Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Us20180071653a1 1 5
Us20180071653a1 1 5
Uploaded by
Irena HidayaniOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Us20180071653a1 1 5
Us20180071653a1 1 5
Uploaded by
Irena HidayaniCopyright:
Available Formats
US 2018/0071653 A1 Mar.
15 , 2018
INTEGRATED PRODUCTION OF UREA FOR needed in urea finishing technology and also that by-prod
DIESEL EXHAUST FLUID AND UREA ucts such as additives used or produced during finishing, for
AMMONIUM NITRATE example formaldehyde or biuret (which is a urea byproduct),
need to be removed to produce a product of the desired
FIELD OF THE INVENTION specification . Typical biuret concentrations in finished prod
ucts are 0 . 9 to 1. 1 wt. % . This consequently results in a
[0001] The invention is in the field of the production of biuret content in final DEF product which is over 0 .3 wt. %
urea , and in particular pertains to a method for the combined thus resulting in off spec material. The current specification
production of a urea solution suitable for the abatement of according to ISO 22241 allows maximum 0 . 3 % . The higher
NO in combustion engine exhaust gases, for example biuret concentration results in a less effective DEF solution
exhaust gases produced from Diesel engines (DEF : Diesel with respect to the capture of NO as less urea is available
Exhaust Fluid ) , and the production of urea ammonia nitrate to capture the NOx . Furthermore , during the production of
solution (UAN ). The invention also pertains to a plant for granulate and prills large amounts of water are removed
carrying out the method . which are later added during the dissolution step . This
requires significant amounts of energy which leads to addi
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION tional costs .
[ 0002 ] Urea is generally produced from ammonia and [0007 ] An improved process, disclosed in EP1856038A1,
carbon dioxide . It can be prepared by introducing an ammo is to use a urea aqueous solution obtained directly from or
nia excess together with carbon dioxide at a pressure after the recovery section of the urea melt plant, and dilute
between 12 and 40 MPa and at a temperature between 150° said urea aqueous solution with water to obtain the desired
C . and 250° C . into a urea synthesis section . Typical urea solution . The urea aqueous solution would otherwise be sent
production plants further comprise a recovery section and a to the evaporation section to remove the water from the urea
finishing section . In the recovery section non - converted melt for the production of solid urea via fluid bed granula
ammonia and carbon dioxide are recovered and recirculated tion , pelletizing or prilling. In this way the need for evapo
to the synthesis section. The recovery section is generally ration of water is eliminated , but the urea aqueous solution
followed by an evaporation section . Therein the urea con may contain relatively high levels of ammonia which exceed
centration is further increased by the evaporation of water, the specification for the final DEF product. EP1856038A1
resulting in a highly concentrated solution that is generally discloses that the ammonia level ( as free ammonia or in the
referred to as a urea melt. In the finishing section , typically, form of ammonium carbamate ) in the solution may be
the urea melt is brought into a desired solid , particulate form , reduced by subjecting the urea aqueous solution to disso
generally involving techniques such as prilling , granulation , ciation , for example by the addition of heat or the reduction
or pelletizing . of pressure , optionally with the addition of a stripping
[ 0003] In the evaporation section still considerable medium or a combination of the foregoing . This step is
amounts of CO2 and particularly NH3 are removed . By effectively the same as and may be carried out in the same
treatment in a scrubber the ammonia is removed . This then type of equipment as the evaporation step in a conventional
goes to a waste water treatment unit which is a very costly finishing section of a urea plant and is therefore sometimes
and energy intensive operation . called ' evaporation step ' or ' pre - evaporation step '. The
10004 ] An interesting urea product is a solution for NOX pre -evaporation step is designed to produce a urea aqueous
abatement such as used in selective reduction , which may be solution which, after dilution with water , meets the require
a non - catalytic thermal process or a selective catalytic ments of Diesel Exhaust Fluid .
