Professional Documents
Culture Documents
S7300ce 140903150130 Phpapp01
Uploaded by
Suhendri SaputraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
S7300ce 140903150130 Phpapp01
Uploaded by
Suhendri SaputraCopyright:
Available Formats
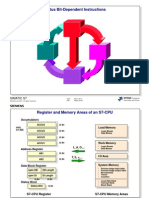
Automation and Drives
Totally Integrated Automation
SIMATIC
S7-300
The universal, small
control system
supplemented by new,
compact CPUs
S7-300 Compact A&D BD/AS, Slide 1
Automation and Drives
SIMATIC S7-300
in the system family
Overview
Comparison Upper and mid
I/O‘s performance range
Process Functions S7-400
Communication
MMC Lower and mid S7-300 - the universal,
small control system for
performance range versatile applications in
S7-300 automation engineering
Bottom
performance range
S7-200
+ Programming devices
+ STEP 7 software
+ Communication
+ HMI
S7-300 Compact A&D BD/AS, Slide 2
Automation and Drives
The new S7-300 compact CPUs
A strong team
Overview 3 basic types: The versions differ with respect to
Comparison - I/Os
I/O‘s With different memory - Onboard interfaces
Process Functions sizes and performances - Process functions
Communication
MMC
312C: 16 Kbyte 312C
313C: 32 Kbyte 313C
313C-2 PtP
313C-2 DP
314C: 48 Kbyte 314C-2 PtP
314C-2 DP
S7-300 Compact A&D BD/AS, Slide 3
Automation and Drives
Dimensions and design
Overview
Comparison
313C-2 PtP 314C-2 PtP
I/O‘s
312C 313C 313C-2 DP 314C-2 DP
Process Functions
Communication
MMC
125 mm
80 mm 120 mm 120 mm 120 mm
Onboard I/Os: DI/DO DI/DO + AI/AO DI/DO DI/DO + AI/AO
Integral interfaces: MPI MPI MPI + MPI + PtP/DP
PtP/DP
Max. design: 1 tier 4 tiers 4 tiers
4 tiers
S7-300 Compact A&D BD/AS, Slide 4
Automation and Drives
Memory, performance and quantity breakdown
Overview
Comparison
I/O‘s
Process Functions
Communication
MMC
312C 313C 314C
Main memory 16 kB 32 kB 48 kB
Statements 5k 10 k 16 k
Loading memory plug-in 64k-4MB plug-in 64k-4MB plug-in 64k-4MB
Instruction runtime min. 0.2 µs min. 0.1 µs min. 0.1 µs
Alarm response time 800 µs 400 µs 400 µs
Bit memories 1024 2048 2048
Timers / counters 128 / 128 256 / 256 256 / 256
Address space I/O 1024 / 1024 byte 1024 / 1024 byte 1024 / 1024 byte
No. of digital channels 266 1000 1000
No. analog chann. I/O 64 / 64 248 / 248 248 / 248
S7-300 Compact A&D BD/AS, Slide 5
Automation and Drives
Integral I/Os - summary
Overview Low-cost onboard I/O channels for universal use
Comparison Every digital input can be used as an alarm input
I/O‘s
Process Functions
Analog inputs can also be used as digital inputs
Communication
MMC
312C 313C 314C
313C 313C-2 PtP / DP 314C-2 PtP / DP
Number of DIs 10 24 16 24
Number of DOs 6 16 16 16
Number of AIs -/- 4 + 1* -/- 4 + 1*
Number of AOs -/- 2 -/- 2
* Additional input for resistance measurement
S7-300 Compact A&D BD/AS, Slide 6
Automation and Drives
Integral digital I/Os
Overview
Comparison
I/O‘s
Digital Digital
Process Functions
inputs outputs
Communication
MMC Rated voltage DC 24 V DC 24 V
Permissible range DC 20.4 - 28.8 V DC 20.4 - 28.8 V
Current range --- 0.5 A
Input delay 0.1/0.5/3/15 ms ---
Switch-off delay --- 2 ms
Electrical isolation from yes yes
backplane bus
Groups of 16 8
Max. frequency --- 100 Hz
S7-300 Compact A&D BD/AS, Slide 7
Automation and Drives
Integral analog I/Os
Overview
Comparison
I/O‘s
Analog Analog
Process Functions
inputs outputs
Communication
MMC Measuring ranges
Voltage ±10V; 0..10V ±10V; 0..10V
Current ±20mA; 0/4..20mA ±20mA; 0/4..20mA
Resolution 11 bits+sign 11 bits+sign
Filter (50/60 Hz) selectable ---
Input delay 5 ms ---
Output delay --- 1,2 ms
Electrical isolation from yes yes
backplane bus
S7-300 Compact A&D BD/AS, Slide 8
Automation and Drives
Summary of process functions
Overview
Comparison
I/O‘s
Process Functions
Communication 312C 313C 314C
MMC Counting
Connectable sources Incremental encoder, Incremental encoder, Incremental encoder,
pulse generator with pulse generator with pulse generator with
