100% found this document useful (1 vote)
5K views6 pagesNPL Flatness Interferometer
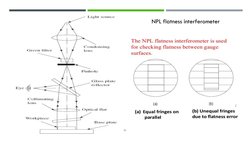
The document discusses the working of an NPL flatness interferometer. It begins by providing background on interferometers, noting that they are widely used to measure small displacements, refractive index changes, and surface irregularities by splitting light into two beams and recombining them to produce interference fringes. It then explains the working of the NPL flatness interferometer, which uses a mercury vapor lamp, pinhole, and optical flat to project parallel light onto a gauge, forming interference fringes that indicate if its surface is flat or has an error. Finally, it discusses applications of interferometry like precisely calculating flatness, an important metric for technical components requiring accuracy in construction and assembly.
Uploaded by
Moula MoulaliCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
5K views6 pagesNPL Flatness Interferometer
The document discusses the working of an NPL flatness interferometer. It begins by providing background on interferometers, noting that they are widely used to measure small displacements, refractive index changes, and surface irregularities by splitting light into two beams and recombining them to produce interference fringes. It then explains the working of the NPL flatness interferometer, which uses a mercury vapor lamp, pinhole, and optical flat to project parallel light onto a gauge, forming interference fringes that indicate if its surface is flat or has an error. Finally, it discusses applications of interferometry like precisely calculating flatness, an important metric for technical components requiring accuracy in construction and assembly.
Uploaded by
Moula MoulaliCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Title Page: The title page introduces the project on NPL Flatness Interferometer, including submission details.
- Introduction: The introduction outlines the basic function and significance of interferometers in scientific and industrial applications.
- Diagram and Description: This section presents a diagram of the interferometer setup and explains its function for checking flatness between gauge surfaces.
- Working: Details the operational process of the interferometer, describing how light is used to measure flatness accurately.
- Applications: Discusses various applications of interferometry in industry and manufacturing, emphasizing accuracy and precision.
- Conclusion: Concludes the presentation with a closing remark.