reduction (SCR ) process . An example of a solution for SCR [0008 ] A major disadvantage is that the pre -evaporating
is diesel exhaust fluid (DEF ), which term is used in descrip step releases ammonia with inerts from the urea aqueous
tion to generally refer to urea solutions for NOx abatement. solution which may need to be removed to meet ammonia
[0005 ] DEF is a 32 .5 wt. % urea solution in demineralized emission regulations, requiring a dedicated condensation
water with a composition that has maximum 0 .3 wt. % biuret scrubbing section and a subsequent waste water treatment
and maximum 0 .2 wt. % of alkalinity as ammonia . DEF is section integrated with the ureamelt plant in order to recover
marketed under the (commercial) trade names Ad-Blue® , the ammonia released .
Airl® , Arla 32 and AUS - 32 and is injected in the tail gas of 10009 ]. Urea Ammonium Nitrate (UAN ) is a fertilizer
combustion engines to capture NO to prevent it from escap which is generally used as an aqueous solution of urea and
ing to the atmosphere . The purpose of the DEF is to convert ammonium nitrate . Ammonium nitrate is produced by react
the NO , via the reaction : urea + NO , > N , + H , O into harmless ing ammonia with a strong solution of nitric acid while
nitrogen and water. Reduction of NO , from combustion maintaining the pH of the solution within narrow boundar
engines is widely applied as NO , is one of the main sources ies . The resulting solution is then mixed with an aqueous
for environmental pollution indicated for global warming urea solution to obtain UAN . Typical UAN products contain
such as the Global Warming Potential (GWP), Tropospheric 28 wt. % to 32 wt. % of total nitrogen and typically of from
Ozone Formation Potential ( TOFP ) and Ozone Depletion 29 wt. % to 38 wt. % urea and of from 36 wt. % to 48 wt.
Potential (ODP ). % of ammonium nitrate , with the remainder being water.
[0006 ] The production of Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF ) is [0010 ] The demand for UAN is generally subject to strong
generally achieved by dissolving solid urea product in seasonal fluctuations, which makes it desirable to find a way
demineralized water. The solid urea product, for example to operate a plant for UAN in such a way that it can also be
produced via one of the aforementioned finishing technolo - put to economically attractive use at times of low demands
gies and the demineralized water are combined and the for UAN . It is thereby noted that an aqueous urea solution
solution is mixed until the urea is fully dissolved . This produced in a typicalUAN plant for the production of a final
method has the disadvantage that significant investment is UAN product cannot generally be used for the production of
You might also like
- STP 543-1974Document273 pagesSTP 543-1974Tim SchouwNo ratings yet
- Aqueous Ammonia Stripping TechnologyDocument10 pagesAqueous Ammonia Stripping TechnologyMustaqim RazakNo ratings yet
- Emulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingFrom EverandEmulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Urea Synthesis With Pool CondenserDocument1 pageUrea Synthesis With Pool Condensersite commissing teamNo ratings yet
- Toyo Approach Environmental Protection Urea PlantsDocument7 pagesToyo Approach Environmental Protection Urea Plantsjulioscribd1No ratings yet
- Urea Prilling Tower DustDocument14 pagesUrea Prilling Tower DustRajeshkumar ElangoNo ratings yet
- Urea Tech Manual 2006Document15 pagesUrea Tech Manual 2006Khalid GamalNo ratings yet
