Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prbset 064324
Uploaded by
Hansen NagariaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Prbset 064324
Uploaded by
Hansen NagariaCopyright:
Available Formats
EMA 4324 Problem Set 6
6-1 [Jones 3-6] Using appropriate polarization [Evans] diagrams, determine the effect of the following
parameters on the corrosion potential and corrosion rate [CPR] of metal M corroding to M+ in an
acid solution: [a] increasing jo of the anodic reaction; [b] increasing jo of the cathodic reaction; [[c]
increasing the concentration of dissolved H+; and [d] increasing the Tafel constant for the anodic
reaction.
6-2 [Jones 3-8] [a] Plot the appropriate polarization curves for the following “half-cell” reactions and
determine the corrosion potential and corrosion rate [CPR, current density] assuming activation
control of both the anodic and cathodic processes. [b] Same as [a], but assume the limiting current
density for the reduction reaction is 10-5 A/cm2 . Again, determone the corrosion potential and
corrosion rate [CPR, current density] from your plot.
reaction ENernst, VSHE jo , A/cm2 β, V
M+1 + 1e- = M -0.70 10-8 0.1
+ -
2H + 2e = H2 0.10 10-6 0.1
My sign convention will result in a positive value for β since I define η in such
a way that it is always positive. Otherwise, β can be negative with a negative
overpotential for a process....
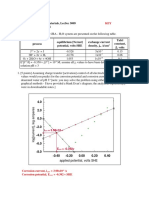
6-3 [Jones 3-10] Plot the polarization data shown below for an electrode of 1.13 cm2 of the metal M in
an acid solution of unit activity bubbled with pure hydrogen [unit pressure]. How might the
potentials be measured experimentally? From your plot [data, not cemetery], determine the
corrosion rate [A/cm2 ] and the exchange current density for the hydrogen reduction reaction on the
surface of metal M. Comment on the accuracy of your determinations.
Current, A Potential, V SHE Current, A Potential, V SHE
-2x10-4 -0.4843 -1x10-2 -0.6267
-5x10-4 -0.4939 -2x10-2 -0.6425
-1x10-3 -0.5075 -5x10-2 -0.7117
-2x10-3 -0.5287 -1x10-1 -0.7375
-5x10-3 -0.5663
You might also like
- Quiz 3 Ema 4324, Stability of Materials, Lecsec 3009 Monday, October 11, 2004Document2 pagesQuiz 3 Ema 4324, Stability of Materials, Lecsec 3009 Monday, October 11, 2004Bryan de BarrosNo ratings yet
- 10Document4 pages10ZenPhiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Regression Practice ProblemsDocument7 pagesChapter 9 Regression Practice ProblemsMathaneshan RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics DETERMINATION OF RATE LAW AND ORDER OF A REACTIONDocument2 pagesChemical Kinetics DETERMINATION OF RATE LAW AND ORDER OF A REACTIONFrancoise GurangoNo ratings yet
- The Bromination of Acetone Lab ReportDocument4 pagesThe Bromination of Acetone Lab ReportSammy Njenga KhanNo ratings yet
- The Bromination of Acetone Lab ReportDocument4 pagesThe Bromination of Acetone Lab ReportSammy Njenga KhanNo ratings yet
- Nuerical Method CombinedDocument70 pagesNuerical Method CombinedMuhammed RazaNo ratings yet
- Creating Estimated S-N Diagram: S S Loading Axial S S BendingDocument56 pagesCreating Estimated S-N Diagram: S S Loading Axial S S BendingAlberto IcazattiNo ratings yet
- 3 Crisp and Fuzzy RelationsDocument22 pages3 Crisp and Fuzzy RelationsRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Prokon FinalDocument6 pagesProkon FinalKem RaiNo ratings yet
- Maths Unit1 Question BankDocument8 pagesMaths Unit1 Question BankAimaan SharifaNo ratings yet
- Influence Lines - Solved ExamplesDocument15 pagesInfluence Lines - Solved ExamplesBrian DuloNo ratings yet
- CHE 509 - Past Exam QuestionsDocument12 pagesCHE 509 - Past Exam QuestionsJane Eilyza Aballa100% (1)
- PROBLEM STATEMENT: Formulate A Mathematical Correlation Between The DamageDocument6 pagesPROBLEM STATEMENT: Formulate A Mathematical Correlation Between The DamageJothi maniNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Soln PDFDocument8 pagesAssignment 1 Soln PDFVincent0% (1)
- Assignment 1 Soln PDFDocument8 pagesAssignment 1 Soln PDFVincentNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument8 pagesReportDeep Kumar PalNo ratings yet
- QSARDocument46 pagesQSARQuty Papa KannaNo ratings yet
- Homework v.1Document5 pagesHomework v.1RasedulIslam50% (2)
- Tut-371 No.2Document8 pagesTut-371 No.2fletusdiabloiNo ratings yet
- Plasma Enhanced Shielded Metal Arc WeldingDocument8 pagesPlasma Enhanced Shielded Metal Arc WeldingMaharshiMishraNo ratings yet
