Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fire Technology and Arson Investigation
Uploaded by
Kent Ivan LeeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fire Technology and Arson Investigation
Uploaded by
Kent Ivan LeeCopyright:
Available Formats
1
FIRE TECHNOLOGY AND ARSON INVESTIGATION
I. FIRE TECHNOLOGY
- deals with the science and study of the chemistry of fire and mechanics of combustion, to include
the principles and fundamentals of fire protection
FIRE
- An active chemical reaction that takes place between fuel, heat and oxygen in the form of light of
noticeable heat
- rapid oxidation of matter accompanied by heat and light
- product of combustion or burning
COMBUSTION
- the rapid oxidation of substances accompanied by heat and light
OXIDATION
- a chemical process involving physical change (transformation)
FORMS OF OXIDATION
1) slow oxidation
- decaying
- rotting
- aging
- rusting
2) rapid oxidation
- fire
- explosion
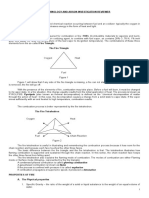
ELEMENTS OF FIRE/TRIANGLE OF FIRE
1) FUEL
o anything that is capable of burning
o the most important element of the triangle
2) HEAT
o a form of energy and initiator of fire
3) OXYGEN
o a tasteless, odorless and colorless gas which is vital to sustain fire
THREE PHASES OF FIRE
1) INITIAL PHASE
- the beginning of fire
- the base area of the fire has a temperature of 400 to 800 degrees Fahrenheit
- can be easily controlled and subdued
2) FREE BURNING
- the acceleration of pyrolytic process
- the maximum heat and destructive capabilities of fire develop
- the base temperature of the fire is around 800 to 1,000 degrees Fahrenheit and ceiling temperature
is up to 1,600 degrees Fahrenheit
3) SMOLDERING
- the stage where the fire glows and the combustible materials smolder
- flames would not be visible but a large amount of carbon monoxide is produced
- sudden introduction of oxygen with superheated fuel under pressure can cause an explosion
METHODS OF HEAT TRANSFER
1) CONDUCTION
o by direct contact or through a conductor
2) CONVECTION
o through the movement of hot gases or liquid
3) RADIATION
o through medium of space or atmosphere
COMPONENTS OF COMBUSTION (TETRAHEDRON OF FIRE)
1) fuel
2
2) source of ignition (heat)
3) air (oxygen)
4) uninhibited chemical chain reaction
FACTORS THAT AFFECT THE RATE OF INTENSITY OF HEAT
1) amount of materials available for burning
2) calorific value of burning
3) oxygen supply available
4) surface area of exposure
5) flame length
CLASSES OF FIRE
1) CLASS A
- the fuel is comprised of normal combustible materials such as wood, paper, fiber, draperies and
trash
- requires saturation by water or water fog
2) CLASS B
- the fuel is flammable liquid such as gasoline, kerosene, cleaning fluids, grease and alcohol
- must be smothered to deprive them of oxygen, hence, foam extinguishers and CO2 may be utilized
3) CLASS C
- those which starts with live electrical wires, equipment and electrical appliances
- commonly known as electrical fire
- easily extinguished by a non-conducting agent such as CO2 and dry chemicals
4) CLASS D
- this type of fire is rare, usually occurs in manufacturing facilities
- combustible materials are certain metals
- can be extinguished by using dry powder, ABC chemical, baking soda or sand
FLASH POINT
- the minimum temperature at which vapor starts to rise from any fuel subjected to heat
- temperature at which a flammable liquid forms a vapor air mixture that ignites
IGNITION TEMPERATURE OR KINDLING TEMPERATURE
- the minimum temperature to which the substance in the air must be heated in order to initiate
combustion without the addition of heat from outside sources
NORMAL ROOM TEMPERATURE – 37.8º Celsius
BOILING POINT OF WATER – 100º Celsius
FLAMMABLE MATERIAL
- any fuel that has a flashpoint at or below normal room temperature
COMBUSTIBLE MATERIAL
- any fuel that has a flashpoint above normal room temperature
IGNITABLE MIXTURE
- combination of vapor and oxygen
- happens when vapor continues to rise and reaches a proportional value to combine with oxygen in
the air
CALORIFIC VALUE
- the amount of heat energy stored within the burning material
- the chemical composition of the object
HOW WILL A FIRE START?
