinux System Components Kernel Libraries Utilitiesiftikhar ahmedNo ratings yet
- Os LinuxDocument2 pagesOs LinuxDavid D'bayuNo ratings yet
- Null 9Document4 pagesNull 9Josue SipingNo ratings yet
- ACT03Document3 pagesACT03Jericho MosquedaNo ratings yet
- Linux Operating SystemDocument11 pagesLinux Operating SystemNaval BihaniNo ratings yet
- Structure of UNIX OSDocument6 pagesStructure of UNIX OSKenny Pratheep KumarNo ratings yet
- Linux PDFDocument5 pagesLinux PDFParul SinghNo ratings yet
- Linux Operating System Components and ServicesDocument24 pagesLinux Operating System Components and ServicesvenkatNo ratings yet
- Linux Admin Lecture 1Document12 pagesLinux Admin Lecture 1bekesy7No ratings yet
- Linux Operating System Components and ServicesDocument36 pagesLinux Operating System Components and ServicesAnish A RNo ratings yet
- Mscse 3 Oss Iset64Document178 pagesMscse 3 Oss Iset64Undergraduate LibraryNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Linux OS: Nbkrist Iv B.Tech Cse-Ii SemDocument46 pagesIntroduction To Linux OS: Nbkrist Iv B.Tech Cse-Ii SemSiva Prathap MNo ratings yet
- LinuxDocument19 pagesLinuxDashrathNo ratings yet
- Prajwal GaykwadDocument8 pagesPrajwal GaykwadVaibhav KokitkarNo ratings yet
- Oss Unit2Document20 pagesOss Unit2Akash ShuklaNo ratings yet
- 3CS LSP Unit 1-1Document15 pages3CS LSP Unit 1-1Deepak KumarNo ratings yet
- 3CS LSP Unit 1Document20 pages3CS LSP Unit 1Deepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Linux and Shell Programming UNIT I: Introduction To LINUX Operating System: Introduction - The LINUX OperatingDocument4 pagesLinux and Shell Programming UNIT I: Introduction To LINUX Operating System: Introduction - The LINUX OperatingVivetha 20IT56No ratings yet
- Unit IDocument67 pagesUnit Isk9271054No ratings yet
- LinuxDocument7 pagesLinuxnikitasingh222001No ratings yet
- LINUX Module 1Document15 pagesLINUX Module 1Vignesh C MNo ratings yet
- Case Study of LinuxDocument8 pagesCase Study of LinuxabhyaNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument17 pagesCase StudySumeet KaurNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Linux Operating SystemDocument9 pagesIntroduction to Linux Operating SystemHimañshu BhattNo ratings yet
- 3Document6 pages3lgugunashviliNo ratings yet
- MOS Unit 05 Linux Operating Systems FullDocument23 pagesMOS Unit 05 Linux Operating Systems FullSEENIVASNo ratings yet
- LINUXDocument3 pagesLINUXReds Vharshan MahandrenNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document3 pagesUnit 1parmarkrish531No ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Introduction To Linux Operating SystemDocument25 pagesChapter Two: Introduction To Linux Operating Systembalj balhNo ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument53 pagesUnit IIammulove1303No ratings yet
- Linux Unit 1Document8 pagesLinux Unit 1Adeefa AnsariNo ratings yet
- Unix Linux Architecture QuestionsDocument12 pagesUnix Linux Architecture QuestionsMohan Venkat ChandaluruNo ratings yet
- Linux: A Comprehensive Guide to Linux Operating System and Command LineFrom EverandLinux: A Comprehensive Guide to Linux Operating System and Command LineNo ratings yet
- 01 Starting With Linux ShellsDocument36 pages01 Starting With Linux ShellsStephen EfangeNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems Explained in 40 CharactersDocument22 pagesOperating Systems Explained in 40 CharactersRajdeep BorgohainNo ratings yet
