Professional Documents
Culture Documents
10 Principles of Economics Homework
Uploaded by
Poddmo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views3 pagesThe document outlines 10 principles of economics according to Gregory Mankiw. It describes that people face tradeoffs when making decisions, the cost of something is what is given up to get it, and rational people think at the margin and respond to incentives. It also notes that trade can benefit all parties, markets are generally effective at organizing economic activity but governments can improve outcomes during market failures, and a country's production determines its standard of living. Additionally, it states that prices rise when a government prints too much money and there is a short-term tradeoff between inflation and unemployment.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document outlines 10 principles of economics according to Gregory Mankiw. It describes that people face tradeoffs when making decisions, the cost of something is what is given up to get it, and rational people think at the margin and respond to incentives. It also notes that trade can benefit all parties, markets are generally effective at organizing economic activity but governments can improve outcomes during market failures, and a country's production determines its standard of living. Additionally, it states that prices rise when a government prints too much money and there is a short-term tradeoff between inflation and unemployment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views3 pages10 Principles of Economics Homework
Uploaded by
PoddmoThe document outlines 10 principles of economics according to Gregory Mankiw. It describes that people face tradeoffs when making decisions, the cost of something is what is given up to get it, and rational people think at the margin and respond to incentives. It also notes that trade can benefit all parties, markets are generally effective at organizing economic activity but governments can improve outcomes during market failures, and a country's production determines its standard of living. Additionally, it states that prices rise when a government prints too much money and there is a short-term tradeoff between inflation and unemployment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
10 Principles of Economics
Gregory Mankiw, describes 10 principles
of Economics, which are summarized below:
1. People Face Tradeoffs
To get one thing, we usually have to give up something else
Going to a party the night before your midterm leaves less time for
studying.
Having more money to buy stuff requires working longer hours, which
leaves less time for leisure.
Protecting the environment requires resources that could otherwise be
used to produce consumer goods.
Sleep vs. Morning Classes
2. The Cost of Something is What You Give Up to Get It
Opportunity cost is the second best alternative foregone.
Example: The opportunity cost of going to college is the money you
could have earned if you used that time to work.
3. Rational People Think at the Margin
People will only take action of the marginal benefit exceed the marginal
cost. Marginal changes are small, incremental changes to an existing
plan of action
Example: Deciding to produce one more pencil or not
4.People Respond to Incentives
Incentive is something that causes a person to act. Because people use cost
and benefit analysis, they also respond to incentives
Example: Higher taxes on cigarettes to prevent smoking
5. Trade Can Make Everyone Better Off
Trade allows countries to specialize according to their
comparative advantages and to enjoy a greater variety of goods
and services
6. Markets Are Usually a Good Way to Organize Economic
Activity
Adam Smith made the observation that when households and
firms interact in markets guided by the invisible hand, they will
produce the most surpluses for the economy
7. Governments Can Sometimes Improve Economic Outcomes
Market failures occur when the market fails to allocate
resources efficiently. Governments can step in and intervene in
order to promote efficiency and equity.
8. The Standard of Living Depends on a Country's Production
The more goods and services produced in a country, the higher
the standard of living. As people consume a larger quantity of
goods and services, their standard of living will increase
9. Prices Rise When the Government Prints Too Much Money
When too much money is floating in the economy, there will be
higher demand for goods and services. This will cause firms to
increase their price in the long run causing inflation.
10. Society Faces a Short-Run Tradeoff Between Inflation and
Unemployment
In the short run, when prices increase, suppliers will want to
increase their production of goods and services. In order to
achieve this, they need to hire more workers to produce those
goods and services. More hiring means lower unemployment
while there is still inflation. However, this is not the case in the
long-run
Thank You!
