Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DYNAMICS LAB VIVA QUESTIONS Full
Uploaded by
Sudipta Nath0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views4 pagesThis document contains questions and answers related to dynamics lab experiments involving mechanisms like the slider crank mechanism, beams, cams, governors, gyroscopes, and gear trains. Some key points covered include:
1) The slider crank mechanism converts rotational motion to translational motion. Beams experience loads that produce bending moments. Cams are used to convert rotary to linear motion.
2) Governors regulate the speed of engines using centrifugal or inertia forces. Gyroscopes maintain orientation using angular momentum. Gear trains transmit motion between shafts via toothed wheels.
3) Dynamics concepts examined include velocity, angular acceleration, natural frequency, moment of inertia, centrifugal force, and degrees of freedom.
Original Description:
Original Title
DYNAMICS LAB VIVA QUESTIONS full
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains questions and answers related to dynamics lab experiments involving mechanisms like the slider crank mechanism, beams, cams, governors, gyroscopes, and gear trains. Some key points covered include:
1) The slider crank mechanism converts rotational motion to translational motion. Beams experience loads that produce bending moments. Cams are used to convert rotary to linear motion.
2) Governors regulate the speed of engines using centrifugal or inertia forces. Gyroscopes maintain orientation using angular momentum. Gear trains transmit motion between shafts via toothed wheels.
3) Dynamics concepts examined include velocity, angular acceleration, natural frequency, moment of inertia, centrifugal force, and degrees of freedom.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views4 pagesDYNAMICS LAB VIVA QUESTIONS Full
Uploaded by
Sudipta NathThis document contains questions and answers related to dynamics lab experiments involving mechanisms like the slider crank mechanism, beams, cams, governors, gyroscopes, and gear trains. Some key points covered include:
1) The slider crank mechanism converts rotational motion to translational motion. Beams experience loads that produce bending moments. Cams are used to convert rotary to linear motion.
2) Governors regulate the speed of engines using centrifugal or inertia forces. Gyroscopes maintain orientation using angular momentum. Gear trains transmit motion between shafts via toothed wheels.
3) Dynamics concepts examined include velocity, angular acceleration, natural frequency, moment of inertia, centrifugal force, and degrees of freedom.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
DYNAMICS LAB VIVA QUESTIONS
1. What is meant by mechanism?
a system of parts working together in a machine; a piece of machinery.
2. Define Machine.
A machine is a device which receives energy in some available form and utilizes it to some
particular type of work.
3. Define Dynamics of Machines.
It deals with the study of forces acting on the parts of a machines.
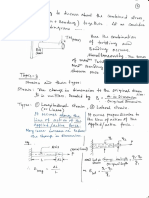
4. What is meant by slider crank mechanism?
The Slider-crank mechanism is used to transform rotational motion into translational motion by
means of a rotating driving beam, a connection rod and a sliding body.
5. What is your aim of the experiment?
To find out the slider velocity and angular velocity of the experiment.
6. Applications of slider crank mechanism?
· Almost all reciprocating engines use cranks (with connecting rods) to transform the back-and-forth
motion of the pistons into rotary motion. The cranks are incorporated into a crankshaft.
Mechanical pencil sharpener
Fishing reel and other reels for cables, wires, ropes, etc.
Manually operated car window.
7. What is meant by velocity?
the speed of something in a given direction.
8. What is meant by angular acceleration?
Angular acceleration, also called rotational acceleration, is a quantitative expression of the change
in angular velocity that a spinning object undergoes per unit time. It is a vector quantity, consisting
of a magnitude component and either of two defined directions or senses.
9. What is meant by beam?
Beams are generally horizontal structural members which transfer loads horizontally along their
length to the supports where the loads are usually resolved into vertical forces. Beams are used for
resisting vertical loads, shear forces and bending moments
10. What are the types of beam?
a. Simply Supported Beam
b. Fixed Beam
c. Cantilever Beam
d. Continuously Supported Beam
11. What are the types of Loading?
a. Point load
b. Uniformly distributed load
c. Uniformly varying load
12. What Is the aim of experiment?
To find the natural efficiency of the beam.
13. What is meant by natural frequency?
the frequency at which a system oscillates when not subjected to a continuous or repeated external
force.
14. What is meant by frequency?
It is defined as the number of cycles per second.
