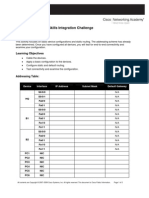
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Principles of Economics With Examples
Uploaded by
Taham Ahmed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views2 pagesEconomics is the study of how society uses its limited resources to produce, distribute, and consume goods and services. Gregory Mankiw outlines ten principles of economics, including that people face tradeoffs, rational people think at the margin, and markets are usually a good way to organize economic activity but governments can sometimes improve outcomes. The principles also discuss how incentives affect behavior, trade benefits all parties, and a country's standard of living depends on productivity.
Original Description:
Original Title
Principles of economics with examples.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEconomics is the study of how society uses its limited resources to produce, distribute, and consume goods and services. Gregory Mankiw outlines ten principles of economics, including that people face tradeoffs, rational people think at the margin, and markets are usually a good way to organize economic activity but governments can sometimes improve outcomes. The principles also discuss how incentives affect behavior, trade benefits all parties, and a country's standard of living depends on productivity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views2 pagesPrinciples of Economics With Examples
Uploaded by
Taham AhmedEconomics is the study of how society uses its limited resources to produce, distribute, and consume goods and services. Gregory Mankiw outlines ten principles of economics, including that people face tradeoffs, rational people think at the margin, and markets are usually a good way to organize economic activity but governments can sometimes improve outcomes. The principles also discuss how incentives affect behavior, trade benefits all parties, and a country's standard of living depends on productivity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Economics is the study of how society uses its limited resources.
Economics is a social science
that deals with the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
Gregory Mankiw in his Principles of Economics outlines Ten Principles of Economics that we will
replicate here, they are:
1. People face trade-offs:
Making decisions requires trading off one goal against another.
Example:
The parents offer a great meal, and this money could have been used in the cinema.
2. The cost of something is what you give up to get it:
Because people face tradeoffs, making decisions requires comparing the costs and
benefits of alternative course of action.
Example:
You are having a free product, you are wasting time in the line.
3. Rational people think at the margin:
Decisions are not usually in the extreme points. We say in marginal changes.
Example:
Exercising.
Education.
4. People respond to incentives:
Because people make decision by comparing costs and benefits, their behavior may
change when the costs or benefits change.
Example:
Discount to museums on Sundays.
5. Trade can make everyone better off:
Trade allows each person to specialize in the activities he or she does best and to enjoy a
variety of goods and services at lower cost.
Example:
Colombia in coffee.
James in soccer.
6. Markets are usually a good way to organize economic activity:
Market economy: Economy that allocates resources through the decentralized decision
of many firms and households as they interact in markets for goods and services.
Example:
Firms decide what they will produce.
7. Governments can sometimes improve market outcomes:
Two reasons to intervene the economics: efficiency and equity. When there are market
failures.
Externality: The impact of one person’s action on the well-being of another person.
Example:
Invention.
Noise from your neighbor.
8. A country's standard of living depends on its ability to produce goods and services:
Citizens of high-income countries have more TV sets, more cars, better nutrition, and better
health care. Almost all variation in countries productivity.
9. Prices rise when the government prints too much money:
Inflation, an increase in the overall level of prices in the economy.
Growth of the quantity in the economy.
When there is too much money, the Price of it is lower.
Example:
Venezuela
10. Society faces a short-run tradeoff between Inflation and unemployment:
Inflation for many countries is primordial activity for the economy.
Why is so hard to control it?
There is a temporary unemployment rise. Philips curve.
Prices are slow to adjust. Imagine that the government reduces the quantity of money in
the economy.
- Lower sales.
- Firms have to lay off workers.
Until the prices adjust.