You might also like
- Acoute Summary of: N. Gregory Mankiw's Principles of Microeconomics (7th edition)From EverandAcoute Summary of: N. Gregory Mankiw's Principles of Microeconomics (7th edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Small Business Turnaround StrategiesDocument6 pagesSmall Business Turnaround StrategiesDave WestfallNo ratings yet
- Ten Principles of EconomicsDocument4 pagesTen Principles of EconomicsNouman ShafiqNo ratings yet
- Principles of Microeconomics CH 1&2 NotesDocument9 pagesPrinciples of Microeconomics CH 1&2 NotesAnnyoung93No ratings yet
- E-Mobile Business ProposalDocument22 pagesE-Mobile Business ProposalSabrina Abdurahman100% (2)
- 10 Principles of EconomicsDocument3 pages10 Principles of EconomicsGrace Carrasco100% (3)
- Economics and International BusinessDocument21 pagesEconomics and International BusinessVictor SundahNo ratings yet
- Web Generated Bill: Lahore Electric Supply Company - Electricity Consumer BillDocument7 pagesWeb Generated Bill: Lahore Electric Supply Company - Electricity Consumer BillAsad123Asad123Asad0% (1)
- Mankiw's Ten Principles of EconomicsDocument3 pagesMankiw's Ten Principles of EconomicsVeronica KateNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of EconomicsDocument23 pagesBasic Principles of EconomicsFrank WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Employee Benefits Exercises-ANSWERSDocument12 pagesEmployee Benefits Exercises-ANSWERSfaye pantiNo ratings yet
- Urban Water PartnersDocument2 pagesUrban Water Partnersutskjdfsjkghfndbhdfn100% (2)
- What Are The Principles of Economics? Describe EachDocument2 pagesWhat Are The Principles of Economics? Describe EachMaria Evelyn WonNo ratings yet
- 10 Principles of EconomicsDocument2 pages10 Principles of EconomicsHanna Mae GapasNo ratings yet
- Guide of Economy TestDocument2 pagesGuide of Economy TestJesus Abraham Gonzalez CollazoNo ratings yet
- Gumandoy (Entrep Ass 2)Document2 pagesGumandoy (Entrep Ass 2)Chadel Rose D. GumandoyNo ratings yet
- Desy Wahyu Rahmawati Imabs A (20180410104) : Economics AssignmentDocument5 pagesDesy Wahyu Rahmawati Imabs A (20180410104) : Economics AssignmentDesy Wahyu RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Economic Concept and PrinciplesDocument11 pagesEconomic Concept and PrinciplesJuneville Vincent AndoNo ratings yet
- 10 Economics PrincipleDocument3 pages10 Economics PrincipleM Hoqqil FatwaNo ratings yet
- 10 Principle of EconomicsDocument4 pages10 Principle of EconomicsAli RAZANo ratings yet
- Ten Economic PrinciplesDocument2 pagesTen Economic PrinciplesAngelo Aldous O. MarchadeschNo ratings yet
- Ten Principles of EconomicsDocument2 pagesTen Principles of EconomicsDucki ChanNo ratings yet
- Ten Principles of EconomicsDocument1 pageTen Principles of EconomicsSubrat RathNo ratings yet
- Economics and International BusinessDocument37 pagesEconomics and International BusinessChavez RamonNo ratings yet
- Definition of Managerial Economics: 1. Art and ScienceDocument18 pagesDefinition of Managerial Economics: 1. Art and ScienceABHISHEK SHARMANo ratings yet
- MathDocument18 pagesMathLadyrose SalazarNo ratings yet
- Econ 122Document2 pagesEcon 122kyligaia69No ratings yet
- Economics and International BusinessDocument23 pagesEconomics and International BusinessEthelyn Cailly R. ChenNo ratings yet
- Chap 1Document3 pagesChap 1devilanghaianhphamNo ratings yet
- Principles of EconomicsDocument26 pagesPrinciples of EconomicsJAGATHESANNo ratings yet
- Principles of Economics:: 1) People Face Trade-Offs: Due To Scarcity of Resources One Needs To PayDocument5 pagesPrinciples of Economics:: 1) People Face Trade-Offs: Due To Scarcity of Resources One Needs To PayAVIRAL PRATAP SINGH CHAWDANo ratings yet
