Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MCB Lec Reviewer
MCB Lec Reviewer
Uploaded by
Jhoanna Mae MinionOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MCB Lec Reviewer
MCB Lec Reviewer
Uploaded by
Jhoanna Mae MinionCopyright:
Available Formats
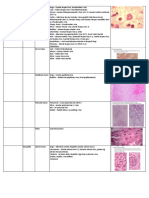
CHARACTERISTICS REPRODUCTION GROUPS SPECIAL STRUCTURE OTHERS
FUNGI + chemoheterotrophic Sexual—plasmogamy, ascomycota (yeast and sac fungi) + haustoria- hyphal tip lichens- association
+ protoplasm of a karyogamy, meiosis— basidiomycota (club fungi, that penetrates host’s tissue between fungi
hypha is surrounded by gametangial mushrooms) and draws nutrients from it (mycobiont) and
rigid wall—chitin Asexual—fragmentation, Chytridiomycota (chytrids) + stolon- hypha that algae/cyanobacteria
fission,budding,spores deuteromycota (imperfect fungi) connects two rhizoids (photobiont)
Glomeromycota (arbuscular + rhizoid- root-like mycorrhizae-
mycorrhizae) structures association between
Zygomycota (bread molds) plant roots and fungi
ALGAE + photoautotrophs Sexual--Conjugation chlorophyta (green) +pigments—
+cell wall is thin and Asexual—binary fission, phaeophyta (brown) chlorophylls,
rigid fragmentation rhodophyta (red) carotenoids (carotene,
pyrrophyta (dinofllagelates) xanthophylls)
euglenophyta (euglena)
chrysophyta (diatoms)
PROTOZOA + heterotrophic—obtain Sexual-conjugation Mastigophora (flagellates)– 2 or locomotory distribution
food by endocytosis Asexual-simple fission, more flagella pseudopodia, flagella, cilia free-living—aquatic
multiple fisson (schizogony) Sarcodina (Amoebas)- amoeboid nuclei and terrestrial
Reproduction in motion due to pseudopodia macronucleus(locomotion), symbiotic—parasitic,
paramecium Ciliophora (ciliates)- cilia moves in micronucleus(sexual mutualistic
+ binary fission unison to propel cell/ bring food to reproduction)
+ conjugation* its cytostome (mouth) vacuoles
+ endomixis* Sporozoa (sporozoans)- non motile, secretory(specific
+ autogamy* obligate intracellular parasite enzymes), phagocytic(food
+ cytogamy* microspore (microsporans)- no digestion),
*new macronucleus is microtubules and mitochondria contractile(excretion)
formed
VIRUSES, VIROIDS, PRIONS + Amniotic inoculation- for primary isolation of influenza
Terminologies virus and the mumps virus.
capsid- protein shell that encloses the nucleic acid + yolk sac inoculation- simplest method for growth and
capsomere- capsid subunits multiplication of virus.