You might also like
- Guide of Economy TestDocument2 pagesGuide of Economy TestJesus Abraham Gonzalez CollazoNo ratings yet
- Ten Principles of EconomicsDocument37 pagesTen Principles of Economicschoutu97No ratings yet
- Economic PrinciplesDocument6 pagesEconomic PrinciplesRockacerNo ratings yet
- Ten Principles of EconomicsDocument34 pagesTen Principles of EconomicsvarshitaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Economics:: 1) People Face Trade-Offs: Due To Scarcity of Resources One Needs To PayDocument5 pagesPrinciples of Economics:: 1) People Face Trade-Offs: Due To Scarcity of Resources One Needs To PayAVIRAL PRATAP SINGH CHAWDANo ratings yet
- Economics and International BusinessDocument37 pagesEconomics and International BusinessChavez RamonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Ten Principles of Economics: Instructor: A Tabassum Class Notes ECON 1000Document2 pagesChapter 1-Ten Principles of Economics: Instructor: A Tabassum Class Notes ECON 1000AmanNo ratings yet
- Economics S2&3 ReviewerDocument4 pagesEconomics S2&3 ReviewerIñigo Mathay RojasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 2Document11 pagesLecture 1 2JL ManabaNo ratings yet
- 10 Principles of EconDocument9 pages10 Principles of EconRish DagaragaNo ratings yet
- Economics and International BusinessDocument23 pagesEconomics and International BusinessEthelyn Cailly R. ChenNo ratings yet
- Economics and International BusinessDocument21 pagesEconomics and International BusinessVictor SundahNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 M1Document9 pagesChap 2 M1science boyNo ratings yet
- ECON Principles of EconomicsDocument4 pagesECON Principles of EconomicsDaisy Marie A. RoselNo ratings yet
- MicroeconomicsDocument48 pagesMicroeconomicsattaullahNo ratings yet
- 10 Economics PrincipleDocument3 pages10 Economics PrincipleM Hoqqil FatwaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Ten Principles of MicroeconomicsDocument3 pagesChapter 1: Ten Principles of MicroeconomicsSavannah Simone Petrachenko50% (2)
- Mankiw's Ten Principles of EconomicsDocument3 pagesMankiw's Ten Principles of EconomicsVeronica KateNo ratings yet
- Macro SummmaryDocument116 pagesMacro SummmaryJeevikaGoyalNo ratings yet
- Principles of Microeconomics CH 1&2 NotesDocument9 pagesPrinciples of Microeconomics CH 1&2 NotesAnnyoung93No ratings yet
- 001b 10 Principles of EconomicsDocument7 pages001b 10 Principles of EconomicsAbigael Esmena100% (1)
- Chapter 1: Ten Principles of Microeconomics: Economy Households and EconomiesDocument3 pagesChapter 1: Ten Principles of Microeconomics: Economy Households and EconomiesManel KricheneNo ratings yet
- Ten Principles of EconomicsDocument2 pagesTen Principles of EconomicsDucki ChanNo ratings yet
- Ten Principles of EconomicsDocument1 pageTen Principles of EconomicsSubrat RathNo ratings yet
- Ten Principles of EconomicsDocument21 pagesTen Principles of EconomicsYvonne Llaban RangabanNo ratings yet
- Summary of MicroeconomicsDocument37 pagesSummary of MicroeconomicsMuhammad FaizanNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics MIDTERM REVIEWERDocument13 pagesApplied Economics MIDTERM REVIEWERKate JavierNo ratings yet
- 10 Principles of EconomicsDocument18 pages10 Principles of EconomicsanujjalansNo ratings yet
- ECO1104 Microeconomics NotesDocument26 pagesECO1104 Microeconomics NotesPriya Srinivasan100% (1)
- Ten Principles of EconomicsDocument4 pagesTen Principles of EconomicsNouman ShafiqNo ratings yet
- Ssed 11 Module 1 Lesson 1Document11 pagesSsed 11 Module 1 Lesson 1Shiela IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EconomicsDocument14 pagesIntroduction To EconomicsKemalNo ratings yet