direction signal direction signal direction signal
Number of channels 2 3 4
Cut-off frequency 10 kHz 30 kHz 60 kHz
Frequency measurem. yes yes yes
PWM
Number of outputs 2 3 4
Cut-off frequency 2.5 kHz 2.5 kHz 2.5 kHz
Positioning no no 1 axis
Control - PID PID
S7-300 Compact A&D BD/AS, Slide 9
Automation and Drives
Integral counters
Overview Integral counters in all compact CPUs
Comparison
I/O‘s
- Recording of pulse and incremental encoder
signals (DC 24V)
Process Functions
Communication
- Forward/reverse with reference values which
can be changed during operation
MMC
- 10 - 60 kHz (depending on CPU)
Various operating modes possible
t
- Single counting (e.g. filling, dosing)
- Periodic counting (e.g. recording of angle)
- Counting with gate control (e.g. length measurement)
Frequency measurement
- Counting with fixed time base
S7-300 Compact A&D BD/AS, Slide 10
Automation and Drives
PWM outputs
Overview Pulse outputs on all compact CPUs
Comparison
- Direct control of valves, actuators, switchgear,
I/O‘s heaters etc. (DC 24 V/ 0.5 A)
Process Functions
Communication
- Period and pulse/pause ratio can be changed
during operation
MMC
- 2.5 kHz switching frequency, up to 4 outputs
(depending on CPU)
S7-300 Compact A&D BD/AS, Slide 11
Automation and Drives
Simple motion control
without additional components
Overview
Low-price
Comparison Since no additional modules required
I/O‘s v
Optimum memory requirements and runtime
Process Functions
Communication
No additional programming requirements
MMC
since function is component of operating
system
t
Flexible
Parameters (delay, acceleration etc.) can be
changed for each travel
Various operating modes selectable: absolute
or relative positioning, inching etc.
Simple
Prepared functionality can be linked into
application program using standard blocks
S7-300 Compact A&D BD/AS, Slide 12
Automation and Drives
Summary of communications
Overview
Comparison
I/O‘s
Process Functions
Communication
312C 313C-2 PtP 313C-2 DP
MMC
313C 314C-2 PtP 314C-2 DP
Interface present on all CPUs - networking of CPU, programming device and OPs
MPI Low-cost communications without additional HW - extremely simple configuring
Communication with up to 7 OPs simultaneously (depending on type of CPU)
Serial onboard interface
Point-to-
Data exchange e.g. with
point devices from other
vendors
Fast, cyclic data exchange
PROFIBUS High data security
DP
S7-300 Compact A&D BD/AS, Slide 13
Automation and Drives
On every CPU:
multipoint interface MPI
Data exchange: 187.5 kbit/s
Overview
Comparison Up to 32 bus stations, up to 12
I/O‘s active connections per CPU
Process Functions
Communication
Communications functions:
MMC - Programming device/operator
panel functions
- Global data communications
without programming input
- S7 basic communication up to 76
byte
- S7 communication (only server)
Low-cost communication
without additional hardware
S7-300 Compact A&D BD/AS, Slide 14
Automation and Drives
Point-to-point interface (RS422/485)
Connection of non-system components
Overview CPU 313C-2 PtP / 314C-2 PtP
Comparison
Transmission physics:
I/O‘s
Process Functions
- RS 422/485 (X.27)
Communication
- Transmission rate: up to 19.2 / 38.4 kbit/s (half duplex/full duplex)
MMC
Protocols: PCs, computers,
programming
- ASCII devices Robot
controls
- 3964(R)
Scanners,
- RK 512 bar code readers,
- (only 314C-2 PtP) ID systems
Opto
electronics S7-300 C
S7-300 Weighing
systems,
controllers
SIMATIC S5
S7-300 Compact A&D BD/AS, Slide 15
Automation and Drives
CPU 313C-2 DP, 314C-2 DP,
integral PROFIBUS-DP
Overview
Versatile use:
Comparison
master or slave function PG
I/O‘s
Process Functions Data exchange at 12 Mbit/s
Communication
Up to 32 DP stations
MMC
to master interface
P R O C E S S F IE L D B U S
Max. distance 23 km using FO
Communications functions:
- All programming device/OP
functions
-
SIEMENS
PROFIBUS-DP
No additional module
or software required!