- Linux KernelDocument9 pagesLinux KernelNavneetMishraNo ratings yet
- Case Study on Linux Evolution and ComponentsDocument40 pagesCase Study on Linux Evolution and ComponentsRupesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Case Study on Linux Evolution and ComponentsDocument40 pagesCase Study on Linux Evolution and ComponentsDivyanshuNo ratings yet
- Linux Interactive by BALJEET SINGH/1Document6 pagesLinux Interactive by BALJEET SINGH/1tuniya4No ratings yet
- Linux FundamentalsDocument4 pagesLinux FundamentalsPratham MishraNo ratings yet
- LinuxDocument3 pagesLinuxTejas JadhavNo ratings yet
- Linux Notes: Operating System, Features & CommandsDocument21 pagesLinux Notes: Operating System, Features & CommandsAbhishek ManeNo ratings yet
- In The Today's Session We'll ReadDocument18 pagesIn The Today's Session We'll ReadRupesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- LINUX Unit 1Document50 pagesLINUX Unit 1Ishan PatwalNo ratings yet
- LINUX Programming: INSTRUCTOR: Ms. M. KeerthikaDocument4 pagesLINUX Programming: INSTRUCTOR: Ms. M. KeerthikaKeerthika MNo ratings yet
- Linux Operatig SystemDocument21 pagesLinux Operatig SystemMuhammad Yusif AbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Os FileDocument57 pagesOs Fileguptatulsi31No ratings yet
- Introducing Linux OSDocument24 pagesIntroducing Linux OSGeorge JNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Linux Ms. Jaya GangwaniDocument40 pagesCase Study On Linux Ms. Jaya GangwaniArpit GoswamiNo ratings yet
- LINUX MODULE-1 - NewDocument66 pagesLINUX MODULE-1 - NewFausiya SalimNo ratings yet
- At The End of This Lecture You Will Be Able To:: - Linux Operating SystemDocument11 pagesAt The End of This Lecture You Will Be Able To:: - Linux Operating SystemAlex KharelNo ratings yet
- Intro To OsDocument16 pagesIntro To OsAkhina IlamakNo ratings yet
- Linux and Kernel ComponentDocument17 pagesLinux and Kernel Componentsindhu4sind100% (1)
- 9086 LessonPlanTheoryDocument2 pages9086 LessonPlanTheorycvarun98No ratings yet
- Linux Introduction & InstallationDocument5 pagesLinux Introduction & InstallationLalitNo ratings yet
- The Linux Operating System's Core ComponentsDocument28 pagesThe Linux Operating System's Core ComponentsG.pradeep ReddyNo ratings yet
- Mastering Linux Administration: A Comprehensive Guide: The IT CollectionFrom EverandMastering Linux Administration: A Comprehensive Guide: The IT CollectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Unit 5Document8 pagesUnit 5Samyak JadhavNo ratings yet
- Linux Practical FileDocument41 pagesLinux Practical FilePrashant Kumar100% (1)
- Module 1Document29 pagesModule 1sanya gargNo ratings yet
- Page Replacement AlgoDocument2 pagesPage Replacement Algosanya gargNo ratings yet
- LTS STSDocument2 pagesLTS STSsanya gargNo ratings yet
- System Call and Its TypeDocument4 pagesSystem Call and Its Typesanya gargNo ratings yet
- Page Replacement AlgoDocument2 pagesPage Replacement Algosanya gargNo ratings yet
- Critical Section SolutionDocument2 pagesCritical Section Solutionsanya gargNo ratings yet
- Instance ExplanedDocument1 pageInstance Explanedsanya gargNo ratings yet
- CO LecturenoteDocument39 pagesCO LecturenoteBinuVargisNo ratings yet
- Here: C Programming by Balagurusamy 6th Edition PDFDocument2 pagesHere: C Programming by Balagurusamy 6th Edition PDFBalasubramanian50% (2)