Fire will start when there is an initial source of heat applied to a material, accompanied by the triangle
of fire.
HOW WILL FIRE SPREAD?
Fire will spread through the different ways of heat transfer.
3
HOW WILL IT INTENSIFY?
Fire will intensify through the factors that affect the rate of intensity of heat.
II. ARSON INVESTIGATION
ARSON
- the malicious destruction of property by fire
PD 1613 – the law amending the law on arson provided by the RPC
ELEMENTS OF ARSON
1) That the property burned is the exclusive property of the offender
2) That the purpose of the offender in burning is to:
a) to defraud or to cause damage to another
b) prejudice is actually caused
c) the thing burned is a building in an inhabited place
PRIMA FACIE EVIDENCE OF ARSON
1) If the fire started simultaneously in more than one part of the building or establishment;
2) If substantial amount of flammable substances or materials are stored within the building not
necessary in the business of the offender nor for household use;
3) If gasoline, kerosene, petroleum or other flammable or combustible substances or materials, or any
mechanical, electrical, chemical or electronic devises designed to start a fire are found in the ruins
or premises of the burned property;
4) If the building or property is insured for substantially more than its actual value at the time of the
issuance of the policy;
5) If during the lifetime of the corresponding fire insurance policy, more than two fires have occurred in
the same or other premises owned or under the control of the offender and/or insured;
6) If shortly before the fire, a substantial portion of the effects insured and stored in a building had
been withdrawn from the premises except in the ordinary course of business;
7) If a demand for money or other valuable consideration was made were the fire in exchange for the
desistance of the offender or for the safety of the person or property of the victim.
THREE KINDS OF FIRE
1) PROVIDENTIAL
- caused by act of God
- can never be prevented and usually hard to control
- comes in the form of lightning bolts, erupting volcanoes and other forms of natural calamities
2) ACCIDENTAL
- caused by human error and negligence
- such as smoking in bed, defective LPG containers, faulty electrical wiring etc
3) INTENTIONAL
- also called incendiary
- also classified as arson
- caused by a person with malicious intent or purpose
INVESTIGATION
- deals with the two phases of investigation:
a) fire investigation
b) arson investigation
FIRE INVESTIGATION
- conducted to determine the origin, cause and nature of the fire
ORIGIN OF THE FIRE
- the specific place where the fire started
GUIDE IN DETERMINING THE ORIGIN:
- take note of the lowest point of burning
- take note of charring effects made by the fire on wood by observing “alligator skin” pattern on
charred wood
- look for half-moon pattern on concrete walls or observe spalling effects made by the fire on
concrete
4
- use reverse technique by starting from the place last reached by the fire and retracing the path
made by the fire to the place of origin
CAUSE OF THE FIRE
- initial source of heat
GUIDE IN DETERMINING THE CAUSE
- secure and cordon the origin
- use layer-checking technique in collecting physical evidence
- consider every possible source of heat which may normally be found at the origin
- analyze each piece of physical evidence collected
- eliminate possibilities
NATURE OF THE FIRE
- manner and circumstances surrounding the fire incident
GUIDE IN DETERMINING THE NATURE
- all fires are presumed to be accidental in nature unless proven otherwise
- look for indications of malicious intent:
a) prima facie evidence of arson
b) preparation made by the perpetrators
c) motives
INCENDIARY DEVICES
1) plant – a device used to start the fire
2) accelerant – a flammable substance used to speed up burning
3) trailer – a device used to direct the path of the fire