15. What is the unit of frequency?
The SI unit of frequency is the hertz (Hz), named after the German physicist Heinrich Hertz.
One hertz means that an event repeats once per second. A previous name for this unit was cycles per
second (cps). The SI unit for period is the second.
16. What is the use of cam?
A cam is a rotating or sliding piece in a mechanical linkageused especially in transforming rotary
motion into linear motion or vice versa.
17. What is meant by camp jump phenomenon?
Follower looses contact with cam surface when cam rotates beyond particular speed due to inertia
forces.
18. What are types of cam?
a. Wedge or flat cams
b. Radial or Disc Cams
c. Spiral cams
d. Cylindrical cams
e. Conjugate cams
f. Globoidal Cams
g. Spherical cams
19. What are the types of follower available?
a. (a) Knife edge follower
b. (b) Roller follower
c. (c) Flat faced follower
d. (d) Spherical follower
20. What is the aim of this experiment?
jump-speed characteristics of the cam & follower mechanism.
21. What is meant by governor?
Governors are also known as speed limiters; they are used in different places like engines to measure
and regulate the speed of an engine.
22. What are types of governors?
a. Watt governor
b. Porter governor
c. Proell governor
d. Hartnell governor
23. What is meant by stiffness of spring?
For an elastic body with a single degree of freedom (DOF) (for example, stretching or compression of
a rod), the stiffness is defined as k = F δ {\displaystyle k={\frac {F}{\delta }}} ... δ is the
displacement produced by the force along the same degree of freedom (for instance, the change in
length of a stretched spring).
24. What is meant by sensitivity of governor?
Sensitivity is definedas the ratio of the mean speed to the speed range of the governor over its limits
of operation.
25. What are classification of governors?
Generally Governors can be classified as either Centrifugal orInertia.
26. What is meant by centrifugal governor?
The effort of the governor is obtained from the change in centrifugal force on (usually) two rotating
masses known as Balls, when an increase or decrease in governor speed occurs.
27. What is meant by inertia governors?
Inertia Governors work on a different principle. The governor balls are arranged so that the inertia
forces caused by angular acceleration or retardation of the governor shaft tend to alter their positions.
The amount of the displacement of the balls is controlled by springs and the governor mechanism to
alter the supply of energy to the engine.
28. What is meant by gyroscope?
a device consisting of a wheel or disc mounted so that it can spin rapidly about an axis which is itself
free to alter in direction. The orientation of the axis is not affected by tilting of the mounting, so
gyroscopes can be used to provide stability or maintain a reference direction in navigation systems,
automatic pilots, and stabilizers.
29. What is meant by gyroscope couple?
Gyroscopic Couple. If a uniform disc of polar moment of inertia is rotated about its axis with an
angular velocity , its Angular Momentum is a vector and can be represented in diagram (c) by the line
up which is drawn in the direction of the axis of rotation.
30. What is the use of gyroscope couple?
Gyroscopes can be very perplexing objects because they move in peculiar ways and even seem to
defy gravity. These special properties make gyroscopes extremely important in everything from
your bicycle to the advanced navigation system on the space shuttle. A typical airplane uses about a
dozen gyroscopes in everything from its compass to its autopilot. The Russian Mir space station used
11 gyroscopes to keep its orientation to the sun, and the Hubble Space Telescope has a batch of
navigational gyros as well.
31. What is meant by centrifugal force?
a force, arising from the body's inertia, which appears to act on a body moving in a circular path and
is directed away from the centre around which the body is moving.
32. What is meant by moment of inertia?
a quantity expressing a body's tendency to resist angular acceleration, which is the sum of the
products of the mass of each particle in the body with the square of its distance from the axis of
rotation.
33. What is meant by whirling of shaft?
Whirling speed is also called as Critical speed of ashaft. It is defined as the speed at which a
rotatingshaft will tend to vibrate violently in the transverse direction if the shaft rotates in horizontal
direction. In other words, the whirling or critical speed is the speed at which resonance occurs.
34. What is meant by flywheel?
A flywheel is a rotating mechanical device that is used to store rotational energy. Flywheels have an
inertia called the moment of inertia and thus resist changes in rotational speed. The amount of energy
stored in a flywheel is proportional to the square of its rotational speed.