nucleocapsid- capsid + enclosed nucleic acid 3. Cell Culture
virion- complete virus particle
HOST Viriods- cause serious plant disease
+Bacteria Prions by Stanley Prusiner
+ animals e.g. Madcow disease, Creutzfeld Jacod Disease
+ higher plants PrPSc –prios behind diseases
+ algae PrPc –normal
VIRUS STRUCTURE
+ icosahedral- 20 triangular faces, 12 vertices, 30 sides
e.g. herpes simple virus, poliovirus, parvovirus
+ helical
e.g. tobacco mosaic virus, measles virus, rabies virus
+ complex
e.g. bacteriophages, smallpox virus, influenza virus
LIFE CYCLE
+lytic virulent- cause lysis—destruction of cell
- Upon infection, host responds by producing a lot of
virions cell bursts virions released
- Attachmentpenetrationtranscriptionbiosynthesisas
sembly release
+lysogenic cycle
- no lysis occurs but lytic cycle may be spontaneously
expressed
CULTIVATION
1. Animal Inoculation
2. Inoculation into embryonated egg
+ Chlorioallantoic membrane inoculation- for growing
poxvirus
+ allantoic inoculation- for production of vaccine of influenza
virus, yellow fever, rabies.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Important Viral Disease of Cat and Dog by Md. SalauddinDocument23 pagesImportant Viral Disease of Cat and Dog by Md. SalauddinSalauddinNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Diagnosis of Viral Infections in Animal TissuesDocument3 pagesDiagnosis of Viral Infections in Animal TissuesRandy Butternubs100% (2)
- Economic Importance of VirusesDocument24 pagesEconomic Importance of VirusesFakhir Rahmani100% (2)
- Fungal Classification, Structure, and ReplicationDocument23 pagesFungal Classification, Structure, and ReplicationDoc RomeoNo ratings yet
- Flora GIT PDFDocument6 pagesFlora GIT PDFMaghfira Puspita ANo ratings yet
- Ornithine Hippurate Nitrate VP/MR Casein/ Tyrosine Niacin Tween 80 HOH Pyrazinamidas eDocument2 pagesOrnithine Hippurate Nitrate VP/MR Casein/ Tyrosine Niacin Tween 80 HOH Pyrazinamidas eKristine PangahinNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Classification andDocument15 pagesProkaryote Classification andAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Praktikum Mikrobiologi Gram NegatifDocument44 pagesPraktikum Mikrobiologi Gram Negatifrids_No ratings yet
- Lecture 1B - Benzer's Work and Complementation TestDocument5 pagesLecture 1B - Benzer's Work and Complementation TestLAKSHAY VIRMANI100% (1)
- Biofire FilmArray Full Panel Menu Info SheetDocument3 pagesBiofire FilmArray Full Panel Menu Info SheetAnne Jillian Castillo100% (1)
- Lecture 2 VirologyDocument15 pagesLecture 2 VirologyNawazNo ratings yet
- (Methods in Microbiology 17) P.M. Bennett and J. Grinsted (Eds.) - Plasmid Technology-Academic Press (1984) PDFDocument320 pages(Methods in Microbiology 17) P.M. Bennett and J. Grinsted (Eds.) - Plasmid Technology-Academic Press (1984) PDFStella RodicaNo ratings yet
- Mic 301 2014-1Document40 pagesMic 301 2014-1mellier2468309No ratings yet
- 2.02 Classes of MicroorganismsDocument16 pages2.02 Classes of MicroorganismsMARIA LOURDES MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 VirusesDocument8 pagesChapter 19 Virusesjpayne655No ratings yet
- PROTEOBACTERIADocument35 pagesPROTEOBACTERIANurul AnisshaNo ratings yet
- Gram StainingDocument9 pagesGram StainingGayatri PandaNo ratings yet
- DSMZ BactnamesDocument247 pagesDSMZ BactnamesGeraldNo ratings yet
- Microbiology SyllabusDocument5 pagesMicrobiology Syllabushhg100% (1)
- Microbe ListDocument2 pagesMicrobe ListSkye AllisonNo ratings yet
- Wa0040Document26 pagesWa0040ROHITNo ratings yet
- Filaments Bacteria Actinomyces, Nocardia, StreptomycesDocument7 pagesFilaments Bacteria Actinomyces, Nocardia, StreptomycesMohamedNo ratings yet
- Ws 3Document5 pagesWs 3Vishal JalanNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document25 pagesPresentation 1Saurav Suman100% (1)
- ConjugationDocument2 pagesConjugationIwan MuzakiNo ratings yet
- Expt 11 Lab ReportDocument11 pagesExpt 11 Lab ReportGracechel PormildaNo ratings yet
- Cauliflower Mosaic VirusDocument15 pagesCauliflower Mosaic Virussivagurunathan.P100% (5)
- EFFECT of TemperatureDocument3 pagesEFFECT of Temperatureswati sharmaNo ratings yet
- Coli-Test in Cancabato BayDocument5 pagesColi-Test in Cancabato BayAlvin MontesNo ratings yet
- Gizmo - Virus Lytic Cycle SeDocument6 pagesGizmo - Virus Lytic Cycle SeMarques AlsoppNo ratings yet