Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Legal Med Causes of Injury
Legal Med Causes of Injury
Uploaded by
Geraldine Marie SalvoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Legal Med Causes of Injury
Legal Med Causes of Injury
Uploaded by
Geraldine Marie SalvoCopyright:
Available Formats
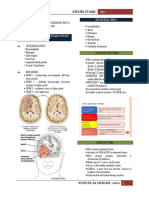
LEGAL
MEDICINE CAUSES OF INJURY
DR. LISING
CAUSES OF INJURY
• Mauling Sport injuries
• Domestic Injury • Boxing
• Industrial Accident • Wrestling
• Vehicular Accident • Newer sports with attendant risks:
• Sports Injury o Mixed Martial Arts
• Stabbing Injuries o Extreme Games
• Gunshot Injuries o Sky Diving
Mauling Injuries common in combat sports
• Results from a violent altercation between 2 persons or • Lacerations to the eyebrow & malar region (cheek)
groups of persons • Hemorrhage secondary to the blood vessel rupture or
• Injury may be sustained by: fracture of the orbital plate of the frontal bone known as
o The feuding parties Spectacle Hematoma
o Bystanders • Hematoma of pinna with auricular cartilage necrosis
known as Cauliflower ears
Domestic & Industrial accidents • Cerebral concussion
• Usually results from the myriad of combinations of
accidents at home or at work
• A physician must note whether there is presence of
alcohol on the patient
Vehicular Accidents
• Factors responsible in VAs
o Human factor
o Environmental factor
o Mechanical factor
• Subdural hemorrhage (most common)
o Social factor
o Pedestrian
Human factors
• Mental Attitude
• Perception Defects
• Delayed or Sluggish Reaction Times
• Disease
• Chemical Factors
Factors responsible for passenger and driver injury
• Impact within structures • Pontine hemorrhage (known as boxer’s hemorrhage)
• Ejection
• Direct impact with other vehicle occupants
• Acceleration-‐deceleration injury (Whiplash)
Pedestrian-‐vehicle collision
• Primary impact
o Causes injuries such as bumper fractures as well
as patterned wounds of the front grills
• Secondary impact
• Run over injuries Stabbing injuries
o Usually results to patterned injuries such as tire • Anything with an edge could be used for injuries of this
tread contusion as well as abrasions type
• Hit and Run injuries o Knives
o Bolo/Machete
Motorcycle injuries o Broekn bottles
• Is the leading cause of vehicular accidents o Scalpels
• Reason for increase: o Sharpened instruments such as shanks
o Relatively number of motorcycles
o Relatively small profile of motorcycles Legal Classification
o Continued failure to use mandated safety • Mutilation (Art 262 RPC)
equipment o Intentionally depriving a person, totally or partially
o Very little material in a motorcycle to cushion the of some of the essential organs of reproduction
impact
TRANSCOM | DRA. JACKIE 1
LEGAL MEDICINE CAUSES OF INJURY
DR. LISING
o Intentionally depriving a person, totally or partially o There is a tumultuous affray
of any part other than that of theessential organs of o Participants suffered from serious physical injuries
reproduction o Persons who inflicted could not be identified
• Serious Physical Injuries (Art 263 RPC) o All those who appear to have used violence upon
o Done by: the offended party shall be penalized by arresto
! Wounding from 5 to 15 days
! Beating
! Assaulting PD 169
! Administering injurious substances without the • A physician must report cases of serious and less serious
intent to kill physical injuries
o Graduated
! Prision mayor GUNSHOT INJURY
• Person shall become insane, imbecile,
impotent or blind FIREARM
! Prision correctonal (medium to maximum) • An instrument used for the propulsion of a projectile using
• Loss of the use of speech, power to expansive force of gases coming from the burning of
hear/smell loss of an eye, hand, foot, arm gunpowder
& leg
• Includes:
• Loss of use of any such member
o Rifles
• Becomes incapacitated for the work in
which he was habitually engaged
o Muskets
! Prision correcional (minimum to medium) o Shotguns
• Person shall become deformed o Revolvers
