Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biochemistry MIDTERMS LAB
Uploaded by
cha cuteOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biochemistry MIDTERMS LAB
Uploaded by
cha cuteCopyright:
Available Formats
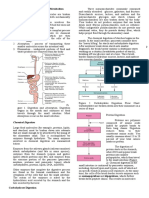
Biochemistry – midterm period Lipids experiment 1.
Molisch test
The term “lipid” refers to both true fats and fat-like substances. These Principle: Molisch test is Specific for all carbohydrates – To
are biomolecules that are insoluble in water but are soluble in organic differentiate between Proteins & Amino Acids (-ve), and Carbohydrates
solvents. (+ve).
Another important function of lipids is the storage energy in the form This test is based on the fact that pentoses and hexoses are
of body fat. The brain and nerve tissues are rich in certain lipids, a fact dehydrated by conc. H2SO4 acid to form furfural or
that indicates the importance of these compounds in the maintenance hydroxymethylfurfural, respectively.
of life.
1. Molisch test
Five groups of lipids:
Result: Reddish Violet ring at the interface - Any Carbohydrate
1. Fats and oils 2. Waxes 3. compound lipids
4. Sterols and steroids 5. Derived lipids No change - Non carbohydrate
General objectives:
At the end of the experiment, the student must be able to: 2. Ninhydrin test
1. Familiarize himself/herself with the different classes of lipids; and
Principle: This test is due to a reaction between a amino group of free
2. Identify each kind of lipid based on the chemical properties of its
amino acid and ninhydrin. Ninhydrin is a powerful oxidizing agent and
hydrolyzed products.
its presence, amino acid undergo oxidative deamination liberating
a. Spotting effect
ammonia, CO2, a corresponding aldehyde and reduced form of
All the lipids are greasy in nature. Therefore the test may be taken as
ninhydrin ( hydrindantin). The NH3 formed from a amino group reacts
group test for lipids.
with another molecule of ninhydrin and is reduced product
PRINCIPLE: the oil does not wet the paper
( hydrindatin) to give a blue substance diketohydrin ( Ruhemanns
b. Solubility
complex).
This test is based on the
Positive compound: Phosphatidylserine
property of solubility of lipids in
organic solvents and insolubility Visible result: blue violet or dark blue solution
in water.
3. Soda lime test
PRINCIPLE: The oil will float on
water because of lesser specific test for amino and amino group// test for acidity and basicity
gravity.
Soda lime positive compound: Sphingomyelin and phosphatidylserine
c. Test for unsaturation (bromine water test)
Principle: deamination and acid-base reaction
PRINCIPLE: All neutral fats contain glycerides of some unsaturated
Visible result:
fatty acids. These unsaturated fatty acids become saturated by taking
- Red litmus -> Blue - Blue Litmus -> Blue
up iodine.
4. Ammonium molybdate test
This test identifies the level of saturation and the number of bonds an
oil, fat, or lipid has. It detects the presence of phosphate group
Visible result: Colorless Test positive compound: Phospholipids
d. Acrolein test Principle: Hydrolysis and double decomposition
It is used to detect the presence of glycerol or fat. When fat is treated Visible results:
strongly in the presence of a dehydrating agent like potassium
bisulphate (KHSO4), the glycerol portion of the molecule is dehydrated yellow precipitate (ammonium phosphomolybdate) insoluble in nitric
to form an unsaturated aldehyde, acrolein that has a pungent acid
irritating odor. lecithin (yellow orange)
Pigs brain (yellow)
e. Extraction of brain lipids
5. Liebermann – burchard test
Brain submerged in Ether
This test is used for the detection of cholesterol. The formation of a
Extracts ceramides, sphingomyelins, choline glycerophospholipids, green or green-blue color after a few minutes is positive.
ethanolamine glycerophospholipids and phosphatidylserines.
Lieberman–Burchard is a reagent used in a colorimetric test to detect
Not all lipids are soluble in Ether, therefore separates polar and non cholesterol, which gives a deep green color.