- Urea Manufacturing Process: BY Ashvani Shukla C&I RelianceDocument18 pagesUrea Manufacturing Process: BY Ashvani Shukla C&I RelianceAdam RizkyNo ratings yet
- The Urea Manufacturing Process: Ammonium CarbamateDocument5 pagesThe Urea Manufacturing Process: Ammonium CarbamateIVAN SAMCRUZNo ratings yet
- How Industrial Businesses Can Reduce Production Costs With Reverse Osmosis: Industrial Reverse OsmosisFrom EverandHow Industrial Businesses Can Reduce Production Costs With Reverse Osmosis: Industrial Reverse OsmosisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Snamprogetti Urea ProcessDocument106 pagesSnamprogetti Urea ProcessHeba Ramadan95% (19)
- Co2 StripperDocument5 pagesCo2 StripperOkta Ochan Chandra100% (1)
- Uhde Technology ProcessDocument20 pagesUhde Technology Processjoko100% (1)
- Urea ManufacturingDocument25 pagesUrea Manufacturingpf06No ratings yet
- Urea BrochureDocument0 pagesUrea BrochureiosiiosiNo ratings yet
- Ammonia ProductionDocument7 pagesAmmonia ProductionIkhtiander IkhtianderNo ratings yet
- Stamicarbon Project PDFDocument30 pagesStamicarbon Project PDFMir Hasib Ul Latif100% (7)
- A On Report Comparison Among All Manufacturing ProcessesDocument11 pagesA On Report Comparison Among All Manufacturing ProcessesMohit BayerNo ratings yet
- Urea Tech Manual 2006Document16 pagesUrea Tech Manual 2006Talha Bin ZubairNo ratings yet
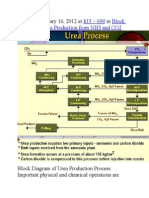
- Published January 16, 2012 at In: 813 × 699 Block Diagram of Urea Production From NH3 and CO2Document9 pagesPublished January 16, 2012 at In: 813 × 699 Block Diagram of Urea Production From NH3 and CO2himanshuchawla654No ratings yet
- Urea Plant Nangal 2014Document8 pagesUrea Plant Nangal 2014Ishan HaiderNo ratings yet
- Acp Module 5Document32 pagesAcp Module 5Mechel Cabaltera87% (15)
- Global hydrogen trade to meet the 1.5°C climate goal: Part II – Technology review of hydrogen carriersFrom EverandGlobal hydrogen trade to meet the 1.5°C climate goal: Part II – Technology review of hydrogen carriersNo ratings yet
- Urea 2Document16 pagesUrea 2ginga716No ratings yet
- Urea Manufacturing Plant-StamicarbonDocument4 pagesUrea Manufacturing Plant-StamicarbonRadhika PillayNo ratings yet
- Sour Water Treatment UnitDocument16 pagesSour Water Treatment Unitpkgarg_iitkgp100% (2)
- Urea Toyo ACES21 - BrochureDocument8 pagesUrea Toyo ACES21 - BrochureSanti SevenfoldNo ratings yet
- A BRIEF REPORT ON UraeDocument6 pagesA BRIEF REPORT ON UraeBigya UpadhyayaNo ratings yet
- US20120302789A1Document10 pagesUS20120302789A1Nestor TamayoNo ratings yet
- Urea-1 PlantDocument34 pagesUrea-1 PlantAjeet SinghNo ratings yet
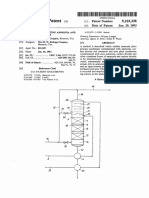
- March 9, 1965 L. Mavrovic: Filed June 16, 1961Document6 pagesMarch 9, 1965 L. Mavrovic: Filed June 16, 1961baharuNo ratings yet
- 789570a3-cee9-425e-8549-c161ad7146faDocument24 pages789570a3-cee9-425e-8549-c161ad7146faĐihiđrô MonoxitNo ratings yet
- Manufacture of UreaDocument9 pagesManufacture of Ureaacharyay72No ratings yet
- European Patent Application: Method and Plant For The Production of Ethanol AminesDocument17 pagesEuropean Patent Application: Method and Plant For The Production of Ethanol AmineswanNo ratings yet
- Nitrate Fertilisers: Rupp Industrial SolutionsDocument20 pagesNitrate Fertilisers: Rupp Industrial SolutionsCarlos Manuel Castillo SalasNo ratings yet
- Nitrogenous Fertilizer Plants: Environmental Guidelines ForDocument6 pagesNitrogenous Fertilizer Plants: Environmental Guidelines ForMuhammad Musharib Islam KhanNo ratings yet