FIRE SAFETY
- protection of lives and property from the hazards of fire
PD 1185 - FIRE CODE OF THE PHILIPPINES
- approved on 26 August 1977
OBJECTIVES OF FIRE PROTECTION
1) to prevent fire from starting
2) to save lives and property
3) to confine the fire in its point of origin
4) to put out the fire
FIRE HAZARD
- any act or condition which increases or may cause an increase in the probability of the occurrence of
fire, or which may delay, obstruct, hinder or interfere with firefighting operations or the safeguarding of life and
property
FACTORS WHICH AFFECT DEGREE OF HAZARD
1) construction materials used
2) combustibility of contents
3) type of occupancy
4) occupant load
5) height from the ground
6) longest travel distance to exit
7) availability of fire protective alarm and warning devices or systems
FIRE SUPPRESSION
- the act of process of putting out the fire
FIRE CONTROL
- the act or process of preventing the fire from spreading and incurring further damages
You might also like
- Fire Pattern AnalysisDocument16 pagesFire Pattern AnalysisMs Paperworks100% (1)
- Fire Technology and Arson Management (Cdi 18) Module 7Document13 pagesFire Technology and Arson Management (Cdi 18) Module 7Divina DugaoNo ratings yet
- Arson Investigation: How Investigators Solve Arson CasesDocument15 pagesArson Investigation: How Investigators Solve Arson CasesAngeline ManosaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 - Q3 - Module 5 - Climatic Phenomena Occurring On A Global LevelDocument25 pagesScience 9 - Q3 - Module 5 - Climatic Phenomena Occurring On A Global LevelMelanie Trinidad100% (1)
- Notes in Fire Technology & Arson Investigation Evolution of FireDocument41 pagesNotes in Fire Technology & Arson Investigation Evolution of FireYangBedoyaNo ratings yet
- Fire Technology and Arson Investigation ReviewerDocument16 pagesFire Technology and Arson Investigation ReviewerDonald Kim100% (1)
- Fire Technology and Arson-InvestigationDocument43 pagesFire Technology and Arson-Investigationjeric deleon100% (1)
- Fire Technology and Arson Investigation FDDocument200 pagesFire Technology and Arson Investigation FDChinmarc GeneralaoNo ratings yet
- Fire Technology and Arson InvestigationDocument27 pagesFire Technology and Arson InvestigationJeany GamunganNo ratings yet
- Fire Technology and Arson InvestigationDocument5 pagesFire Technology and Arson InvestigationMarcel CataynaNo ratings yet
- Fire Tech and Arson InvestigationDocument12 pagesFire Tech and Arson InvestigationQueen Vi BenedictoNo ratings yet
- Arson Invest 2Document100 pagesArson Invest 2Harrison sajorNo ratings yet
- Fire TechnologyDocument106 pagesFire TechnologyCJ LicoNo ratings yet
- ARSONDocument122 pagesARSONJerry Glenn GimotoNo ratings yet
- Fire Protection and Arson InvestigationDocument14 pagesFire Protection and Arson Investigationjm100% (2)
- Mervic M. Pariñas, Ms CrimDocument14 pagesMervic M. Pariñas, Ms CrimMarcel CataynaNo ratings yet
- Cdi 6 Fire Technology and Arson Investigation 1Document12 pagesCdi 6 Fire Technology and Arson Investigation 1Russell GaylaNo ratings yet
- Notes in Fire Technology and Arson InvestigationDocument25 pagesNotes in Fire Technology and Arson InvestigationEarl Jann LaurencioNo ratings yet
- Cdi 6 Fire Protection and Arson InvestigationDocument117 pagesCdi 6 Fire Protection and Arson InvestigationTodd RamiscalNo ratings yet
- Novmeber 2018 ChE Licensure ExamDocument9 pagesNovmeber 2018 ChE Licensure ExamDominic Careo100% (1)
- Study Material Class 10 Chapter 14 2017 PDFDocument13 pagesStudy Material Class 10 Chapter 14 2017 PDFShivam Tiwari67% (3)
- 2 Chemistry of FireDocument53 pages2 Chemistry of FireCsjdm Bfp Bulacan100% (1)
- Notes in CDI 4 Organized Crime InvestigationDocument3 pagesNotes in CDI 4 Organized Crime InvestigationQueen Vi BenedictoNo ratings yet