35. What do you mean by inertia?
The property of matter offering resistance to any change of its state of rest or of uniform motion in a
straight line is known as inertia.
36. What is meant by axisymmetric?
symmetrical about an axis.
37. What is meant by degree of freedom?
In statistics, the number of degrees of freedom is the number of values in the final calculation of a
statistic that are free to vary. The number of independent ways by which a dynamic system can move,
without violating any constraint imposed on it, is called number of degrees of freedom.
38. What is meant by gear?
a toothed wheel that works with others to alter the relation between the speed of a driving mechanism
(such as the engine of a vehicle) and the speed of the driven parts (the wheels).
39. What is meant by gear ratio?
The Gear Ratio is defined as the input speed relative to the output speed.
40. What is meant by gear train?
a system of gears which transmits motion from one shaft to another.
41. What is meant by radius of gyration?
the distance from an axis at which the mass of a body may be assumed to be concentrated and at
which the moment of inertia will be equal to the moment of inertia of the actual mass about the axis,
equal to the square root of the quotient of the moment of inertia and the mass.
42. What is meant by balancing of rotating mass?
The balancing of rotating bodies is important to avoid vibration. In heavy industrial machines such
as gas turbines and electric generators, vibration can cause catastrophic failure, as well as noise and
discomfort. In the case of a narrow wheel, balancing simply involves moving the centre of gravity to
the centre of rotation. For a system to be in complete balance both force and couple polygons should
be closed.
43. What is meant by mechanism?
When one of the links of a kinematics chain is fixed, the chain is known as mechanism. It may be
used for transmitting or transforming motion e.g. engine indicators, typewriter etc.
You might also like
- KOM Interview Questions PDFDocument4 pagesKOM Interview Questions PDFsrinivas pavan kumar ANo ratings yet
- Theory of MachineDocument21 pagesTheory of MachineVaibhav Vithoba NaikNo ratings yet
- DTS-Short Questions and AnswerDocument7 pagesDTS-Short Questions and AnswerAlfred Franklin V100% (1)
- Effect of Gyroscopic Couple On A NAVAL SHIPDocument16 pagesEffect of Gyroscopic Couple On A NAVAL SHIPaakash waychal100% (2)
- CH 19Document21 pagesCH 19Sanjay Kumar100% (1)
- Dynamics of Machinery 2 Marks All 5 UnitsDocument14 pagesDynamics of Machinery 2 Marks All 5 UnitsDHINAKARANVEEMAN100% (2)
- Viva Questions - DomDocument2 pagesViva Questions - DomDyggdgdNo ratings yet
- Automotive Transmission - Lecture Notes Complete PDFDocument156 pagesAutomotive Transmission - Lecture Notes Complete PDFcemokszNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document41 pagesLecture 1norhaslina_aa33% (3)
- Theory of Machines Interview Questions and AnswersDocument11 pagesTheory of Machines Interview Questions and Answerskumarmohit0203No ratings yet
- ME6601 Design of Transmission Systems 2 Marks With AnswersDocument6 pagesME6601 Design of Transmission Systems 2 Marks With Answerspremgmech762No ratings yet
- Design Calculation of Propeller Shaft (Landcruiser) : Abstract - The Power Transmission System Is The GreatestDocument5 pagesDesign Calculation of Propeller Shaft (Landcruiser) : Abstract - The Power Transmission System Is The GreatestDr. Aung Ko Latt100% (1)
- Basic Mechanical Lab Manual PDFDocument60 pagesBasic Mechanical Lab Manual PDFNATIONAL XEROX0% (1)
- Master PPT DesignDocument15 pagesMaster PPT DesignUsama Epn Abdelmksoud AhmedNo ratings yet