polar lipids
f. Detection of brain lipids
You might also like
- Biochem LabMidtermDocument6 pagesBiochem LabMidtermRafael PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Characterization of LipidsDocument4 pagesCharacterization of LipidsEzraela Neriah AmodoNo ratings yet
- Qualitative and Quantitative Lipid TestsDocument11 pagesQualitative and Quantitative Lipid TestsAurian TormesNo ratings yet
- Xt202000826@wmsu@edu - PH: Activity No. 5 Reaction of LipidsDocument5 pagesXt202000826@wmsu@edu - PH: Activity No. 5 Reaction of LipidsJohanna Marie GantalaoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5bDocument4 pagesExperiment 5bKaten KyoukotsuNo ratings yet
- Analysis of LipidDocument6 pagesAnalysis of LipidanaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report LipidsDocument5 pagesLab Report LipidsKhamis Tolentino100% (1)
- Experiment 5: Analysis of Carbohydrates (Post-Lab Report)Document9 pagesExperiment 5: Analysis of Carbohydrates (Post-Lab Report)Jemina SacayNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis of Lipids Through The Extraction of Total Lipids From Chicken Egg YolkDocument5 pagesQualitative Analysis of Lipids Through The Extraction of Total Lipids From Chicken Egg YolkJessa Mateum VallangcaNo ratings yet
- QUALITATIVE TESTS FOR LIPIDSDocument2 pagesQUALITATIVE TESTS FOR LIPIDSTrixie Delos Reyes BuñoNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Tests For CarbohydratesDocument91 pagesQualitative Tests For CarbohydratesAllyssa Jiselle Cabalonga100% (2)
- Milk - Experiment 11Document16 pagesMilk - Experiment 11Joshuel MontecilloNo ratings yet
- Concept of PH and BufferDocument27 pagesConcept of PH and BufferRolling Coast100% (1)
- Analysis of Lipids in Egg YolkDocument2 pagesAnalysis of Lipids in Egg YolkHydieNo ratings yet
- POstlab Biochem Experiment 4 8BDocument80 pagesPOstlab Biochem Experiment 4 8BGeline Joy D. Samillano60% (5)
- Biochem Lab ReportDocument4 pagesBiochem Lab ReportChryza Faith QuicoyNo ratings yet
- Biochem Post Lab 5aDocument12 pagesBiochem Post Lab 5aJessica Lorenz PablicoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9 Properties of ProteinsDocument5 pagesExperiment 9 Properties of ProteinsLara MonevaNo ratings yet
- Biochem 7Document14 pagesBiochem 7Clint Danniel GuarinNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 - Laboratory Activity Chemical Tests For The Components of Nucleic AcidDocument4 pagesExperiment 3 - Laboratory Activity Chemical Tests For The Components of Nucleic AcidDelosreyes ChildrenNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument22 pagesLipidsJoren Angela Galang83% (6)
- Isolation, Hydrolysis, and Characterization of GlycogenDocument4 pagesIsolation, Hydrolysis, and Characterization of GlycogenRyan Enriquez100% (1)
- Bial's Orcinol TestDocument2 pagesBial's Orcinol TestVennice Dela PenaNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Characterization of Ribonucleic Acid From YeastDocument4 pagesIsolation and Characterization of Ribonucleic Acid From YeastPatrick Daniel Libiran100% (1)
- Qualitative Analysis of Carbohydrates ExperimentDocument12 pagesQualitative Analysis of Carbohydrates Experimentasdf653652547No ratings yet
- Biochem LipidsDocument15 pagesBiochem LipidsDERRICKKEANNo ratings yet
- Biochem Laboratory MidtermDocument15 pagesBiochem Laboratory MidtermNica DonioNo ratings yet
- Lipids Chemical TestDocument9 pagesLipids Chemical TestMiles Acosta100% (2)
- Francisco, Estelle Rhine - Activity 1Document3 pagesFrancisco, Estelle Rhine - Activity 1ESTELLE RHINE HINDAP FRANCISCONo ratings yet
- Rna Qualitative TestsDocument5 pagesRna Qualitative TestsPeter Paul RecaboNo ratings yet
- Classification of Carbonyl and Hydroxyl Containing CompoundsDocument7 pagesClassification of Carbonyl and Hydroxyl Containing CompoundsSamantha Hope SyNo ratings yet
- Protein Denaturation: Effects of Heat, Acids, Salts, and AcetoneDocument4 pagesProtein Denaturation: Effects of Heat, Acids, Salts, and AcetoneRena Emmanuelle PalenciaNo ratings yet