S7-300 Compact A&D BD/AS, Slide 16
Automation and Drives
SIMATIC Micro Memory Card
Many functions - small format
Can be used in every S7-300 compact CPU
Overview Functions as program memory, non-volatile and
Comparison
resistant to overall reset; transportable for simple
I/O‘s
program updating
Process Functions
Communication Functions as loading memory - flexible as result
MMC of selectable MMC sized between 64kB and 4MB
Permits project storage on CPU - save your
complete project on the MMC
Access to the MMC during RUN mode of CPU
- Load data into CPU (recipe)
- Write data onto MMC (archive)
MMC buffers your data in the main memory in
event of power failure
no backup battery required
MMC is required to operate the compact CPUs
S7-300 Compact A&D BD/AS, Slide 17
Automation and Drives
The universal, small control system
with emphasis on production engineering
Totally Integrated
Automation
with
SIMATIC
S7-300
S7-300 Compact A&D BD/AS, Slide 18
You might also like
- Active Disturbance Rejection Control for Nonlinear Systems: An IntroductionFrom EverandActive Disturbance Rejection Control for Nonlinear Systems: An IntroductionNo ratings yet
- Simatic S7-300: The Universal, Small Control System Supplemented by New, Compact CpusDocument18 pagesSimatic S7-300: The Universal, Small Control System Supplemented by New, Compact CpusSunil SinghNo ratings yet
- Simatic S7-200Document30 pagesSimatic S7-200Bui Hong PhongNo ratings yet
- SIMATIC S7-200: Simatic Hmi The Human Machine Interface SIMATIC S7-200Document30 pagesSIMATIC S7-200: Simatic Hmi The Human Machine Interface SIMATIC S7-200gaston100% (1)
- d05 Cpu315 Et200s PDFDocument34 pagesd05 Cpu315 Et200s PDFMazarel AurelNo ratings yet
- 6ra70 PDFDocument232 pages6ra70 PDFChowdary MnchowdaryNo ratings yet
- PLC and Its Application Final-1Document83 pagesPLC and Its Application Final-1Mohsin razaNo ratings yet
- PLC K SaraswathiDocument105 pagesPLC K SaraswathiKoushik SgNo ratings yet
- PLC Siemens S7-300 Cpu 312C ManualDocument176 pagesPLC Siemens S7-300 Cpu 312C ManualKique KiNo ratings yet
- PLC Programming Languages for S7-1200Document15 pagesPLC Programming Languages for S7-1200asapNo ratings yet
- Electrical Wiring DigramDocument15 pagesElectrical Wiring DigramSunilMurkikarNo ratings yet
- How To Upload Program From Cpu Using Simatic Manager - PLC BasicsDocument11 pagesHow To Upload Program From Cpu Using Simatic Manager - PLC BasicsMohamed Elsayed100% (1)
- Easy S7-1200 PLC IntroductionDocument186 pagesEasy S7-1200 PLC IntroductionamzadNo ratings yet
- How To Make Your PLC System For DummiesDocument36 pagesHow To Make Your PLC System For Dummiesdavid carrilloNo ratings yet
- Statement List InstructionsDocument50 pagesStatement List InstructionsMiladShahabiNo ratings yet
- 8085 Microproceesor - PPTDocument59 pages8085 Microproceesor - PPTShanagonda Manoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Wago PLCDocument2 pagesWago PLCgenibra100% (1)
- Indralogic 1 Operating and ProgrammingDocument384 pagesIndralogic 1 Operating and ProgrammingCristopher EntenaNo ratings yet
- Siemens SIMATICDocument8 pagesSiemens SIMATICsharib26No ratings yet
- Simatic Pcs7 BoxDocument4 pagesSimatic Pcs7 BoxRaj ChavanNo ratings yet
- Timer SimaticDocument16 pagesTimer Simaticeman sulaemanNo ratings yet