- Som Part B CDocument16 pagesSom Part B CSrini VasanNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Fill in The BlanksDocument3 pagesStrength of Materials Fill in The BlanksAshok Kumar100% (1)
- 2 MARKS MOM With AnswersDocument14 pages2 MARKS MOM With Answersjeroldscd100% (1)
- Dynamics of Machinery Questions and AnswersDocument24 pagesDynamics of Machinery Questions and Answerssivaeinfo0% (1)
- Dynamics of Machinery - 2 Marks - All 5 UnitsDocument13 pagesDynamics of Machinery - 2 Marks - All 5 UnitsMohan Prasad.M58% (12)
- Copyjjjj of Viva Voice QuestionDocument6 pagesCopyjjjj of Viva Voice QuestionVigy BossNo ratings yet
- Design of Bed of Lathe MachineDocument6 pagesDesign of Bed of Lathe MachineAbhay Jaswal100% (4)
- KDM 6Document54 pagesKDM 6KarthikeyanRamanujamNo ratings yet
- 1.experiment On Single Rotor SystemDocument8 pages1.experiment On Single Rotor SystemRahul Kumar DwivediNo ratings yet
- Design of Transmission SystemDocument23 pagesDesign of Transmission Systemspsurya2013100% (2)
- BME Unit 8 Power TransmissionDocument8 pagesBME Unit 8 Power Transmissionalysonmicheaala100% (1)
- Notes-1 (Turbomachines)Document24 pagesNotes-1 (Turbomachines)VIRAJ HADKARNo ratings yet
- 64217Document28 pages64217amdevaNo ratings yet
- Experiment #1: Whirling of ShaftsDocument7 pagesExperiment #1: Whirling of ShaftsJibran Ansari0% (1)
- Design of Machine Elements 2 Marks - 5 UnitsDocument20 pagesDesign of Machine Elements 2 Marks - 5 UnitsArjun Arumugaswamy100% (4)
- ECM Process Parameter 1Document8 pagesECM Process Parameter 1K O100% (1)
- Design of Speed and Feed Gear BoxesDocument67 pagesDesign of Speed and Feed Gear BoxesBhotka BhutkiNo ratings yet
- Worm Gearl Design ProjectDocument39 pagesWorm Gearl Design ProjectMajestic Egy SoldNo ratings yet
- Design of Transmission System Question BankDocument18 pagesDesign of Transmission System Question BankAravind50% (2)
- Automats and Tool LayoutsDocument20 pagesAutomats and Tool LayoutsAyesha IshuNo ratings yet
- Unit I DME II Spur Gears by Sachin DhavaneDocument63 pagesUnit I DME II Spur Gears by Sachin DhavaneSachiin Dhavane100% (1)
- Stresses Due To RotationDocument10 pagesStresses Due To Rotationswordstoker0% (1)
- Kinematics of Machine ToolsDocument28 pagesKinematics of Machine ToolsRohit Kaushik100% (6)
- Theory of Machine Unit 1Document122 pagesTheory of Machine Unit 1Deepak PrajapatNo ratings yet
- Hoisting EquipmentDocument56 pagesHoisting EquipmentbroNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering-Theory of Machines MCQ PDFFWWW - alleXAMREVIEWDocument23 pagesMechanical Engineering-Theory of Machines MCQ PDFFWWW - alleXAMREVIEWwalunjmayur45275No ratings yet
- Helical Spring DesignDocument47 pagesHelical Spring DesignHKHKBOOKS100% (1)
- Unit I&II Gear DesignDocument130 pagesUnit I&II Gear DesignVishal JaiswalNo ratings yet
- 27-11 Mechanical Vibration (ME)Document3 pages27-11 Mechanical Vibration (ME)Mahir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Baja Sae India Design ReportDocument13 pagesBaja Sae India Design Reportgobajasaeindia93% (15)
- Problems On FlywheelDocument16 pagesProblems On FlywheelkarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- 2 CI Engine Normal and Abnormal Combustion-KnockingDocument9 pages2 CI Engine Normal and Abnormal Combustion-Knockingselvaraj9223No ratings yet
- Viva Questions For Torsion Testing and DesignDocument12 pagesViva Questions For Torsion Testing and DesignSreejith SreeNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials 2 Mark QuestionsDocument21 pagesStrength of Materials 2 Mark Questionsrameshbabu_1979No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Whirling of Shaft and GovernorDocument4 pagesUnit 5 Whirling of Shaft and GovernorSudipta NathNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery (Me35) - 1 PDFDocument15 pagesKinematics of Machinery (Me35) - 1 PDFPraveen RajaNo ratings yet
