Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Designing Joints and Pressure Vessels
Uploaded by
sutha_me20098282Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Designing Joints and Pressure Vessels
Uploaded by
sutha_me20098282Copyright:
Available Formats
1. A knuckle joint is required to withstand a tensile load of 25 kN.
Design the joint if the
permissible stresses are : t = 56 MPa ; = 40 MPa and c = 70 MPa.
[Ans. d = d1 = 28 mm ; d2 = 56 mm ; d3 = 42 mm ; t1 = 21 mm]
2. A shaft 80 mm diameter transmits power at maximum shear stress of 63 MPa. Find
the length of a 20 mm wide key required to mount a pulley on the shaft so that the
stress in the key does not exceed 42 MPa. [Ans. 152 mm]
3. A shaft 30 mm diameter is transmitting power at a maximum shear stress of 80 MPa.
If a pulley is connected to the shaft by means of a key, find the dimensions of the key
so that the stress in the key is not to exceed 50 MPa and length of the key is 4 times
the width. [Ans. l = 126 mm]
4. A steel cylinder of 1 metre diameter is carrying a fluid under a pressure of 10 N/mm 2.
Calculate the necessary wall thickness, if the tensile stress is not to exceed 100 MPa.
[Ans. 50 mm]
5. A steam boiler, 1.2 metre in diameter, generates steam at a gauge pressure of 0.7
N/mm2. Assuming the efficiency of the riveted joints as 75%, find the thickness of the
shell. Given that ultimate tensile stress = 385 MPa and factor of safety = 5.
[Ans. 7.3 mm]
6. Find the thickness of a cast iron cylinder 250 mm in diameter to carry a pressure of
0.7 N/mm2. Take maximum tensile stress for cast iron as 14 MPa. [Ans. 6.25 mm]
7. A pressure vessel has an internal diameter of 1 m and is to be subjected to an internal
pressure of 2.75 N/mm2 above the atmospheric pressure. Considering it as a thin
cylinder and assuming the efficiency of its riveted joint to be 79%, calculate the plate
thickness if the tensile stress in the material is not to exceed 88 MPa. [Ans. 20 mm]
8. A spherical shell of 800 mm diameter is subjected to an internal pressure of 2 N/mm 2.
Find the thickness required for the shell if the safe stress is not to exceed 100 MPa.
[Ans. 4 mm]
1. The eye bolts are used for
(a) transmission of power (b) locking devices (c) lifting and transporting heavy machines (d)
absorbing shocks and vibrations
2. The taper on a rectangular sunk key is
(a) 1 in 16 (b) 1 in 32 (c) 1 in 48 (d) 1 in 100
3. The usual proportion for the width of key is
(a) d/8 (b) d/6 (c) d/4 (d) d/2
where d = Diameter of shaft.
4. A key made from a cylindrical disc having segmental cross-section, is known as
(a) feather key (b) gib head key (c) woodruff key (d) flat saddle key
5. A feather key is generally
(a) loose in shaft and tight in hub (b) tight in shaft and loose in hub (c) tight in both shaft and
hub (d) loose in both shaft and hub.
6. The type of stresses developed in the key is/are
(a) shear stress alone (b) bearing stress alone (c) both shear and bearing stresses (d) shearing,
bearing and bending stresses.
7. In a thick cylindrical shell, the maximum radial stress at the outer surfaces of the shell is
(a) zero (b) p (c) – p (d) 2p
8. In case of thick cylinders, the tangential stress across the thickness of cylinder is
(a) maximum at the outer surface and minimum at the inner surface
(b) maximum at the inner surface and minimum at the outer surface
(c) maximum at the inner surface and zero at the outer surface
(d) maximum at the outer surface and zero at the inner surface
9. The design of the pressure vessel is based on
(a) longitudinal stress (b) hoop stress (c) longitudinal and hoop stress (d) none of these
10. In case of pressure vessels having open ends, the fluid pressure induces
(a) longitudinal stress (b) circumferential stress (c) shear stress (d) none of these
You might also like
- Commodore 64 Assembly Language Programming PDFDocument243 pagesCommodore 64 Assembly Language Programming PDFbandihoot100% (1)
- Design and Fabrication of Lawn Mower: N.Nagarajan, N.S.Sivakumar and R.SaravananDocument5 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Lawn Mower: N.Nagarajan, N.S.Sivakumar and R.SaravananAmar RahinjNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Guide To Become Big Data DeveloperDocument15 pagesStep by Step Guide To Become Big Data DeveloperSaggam Bharath75% (4)
- Physics Problems on Mechanics and DynamicsDocument34 pagesPhysics Problems on Mechanics and DynamicsHatsady ThonginNo ratings yet