- Economics Placement Preparation MaterialDocument17 pagesEconomics Placement Preparation MaterialTopsy KreateNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Intro To Macro and Measuring Macro VariablesDocument87 pagesChapter 1 Intro To Macro and Measuring Macro VariablesK60 Nguyễn Mai ChiNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1 - Ten Principles of Economics 1Document25 pagesCh. 1 - Ten Principles of Economics 1Darshan VadherNo ratings yet
- What Is Economic System2Document2 pagesWhat Is Economic System2Camille Patricia Salazar RopaNo ratings yet
- 10 Principles of EconomicsDocument3 pages10 Principles of EconomicsGrace Carrasco100% (3)
- Ten Principles of EconomicsDocument5 pagesTen Principles of Economicshjpa2023-7388-23616No ratings yet
- Unit1-Topic2 Handout-Ten Principles of EconomicsDocument4 pagesUnit1-Topic2 Handout-Ten Principles of EconomicsRudolph FelipeNo ratings yet
- 10 Principles of Economics by Gregory MankiwDocument2 pages10 Principles of Economics by Gregory MankiwruthNo ratings yet
- 10 Principles of Economics - WikiversityDocument24 pages10 Principles of Economics - WikiversityprudenceNo ratings yet
- Environmental Economics Lectue 1Document5 pagesEnvironmental Economics Lectue 1maryam gullNo ratings yet
- CH1 Micro NotesDocument4 pagesCH1 Micro NotesJas JasNo ratings yet
- Chap 1Document3 pagesChap 1devilanghaianhphamNo ratings yet
- Eco Test K LiyeDocument10 pagesEco Test K LiyemilanNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Managerial EconomicsDocument23 pagesAn Overview of Managerial Economicsnitin heart hakerNo ratings yet
- AP Microeconomics Class Notes - Chapter 1 - Ten Principles of EconomicsDocument5 pagesAP Microeconomics Class Notes - Chapter 1 - Ten Principles of EconomicshiralltaylorNo ratings yet
- 10 Principles of Economics HomeworkDocument3 pages10 Principles of Economics HomeworkPoddmoNo ratings yet
- Summary of Principles of Economy Chapter 1Document6 pagesSummary of Principles of Economy Chapter 1Arizfa100% (1)
- Chapter IDocument5 pagesChapter IAdonis GaoiranNo ratings yet
- Gregory MankiwDocument3 pagesGregory MankiwPj FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Economics Is About Decision Making in Situations oDocument7 pagesEconomics Is About Decision Making in Situations oSPECIAL MOOTNo ratings yet
- Desy Wahyu Rahmawati Imabs A (20180410104) : Economics AssignmentDocument5 pagesDesy Wahyu Rahmawati Imabs A (20180410104) : Economics AssignmentDesy Wahyu RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- CH 1 - 10 Principles of EconomicsDocument1 pageCH 1 - 10 Principles of EconomicsSalma MoralyNo ratings yet
- Principles of Economics,: Powerpoint® Lecture PresentationDocument30 pagesPrinciples of Economics,: Powerpoint® Lecture PresentationuniqueMyomNo ratings yet
- Basic Economic ConceptsDocument18 pagesBasic Economic ConceptsShakarim AubakirovNo ratings yet
- Abu Naser Mohammad Saif: Assistant ProfessorDocument29 pagesAbu Naser Mohammad Saif: Assistant ProfessorSH RaihanNo ratings yet
- AE - Topic 7 HandoutDocument9 pagesAE - Topic 7 Handoutromeroglenda101106No ratings yet
- Pengantar Ilmu Ekonomi (Principles of Economics) : Dr. Ir. Satiri, MM, MBA E-Mail: Phone: 0811-107948Document36 pagesPengantar Ilmu Ekonomi (Principles of Economics) : Dr. Ir. Satiri, MM, MBA E-Mail: Phone: 0811-107948Sella Arthenia IllahiNo ratings yet
- Acoute Guide to McConnell Brue and Flynn's Microeconomics: Problems, Principles, and Policies (20th edition)From EverandAcoute Guide to McConnell Brue and Flynn's Microeconomics: Problems, Principles, and Policies (20th edition)Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Lesson Plan in Elementary Mathematics Grade 4Document4 pagesLesson Plan in Elementary Mathematics Grade 4Joanna Mari Malana50% (2)