- Introduction To CourseDocument72 pagesIntroduction To CourseAryan AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Intro To Macro and Measuring Macro VariablesDocument87 pagesChapter 1 Intro To Macro and Measuring Macro VariablesK60 Nguyễn Mai ChiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Slides NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Slides Notesسید یاور امام کاظمیNo ratings yet
- Ten Principles of EconomicsDocument37 pagesTen Principles of Economicschoutu97No ratings yet
- What Is Economic System2Document2 pagesWhat Is Economic System2Camille Patricia Salazar RopaNo ratings yet
- 10 Principles of EconomicsDocument3 pages10 Principles of EconomicsBagsurge CornerNo ratings yet
- AE - Topic 7 HandoutDocument9 pagesAE - Topic 7 Handoutromeroglenda101106No ratings yet
- Economic PrinciplesDocument6 pagesEconomic PrinciplesRockacerNo ratings yet
- Principles of Economics With ExamplesDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Economics With ExamplesTaham AhmedNo ratings yet
- 4 EverDocument3 pages4 Everabdilaahi almisNo ratings yet
- 10 Principles of EconDocument9 pages10 Principles of EconRish DagaragaNo ratings yet
- Ten Principles of EconomicsDocument5 pagesTen Principles of Economicshjpa2023-7388-23616No ratings yet
- Ten Principles of EconomicsDocument24 pagesTen Principles of Economics428SHUBHASHEESH SAXENANo ratings yet
- 10 Principles of EconomicsDocument3 pages10 Principles of EconomicsArlette MovsesyanNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics MIDTERM REVIEWERDocument13 pagesApplied Economics MIDTERM REVIEWERKate JavierNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 M1Document9 pagesChap 2 M1science boyNo ratings yet
- Unit1-Topic2 Handout-Ten Principles of EconomicsDocument4 pagesUnit1-Topic2 Handout-Ten Principles of EconomicsRudolph FelipeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Ten Principles of Microeconomics: Economy Households and EconomiesDocument3 pagesChapter 1: Ten Principles of Microeconomics: Economy Households and EconomiesManel KricheneNo ratings yet
- Ten Lessons From Economics: Solutions To Text ProblemsDocument5 pagesTen Lessons From Economics: Solutions To Text ProblemsterrancekuNo ratings yet
- 10 Principles of EconomicsDocument12 pages10 Principles of EconomicsAbdul Rehman AhmadNo ratings yet
- Tugas Resume Chapter 1 Dan 4 Satriya Nazar 2001378 TD 1.1Document8 pagesTugas Resume Chapter 1 Dan 4 Satriya Nazar 2001378 TD 1.1Satriya NazarNo ratings yet
- Environmental Economics Lectue 1Document5 pagesEnvironmental Economics Lectue 1maryam gullNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Economics 10 Economics Principle Resume: Name: Muhammad Hoqqil Fatwa NIM: 19522214Document2 pagesIntroduction To Economics 10 Economics Principle Resume: Name: Muhammad Hoqqil Fatwa NIM: 19522214M Hoqqil FatwaNo ratings yet
- Macro SummmaryDocument116 pagesMacro SummmaryJeevikaGoyalNo ratings yet
- Project in BasicMicroDocument4 pagesProject in BasicMicrohohmannjasmin65No ratings yet
- Ssed 11 Module 1 Lesson 1Document11 pagesSsed 11 Module 1 Lesson 1Shiela IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Mod 1 MicroecoDocument23 pagesMod 1 MicroecoHeina LyllanNo ratings yet
- Ten Principles of EconomicsDocument34 pagesTen Principles of EconomicsvarshitaNo ratings yet
- Gregory MankiwDocument3 pagesGregory MankiwPj FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Business Economics ECN520MDocument32 pagesBusiness Economics ECN520MRush YuviencoNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Summary NotesDocument4 pagesChapter One Summary NotesUmar FarooqNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Chapter 1Document2 pagesMultiple Choice Chapter 1Den NgNo ratings yet
- 10 Principles of Economics - WikiversityDocument24 pages10 Principles of Economics - WikiversityprudenceNo ratings yet