- Nitrogeno US: FertilizerDocument69 pagesNitrogeno US: FertilizerKATHIRIYA NIKUNJNo ratings yet
- Patente Tratamiento de Condensando de AmonioDocument6 pagesPatente Tratamiento de Condensando de AmonioJesus PerezNo ratings yet
- Stamicarbon - Urea Process NarrativeDocument5 pagesStamicarbon - Urea Process NarrativevikramjaidkaNo ratings yet
- Ammonia and Derivatives - Trans & Gas UsageDocument17 pagesAmmonia and Derivatives - Trans & Gas UsageragilpriyantoNo ratings yet
- Q3. Urea ProductionDocument2 pagesQ3. Urea ProductionTusharNo ratings yet
- Amine Gas Treating: Description of A Typical Amine TreaterDocument4 pagesAmine Gas Treating: Description of A Typical Amine TreaterjfkdlsjsakNo ratings yet
- FF - Mar-Apr - 2018 - Zero Waste Urea Production - ONLINEDocument3 pagesFF - Mar-Apr - 2018 - Zero Waste Urea Production - ONLINEdonyaNo ratings yet
- NPK Fertilizers - Nitrophosphate RouteDocument9 pagesNPK Fertilizers - Nitrophosphate RouteHoàng TuấnNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iii Supporting Functional Units in LNG Plants: Gas Pretreatment: Slug Catcher - NGLDocument21 pagesUnit - Iii Supporting Functional Units in LNG Plants: Gas Pretreatment: Slug Catcher - NGLMeghana SNo ratings yet
- Capstone 1Document3 pagesCapstone 1Michael Taylor WarrenNo ratings yet
- AdsorbateDocument25 pagesAdsorbatealok sahuNo ratings yet
- March 31, 1970 Kazumichi Kana Et Al 3,503,970: Integrated Process For Froducing Urea and MelamineDocument6 pagesMarch 31, 1970 Kazumichi Kana Et Al 3,503,970: Integrated Process For Froducing Urea and MelamineAndresNo ratings yet
- UreaDocument19 pagesUreaTalha waheedNo ratings yet
- Lectures 14 Urea - Part 1Document8 pagesLectures 14 Urea - Part 1Nour Saad EdweekNo ratings yet
- Production of UreaDocument2 pagesProduction of UreaSk jahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- KM FTE ProjectDocument13 pagesKM FTE Projectkrishnamasalkar76No ratings yet
- Httpsdacemirror - Sci Hub - Sejournal Articlabarmaki2009.Pdfdownload TrueDocument12 pagesHttpsdacemirror - Sci Hub - Sejournal Articlabarmaki2009.Pdfdownload TrueNur SyarafanaNo ratings yet
- Urea ProductionDocument2 pagesUrea Productiongaur1234No ratings yet
- CPT Lecture Urea ProcessDocument31 pagesCPT Lecture Urea ProcesssaisounyaNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument10 pagesProjectMuhammad JafarNo ratings yet
- Economic Aspects of Setting Up Purge Gas Recovery Unit (PGRU) With Ammonia Production ProcessDocument7 pagesEconomic Aspects of Setting Up Purge Gas Recovery Unit (PGRU) With Ammonia Production ProcessWilly ChandraNo ratings yet
- United States: (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0206902 A1Document9 pagesUnited States: (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0206902 A1BeningNo ratings yet
- UreaDocument15 pagesUreahamza ahmad0% (1)
- Ammonia Stripping MethodDocument2 pagesAmmonia Stripping MethodsagbvnNo ratings yet
- Chemical Technology Subject Code: CH2001 Module II-Lecture 2 Urea ProductionDocument12 pagesChemical Technology Subject Code: CH2001 Module II-Lecture 2 Urea ProductionU SANKAR TEJONo ratings yet
- The Urea Manufacturing ProcessDocument5 pagesThe Urea Manufacturing ProcessJhonny Huanca ChampiriNo ratings yet
- Alia AMF301 Electromagnetic FlowmeterDocument4 pagesAlia AMF301 Electromagnetic FlowmeterRexCrazyMindNo ratings yet
