Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ChemLab Expt#1
Uploaded by
Kathleen Joy Temporal NavaseroCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ChemLab Expt#1
Uploaded by
Kathleen Joy Temporal NavaseroCopyright:
Available Formats
Expt #: 1 Date: 02/13/20
Expt Title: Separation and Purification of Organic Compounds (CRYSTALLIZATION)
Introduction:
Crystallization is simple, effective and very important technique to separate and purify
solids. It is based on the fact that all organic compounds are more soluble in hot than in cold
solvents, so that solid gets dissolved on heating and is obtained back on cooling. And to carry out
the purification, we have been employed various techniques of crystallization. It involves the
process of dissolving the material to form a saturated solution in a suitable solvent at an elevated
temperature, filtering while hot to remove any suspended insoluble particles, and letting
crystallization proceed.
Materials:
Apparatus: Test Compounds: Reagents:
beaker test tube benzoic acid animal charcoal
Erlenmeyer flask filter paper sodium chloride 5% nitric acid solution
glass rod pipette methylene blue 1% silver nitrate solution
hot plate ice brown sugar distilled water
medicine dropper funnel
watch glass
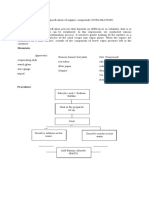
Procedure:
Test Compounds
Benzoic acid &NaCl Brown Sugar
Prepare the Sample Control Filtrate
(Mix 1g benzoic acid, pinch of
NaCl, 10 drops methylene blue & Dissolution of the Heat the Solution
100 ml distilled water) Sample
(Heat the remaining
Dissolution of the Sample (Dissolve 1g of brown solution to nearly
(Dissolve the benzoic acid & NaCl sugar in 25ml distilled boiling point
heating near at its boiling point) water and set aside 2ml
solution in a test tube) Decolourisation of
Decolourisation of the Solution the Solution
(add 0.5 g of animal charcoal (add 0.5 g of animal
while heating and stirring) charcoal while
heating and stirring)
Hot Filtration
Hot Filtration
Cooling for crystallization
(Collect the filtrate into two test tube (5ml
each), labeled one as “slow cooling” and set
aside it. Labeled another one as “rapid
cooling” and submerge it into ice water)
Cold Filtration
(After cooling, separate the
crystals by filtration )
Washing the crystals
Checking the purity
(Dissolve crystals into 1ml hot distilled water, add
Drying the crystals
1 drop of 5% nitric acid and 2 drops of 1% AgNO₂)
Results and Discussion:
Test Compounds Observation Interpretation
A. Benzoic acid & NaCl
1. Description of Mixture Benzoic acid and NaCl were both
The liquid is organic compounds. They do not easily
1.1 Before Heating blue in color. dissolve in a solvent with a lower
The Benzoic temperature, since the principle behind
acid and NaCl crystallization is that the amount of
submerged in solute that can be dissolved by a solvent
the liquid. increase with temperature; therefore,
they are relatively insoluble in room
temperature.
1.2 While Heating
The Benzoic A solution is created by dissolving a
acid and NaCl solute in a solvent at or near its boiling
dissolved in the point. At this high temperature, the
liquid after solute has a greatly increased solubility
being heated in the solvent, so a much smaller quantity
near in its of hot solvent is needed than when the
boiling point solvent is at room temperature;
and stirred therefore; the solute was much more
vigorously. soluble at higher temperature.
2. Formation of Crystals The crystals
formed in rapid Ice was used as the catalyst to rapidly
2.1 Rapid Cooling cooling were cool the solution. Rate of crystallization
smaller than the slows as temperature decreases. If the
crystals in slow solution cools quickly, the crystals do
cooling. not have much time to form, so they are
very small.
The crystals
2.2 Slow Cooling formed in slow
cooling were If the solution cool slowly, then the
larger and finer crystals have enough time to grow and
than the crystal become large.
in rapid cooling.