- Fire Protection and Arson Investigation: By: Ms. Catherine G. Acedo, RcrimDocument31 pagesFire Protection and Arson Investigation: By: Ms. Catherine G. Acedo, RcrimCJ CuisonNo ratings yet
- Arson Prelim TopicDocument27 pagesArson Prelim TopicRALPH REVIN MALOONNo ratings yet
- Adr Ian Forty NatureDocument20 pagesAdr Ian Forty NatureElenore Phan100% (2)
- Fire Behavior and Arson InvestigationDocument16 pagesFire Behavior and Arson InvestigationCherry Mie RautrautNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes On Fire Technology and InvestigationDocument102 pagesSummary Notes On Fire Technology and InvestigationkaharNo ratings yet
- Fire Technology and Arson InvestigationDocument21 pagesFire Technology and Arson InvestigationEugene Alpheus Avila100% (1)
- Cdi6 Arson InvesDocument28 pagesCdi6 Arson InvesKARLVINNo ratings yet
- What Is A BackdraftDocument1 pageWhat Is A BackdraftAlin MocioiNo ratings yet
- Arson and Fire ChemistryDocument15 pagesArson and Fire Chemistrydarius mercadoNo ratings yet
- ARSON ModuleDocument16 pagesARSON ModuleTimmicpao AiraNo ratings yet
- Cdi 106Document1 pageCdi 106Uzo MakiNo ratings yet
- 5 Fundamentals of Fire FightingDocument15 pages5 Fundamentals of Fire FightingCsjdm Bfp BulacanNo ratings yet
- Firefighting Apparatus, Tools and EquipmentDocument29 pagesFirefighting Apparatus, Tools and Equipmentyvonne lang-ayNo ratings yet
- Photographing THE Fire Scene: Group 2Document10 pagesPhotographing THE Fire Scene: Group 2Calixtro Sunshine OreniaNo ratings yet
- Fire InvestigationDocument12 pagesFire InvestigationJose Li ToNo ratings yet
- Arson Review NotesDocument27 pagesArson Review NotesMonic BasconNo ratings yet
- Cdi Notes RKMDocument166 pagesCdi Notes RKMNhickoLetKwOnNo ratings yet
- Ignition Temperature (Temperature Needed To Burn), and If There Is Enough Oxygen Present, TheDocument24 pagesIgnition Temperature (Temperature Needed To Burn), and If There Is Enough Oxygen Present, TheRalph CelesteNo ratings yet
- Foe Sample QuistionSDocument21 pagesFoe Sample QuistionSYuGenNo ratings yet
- Arson Module 3rd YearDocument16 pagesArson Module 3rd Yearrodne rufinoNo ratings yet
- Causes of FireDocument10 pagesCauses of Firedray pogiNo ratings yet
- Criminal Detection and InvestigationDocument201 pagesCriminal Detection and InvestigationJackieNo ratings yet
- ArsonDocument10 pagesArsonBimboy CuenoNo ratings yet
- Fire Technology and Arson InvestigationDocument74 pagesFire Technology and Arson InvestigationDonita BernardinoNo ratings yet
- 8.PRINCIPLE OF FIRE FIGHTING 10 Phases of FireDocument13 pages8.PRINCIPLE OF FIRE FIGHTING 10 Phases of FireDarwin FranciscoNo ratings yet
- A Self-Learning Module For BS Criminology Course Code: Cdi 6 Fire Technology and Arson InvestigationDocument28 pagesA Self-Learning Module For BS Criminology Course Code: Cdi 6 Fire Technology and Arson InvestigationMelanie Garcia CanonizadoNo ratings yet
- Cagayan State University: College of Criminal Justice Education Module in Cdi 6 Fire Technoloy & Arson InvestigationDocument3 pagesCagayan State University: College of Criminal Justice Education Module in Cdi 6 Fire Technoloy & Arson InvestigationStephen EstalNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles in Fire and Arson InvestigationDocument3 pagesBasic Principles in Fire and Arson InvestigationDENNIS ZOZOBRADONo ratings yet
- Providential Fires Are Caused by Act of God, Like LightningDocument3 pagesProvidential Fires Are Caused by Act of God, Like LightningJeffrey GalvezNo ratings yet
- Fire and Arson InvestigationDocument13 pagesFire and Arson Investigation8ykq4hw89zNo ratings yet
- The Bureau of Fire Protection'sDocument2 pagesThe Bureau of Fire Protection'sChampagne MorenoNo ratings yet
- Fire Technology and Arson Investigation ModuleDocument15 pagesFire Technology and Arson Investigation ModuleNinoboy BaligatNo ratings yet