- Matter How Are Materials Classified?: WMSU-ISMP-GU-001.00 Effective Date: 7-DEC-2016Document6 pagesMatter How Are Materials Classified?: WMSU-ISMP-GU-001.00 Effective Date: 7-DEC-2016Joycee DhNo ratings yet
- 2 Up To Unit OperationDocument99 pages2 Up To Unit OperationTemesgen MuletaNo ratings yet
- Activity 2A - Reactions To CarbohydratesDocument5 pagesActivity 2A - Reactions To CarbohydratesMy Roses Are RosèNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Additives in Hot Asphalt MixturesDocument20 pagesThe Effect of Additives in Hot Asphalt Mixtureszeidan111No ratings yet
- Google Patents - WO2021170827A1 - Application of Punicalagin-Ellagic Acid To Improve Oxidative and Colloidal Stability of Beverages (Esp. Beer)Document17 pagesGoogle Patents - WO2021170827A1 - Application of Punicalagin-Ellagic Acid To Improve Oxidative and Colloidal Stability of Beverages (Esp. Beer)FreekNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Area Classification: Codes of Practice and StandardsDocument13 pagesHazardous Area Classification: Codes of Practice and StandardsborrowmanaNo ratings yet
- Chemestry Ponderal LawsDocument2 pagesChemestry Ponderal LawsMarinö Chavez100% (1)
- Enviroline 124 Application GuidelineDocument12 pagesEnviroline 124 Application GuidelineAhmed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- BAVARIA Phoenix - Technical Spec - 2018Document2 pagesBAVARIA Phoenix - Technical Spec - 2018Kareem Abo SeifNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument28 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureANITA YADAVNo ratings yet
- 1 716554253262394542Document4 pages1 716554253262394542AfzaalUmairNo ratings yet
- Aits-20 Jee Main 16.05.2021 (CRT-4)Document18 pagesAits-20 Jee Main 16.05.2021 (CRT-4)Subhamoy BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Imat 2017Document45 pagesImat 2017YarenNo ratings yet
- A Study On Mechanical Properties of Bamboo Fiber RDocument8 pagesA Study On Mechanical Properties of Bamboo Fiber RRachapalli AnjaliNo ratings yet
- ACNV TestDocument1 pageACNV TestRana ThakurNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy Vaporization InorgDocument2 pagesEnthalpy Vaporization InorgKatherine TamayoNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy 1Document15 pagesMetallurgy 1abhishekNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0016236123029125 MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S0016236123029125 Mainfajar marendraNo ratings yet
- Iraj Beheshti - 2018 (Detailed Resume)Document6 pagesIraj Beheshti - 2018 (Detailed Resume)Mohamadreza JafaryNo ratings yet
- What Is BariteDocument2 pagesWhat Is BariteirfanNo ratings yet
- 3M 8514-MSDS-2014Document8 pages3M 8514-MSDS-2014Michael TadrosNo ratings yet
- Dry-Jet-Wet SpinningDocument16 pagesDry-Jet-Wet SpinningaadishNo ratings yet
- DBL 5818Document48 pagesDBL 5818Marko SamardžićNo ratings yet
- Preserving Archaeological Remains in Situ. Proceedings of The 4th International Conference by David GregoryDocument490 pagesPreserving Archaeological Remains in Situ. Proceedings of The 4th International Conference by David GregoryXinyu ZhNo ratings yet
- Forensic Ballistic PPT Set-4Document53 pagesForensic Ballistic PPT Set-4cjaldaya25No ratings yet
- Lec 6C Alkyne Structure and ReactivityDocument37 pagesLec 6C Alkyne Structure and Reactivityseanroi.villas.lawNo ratings yet
- Vdocuments - MX - Customer Specification Specification Specification Specification Name RevisionDocument67 pagesVdocuments - MX - Customer Specification Specification Specification Specification Name Revisionedgar50% (2)