- Dynamic WizardDocument348 pagesDynamic WizardEshita SangodkarNo ratings yet
- PLC Basics: An Introduction to Programmable Logic ControllersDocument140 pagesPLC Basics: An Introduction to Programmable Logic Controllersbernabas0% (1)
- Here is the PLC ladder logic diagram to meet the given requirements:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8| | | | | | | |K1-NO LED Green|K2-NO|LED Red|K1-NC|K2-NCDocument116 pagesHere is the PLC ladder logic diagram to meet the given requirements:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8| | | | | | | |K1-NO LED Green|K2-NO|LED Red|K1-NC|K2-NCABHISHEK THAKURNo ratings yet
- The Codesys Visualization: Supplement To The User Manual For PLC Programming With Codesys 2.3Document67 pagesThe Codesys Visualization: Supplement To The User Manual For PLC Programming With Codesys 2.3veintimillaaNo ratings yet
- CPU 410 en en-USDocument422 pagesCPU 410 en en-USHammad AshrafNo ratings yet
- AGI 4xx Installation Instructions 4189341102 UKDocument5 pagesAGI 4xx Installation Instructions 4189341102 UKJOSE LUIS CRISTANCHO100% (1)
- Twido HardwareDocument31 pagesTwido Hardwarekhusnul bmjNo ratings yet
- Users Manual WinCC Flexible en-USDocument466 pagesUsers Manual WinCC Flexible en-USAlvin NguyenNo ratings yet
- V20 LaunchedDocument147 pagesV20 LaunchedNguyễn Viết HùngNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 1 1Document71 pagesChapter # 1 1AbeerAhmedNo ratings yet
- Vijeo Quick Start Tutorial V720Document114 pagesVijeo Quick Start Tutorial V720ssgfreemailNo ratings yet
- Simatic Step 7 DownloadDocument3 pagesSimatic Step 7 DownloadZdravko PeranNo ratings yet
- Basic Programming Simatic S7-300Document40 pagesBasic Programming Simatic S7-300Mst ThangarajuNo ratings yet
- STM32F30xx-31xx Standard Peripheral Library UM1581Document584 pagesSTM32F30xx-31xx Standard Peripheral Library UM1581John LeungNo ratings yet
- Presentacion M580Document25 pagesPresentacion M580RegionSur MusaGrillNo ratings yet
- Ps7Migrate v6 To v8Document84 pagesPs7Migrate v6 To v8alanNo ratings yet
- PRO2 01eDocument14 pagesPRO2 01eghita_gabrielNo ratings yet
- GMWIN 01 The StartDocument9 pagesGMWIN 01 The StartmidahsNo ratings yet
- Automation Studio 4Document40 pagesAutomation Studio 4pipikikikiNo ratings yet
- Siemens Top MistakesDocument80 pagesSiemens Top Mistakesbudak1No ratings yet
- Beckhoff and TwinCAT GuideDocument17 pagesBeckhoff and TwinCAT Guidevoltus88No ratings yet
- VBScripting Manual - Rev 2013Document42 pagesVBScripting Manual - Rev 2013basamvenkatNo ratings yet
- Free PLC Programming Tutorial PDFDocument2 pagesFree PLC Programming Tutorial PDFJavierNo ratings yet
- How Do You Establish A Modbus - TCP Communication From A SIMATIC S7-300 - S7-400 and W... - ID - 22660304 - Industry Support SiemensDocument2 pagesHow Do You Establish A Modbus - TCP Communication From A SIMATIC S7-300 - S7-400 and W... - ID - 22660304 - Industry Support Siemensshashank PathakNo ratings yet
- S7-300 Module DataDocument676 pagesS7-300 Module DatagustavoNo ratings yet
- D - Manuals - Wonderware - Notas Tecnicas - Configuring O PDFDocument23 pagesD - Manuals - Wonderware - Notas Tecnicas - Configuring O PDFAngelito_HBKNo ratings yet
- Calog ManualDocument34 pagesCalog Manualpatitay036817No ratings yet
- Csharp OPC Client DOKU v10 eDocument117 pagesCsharp OPC Client DOKU v10 eÖzkan KayacanNo ratings yet