- Fire Technology and Arson InvestigationDocument20 pagesFire Technology and Arson InvestigationApplegrace Osing Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- PRELIM Fire Technology and Arson InvestigationDocument6 pagesPRELIM Fire Technology and Arson InvestigationIgnacio Burog RazonaNo ratings yet
- CA 1 2 Top RankDocument122 pagesCA 1 2 Top RankGeefren Dela Cruz GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Fire Tech Lecture NotesDocument34 pagesFire Tech Lecture NotesFitz Kennedy CannogNo ratings yet
- Industrial Explosives 12Document12 pagesIndustrial Explosives 12Heren me100% (2)
- Notes On Fire TechnologyDocument8 pagesNotes On Fire TechnologyIsavelle Mae SupremidoNo ratings yet
- Fire Origin Recognized by The Philippine Supreme CourtDocument3 pagesFire Origin Recognized by The Philippine Supreme CourtAnwar MokalamNo ratings yet
- Origin of PetroleumDocument2 pagesOrigin of PetroleumIrfan ShaikNo ratings yet
- Mixing in Lakes and ReservoirsDocument14 pagesMixing in Lakes and ReservoirsNatalia HernandezNo ratings yet
- ESP Evaluation SourcesDocument9 pagesESP Evaluation SourcesĐoan TrangNo ratings yet
- Igcse Phy Past PaperDocument16 pagesIgcse Phy Past Paperlikitha0% (1)
- Analysis of Compressive Strength of M-25 Grade Concrete Using Fly Ash As Partial Replacement of CementDocument49 pagesAnalysis of Compressive Strength of M-25 Grade Concrete Using Fly Ash As Partial Replacement of CementRais AlamNo ratings yet
- 24 Nuclear ChemistryDocument2 pages24 Nuclear Chemistryerice12No ratings yet
- Conversion of Biomass To Methanol and Ethanol: October 2019Document13 pagesConversion of Biomass To Methanol and Ethanol: October 2019Fong Cai YingNo ratings yet
- 1Document22 pages1Anonymous o29GUBm1TcNo ratings yet
- 1Q19 Presentation EECL VFDocument45 pages1Q19 Presentation EECL VFHelena AraujoNo ratings yet
- Weather Variables Review SheetDocument3 pagesWeather Variables Review Sheetapi-283242736No ratings yet
- Time Table Exam 2020 New Dates 1.30Document9 pagesTime Table Exam 2020 New Dates 1.30Syed Muhammad Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Tube Velocity in Heat Exchangers PDFDocument19 pagesTube Velocity in Heat Exchangers PDFponmanikandan1No ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Sample Paper 01Document16 pages11 Chemistry Sample Paper 01loduuNo ratings yet
- Isa PDFDocument7 pagesIsa PDFairsorNo ratings yet
- Hyundai M6 Shingled VGBF - 25y 210901Document2 pagesHyundai M6 Shingled VGBF - 25y 210901subtirelu lucianNo ratings yet
- What Type of Connection Is Used at Transformers Used at Generation Side and Distribution Side PDFDocument1 pageWhat Type of Connection Is Used at Transformers Used at Generation Side and Distribution Side PDFcharanNo ratings yet
- 4 - Conybeare - 1976 - Geomorphology of Oil and Gas Fields in Sandstone BodiesDocument337 pages4 - Conybeare - 1976 - Geomorphology of Oil and Gas Fields in Sandstone BodiesAnca SesermanNo ratings yet
- Earth's Water: ConnectionsDocument9 pagesEarth's Water: Connectionsdiana ruizNo ratings yet
- Final BTP Thesis 2Document20 pagesFinal BTP Thesis 2mdsingh77No ratings yet
- Chemistry Class 10 Meatals and NonmetalsDocument9 pagesChemistry Class 10 Meatals and NonmetalsGokulNo ratings yet
- Answer Keys: NCERT Booster Programme For NEET-2024 (XII Studying) - Physics - Poll-08Document14 pagesAnswer Keys: NCERT Booster Programme For NEET-2024 (XII Studying) - Physics - Poll-08Rohit LokvaniNo ratings yet
- Wind Turbines StudyDocument5 pagesWind Turbines StudyStar BitoonNo ratings yet
- Minerals: Rock-Forming Minerals Ore-Forming MineralsDocument3 pagesMinerals: Rock-Forming Minerals Ore-Forming MineralsDarcy EvansNo ratings yet
- CourseBOOKv5 PDFDocument132 pagesCourseBOOKv5 PDFantilelosNo ratings yet
- Chalmers LOIDocument1 pageChalmers LOIDelwin SaldanhaNo ratings yet
- Class9 Chemistry Matter Around Us Notes-2Document22 pagesClass9 Chemistry Matter Around Us Notes-2Bhaavi ParekhNo ratings yet