- Sample Lab Report 5 Alain NowDocument10 pagesSample Lab Report 5 Alain NowNur SetsuNo ratings yet
- The Molisch TestDocument12 pagesThe Molisch Testkamaksi100% (1)
- Chem Lab Final Exam Notes 2Document7 pagesChem Lab Final Exam Notes 2Jaira Emmarina100% (1)
- Isolation and Qualitative Analysis of Nucleic Acids (DNA From Onion)Document3 pagesIsolation and Qualitative Analysis of Nucleic Acids (DNA From Onion)Elina Lantion100% (1)
- Isolation and Characterization of RNADocument3 pagesIsolation and Characterization of RNAEvans DionNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Characterization of CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesIsolation and Characterization of CarbohydratesEvans DionNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Saponifiable LipidsDocument73 pagesCharacterization of Saponifiable LipidsDing Regino100% (1)
- Characterization of Saponifiable LipidsDocument6 pagesCharacterization of Saponifiable LipidsChristian Vincent Maranan LumabanNo ratings yet
- Expt. 1 Qualitative Analysis Test For CarbohydratesDocument8 pagesExpt. 1 Qualitative Analysis Test For CarbohydratesMary Ella Mae PilaNo ratings yet
- The Molisch TestDocument9 pagesThe Molisch TestrawatanandNo ratings yet
- Biochem Proteins LabDocument3 pagesBiochem Proteins LabDaneva ReyesNo ratings yet
- Bials Orcinol Test Group 5 BMLS 2IDocument12 pagesBials Orcinol Test Group 5 BMLS 2ITom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab - Lipids (Corpuz, R)Document6 pagesBiochem Lab - Lipids (Corpuz, R)Reynand MaelNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5a Pre Post LabDocument9 pagesExperiment 5a Pre Post LabRue Cheng Ma100% (1)
- Lipids ReviewerDocument7 pagesLipids ReviewerMaria Treshia AlabNo ratings yet
- Expt 2 BIOCHEMLABDocument5 pagesExpt 2 BIOCHEMLABEloisah Vin Santiago Ragodon100% (1)
- Carbohydrate Detection Tests: Molisch and Iodine ReactionsDocument29 pagesCarbohydrate Detection Tests: Molisch and Iodine ReactionsTom Anthony Tonguia0% (4)
- Activity 2B Precipitation Test For ProteinDocument6 pagesActivity 2B Precipitation Test For ProteinAshley Nicole DelizoNo ratings yet
- Identify Oils and FatsDocument6 pagesIdentify Oils and FatsKeth Samuel AdesasNo ratings yet
- Analysis of LipidsDocument2 pagesAnalysis of LipidsHoney Joy Cruz CapiralNo ratings yet
- Isolation, Purification, and Partial Characterization of A Lipid Extract From NutmegDocument12 pagesIsolation, Purification, and Partial Characterization of A Lipid Extract From NutmegJulio Francisco100% (2)
- Experiments 11 15 NotesDocument16 pagesExperiments 11 15 NotesJoshuel MontecilloNo ratings yet
- LIPID ANALYSISDocument20 pagesLIPID ANALYSIS3amabelle arevalo100% (2)
- Activity 2Document6 pagesActivity 2MARKUS GERARD REYESNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab Activity 5Document47 pagesBiochem Lab Activity 5Nafeesa Cadir100% (1)
- Observation Discussion Olive Oil: Table E. Unsaturation TestDocument1 pageObservation Discussion Olive Oil: Table E. Unsaturation TestDaBestMusicNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument5 pagesLipidsmaggan donnaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test For MacromoleculesDocument4 pagesLaboratory Test For MacromoleculesOdessa KwonNo ratings yet
- Lipid Metabolism Digestion and AbsorptionDocument10 pagesLipid Metabolism Digestion and Absorptioncha cuteNo ratings yet
- Clinical Teaching 2Document2 pagesClinical Teaching 2cha cuteNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Digestion & MetabolismDocument4 pagesGroup 2 Digestion & Metabolismcha cuteNo ratings yet
- Biochem Reviewer FinalsDocument18 pagesBiochem Reviewer Finalscha cuteNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab FinalsDocument3 pagesBiochem Lab Finalscha cuteNo ratings yet
- Philippine HistoryDocument13 pagesPhilippine HistoryHanna Relator DolorNo ratings yet
- General Principles of Digestion and MetabolismDocument6 pagesGeneral Principles of Digestion and Metabolismcha cuteNo ratings yet
- The Philippine Revolution of 1896Document29 pagesThe Philippine Revolution of 1896cha cuteNo ratings yet