- Design 2 Q2 1Document15 pagesDesign 2 Q2 1HaveOfControlNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1QS8ME Winter2020Document2 pagesAssignment 1QS8ME Winter2020VinayakNo ratings yet
- APS155CH Installation ManualDocument6 pagesAPS155CH Installation ManualTom GibbsNo ratings yet
- Business Process Management (BPM)Document14 pagesBusiness Process Management (BPM)zmrman0% (1)
- Linx Refresher Review: IPD PPD REFRESHERS TRIVIA EXAMINATIONDocument7 pagesLinx Refresher Review: IPD PPD REFRESHERS TRIVIA EXAMINATIONDeyn EstoqueNo ratings yet
- Most Open Valve Concept WWTP EE AnalysisDocument29 pagesMost Open Valve Concept WWTP EE AnalysisRahmi ArslanNo ratings yet
- ME463 - Lab Exercise 1: Design of Flat BeltDocument4 pagesME463 - Lab Exercise 1: Design of Flat BeltJoshua OliverNo ratings yet
- Machine Desing 1 Exam #2 Problem Solving InstructionsDocument2 pagesMachine Desing 1 Exam #2 Problem Solving InstructionsMarc JabarNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Activity No. 1 (Prelim)Document2 pagesModule 1 - Activity No. 1 (Prelim)Leyzer MalumayNo ratings yet
- Chain Drive Design Problems Mechanical Engineering Department Benha UniversityDocument1 pageChain Drive Design Problems Mechanical Engineering Department Benha UniversityAmrAliNo ratings yet
- Clutches, Brakes and FlywheelsDocument23 pagesClutches, Brakes and FlywheelsNauman KhanNo ratings yet
- Machine Design 2 Pre-TestDocument5 pagesMachine Design 2 Pre-TestGreg FelizartaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document6 pagesChapter 7Marco LuigiNo ratings yet
- Sheet 4 Mech - Keys and SplinesDocument1 pageSheet 4 Mech - Keys and SplinesAhmed Rabie Abd Elazeem50% (2)
- Plate No RaDocument5 pagesPlate No RaEdelleNo ratings yet
- COMPRE EXAM Machine Design No ChoicesDocument6 pagesCOMPRE EXAM Machine Design No ChoicesJunalin FabroNo ratings yet
- Apolakai Macdes ProblemDocument18 pagesApolakai Macdes Problempablo valorantNo ratings yet
- Exercises Problem On Spur Gear Force Analysis: Module 2: Activity No. 5Document1 pageExercises Problem On Spur Gear Force Analysis: Module 2: Activity No. 5Ariel GamboaNo ratings yet
- PIPE 180 Updated 2015Document180 pagesPIPE 180 Updated 2015joe1256No ratings yet
- Stresses & Machine Elements: PROBLEM SET (Topic 1)Document7 pagesStresses & Machine Elements: PROBLEM SET (Topic 1)Elisif DeFairNo ratings yet
- Machine Design 1 HandoutsDocument9 pagesMachine Design 1 HandoutsKenn Earl Bringino VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Anto ME463 Plate No. 3Document18 pagesAnto ME463 Plate No. 3Eman Lampago AntoNo ratings yet
- April 1997 MECHANICAL ENGINEER Licensure ExaminationDocument4 pagesApril 1997 MECHANICAL ENGINEER Licensure ExaminationMarcial Jr. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- Copy of Power Plant Plate-A Revised ENGLISH VersionDocument3 pagesCopy of Power Plant Plate-A Revised ENGLISH VersionMariel MirafloresNo ratings yet
- Wdghwahdg PDFDocument2 pagesWdghwahdg PDFKim Howard CastilloNo ratings yet
- Educspace - Pumps - Problems SetDocument3 pagesEducspace - Pumps - Problems SetMatthew John SyNo ratings yet
- Machine Design/Shop Practice Trivia: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument9 pagesMachine Design/Shop Practice Trivia: Multiple Choice QuestionsPaul EdwardNo ratings yet
- ME198D Design ElemetsDocument2 pagesME198D Design ElemetsChloe OlazoNo ratings yet
- Questions and solutions for engineering problemsDocument82 pagesQuestions and solutions for engineering problemsRyan Llona FernandezNo ratings yet
- MAPÚA UNIVERSITY WRITTEN REPORT ON PNEUMATICSDocument14 pagesMAPÚA UNIVERSITY WRITTEN REPORT ON PNEUMATICSAndreNo ratings yet
- A. Flat Belt & Pulleys: Unit I Design of Transmission Systems For Flexible ElementsDocument3 pagesA. Flat Belt & Pulleys: Unit I Design of Transmission Systems For Flexible ElementsVijaya Prabhu KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Macdes BoardsDocument6 pagesMacdes BoardsJerdNo ratings yet
- Belt Drive Design and CalculationsDocument13 pagesBelt Drive Design and CalculationsCllyan ReyesNo ratings yet
- Machine Desig3Document1 pageMachine Desig3Francis John S. TanarteNo ratings yet
- Section 16Document97 pagesSection 16Carolina FerrerNo ratings yet
- Stepped PulleyDocument4 pagesStepped PulleyKram YnarNo ratings yet
- Front Page and Expirement Number 1Document3 pagesFront Page and Expirement Number 1Ron Kristian OpolintoNo ratings yet