• Loss of any other member of his body o Pistols
• Loss the use thereof
• Becomes ill or incapacitated for the Classification of Firearms
performance of work habitually engaged • As to wounding power
in for more than 90 days o Low velocity firearm (<1,400 fps)
! Arresto Mayor (maximum) to Prisioncorrecional
o High power firearm (>1,400 fps but usually
(minimum)
2,200-‐2,500 fps)
• Becomes ill or incapacitated for the
performance of work habitually engaged • As to nature of the bore
in for more than 30 days o Smooth bore
o Rifled bore
• Administering Injurious Substance or Beverages (Art 264 • As to manner of firing
RPC) o Pistol – single handed weapon
o Infliction upon another of any serious physical injury o Rifle – shoulder fired weapon
o It was done knowing that the substance is injurious • As to the nature of the magazine
or took advantage of the victims weakness or o Cylindrical revolving magazine
credulity o Vertical or horizontal magazine
o No intent to kill
Components of a weapon
• Less Serious Physical Injuries (Art 265 RPC) • The Cartridge
o Incapacitate the offended party from labor for more • The Firearm
than 10 days
o Requires medical attendance for more than 10 days The Cartridge
o Qualified by: • Cartridge Case or Shell
! Manifest intent to insult or offend the injured • Primer
person • Powder or propellant
! Circumstance adding ignominy • Bullet or projectile
! Victim is the offender’s parents, ascendants,
guardian, curators or teachers
! Victim is a person of rank or authority
• Slight Physical Injuries (Art 266 RPC)
o Incapacitate the offended party from labor for 1 to 9
days (arrestomenor)
o Causes injury which do no prevent the offended
party from working nor require medical attendance
(arrestomenor, censure)
o Ill-‐treatment by deed
• Physical Injuries Inflicted in a Tumultuous Affray (Art 252
RPC)
TRANSCOM | DRA. JACKIE 2
LEGAL MEDICINE CAUSES OF INJURY
DR. LISING
• Plastic Bullet
• Bullet with Plastic Sabot
• Bullet with Secondary Explosion
• Soft Point Bullets
* Depleting uranium tip
* Teflon
FIREARMS
• Parts
of
the
firearm
of
medicolegalimportance:
o Trigger
with
firing
pin
Cartridge
Case
or
Shell
o Barrel
• Cylindrical
structure
with
a
base
which
houses
the
different
parts
of
the
ammunition
Trigger
• May
be:
• Part
of
the
firearm
which
causes
the
firing
evolution
o Cartridge
with
a
rim
• Classification:
o Rimless
cartridge
o Relation
of
cocking
&
trigger
pressure
o Semi-‐rimless
cartridge
! Single
action
o Belted
cartridge
! Double
action
o Number
of
shots
on
pressure
on
the
trigger
Primer
! Single
shot
firearm
• Functions
to
transform
the
mechanical
energy
of
the
! Automatic
firearm
firing
pin
to
chemical
energy
by
its
rapid
combustion
• Located
at
the
base
of
the
cartridge
and
covered
by
a
Barrel
small
disc
of
soft
metal
known
as
percussion
cap
or
• Riflings
primer
cap
o Series
of
parallel
spiral
grooves
on
the
whole
• Center
fire
cartridge
length
o Percussion
cap
located
at
the
center
• Land
o Most
common
o Space
between
2
grooves
• Rimfire
cartridge
o Primer
is
placed
inside
the
rim
of
the
shell
o Common
in
0.22
caliber
firearm
• Firearm
with
a
pin
Gunpowder/propellant
• Primary
propulsive
force
in
the
cartridge
• Types
of
Propellant
o Black
powder
(80%KNO3,
15%S,
10%C)
o Smokeless
powder
! Single
base
(either
cellulose
1)
Number
–
varies
from
2-‐12
nitrate
or
nitroglycerin)
! Double
base
(contains
both)
2)
Twist
Rate
–
expression
of
1
complete
twist
o Semi-‐smokeless
powder
(80%black
&
20%smokeless)
3)
Direction
–
clockwise
or
counterclockwise
Bullet
4)
Width
• The
projectile
attached
to
the
free
end
of
the
cartridge
case
• Determination
of
caliber
• Classification:
o Distance
of
the
barrel
between
2
lands
o Shape
of
the
tip
! Conical
Mechanism
of
Firearm
action
! Hemispherical
! Wad
cutter
(square
nose)
! Hollow
point
o Presence
or
absence
of
jacket
! Naked
lead
bullet
! Jacketed
bullet
(full
or
semi)
Special
Bullets
• Armour
piercing
bullets
• Phosphorus
flare
or
tracer
bullet
TRANSCOM | DRA. JACKIE 3
LEGAL MEDICINE CAUSES OF INJURY