- Instance ExplanedDocument1 pageInstance Explanedsanya gargNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Computer Application (Part-1,2,3)Document31 pagesBachelor of Computer Application (Part-1,2,3)sanya gargNo ratings yet
- RCC.71 v1.0Document237 pagesRCC.71 v1.0Rahul KumarNo ratings yet
- ECZ Computer Studies P1 Past Paper 2015 2016 2017Document27 pagesECZ Computer Studies P1 Past Paper 2015 2016 2017Bricious Mulimbi100% (2)
- Plekhanov Russian University of Economics International Business SchoolDocument7 pagesPlekhanov Russian University of Economics International Business SchoolAdelya AkhtyamovaNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument76 pagesReadmea406458No ratings yet
- Praveen Meduri ResumeDocument5 pagesPraveen Meduri ResumePraveen MeduriNo ratings yet
- APN Partner Marketing How-To GuideDocument1 pageAPN Partner Marketing How-To GuideRommel Jermie BeswinNo ratings yet
- SAP BW Migration To HANA-eBookDocument75 pagesSAP BW Migration To HANA-eBookWarwick81100% (1)
- LKGPS ProtocolDocument10 pagesLKGPS Protocolmichaelj234100% (1)
- Lab 7: Basic RIP Configuration: Topology DiagramDocument4 pagesLab 7: Basic RIP Configuration: Topology DiagramMagi SagiNo ratings yet
- Railway Reservation SRSDocument14 pagesRailway Reservation SRSyfiamataimNo ratings yet
- Cloud Networking Portfolio: Universal Cloud Network and EcosystemDocument4 pagesCloud Networking Portfolio: Universal Cloud Network and EcosystemmethanoxyNo ratings yet
- Motorola Es400Document212 pagesMotorola Es400toshibaNo ratings yet
- Loapi MalwareDocument23 pagesLoapi MalwareFrancisc MoldovanNo ratings yet
- Centum VP Engineerinig Training ReportDocument11 pagesCentum VP Engineerinig Training ReportGloria HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Os Manual Next SemDocument64 pagesOs Manual Next Semswarna_793238588No ratings yet
- The Ultimate Privacy GuideDocument34 pagesThe Ultimate Privacy GuidePablo CastroNo ratings yet
- Yahoo Chat SpyDocument9 pagesYahoo Chat SpyGiovanni CiallellaNo ratings yet
- Business Intelligence Dashboard for Product AnalysisDocument23 pagesBusiness Intelligence Dashboard for Product AnalysisHuynh Ngoc Hai Dang (FGW DN)No ratings yet
- Microprocessor Interfacing AssignmentDocument2 pagesMicroprocessor Interfacing AssignmentnkNo ratings yet
- Embedded Unit Testing FrameworkDocument125 pagesEmbedded Unit Testing Frameworkdinokid08100% (1)
- Virtualization SynopsisDocument3 pagesVirtualization Synopsisvishal sharmaNo ratings yet
- Hospital Management System Proposal-UNIVERSAL PDFDocument11 pagesHospital Management System Proposal-UNIVERSAL PDFedwardNo ratings yet
- Final Doc v1.1 PDFDocument76 pagesFinal Doc v1.1 PDFriya senNo ratings yet
- Nan-36creating Bluetooth® Low Energy Applications Using nRF51822Document35 pagesNan-36creating Bluetooth® Low Energy Applications Using nRF51822rm65457No ratings yet
- IPC Operation ManualDocument10 pagesIPC Operation ManualsaidNo ratings yet
- 5 SKG Intro To CloudDocument86 pages5 SKG Intro To CloudasimgulzarjanNo ratings yet
- Wireless Telephony ApplicationsDocument35 pagesWireless Telephony Applicationsudhayarose29% (7)
- Monitor PinoutsDocument19 pagesMonitor PinoutsUfuk AydınNo ratings yet
- BMC+Automation+Console+20.02 Home 04 21 2020Document168 pagesBMC+Automation+Console+20.02 Home 04 21 2020Luis Daniel Gonzalez100% (2)
- SNMPDocument31 pagesSNMPAstri MayasariNo ratings yet