- MDlab FinalsDocument18 pagesMDlab FinalsNarry StrummerNo ratings yet
- FlywheelDocument1 pageFlywheelAngielou SialanaNo ratings yet
- Fans and Blowers Practice ProblemsDocument2 pagesFans and Blowers Practice ProblemsFour AyesNo ratings yet
- Design of Spring: Impact Loading and Energy ConversionDocument22 pagesDesign of Spring: Impact Loading and Energy ConversionBRYAN PINGOLNo ratings yet
- Pipe Problems Part 1Document100 pagesPipe Problems Part 1Sheena BejasaNo ratings yet
- Machine Design Test 4 - StressesDocument8 pagesMachine Design Test 4 - Stressessylvanaz01No ratings yet
- PADILLAMD Module 7 Exercises Problem No. 4Document2 pagesPADILLAMD Module 7 Exercises Problem No. 4Leyzer MalumayNo ratings yet
- Solar-Powered Fishpond Feeder With Real-Time Water Quality Monitoring SystemDocument6 pagesSolar-Powered Fishpond Feeder With Real-Time Water Quality Monitoring SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Machine Design 2 Final Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesMachine Design 2 Final Exam QuestionsAyuguNo ratings yet
- SteamDocument3 pagesSteamVon A. DamirezNo ratings yet
- Diesel Power Plant GuideDocument10 pagesDiesel Power Plant GuideyanyanNo ratings yet
- Exam Set 09Document1 pageExam Set 09allovidNo ratings yet
- Fan air velocity calculation from total head and static pressureDocument25 pagesFan air velocity calculation from total head and static pressurekristan7No ratings yet
- Introduction to Kinematics of MachinesDocument3 pagesIntroduction to Kinematics of MachinesEmmanuelRomaresNo ratings yet
- 2 Flywheel PDFDocument10 pages2 Flywheel PDFMohammed Safuvan KazhungilNo ratings yet
- Question BAB 5Document3 pagesQuestion BAB 5Justin GriffithNo ratings yet
- MDSP August 2019Document6 pagesMDSP August 2019Mark John DiolosaNo ratings yet
- Clutches and Brakes 0Document16 pagesClutches and Brakes 0gerti gjetjaNo ratings yet
- Dme Question Bank 2Document4 pagesDme Question Bank 2Ronak HadiyaNo ratings yet
- SM Mid3 Model QuestionsDocument3 pagesSM Mid3 Model QuestionsSaitama BackupNo ratings yet
- 9A01401 Strength of Materials - IIDocument4 pages9A01401 Strength of Materials - IIsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Part B QDocument4 pagesModule 2 Part B Qjawad zamanNo ratings yet
- J5Document1 pageJ5sutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- Riveted Joints MCQsDocument1 pageRiveted Joints MCQssutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- All Questions Carry Equal Marks (6x5 30 Marks) Part - ADocument1 pageAll Questions Carry Equal Marks (6x5 30 Marks) Part - Asutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- Jig Final Exam QPDocument2 pagesJig Final Exam QPsutha_me20098282No ratings yet
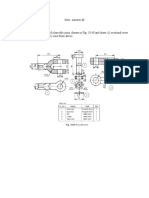
- Assemble Plummer block views: half sectional & topDocument1 pageAssemble Plummer block views: half sectional & topsutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- J4Document1 pageJ4sutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- All Questions Carry Equal Marks (6x5 30 Marks) Part - ADocument1 pageAll Questions Carry Equal Marks (6x5 30 Marks) Part - Asutha_me20098282No ratings yet
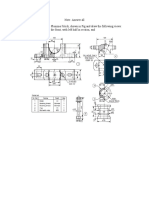
- Assemble knuckle joint parts and draw sectional and top viewsDocument1 pageAssemble knuckle joint parts and draw sectional and top viewssutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- N2Document1 pageN2sutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- Definition of Jigs, Fixtures and ToolingDocument2 pagesDefinition of Jigs, Fixtures and Toolingsutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- J1Document1 pageJ1sutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- Sheet Metal Blanking Process ExplainedDocument2 pagesSheet Metal Blanking Process Explainedsutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- Presses For Sheet Metal Operations Has The Following AdvantagesDocument2 pagesPresses For Sheet Metal Operations Has The Following Advantagessutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- PT1Document2 pagesPT1sutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- PPT5Document2 pagesPPT5sutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- 6Document2 pages6sutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- 4Document2 pages4sutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- Concise Exam Pattern of PG Admn