- Practical 13. Determinant Cyclic Progress BarDocument3 pagesPractical 13. Determinant Cyclic Progress Barnavteshdeore19No ratings yet
- Sandwich PDFDocument26 pagesSandwich PDFIvan BorodavkaNo ratings yet
- QuasquaiDocument29 pagesQuasquaiPaul DresserNo ratings yet
- Dezinfectia AmprentelorDocument6 pagesDezinfectia Amprentelorbarby17_2005No ratings yet
- X9C104PDocument11 pagesX9C104PAntonio CesarioNo ratings yet
- Graph Theory Approach To Transportation Systems DesignDocument8 pagesGraph Theory Approach To Transportation Systems Designsandi nurmansyahNo ratings yet
- CAP-CT-PDS Ultrasound Datasheet 2017Document2 pagesCAP-CT-PDS Ultrasound Datasheet 2017Mario CepedaNo ratings yet
- Tranformasi Pos Indonesia Menjadi Perusahaan Digital - Faizal Rochmad Djoemadi (Watermark)Document30 pagesTranformasi Pos Indonesia Menjadi Perusahaan Digital - Faizal Rochmad Djoemadi (Watermark)Anton Soco100% (5)
- CMP 150 Generator Series DatasheetDocument2 pagesCMP 150 Generator Series DatasheetAquiles Tolosa SotomayorNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Bear Put SpreadDocument14 pagesLesson 8 Bear Put Spreadrishab kumarNo ratings yet
- Multi Crystalline Solar PV ModulesDocument2 pagesMulti Crystalline Solar PV ModulesBorno ShahinNo ratings yet
- Catch Up Friday MATHDocument6 pagesCatch Up Friday MATHrizalyn.devera123No ratings yet
- Director of Teaching and Learning Job DescriptionDocument3 pagesDirector of Teaching and Learning Job DescriptionDale Joseph KiehlNo ratings yet
- Meq 01 2015 0012Document17 pagesMeq 01 2015 0012Anonymous Ja3jvaXNo ratings yet
- Basic Parts of A DesktopDocument2 pagesBasic Parts of A DesktopGo ZerepNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Prelim ExamDocument11 pagesAnswer Key Prelim ExamJerald Jardeliza100% (1)
- Making Basic Strain Measurements: Using 24-Bit HardwareDocument6 pagesMaking Basic Strain Measurements: Using 24-Bit HardwaredemirilkNo ratings yet
- 9TH - Icse - Physics - Worksheet - Reflection of Light 2Document5 pages9TH - Icse - Physics - Worksheet - Reflection of Light 2manojboa100% (3)
- Stc750 Truck Crane 75 Tons Lifting Capacity: Quality Changes The WorldDocument9 pagesStc750 Truck Crane 75 Tons Lifting Capacity: Quality Changes The WorldDidier FernandezNo ratings yet
- E2 PTAct 2 9 1 DirectionsDocument2 pagesE2 PTAct 2 9 1 DirectionsAsad RiazNo ratings yet
- Desigo Control Point - Basic DocumentationDocument42 pagesDesigo Control Point - Basic DocumentationJose sanchezNo ratings yet
- Playfair Cipher: Cipher Is A Manual Symmetric Encryption Technique and Was The First LiteralDocument9 pagesPlayfair Cipher: Cipher Is A Manual Symmetric Encryption Technique and Was The First LiteralJOHN CHARLASNo ratings yet
- Hindi Alphabets With Picture, Hindi Vyanjan Learning, Discover IndiaDocument7 pagesHindi Alphabets With Picture, Hindi Vyanjan Learning, Discover IndiaJag Jagdish100% (5)
- Unit - 2 Exercises (Answers) : English Grammar in Use - 5 EditionDocument2 pagesUnit - 2 Exercises (Answers) : English Grammar in Use - 5 EditionMounir AngadNo ratings yet
- Capacity and VolumeDocument6 pagesCapacity and VolumeUsman Madubun0% (1)
- Syllabus 4th SemDocument3 pagesSyllabus 4th SemPrianca PrathapNo ratings yet
- Cooling Load Calculation ProcedureDocument2 pagesCooling Load Calculation ProcedurezampacaanasNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/11Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/11bali yunNo ratings yet
- Pick-n-Place ApplicationDocument21 pagesPick-n-Place Applicationreek_bhatNo ratings yet