- AT6302 - Mechanics of Machines - Part ADocument13 pagesAT6302 - Mechanics of Machines - Part ApavanraneNo ratings yet
- AE 2201 MOM.2marksDocument9 pagesAE 2201 MOM.2marksdennyfrancis19No ratings yet
- Dynamics of Machinery PDFDocument18 pagesDynamics of Machinery PDFThomas VictorNo ratings yet
- Engineering MechanicsDocument16 pagesEngineering Mechanicsbetelhemterefe wondimagenihuNo ratings yet
- 18md09-Dom Module-1 Part-A-Answer Key PDFDocument7 pages18md09-Dom Module-1 Part-A-Answer Key PDFUdhaya KumarNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Actuation SystemDocument34 pagesMechanical Actuation Systemdildar123100% (2)
- Kinematics of Machinery 2 Marks All 5 UnitsDocument18 pagesKinematics of Machinery 2 Marks All 5 UnitsvelavansuNo ratings yet
- Jahangirabad Institute of TechnologyDocument26 pagesJahangirabad Institute of TechnologyGhulam MurtazaNo ratings yet
- Ijsrdv1i9084 PDFDocument2 pagesIjsrdv1i9084 PDFKanaga VaratharajanNo ratings yet
- Module 1 & First Half of 2 - Two Marks Q & ADocument8 pagesModule 1 & First Half of 2 - Two Marks Q & AMOHAMMED ZAHID BNo ratings yet
- Part I AnswersToSelectedProblems Chapt10Document1 pagePart I AnswersToSelectedProblems Chapt10Sudipta NathNo ratings yet
- Chapter 0 Part 2Document5 pagesChapter 0 Part 2Sudipta NathNo ratings yet
- MIT2 080JF13 Recitation2Document9 pagesMIT2 080JF13 Recitation2Sudipta NathNo ratings yet
- Hooks LawDocument9 pagesHooks LawSudipta NathNo ratings yet
- Module 2 With SolutionsDocument15 pagesModule 2 With SolutionsSudipta NathNo ratings yet
- Chapter 0 Part 1Document4 pagesChapter 0 Part 1Sudipta NathNo ratings yet
- LECT 20, 21 Boundary Problems 01Document12 pagesLECT 20, 21 Boundary Problems 01Sudipta NathNo ratings yet
- Sudipta Nath: Materials EngineeringDocument19 pagesSudipta Nath: Materials EngineeringSudipta NathNo ratings yet
- Sudipta Nath: Materials EngineeringDocument19 pagesSudipta Nath: Materials EngineeringSudipta NathNo ratings yet
- Sudipta Nath: Materials EngineeringDocument15 pagesSudipta Nath: Materials EngineeringSudipta NathNo ratings yet
- Sudipta Nath: Materials EngineeringDocument20 pagesSudipta Nath: Materials EngineeringSudipta NathNo ratings yet
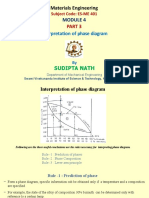
- Materials Engineering: Interpretation of Phase DiagramDocument12 pagesMaterials Engineering: Interpretation of Phase DiagramSudipta NathNo ratings yet
- Sudipta Nath: Materials EngineeringDocument14 pagesSudipta Nath: Materials EngineeringSudipta NathNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 BalancingDocument2 pagesUnit 2 BalancingSudipta NathNo ratings yet
- Materials Engineering: Subject Code: ES-ME 401Document20 pagesMaterials Engineering: Subject Code: ES-ME 401Sudipta NathNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Force AnalysisDocument3 pagesUnit 1 Force AnalysisSudipta NathNo ratings yet
- "3D Printing: An Emerging Era of Future Printing": Mr. Pravin AhirwarDocument25 pages"3D Printing: An Emerging Era of Future Printing": Mr. Pravin AhirwarSudipta NathNo ratings yet
- Unit 3&4 VibrationDocument4 pagesUnit 3&4 VibrationSudipta NathNo ratings yet
- 3D PrintingDocument132 pages3D PrintingSudipta NathNo ratings yet
- 2-Solution ThermodynamicsDocument6 pages2-Solution ThermodynamicsKristel LeeNo ratings yet
- Conductive PenDocument2 pagesConductive Penpepper100No ratings yet
- Write in The Green Cells Only: Droplet Diameter, MicronsDocument25 pagesWrite in The Green Cells Only: Droplet Diameter, Micronsojasmainkar123No ratings yet
- Clinching Joining Technology For Car Body ProductionDocument19 pagesClinching Joining Technology For Car Body ProductionKIRANNo ratings yet