DR. LISING
Thing which come out of the muzzle after firing Destruction Mechanism of Gunshots
• Bullet • Lacerations & permanent cavity of the bullet trajectory
• Flame • Temporary Cavity
• Heated, compressed and expanded gas o The greater the velocity, the greater the cavity
o Instantaneous radial displacement of the soft tissue
• Residue coming from bullet (fragment or lubricant) during the passage of the bullet
• Primer o Secondary to the liberation of kinetic energy
• Powder particles • Hydrostatic force
o Powder grains o The bullets kinetic energy is imparted upon the fluid in
o Soot the fluid filled cavities creating as secondary projectile
o Graphite • Shock wave
• Barrel o Dissipation of kinetic energy in a radial direction
perpendicular to the path of the bullet
o Lubricant
• Fragmentation of the bullet
o Rust, Dust o Bullet breaks apart into multiple projectiles
o Scraping form previous fire • Fragmentation of hard brittle object in the bullet trajectory
• Cartridge Case o Bone fragmentation
• Muzzle blast
Bullet Movement o Occurs in contact fire
• Forward movement • Other complication
• Spinning movement o Hemorrhage
o Infection
• Tumbling movement o Paralysis
• Wobbling movement o Loss of function
• Gravitational Pull
Characteristics of Point of Entry
Factors Responsible for Injurious effect of the bullet • Caliber of the wounding weapon
• Inherent on the bullet • Characteristics inherent to entrance wound
o Speed of the bullet • Direction of fire
o Size and shape • Shape & composition of missile
o Character of the missile’s momentum in flight • Range
• Nature of the target • Kind of weapon
o Density of the target
o Length of tissue involvement Point of Entry – contact fire
o Nature of media traversed • Where bone is superficial
o Importance of the organ involved o Wound is large and stellate shaped
o Edges may be everted
Flame
o Burns, tattooing, smudging & singeing of hair is
• Brought about by the ignition of the propellant present
• Doesn’t not usually go beyond distance of 6” and in pistols o Muzzle imprint on the skin
is often less than 3” • Where bone is deeply located
• Causes burning of the skin in contact or near fire o Wound is usually large, circular & without
radiating laceration
o Edges may be everted, some tissue may be
Heated, Compressed & Expanded Gas found in the gun barrel
• Brought about by the limited space in the chamber of the o Burns, tattooing, smudging & singeing of hair is
firearm present
• Responsible for the Population of the projectile o Muzzle imprint on the skin
• Responsible for the muzzle blast
Point of Entry – near contact fire
Smoke • Wound is usually large & circular depending on the angle
• Product of the complete combustion of the gunpowder of fire
and the propellant • Contusion collar distinct
• Light almost black& only covers the skin • Burns, tattooing, smudging & singeing of hair is present
• May be readily wiped off • Muzzle imprint on the skin present
• May be seen up to a distance of 12” • Blackening of the bullet tract
Powder grains Point of Entry – short range fire 1-‐15cm distance
• Product of the incomplete combustion of the gunpowder • Edges of the wound inverted
• Contusion collar distinct
Contusion Collar • Tattooing & smudging is present
• Caused by the pressure of the bullet on the skin • If within 3”, burns may be present
TRANSCOM | DRA. JACKIE 4
LEGAL MEDICINE CAUSES OF INJURY
DR. LISING
Point of Entry – medium range fire 15-‐60cm 3. Arborescent or Filigree burns (Lichtenberg figures)
• Edges of the wound inverted • Radiating burns from a point
• Contusion collar distinct
• Tattooing & smudging (if less than 30cm) is present but of Effects of lightning
lesser density • Primarily affected is the CNS
• Burns & singeing is absent • Causes spasmodic contraction of the cerebral vessels
causing hypoxia
Point of Entry – greater than 60cm distance
• Edges of the wound inverted Post mortem findings
• Contusion collar distinct 1. Externa
• Tattooing, smudging, burns & singeing is absent • Marked tearing of the clothing