in Central CollegesDocument3 pagesConcise Exam Pattern of PG Admn in Central Collegessutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- Introduction To Jigs and Fixtures: Types of Production 1. Job Production: This Involves The Manufacture ofDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Jigs and Fixtures: Types of Production 1. Job Production: This Involves The Manufacture ofsutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- 4Document2 pages4sutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- Definition of Jigs, Fixtures and ToolingDocument2 pagesDefinition of Jigs, Fixtures and Toolingsutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- PPT5Document2 pagesPPT5sutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- Introduction To Jigs and Fixtures: Types of Production 1. Job Production: This Involves The Manufacture ofDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Jigs and Fixtures: Types of Production 1. Job Production: This Involves The Manufacture ofsutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- 4Document2 pages4sutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- NEET PG Exam PatternDocument1 pageNEET PG Exam Patternsutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- Design of Riveted Joint and Shaft KeyDocument1 pageDesign of Riveted Joint and Shaft Keysutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- Definition of Jigs, Fixtures and ToolingDocument2 pagesDefinition of Jigs, Fixtures and Toolingsutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- Final Exam QPDocument2 pagesFinal Exam QPsutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- DynamicsDocument1 pageDynamicssutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- Design of Riveted Joint and Shaft KeyDocument1 pageDesign of Riveted Joint and Shaft Keysutha_me20098282No ratings yet
- Active Apprentices by Trade and by GenderDocument3 pagesActive Apprentices by Trade and by GenderThe Hamilton SpectatorNo ratings yet
- Gail India LTD VijaipurDocument13 pagesGail India LTD Vijaipuranshul21No ratings yet
- Isis Manual Vol. 2Document168 pagesIsis Manual Vol. 2Νίκος ΚατριβέσηςNo ratings yet
- CD 109 Highway Link Design-Web PDFDocument106 pagesCD 109 Highway Link Design-Web PDFAriel Zeballos LeañoNo ratings yet
- CU-2RE PBE Service ManualDocument110 pagesCU-2RE PBE Service ManualcoronaqcNo ratings yet
- Thyrodur 2210Document1 pageThyrodur 2210Grafički RadoviNo ratings yet
- PHOTO FACT Folder: To OoDocument23 pagesPHOTO FACT Folder: To Oodds94No ratings yet
- CW MasterDocument80 pagesCW MasterArianta RianNo ratings yet
- Lte Epc Umts 3GPPDocument222 pagesLte Epc Umts 3GPPjbarriospNo ratings yet
- Eee342 hw2 Solution PDFDocument7 pagesEee342 hw2 Solution PDFRedion XhepaNo ratings yet
- TMP 727Document40 pagesTMP 727FrontiersNo ratings yet
- Yogesh Kumar Garg Resume Mechanical EngineerDocument3 pagesYogesh Kumar Garg Resume Mechanical EngineerYogeshGargNo ratings yet
- GIS Mapping Powers Electricity Planning in BasraDocument25 pagesGIS Mapping Powers Electricity Planning in BasraYaser Al-SolimiNo ratings yet
- Darshan WORDDocument28 pagesDarshan WORDTRILOCHANPRASADNo ratings yet
- Linksys SRW-2048 User GuideDocument96 pagesLinksys SRW-2048 User GuideshiuksliadezesNo ratings yet
- Aseptic Process TechnologyDocument19 pagesAseptic Process TechnologyHimanshu ShahuNo ratings yet
- Principles of Lighting DesignDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Lighting DesignnpfhenriquesNo ratings yet
- Galaxy Y S5360 Android 2.3.6 Gingerbread Official FirmwareDocument23 pagesGalaxy Y S5360 Android 2.3.6 Gingerbread Official Firmwarekharishkhan0% (1)
- MODEL 90544, Patented Technology: Redundant Lighting and Onboard DiagnostixDocument8 pagesMODEL 90544, Patented Technology: Redundant Lighting and Onboard Diagnostix874895No ratings yet
- 2 Introduction To Quiz Wind Turbine Rotor Speed Control Strategy New CourseraDocument5 pages2 Introduction To Quiz Wind Turbine Rotor Speed Control Strategy New CourseraUsama Majeed33% (3)
- User Manual For AzAmerica - S1005 - 20131023Document35 pagesUser Manual For AzAmerica - S1005 - 20131023Alonso IbacetaNo ratings yet
- Alternator & Regulator - BoschDocument6 pagesAlternator & Regulator - BoschIordan AdrianNo ratings yet
- Frame Generator PDFDocument13 pagesFrame Generator PDFWilly PeralesNo ratings yet
- Honeywell ST9400SDocument6 pagesHoneywell ST9400SPas SommeseNo ratings yet