3. Solution There were Silver precipitates chloride. Silver nitrate
white solution will form an insoluble precipitate with
3.1 Purified crystals + 1- and white chloride ions. Therefore, if sodium
2 drops of 1% AgNO₃ precipitate chloride is present, if you make an
formed. aqueous solution from your crystals and
treat it with silver nitrate, a precipitate
will indicate the presence of sodium
chloride present.
B. Brown Sugar
The control is Brown sugar is an organic compound, it
1. Control
yellowish in dissolves in a water after stirring, and the
(without animal charcoal)
color color diffuse rapidly making the solution
yellowish in color.
2. Filtrate The filtrate is
(with animal charcoal) usually almost The animal charcoal is a decolorizing
colorless carbon that absorbed impurities from the
solution making the solution clear and
colorless.
1. How are colored impurities removed from crystals?
- Colored impurities were removed from crystals through filtration
2. Why is it necessary to filter the solution while still hot?
- It is necessary to filter the solution while still hot to remove insoluble purities because
according on the principles of solubility, compounds tend to be more soluble in hot
liquids. If you allowed it to cool, the solute is no longer soluble in solvent and forms
crystals of pure compound.
3. What are the methods of inducing crystal formation from solution?
- Removal of impurities which may retard or inhibit crystal formation
- Nucleus formation, and
- Encouragement of growth of crystals to visible form
- Crystallization can be induced by reduction in temperature i.e. put in an ice bath or
you can use a technique called seeding where you put a few crystals of the expected
substance in the solution, the other method is to increase the concentration of the
solution by evaporating it, to saturation point, ensure you do not evaporate it dry.
4. What factors cause the difference in the size of crystals formed?
- Variables that control crystal growth include the amount of dissolved material,
evaporation, pressure, and temperature. The higher the amount of dissolved material
in the water, the more pressure that is placed on the material, the bigger the crystals
will grow.
- Nucleation
5. How is the completeness of separation of the benzoic acid crystals from sodium chloride
known with the addition of Ag NO₃ solution?
-If the separation is incomplete, sodium chloride will be an impurity in benzoic acid
crystals. Silver nitrate will form an insoluble precipitate with chloride ions. Therefore, if
sodium chloride is present, if you make an aqueous solution from your crystals and treat it
with silver nitrate, a precipitate will indicate the presence of sodium chloride present.
Silver precipitates chloride. If a precipitate forms the separation is not complete
Question to Post Lab:
What is the used of the animal charcoal? How it helps to purified the solution?
- Animal charcoal is a decolorizing carbon. The fine carbon particles present a large,
active surface upon which soluble colored substances which serve as impurities may
be absorbed making the solution purified.
-
Conclusion:
In the experiment conducted, we learned that allowing a hot solution of the required
compound to cool is called crystallization. If the impure compound is insoluble in cold solvent and
soluble in hot solvent, the suitable crystallization is obtained. Having a best solvent is a must,
because if not, all steps are not obtained. In short, you cannot have a pure compound.
Crystallization have processes mainly: dissolution, hot filtration and drying. Problems occur in
crystallization when the solvent is not suitable and when compound des not crystallize. Organic
compounds are more soluble at high temperature. Methylene blue mixture and was boiled and
mixed with animal charcoal to purify the solution. The slow cooling solution revealed large and
fine crystals while the rapid cooling solution revealed smaller crystals. Brown sugar and water was
yellowish in color and the it was heated and the filtrate with animal charcoal is clear and colorless
since animal charcoal is a decolorizing carbon and that process is called decolorization.
Name:
Kathleen Joy Navasero NJ Lorenzo
Princess Anne Maramag Daniella Jacobe
Jessa Labrador Abigail Macanang
Gwyneth Gatpolitan
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- SublimationDocument4 pagesSublimationKathleen Joy Temporal Navasero100% (2)
- Plant IdentificationDocument43 pagesPlant IdentificationKathleen Joy Temporal Navasero100% (1)
- CrystallizationDocument4 pagesCrystallizationKathleen Joy Temporal NavaseroNo ratings yet
- Cory Group 2Document16 pagesCory Group 2Kathleen Joy Temporal NavaseroNo ratings yet