• Burns of different degree
Point of Exit (outshoot) • Different wound patterns
• No characteristic shape • Magnetization of metals in the clothing
• Edges are usually everted • Fusion of metals & glass
• Singeing of the hair
Special Consideration on Bullets 2. Internal
• Souvenir bullet • Fracture of the bones
• Bullet migration • Internal hemorrhage due to rupture of organs
• Tandem Bullet • Petechial hemorrhage of the lung, pericardium &
brain
ELECTRICAL CURRENT
Shotgun Wounds • Main cause of death is SHOCK
• Classes of shot in a shotgun shell • Principal factor is the intensity of the currentor the
1. Birdshot – small & measuring 200-‐400 shots in the amperage
shell
2. Buckshot – shot ranges from .24 to .33 inch in Factors affecting Electrical shock
diameter. Std 12 gauge = 9 shots • Personal idiosyncracy
3. Single Projectile or Rifled slug • Disease
o Heart Disease, presence of pacemakers
Types of Shotgun • Sleep
• As to number of barrels o Increases resistance to electrical current
o Single barrel • Amperage
o Double barrel o 70-‐80 in AC
• As to the manner of firing & reloading o 250 in DC
o Bolt action • Resistance of the body
o Lever action o Lesser resistance = greater injury
o Pump action • Nature of the current
o Autoloading o AC vs DC
• Grounding
• Duration of contact
LIGHTNING • Kind of conductor
LIGHTNING • Point of entry
• Electrical charge in the atmosphere
• May reach 1 Gigavolts & 10,000 to 200,000 amperes Mechanism of death
• The distribution is variable & unpredictable • Ventricular fibrillation
o Low of cardiac output
Elements which produce injury o Low voltage
• Direct effect of current on the body • Respiratory Failure
• Surface “flash” burns from the discharge o Bulbar paralysis
• Mechanical effect of air expansion o High voltage
• Compression effect of superheated air • Mechanical asphyxia
o Causes sledgehammer-‐like blow on the body o Prolonged convulsions
Classes of Burn in Lightning Injury
1. Surface Burns
• Superficial, usually under metallic objects
2. Linear Burns
• Found in areas of least resistance
• May vary from 1 to 12 inches
TRANSCOM | DRA. JACKIE 5
LEGAL MEDICINE CAUSES OF INJURY
DR. LISING
Electrical Burns Types of Chemical Explosion
• Other names include: • Diffused Reactant Explosion
o Electrical necrosis o Caused by mixture of gas & air and initiated by a
o Electric marks flame
o Current markings o Examples include:
• These may be seen at the point of entry & point of exit ! Internal combustion engine
• Skin is puckered with gray color & traversed by deep ! Fuel Air Bomb
impressions at right angles
• Marks are painless • Condensed Reactant Explosion
• Show no signs of inflammation o Caused by a large quantity of heat & gas
produced as a consequence of a rapid chemical
Metallization reaction in a liquid or solid
• A specific feature of electrical injury o Radiating in an outward direction thus maximal
• Metal of the conductor is volatilized & the particles are damage is sustained nearest the point of origin
driven into the epidermis o Subclassified as:
• Color depends of the conductor ! Low order explosive (Deflagrating
o Iron = yellow brown explosive)
o Copper = bluish ! High order explosive
o
Post mortem findings Low order explosive
• Non specific • Relies on burning & confinement ot produce
explosions
INFECTION • Gunpowder is the best known low order
explosive
• Caused by a pathogen High order explosive
• May be: • Type of explosive which detonates
o Viral • Detonation is a chemical process which results in
o Bacterial the extremely rapid decomposition of
o Parasitic nitrogenous compoung releasing heat & gas as
o Prions its by-‐product
• Discusses further in IM-‐Infectious • Damage is caused by the shock wave
• Of medicolegal importance: o results from the sudden release of
o Weaponized strains pathogens heat & gas
• Types:
Historical Implications o Stable
• Used since time of antiquity o Unstable
o Assyrians – used fungus of poison enemy wells