- Economics Is About Decision Making in Situations oDocument7 pagesEconomics Is About Decision Making in Situations oSPECIAL MOOTNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Slide Presentation Script Slide-1: Slide - 2:: Hello and Welcome To My PresentationDocument3 pagesPowerpoint Slide Presentation Script Slide-1: Slide - 2:: Hello and Welcome To My PresentationPoddmoNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Slide Presentation Script Slide-1: Slide - 2:: Hello and Welcome To My PresentationDocument3 pagesPowerpoint Slide Presentation Script Slide-1: Slide - 2:: Hello and Welcome To My PresentationPoddmoNo ratings yet
- ENG101 Final Writing Test Answer To The Question No. 01: DifferencesDocument1 pageENG101 Final Writing Test Answer To The Question No. 01: DifferencesPoddmoNo ratings yet
- ENG 101 HomeworkDocument1 pageENG 101 HomeworkPoddmoNo ratings yet
- Wordvice Proofreading Sample (Farabi Nawar)Document5 pagesWordvice Proofreading Sample (Farabi Nawar)farabi nawarNo ratings yet
- Chapter - External Analysis MCQDocument11 pagesChapter - External Analysis MCQgamergeeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11-Investments in Noncurrent Operating Assets-Utilization and RetirementDocument33 pagesChapter 11-Investments in Noncurrent Operating Assets-Utilization and RetirementYukiNo ratings yet
- Vendor Invoice Tracker-TVS SCS-2022-2023Document385 pagesVendor Invoice Tracker-TVS SCS-2022-2023bishffxNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Applying International Financial Reporting Standards Picker Leo Loftus Wise Clark Alfredson 3rd EditionDocument48 pagesSolution Manual For Applying International Financial Reporting Standards Picker Leo Loftus Wise Clark Alfredson 3rd EditionCalvinGreeneizfp100% (45)
- 3rd Assignment ABC AnalysisDocument9 pages3rd Assignment ABC AnalysisDivya ToppoNo ratings yet
- MBA Final Year ReportDocument9 pagesMBA Final Year ReportmmddugkyfinanceNo ratings yet
- Final Exam - Decision TreeDocument2 pagesFinal Exam - Decision Treevinilima9No ratings yet
- Instacart BookletDocument14 pagesInstacart BookletHenry VidalNo ratings yet
- Imp KDL CTH Feb-15 (Excel)Document516 pagesImp KDL CTH Feb-15 (Excel)Vivek DomadiaNo ratings yet
- Export Import ProcessDocument26 pagesExport Import ProcessM HarikrishnanNo ratings yet
- Procter & Gamble-Gillette Merger: By: Christine Cruell Kamika Hemphill Antjuan Seawright Jonathan ToneyDocument33 pagesProcter & Gamble-Gillette Merger: By: Christine Cruell Kamika Hemphill Antjuan Seawright Jonathan ToneythorndykNo ratings yet
- Meera Maam DeedDocument13 pagesMeera Maam DeedADIL ABBASNo ratings yet
- Economic Impacts of Covid 19Document19 pagesEconomic Impacts of Covid 19Soorya ShrinivasNo ratings yet
- The Workmen's Compensation Act, 1923Document12 pagesThe Workmen's Compensation Act, 1923dua tanveerNo ratings yet
- Simple & Compound Interest Trainer PDFDocument3 pagesSimple & Compound Interest Trainer PDFDeepak SNo ratings yet
- Yash Raj Films Private LimitedDocument1 pageYash Raj Films Private LimitedKshitij TrivediNo ratings yet
- For Remittances Exceeding USD 25,000 and For All Capital Account TransactionsDocument6 pagesFor Remittances Exceeding USD 25,000 and For All Capital Account TransactionsFor AccounNo ratings yet
- CredDocument4 pagesCredDhruv DuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Governmental AccountingDocument5 pagesChapter 4 Governmental Accountingmohamad ali osmanNo ratings yet
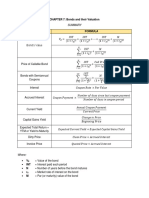
- Bonds and Their Valuation FormulasDocument1 pageBonds and Their Valuation FormulasGabrielle VaporNo ratings yet
- EdDocument5 pagesEdIyyan ParamanandamNo ratings yet
- Examination, 2015 Commerce Specialized Accounting: (Printed Pages 7) Roll. No.Document4 pagesExamination, 2015 Commerce Specialized Accounting: (Printed Pages 7) Roll. No.AbhishekNo ratings yet
- (BOC) PickarooDocument19 pages(BOC) PickarooalfhyoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Events After The Reporting Period PDFDocument4 pagesChapter 12 Events After The Reporting Period PDFAthena LansangNo ratings yet