- Steam Table English UnitDocument9 pagesSteam Table English UnitRanz Kyle BautistaNo ratings yet
- Qualification of Welding Procedure Specification FCDocument14 pagesQualification of Welding Procedure Specification FCmister pogi100% (4)
- Soil EngineeringDocument149 pagesSoil EngineeringRenalyn AndradeNo ratings yet
- Steel in EngineeringDocument3 pagesSteel in EngineeringJay Anne Mae FebreNo ratings yet
- Rask 1989Document27 pagesRask 1989Ruxandra SimionNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document3 pagesExperiment 1Christian Roy CNo ratings yet
- Machine Design: Mechanical EngineeringDocument10 pagesMachine Design: Mechanical EngineeringHeman GladiatorNo ratings yet
- Project Thesis Refining of Used Motor Oil Using Solvent ExtractionDocument77 pagesProject Thesis Refining of Used Motor Oil Using Solvent ExtractionSyed Waqas Haider50% (2)
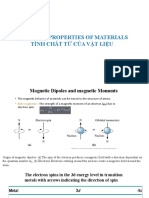
- Magnetic Properties Of Materials Tính Chất Từ Của Vật LiệuDocument88 pagesMagnetic Properties Of Materials Tính Chất Từ Của Vật Liệupham minhNo ratings yet
- Air Purger (CPA-10) - Cool PartnersDocument3 pagesAir Purger (CPA-10) - Cool PartnersMohammad AmerNo ratings yet
- eBook+Introduction+to+Spectroscopy Pavis 32 121Document7 pageseBook+Introduction+to+Spectroscopy Pavis 32 121devi dwi rustaminingrumNo ratings yet
- Brightfield Microscope Definition: Microscope. It Is An Optical Microscope That Uses Light Rays To Produce ADocument5 pagesBrightfield Microscope Definition: Microscope. It Is An Optical Microscope That Uses Light Rays To Produce AShahriar ShamimNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer ExxonMobilDocument30 pagesHeat Transfer ExxonMobilHernan CobaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 PDFDocument13 pagesChapter 8 PDFمحمد سالمNo ratings yet
- R290Document406 pagesR290hermit44535No ratings yet
- Plagiarism - Report - 2Document5 pagesPlagiarism - Report - 2GEMPFNo ratings yet
- The SMP Concept-Based 3D Constitutive Models For Geomaterials - Hajime Matsuoka (Author) - 1, 2006 - CRC Press - 9780415395045 - Anna's ArchiveDocument154 pagesThe SMP Concept-Based 3D Constitutive Models For Geomaterials - Hajime Matsuoka (Author) - 1, 2006 - CRC Press - 9780415395045 - Anna's ArchiveElias Santos SouzaNo ratings yet
- Tides Are The Rise and Fall of Sea Levels Caused by The Combined Effects of Gravitational Forces Exerted by The MoonDocument4 pagesTides Are The Rise and Fall of Sea Levels Caused by The Combined Effects of Gravitational Forces Exerted by The Moonapi-286301523No ratings yet
- Catalogo de Pecas - Mx210 PTDocument134 pagesCatalogo de Pecas - Mx210 PTRafael de AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Sichuan Air SeparationDocument25 pagesSichuan Air SeparationFarshad Asgari0% (1)
- LESSON 5 Genchem2Document20 pagesLESSON 5 Genchem2J NavarroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18:temperature, Heat and The First Law of Thermodynamics (Fundamental of Physics, 10 Edition)Document16 pagesChapter 18:temperature, Heat and The First Law of Thermodynamics (Fundamental of Physics, 10 Edition)BerlinNo ratings yet
- Review On Battery Thermal Management System For Electric VehiclesDocument21 pagesReview On Battery Thermal Management System For Electric Vehiclesal-masri100% (1)
- LECTURE - 6: Ethylene Derivatives: Ethylene Oxide and Ethanol Amines 6.1 Ethylene OxideDocument7 pagesLECTURE - 6: Ethylene Derivatives: Ethylene Oxide and Ethanol Amines 6.1 Ethylene Oxideمحمود محمدNo ratings yet
- Production of Diesel FuelDocument7 pagesProduction of Diesel FuelparminderNo ratings yet
- Climate - Change Book PDFDocument283 pagesClimate - Change Book PDFPantulu MurtyNo ratings yet