o Hannibal – used snakes on enemy ships Stable
o Mongols – animal carcasses to poison enemy • Stable until detonated by another
walls explosive such as a blasting cap
• Advent of germ theory • E.g: dynamite & plastique such as C4 or
o Weaponization of botulism & brucellosis Semtex
Unstable
Weaponization • Easily detonates from heat, flame,
• Incrasing resistance to environmental factors spark or percussion
• Means: • E.g: Picric Acid & Nitroglycerin
o Adding cancer genes to increase the robustness
of the pathogen Other types of explosive
• Usually studied pathogens • Mechanical or Hydraulix
o Small pox o Pressure inside a container exceeds its structural
o Ebola strength
o Lassa • Electrical
o Anthrax o Resutls from electrical arc
• Nuclear
CHEMICAL ENERGY
Injury is due to:
• Primary effects of detonation
• Causes injury when there is a sudden release of potential
o Occurs when the body is in contact with the explosive
energy into kinetic or thermal energy causing a sudden o Causes complete disruption or fragmentation of the
increase in pressure victim’s body
• Results in an explosion
TRANSCOM | DRA. JACKIE 6
LEGAL MEDICINE CAUSES OF INJURY
DR. LISING
o Compression-‐decompression effect brough about by o Barotrauma
sudden rise & fall of atmospheric pressure o Thermal
o Chemical
• Secondary to the blast wave
o Infection
o Body may be thrown some distance and dismembered
o Hollow organs are most heavily dmage
o Triad of blast wave injury is present • Manner of Infliction
1. Punctuate bruises o Hit
2. Abrasions o Thrust/Stab
3. Lacerations o Gunpowder explosion
o Sliding or Rubbing
• Peppering of shrapnel
o Secondary to the effect of blast wave to small
• Depth of the Wound
fragments
o May be metallic or not o Superficial
o Deep
• Other blast wave effects ! Perforating (solid organ)
o May cause fall related injuries ! Perforating (communication between
o Damage to the respiratory organs inner & outer portion of the hollow
o Damage to theear & the tympanic membrane organs)
• Burns from the flame or heated gas
• Relation of the Site of Application of Force & the Location
• Asphyxia due to lack of oxygen
of Injury
• Smoke inhaltion & poisoning o Coup injury
o Carbon monoxide poisoning o Contre-‐Coup injury
o Nitrous or Nitric gases o Coup-‐Contre injury
o Hydrogen sulfide, sulfur dioxide, HCN gas o Locus Minoris Resistencia
o Extensive
• Direct injury from flying debris
Contusion Hematoma
• Injuries from falling debris
• Diffused blood • Diffused blood
PHYSICAL VIOLENCE is in the in newly
interstitial formed cavity
• Wound is a natural disruption of the anatomic integrity of tissue • Always
a tissue of the living body. • No elevation of elevated
• Used synonymously with physical injury however, physical the skin
injury does not always result in a wound • Puncture & • Puncture &
aspiration of aspiration
Physics of wound production the wound yields blood &
• Wound yields no blood subsequent
= kinetic energy x Time x Area x Other factors depression of
2
• Kinetic energy = ½ mv the lesion
Where M = mass
V = velocity (very important because this is the value which changes
most. That is, High powered rifle bullet vs Pistol bullet)
Vital reaction
• Old term for inflammation
o Rubor or redness or congestion
o Calor or sensation of heat
o Dolor or pain
o Loss of function
• Special types of Wounds
Classification of Wounds o Defensive wounds
• Kind of Instrument used o Patterned wounds
o Blunt o Self inflicted wounds
o Sharp o Extensive
! Sharp edged
! Sharp pointed Types of Wounds
! Edged & Sharp • Closed wounds
o Tearing force o No breach in the continuity of the skin
o May be superficial or deep
• Kind of Instrument used • Open wounds
TRANSCOM | DRA. JACKIE 7
LEGAL MEDICINE CAUSES OF INJURY
DR. LISING
Open Wounds
Petechiae 1. Abrasion
• Circumscribed extravasation of blood into the subcutaneous 2. Incised wound
tissues or beneath the mucou membrane 3. Stab wound
• Usually from the capillary systems 4. Punctured wound
• Causes: 5. Lacerated wound
o Asphyxia
o Trauma
o Coronary occlusion