- Structural Theory: By: Engr. Ma. Angelica C. Avillanosa, MsceDocument32 pagesStructural Theory: By: Engr. Ma. Angelica C. Avillanosa, MsceIvy Jill Jurada100% (1)
- ASC Lab Report 4Document6 pagesASC Lab Report 4Daniel Ngenokesho WandyaNo ratings yet
- Electrolytic Conductance Weak ElectrolytesDocument3 pagesElectrolytic Conductance Weak ElectrolytesmylodNo ratings yet
- Straight Line Fitting:: W by Means of A Pulley Block, Find A Linear Law of The BW A P W Using The Following Data P WDocument8 pagesStraight Line Fitting:: W by Means of A Pulley Block, Find A Linear Law of The BW A P W Using The Following Data P WDarshan .BNo ratings yet
- Set 6 Solutions: 1 Find The Ionic Strength of The KNO SolutionDocument4 pagesSet 6 Solutions: 1 Find The Ionic Strength of The KNO SolutionGift BandaNo ratings yet
- JUAS 2019 - Tutorial 2: 1.) S-ParametersDocument6 pagesJUAS 2019 - Tutorial 2: 1.) S-Parameterssultan1786No ratings yet
- CH 11Document76 pagesCH 11Mhmd AlKhreisatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Chemical Kinetics: Answer: ADocument46 pagesChapter 12 - Chemical Kinetics: Answer: A鄭子玄No ratings yet
- 0132497468-Ch10 ISM PDFDocument26 pages0132497468-Ch10 ISM PDFIzam Fatima100% (3)
- Chapter 3Document28 pagesChapter 3jemimahisraelNo ratings yet
- About Geo - 1Document8 pagesAbout Geo - 1Erfandi RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 102 Spring 2000 Lindahl's Sections Problem Set IiDocument13 pagesChemistry 102 Spring 2000 Lindahl's Sections Problem Set Iimix shopNo ratings yet
- 7.12 Common-Ion Effect Student+Document3 pages7.12 Common-Ion Effect Student+Khalifa Mahmood Hussaim Mohammad RasheedNo ratings yet
- Chapter06 Solutions 11eDocument59 pagesChapter06 Solutions 11emo kaNo ratings yet
- Rate Expression and Order of ReactionDocument3 pagesRate Expression and Order of ReactionMartha PrawiradirdjaNo ratings yet
- Low Resolution Spectra and Conformations of Crotony 1978 Journal of MoleculaDocument6 pagesLow Resolution Spectra and Conformations of Crotony 1978 Journal of MoleculaFihad LatheefNo ratings yet
- Kinetics Worksheet AnswersDocument7 pagesKinetics Worksheet AnswerslinaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1 Pipe FrictionDocument5 pagesCase Study 1 Pipe FrictionjulietNo ratings yet
- UEAnal. Ch-4Document12 pagesUEAnal. Ch-4DilekNo ratings yet
- Taller Regresion LinealDocument16 pagesTaller Regresion LinealANDRESNo ratings yet
- Tolerance Analysis 09.04.03Document26 pagesTolerance Analysis 09.04.03maddy_scribdNo ratings yet
- Febbie Jane G. Tibog Written Report in Experimental Designs Factorial ComparisonDocument7 pagesFebbie Jane G. Tibog Written Report in Experimental Designs Factorial ComparisonAnastasia Denise ValdezNo ratings yet
- Low&Teh&Tang 2001bDocument8 pagesLow&Teh&Tang 2001bAnshi MishraNo ratings yet
- Ito Na CaseDocument27 pagesIto Na CaseVeegay Torres KibeteNo ratings yet
- Homework 1Document1 pageHomework 1Sandy VargasNo ratings yet
- The Answer Keys Are at The End of The Document.: Section #1 - These Questions Are Worth Two Marks EachDocument26 pagesThe Answer Keys Are at The End of The Document.: Section #1 - These Questions Are Worth Two Marks Eachdsa0% (1)
- Nsbe9ege Ism Ch12Document88 pagesNsbe9ege Ism Ch12高一二No ratings yet
- Problem Set 6 Problem 1.: R B B P T I Ikz R V VDocument2 pagesProblem Set 6 Problem 1.: R B B P T I Ikz R V VmkpsrtmNo ratings yet
- 2023 JC2 H1 Chem BT MCQ MSDocument7 pages2023 JC2 H1 Chem BT MCQ MSemman tzhNo ratings yet
- Sample Problem 1. Simple Stress: FBD of Joint A FBD of Left of SectionDocument12 pagesSample Problem 1. Simple Stress: FBD of Joint A FBD of Left of SectionHernanie EramisNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 EnzymesDocument7 pagesAssignment 3 EnzymescalliemozartNo ratings yet
- Failure Prediction For Static Loading: Section 6.2Document21 pagesFailure Prediction For Static Loading: Section 6.2Gerard Mercado100% (1)
- 4.stress Paths CSSM WEEK 4 5Document29 pages4.stress Paths CSSM WEEK 4 5ADNo ratings yet
- Iodine LabDocument4 pagesIodine LabHuang ViviNo ratings yet
- Bending and Compression To BS 5950 and BS en 1993-1-1Document5 pagesBending and Compression To BS 5950 and BS en 1993-1-1voegelchNo ratings yet
- 01 - Math Rev and Init RatesDocument6 pages01 - Math Rev and Init RatesJesse PerryNo ratings yet
- Keyws13 4Document9 pagesKeyws13 4aaaaaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsFrom EverandElectrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsAndrzej LewenstamNo ratings yet