- Intro To Embedded Systems - AMIT - NewDocument73 pagesIntro To Embedded Systems - AMIT - NewOmar EzzNo ratings yet
- LAB 10 Introduction To Ladder Logic ProgrammingDocument10 pagesLAB 10 Introduction To Ladder Logic ProgrammingNyanphyo AungNo ratings yet
- Keba Drives PDFDocument44 pagesKeba Drives PDFSSECECENo ratings yet
- How to connect to Siemens CPU and view module informationDocument70 pagesHow to connect to Siemens CPU and view module informationBenny AvilezNo ratings yet
- Motion Control ReportFrom EverandMotion Control ReportRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Lecture4 PIDDocument21 pagesLecture4 PIDSandro MoreroNo ratings yet
- Alternator Commissioning ManualDocument67 pagesAlternator Commissioning ManualRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- @32 1Document910 pages@32 1Suhendri SaputraNo ratings yet
- 2020 Book ProgrammingPersistentMemoryDocument457 pages2020 Book ProgrammingPersistentMemorySuhendri SaputraNo ratings yet
- 07 PID ControllerDocument25 pages07 PID ControllerZuhair HamzaNo ratings yet
- Yokogawa PID Tuning Guide - CsTunerDocument28 pagesYokogawa PID Tuning Guide - CsTunerZohaib Alam100% (2)
- Simocode-Dp Handleiding 1403974 PDFDocument320 pagesSimocode-Dp Handleiding 1403974 PDFAssem SaffariniNo ratings yet
- PLC Producers and Visualization in Lecture 11Document33 pagesPLC Producers and Visualization in Lecture 11al_amin1982No ratings yet
- Siemens PLC Programming Example1Document12 pagesSiemens PLC Programming Example1Pantea IonNo ratings yet
- Basic PLCDocument77 pagesBasic PLCrpshvju100% (1)
- Lecture12 (Dispersion)Document28 pagesLecture12 (Dispersion)Suhendri SaputraNo ratings yet
- Siemens LadderDocument218 pagesSiemens Ladderrph3No ratings yet
- ADC0803, ADC0804: 8-Bit, Microprocessor-Compatible, A/D Converters FeaturesDocument17 pagesADC0803, ADC0804: 8-Bit, Microprocessor-Compatible, A/D Converters FeaturesJorge Luis Castillo GuarachiNo ratings yet
- 7 Habits Summary PDFDocument11 pages7 Habits Summary PDFVu Huong LyNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and Infinitives - Their Noun RolesDocument7 pagesGerunds and Infinitives - Their Noun RolesSuhendri SaputraNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic ConceptsDocument10 pagesFiber Optic ConceptsecarpentieroNo ratings yet
- My Will DreamDocument3 pagesMy Will DreamSuhendri SaputraNo ratings yet
- FSK Demodulator/ Tone Decoder: ... The Analog Plus CompanyDocument24 pagesFSK Demodulator/ Tone Decoder: ... The Analog Plus CompanyLuis Fernando RojasNo ratings yet
- FM Crystal RadioDocument11 pagesFM Crystal RadioSuhendri SaputraNo ratings yet
- 05 Adaptive Resonance TheoryDocument0 pages05 Adaptive Resonance TheorySuhendri SaputraNo ratings yet
- Telemetry PDFDocument2 pagesTelemetry PDFSuhendri SaputraNo ratings yet
- Windows Experience IndexDocument1 pageWindows Experience IndexSuhendri SaputraNo ratings yet
- Spirited AwayDocument5 pagesSpirited AwaySuhendri SaputraNo ratings yet
- My Will DreamDocument3 pagesMy Will DreamSuhendri SaputraNo ratings yet
- Simatic Pcs7 v9 EnglDocument91 pagesSimatic Pcs7 v9 Englmunro_85No ratings yet
- Computer Science Solved Past Paper For IGCSE EDEXCELDocument4 pagesComputer Science Solved Past Paper For IGCSE EDEXCELaayanshehzad09No ratings yet