Abrasion
o Clotting disorders • An injury characterized by the removal of the superficial epithelial
layer secondary to friction against a hard rough surface
• Usually develops at the precise point of impact
Contusion
• May exhibit the pattern of the wounding material
• Effusion of blood into the surrounding tissues
• Results from blunt force trauma
• Does not immediately develop after the trauma
Incised wound
• Medicolegal significance: • Wound produced by a sharp edged instrument
o May correspond to the shape of the object causing it • May be: impact cut or slice cut
o Extent may suggest the degree of force applied
o Distribution may indicate character & manner of injury Incised wound Lacerated wound
• Age can be estimated by color
• Edges are clean • Edges are
o Red to purple = recent
o Green = 4-‐5 days cut, regular & roughly cut,
o Yellow = 7-‐10 days well-‐defined irregular & ill-‐
o Gradual resumption of skin tone = 14-‐15 days • No surrounding defined
hematoma or • There is
Hematoma contusion swelling &
• Extravasation or effusion of blood in a newly formed cavity • Extremities of contusion
underneath the skin the wound are around the
• Usually formed if force is applied where the bone is superficailly sharp, rounded wound
located or contused • Extremities of
• Caused by a the wound are
sharp edged ill-‐defined &
Deep Closed Wounds instrument irregular
1. Musculoskeletal injuries • Caused by blunt
2. Internal Hemorrhage instrument
3. Cerebral Concussion
Stab wound
Musculoskeletal injuries
• Wound produced by the penetration of a sharp pointed &
• Sprain
sharp edged instrument
o Partial or complete distruption in the continuity
of amuscular or ligamentous support of a joint
Punctured wound
o Caused by a blow, kick or torsion force
• Injury resulting from the use of a sharp pointed instrument
• Dislocation
such as an icepick
o Displacement of the articular surface of bones
entering into a joint
Lacerated wound
• Fracture
• Tear of the skin & underlying tissues due to forcible
o Fragmentation of bone resulting loss of
contact with a blunt instrument
continuity
• Strain
o Over-‐stretching of a muscle or ligament
• Subluxation
o Implies the presence of complete or partial
dislocation
Internal hemorrhage
• Rupture of blood vessel which may result in hemorrhage
Cerebral Concussion
• Concussion is a trauma-‐induced change in mental status, with
confusion & amnesia, and with or without a brief loss of
consciousness
• Most commonly caused by vehicular accident & Sports injuries
TRANSCOM | DRA. JACKIE 8
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Mental HealthDocument59 pagesMental HealthGeraldine Marie Salvo97% (29)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Marketing Plan (Pizza Hut)Document13 pagesMarketing Plan (Pizza Hut)Anjali10183% (48)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Stages of LaborDocument5 pagesStages of LaborGeraldine Marie Salvo100% (4)
- Tugas CP 4Document19 pagesTugas CP 4mrr dwi lindawati100% (1)
- Embryology, Anatomy and Physiology & Disease of The LarynxDocument83 pagesEmbryology, Anatomy and Physiology & Disease of The LarynxGeraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- LEGALMED DEception DetectionDocument9 pagesLEGALMED DEception DetectionGeraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- Chest TraumaDocument27 pagesChest TraumaGeraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- Group 1: Histology Case #3Document19 pagesGroup 1: Histology Case #3Geraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- Additional Notes in Pedia Neuro2Document4 pagesAdditional Notes in Pedia Neuro2Geraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- Intro Case Report DinerevisedDocument12 pagesIntro Case Report DinerevisedGeraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- Family Case Presentation: Abat FamilyDocument80 pagesFamily Case Presentation: Abat FamilyGeraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Enzyme Chemistry Part 1Document7 pages4.1 Enzyme Chemistry Part 1Geraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- With Important Actions On Smooth MuscleDocument90 pagesWith Important Actions On Smooth MuscleGeraldine Marie Salvo100% (1)