- 1 Cavitesmutiny 181210114221 PDFDocument35 pages1 Cavitesmutiny 181210114221 PDFcha cuteNo ratings yet
- Agrarian Reform in The PhilippinesDocument19 pagesAgrarian Reform in The Philippinescha cuteNo ratings yet
- Agrarianreform 150318094700 Conversion Gate01Document6 pagesAgrarianreform 150318094700 Conversion Gate01cha cuteNo ratings yet
- .Explosives and Blasting Module - 1628404265000Document85 pages.Explosives and Blasting Module - 1628404265000Cristiano RonaldoNo ratings yet
- SG-920 TDSDocument2 pagesSG-920 TDSRajneesh RallanNo ratings yet
- Isopoly and Heteropoly Acids and SaltsDocument39 pagesIsopoly and Heteropoly Acids and SaltsAhilya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Presentation On Why Its Used in Daily LifeDocument16 pagesChemistry Presentation On Why Its Used in Daily LifesanjamNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical calculations and drug analysisDocument20 pagesPharmaceutical calculations and drug analysisSohail AbdessamadNo ratings yet
- Novec 1230 VS. FP Aerosol Comparison White PaperDocument3 pagesNovec 1230 VS. FP Aerosol Comparison White PaperTri Nguyen100% (1)
- ASSIGNMENT CHM557-mergedDocument3 pagesASSIGNMENT CHM557-mergedAhmad ZakwanNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Cellular FoundationsDocument4 pages1.1 Cellular Foundationsdenniel DelacruzNo ratings yet
- KAOCAST®Document3 pagesKAOCAST®1repsaperuNo ratings yet
- Chemical Stoichiometry Calculations and Balancing EquationsDocument5 pagesChemical Stoichiometry Calculations and Balancing EquationsNeharika PuriNo ratings yet
- Group 18 elements and the periodic tableDocument1 pageGroup 18 elements and the periodic tableDhara PandeyNo ratings yet
- Standard Methods For The Examination of Water and Wastewater 23th (Rodger B. Baird, Eugene W. Rice Etc.) (Z-Library) - 1-2Document2 pagesStandard Methods For The Examination of Water and Wastewater 23th (Rodger B. Baird, Eugene W. Rice Etc.) (Z-Library) - 1-2almirantebenbowNo ratings yet
- Presentation On PVAc AhesivesDocument18 pagesPresentation On PVAc AhesivesJawad SattarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Cdi6Document43 pagesChapter 1 Cdi6Meryl Krisha Mae TomoboNo ratings yet
- Polimeros Adhesivos y Conductores de ElectricidadDocument66 pagesPolimeros Adhesivos y Conductores de ElectricidadDAYANA ALEJANDRA LNPEZ LUJNNNo ratings yet
- CTM 1Document7 pagesCTM 1Sajil KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 11th Chemistry Unit 11 Study Material em 215587Document9 pagesNamma Kalvi 11th Chemistry Unit 11 Study Material em 215587prathiksha6660No ratings yet
- Practical 1BDocument8 pagesPractical 1BHoe Lam WanNo ratings yet
- Flyer Herwig Products FinalDocument2 pagesFlyer Herwig Products Finalkls.thorodinsonNo ratings yet
- Tiocianato Astm D4193-02Document4 pagesTiocianato Astm D4193-02Julio MolinaNo ratings yet
- EST I - Literacy 2 - June 2021Document16 pagesEST I - Literacy 2 - June 2021Hamza WaleedNo ratings yet
- (CHEM CS) Chapter 10 - Organic Chemistry (MIND MAP)Document1 page(CHEM CS) Chapter 10 - Organic Chemistry (MIND MAP)Jie LingNo ratings yet
- Chm102 Lec - FinalsDocument21 pagesChm102 Lec - FinalsChurva EklavuNo ratings yet
- STPM 2022 SEM 2 Mock AnsDocument2 pagesSTPM 2022 SEM 2 Mock Ansm-4306022No ratings yet
- Paper and Pulp WastewaterDocument36 pagesPaper and Pulp WastewaterSandeep TiwariNo ratings yet
- Pcqa Finals All LessonDocument38 pagesPcqa Finals All LessonLazaro, Javen Andrie A.No ratings yet
- Cycles of Matter: Lesson ObjectivesDocument6 pagesCycles of Matter: Lesson Objectivesapi-593653104No ratings yet
- GnsourjoiDocument6 pagesGnsourjoiTan Keat JinNo ratings yet
- CY 1001: Organic Chemistry: Aromaticity: (4 Classes + 1 Tutorial)Document80 pagesCY 1001: Organic Chemistry: Aromaticity: (4 Classes + 1 Tutorial)Sai naveenNo ratings yet
- Separation Techniques: Composed With Epsilon Notes in AndroidDocument7 pagesSeparation Techniques: Composed With Epsilon Notes in AndroidBrãñdøn DzîñgáíNo ratings yet