- Feature Scope Description For SAP HANA 2.0 SPS 07 enDocument44 pagesFeature Scope Description For SAP HANA 2.0 SPS 07 enrvinNo ratings yet
- OS Question Bank Module 1-4Document8 pagesOS Question Bank Module 1-4Vamshidhar Reddy100% (1)
- Maryland Election Integrity LLC V Maryland SBE EXHIBIT O 093113888367Document3 pagesMaryland Election Integrity LLC V Maryland SBE EXHIBIT O 093113888367Christopher GleasonNo ratings yet
- MoTeC C185 User ManualDocument90 pagesMoTeC C185 User ManualIván Suárez AriasNo ratings yet
- Access ControlDocument10 pagesAccess ControlRajesh RajendranNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Computer System Unit (Components)Document31 pagesParts of A Computer System Unit (Components)Anonymous PcPkRpAKD5No ratings yet
- T120h ConfigguideDocument47 pagesT120h ConfigguideOmar sameerNo ratings yet
- Python Mod1 PPTDocument141 pagesPython Mod1 PPTadfqadsfNo ratings yet
- Jimma University: Jimma Institute of TechnologyDocument8 pagesJimma University: Jimma Institute of TechnologyadmachewNo ratings yet
- Computer MCQ 1000Document125 pagesComputer MCQ 1000Bhartendu ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Common Government Job Exam Questions and AnswersDocument8 pagesCommon Government Job Exam Questions and AnswersRozgar ComNo ratings yet
- Database ManagementDocument164 pagesDatabase ManagementSandesh mehraNo ratings yet
- Applications of Flip FlopsDocument2 pagesApplications of Flip FlopsThomas JinduNo ratings yet
- Part I: - Choose The Best Answer (16 Point)Document4 pagesPart I: - Choose The Best Answer (16 Point)Habtamu Hailemariam AsfawNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument10 pagesReportJay KevalramaniNo ratings yet
- IT in Modern Era PRELIM NOTESDocument14 pagesIT in Modern Era PRELIM NOTESCandice LoganNo ratings yet
- Term Paper Topics of CAP663 D1E16Document3 pagesTerm Paper Topics of CAP663 D1E16abhiwave69No ratings yet
- Handbook of Digital Techniques For High-Speed DesignDocument29 pagesHandbook of Digital Techniques For High-Speed DesignJustin FozzardNo ratings yet
- Download ebook Foundations Of Computer Science Pdf full chapter pdfDocument67 pagesDownload ebook Foundations Of Computer Science Pdf full chapter pdfjesse.hall551100% (25)
- Rhel 5 6 7 Cheatsheet 27x36 1014 Jcs Web PDFDocument1 pageRhel 5 6 7 Cheatsheet 27x36 1014 Jcs Web PDFUmer Aziz RanaNo ratings yet
- Directed Signalling Connection Re-EstablishmentDocument12 pagesDirected Signalling Connection Re-EstablishmentTedCasasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 LoadersDocument47 pagesChapter 3 LoadersSky J0% (1)
- C01-01 Comp. Fund.Document3 pagesC01-01 Comp. Fund.Gurjot Singh RihalNo ratings yet
- Cloud-Based Image HostingDocument10 pagesCloud-Based Image HostingManish BroxNo ratings yet
- How To Add A File System To An Existing ZoneDocument6 pagesHow To Add A File System To An Existing Zonefirojin1No ratings yet
- Principles of Business Document Production and Information Management 2.1-3.4Document2 pagesPrinciples of Business Document Production and Information Management 2.1-3.4Nassima56% (9)
- Activity Sheet Quarter 1 - Module 2 Parts and Functions of ComputerDocument10 pagesActivity Sheet Quarter 1 - Module 2 Parts and Functions of ComputerRainman InsanityNo ratings yet
- PL 900Document22 pagesPL 900dumpsit20210% (2)