- 4.2 Enzyme Chemistry Part 2Document6 pages4.2 Enzyme Chemistry Part 2Geraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- 2015 Physical Injury Part 2Document8 pages2015 Physical Injury Part 2Geraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- Medication List For PregnancyDocument1 pageMedication List For PregnancyGeraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiovascular Life SupportDocument43 pagesAdvanced Cardiovascular Life SupportGeraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- AdrenocorticosteroidsDocument64 pagesAdrenocorticosteroidsGeraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- Culminating Activity Creative WritingDocument12 pagesCulminating Activity Creative WritingAnonymous wYyVjWTVib100% (1)
- Tle910 BPP910 Q1 M5Document14 pagesTle910 BPP910 Q1 M5Fernando JoseNo ratings yet
- Saep 306Document15 pagesSaep 306nadeem shaikh100% (1)
- Bukuma Information SystemDocument18 pagesBukuma Information SystemMustafa PeywaNo ratings yet
- WealthDocument1 pageWealthfredglass7No ratings yet
- 60trans PDFDocument20 pages60trans PDFjucamenNo ratings yet
- Hospital Management SystemDocument13 pagesHospital Management SystemOmkarNo ratings yet
- Charak Jigyasa Sutrsthana 1-10 - Dr. Shakti Raj RaiDocument30 pagesCharak Jigyasa Sutrsthana 1-10 - Dr. Shakti Raj RaiAyur PreparationNo ratings yet
- Evidence EDW 1 - A World of Differences and Similarities FCHDocument2 pagesEvidence EDW 1 - A World of Differences and Similarities FCHpablo emilio cortes sanchezNo ratings yet
- Minas A DriverDocument14 pagesMinas A DriverPham Long100% (1)
- Effectiveness of An Online Classroom For Flexible Learning: Christopher DC. Francisco and Marites C. BarcelonaDocument8 pagesEffectiveness of An Online Classroom For Flexible Learning: Christopher DC. Francisco and Marites C. BarcelonaLeigh Ann Cruz MonakilNo ratings yet
- AlliedCrowds November 2015 ReportDocument7 pagesAlliedCrowds November 2015 ReportCrowdfundInsiderNo ratings yet
- 4 Autobiographical ResponsesDocument1 page4 Autobiographical Responsesren180No ratings yet
- Soal Toefl Lit 1Document25 pagesSoal Toefl Lit 1Khzvy 1122No ratings yet
- ANDRESEN, Bent B Van Den BRINK, Katja - Multimedia in Education - Curriculum (UNESCO) (2013)Document139 pagesANDRESEN, Bent B Van Den BRINK, Katja - Multimedia in Education - Curriculum (UNESCO) (2013)projetius100% (1)
- Benchmarking in QFD For Quality Improvement PDFDocument14 pagesBenchmarking in QFD For Quality Improvement PDFĐoàn TâmNo ratings yet
- Westphal BalanceDocument3 pagesWestphal BalanceJade Carlo AntonioNo ratings yet
- Eaton MV Ohmic Voltage Pa022011enDocument2 pagesEaton MV Ohmic Voltage Pa022011enYH TAnNo ratings yet
- Safe Systems of Work 2Document23 pagesSafe Systems of Work 2Hossam AbdelmoneimNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 Study Guide MidtermDocument42 pagesNCM 112 Study Guide MidtermMark Nathaniel ValerioNo ratings yet
- Lets Look at NumbersDocument16 pagesLets Look at NumbersMahobe80% (5)
- Redução. EFFICIENT PERIPHERAL FUNCTIONALIZATIONDocument8 pagesRedução. EFFICIENT PERIPHERAL FUNCTIONALIZATIONGivaldo Dos Santos AndradeNo ratings yet
- Analytical Essay Philippines and Europe 19th CenturyDocument2 pagesAnalytical Essay Philippines and Europe 19th CenturyMarcial BaldoveNo ratings yet
- IGR User GuideDocument20 pagesIGR User Guidesales leotekNo ratings yet
- KP Astrology Shortcut MethodDocument3 pagesKP Astrology Shortcut MethodRaman Sharma100% (2)
- Chapter 1 - Homeostasis and ExcretionDocument51 pagesChapter 1 - Homeostasis and ExcretionSYAZWANI100% (1)
- Ingles 3 Modulo 6Document24 pagesIngles 3 Modulo 6AMBIENTE ORIENTOIL ORIENFLUVIALNo ratings yet
- Huawei OceanStor 2600 V3 Storage System Data SheetDocument6 pagesHuawei OceanStor 2600 V3 Storage System Data Sheetfarari mailNo ratings yet